Formation of Male Repro Sys (Fields)
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fields
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Primordial germ cells develop in the definitive ______ ___ at week ___-__
yolk sac 4-6
Primordial germ cells migrate from the definitive yolk sac to the ____ ___ where the testes are developing
Genital ridge
The testes develop in the
intermediate mesoderm
upper part of the urinary system, testes, and ovaries are developed from
intermediate mesoderm
Primordial germ cells develop into _______
spermatogonia
Essential factors in the intermediate mesoderm that makes indifferent gonad
WT-1
SF-1
Lim-1
The ____ gene is Y linked. Its product is _____
SRY
TDF (testes determining factor)
TDF
Testes determining factor
Turns indifferent gonad to testis
Sry gene product TDF
A mutation in the Sry gene will produce testes dysgenesis (defective development) and sex reversal (the individual will develop a streak gonad and female external and internal sex organs).
Swyer syndrome

Swyer syndrome
Swyer syndrome has a uterus but no
ovaries
IVF possible
In male this gene duplication leads to over-expression of _____ protein, blocks the ____, causes Swyer phenotype (female sex organs)
DAX1
Sry gene
In makes, LOF of this gene inactivates or causes LOF of _____ gene can lead to adrenal hypoplasia, low gonadotropins, and infertility. Does NOT result in female phenotype
DAX1
In females LOF of this gene leads to adrenal hypoplasia, low gonadotropins, and delayed puberty
DAX1
_________ derived cells migrate into the intermediate mesoderm where the testes are developing and form _____ ____ around the germ cells
Peritoneum
Sex cords
Sex cord derived structures
Rete testis
Seminiferous tubules
Peritoneum forms the ___ ___ and it derived from __________ ________
Sex cord
Splanchnic mesoderm
Sertoli cells are derived from the
Intermediate mesoderm
Leydig cells are developed from
Fibroblasts
Approximately ____ testicular lobules in 1 testis
250
___-__ seminiferous tubules per lobule
3-4
Germ cell testicular tumor ___%
95
Stromal cell (fibroblast and Leydig) testicular tumors ___%
1-3
Sertoli cell (sex cord) testicular tumors ____%
1.5
Types of germ cell tumors
Choriocarcinoma
Yolk Sac
Embryonal
Teratoma
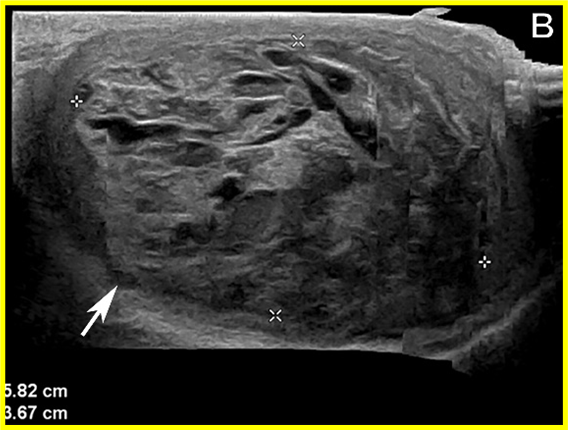
Germ cell tumor in testes
Sertoli cells produce _____, _____, _____, and ______ ______ _____
estrogen
ABP (androgen binding protein)
Inhibin
Mullerian inhibiting factor
Leydig cells produce ______
Testosterone
Estrogen produced by sertoli cells stimulates the ______ to produce _____
Hypothalamus
Gonadotrophins from anterior pituitary
_____ stimulates more estrogen production by Sertoli cells
FSH
_____ stimulates proliferation of spermatogonia stem cells
Estrogen
LH stimulates ______ by ______ cells
testosterone
Leydig cells
_____ stimulates more estrogen release and steroidogenesis and promotes growth of prostate, seminal vesicles, epididymis, ductus deferens, penis, scrotum, urethra
Testosterone
Binds and transports testosterone
ABP
After age 40, testosterone levels decrease by 1% each year. Testosterone levels below ___ ng/dl is associated with ____
300
Andropause
Responsible for male reproductive organs
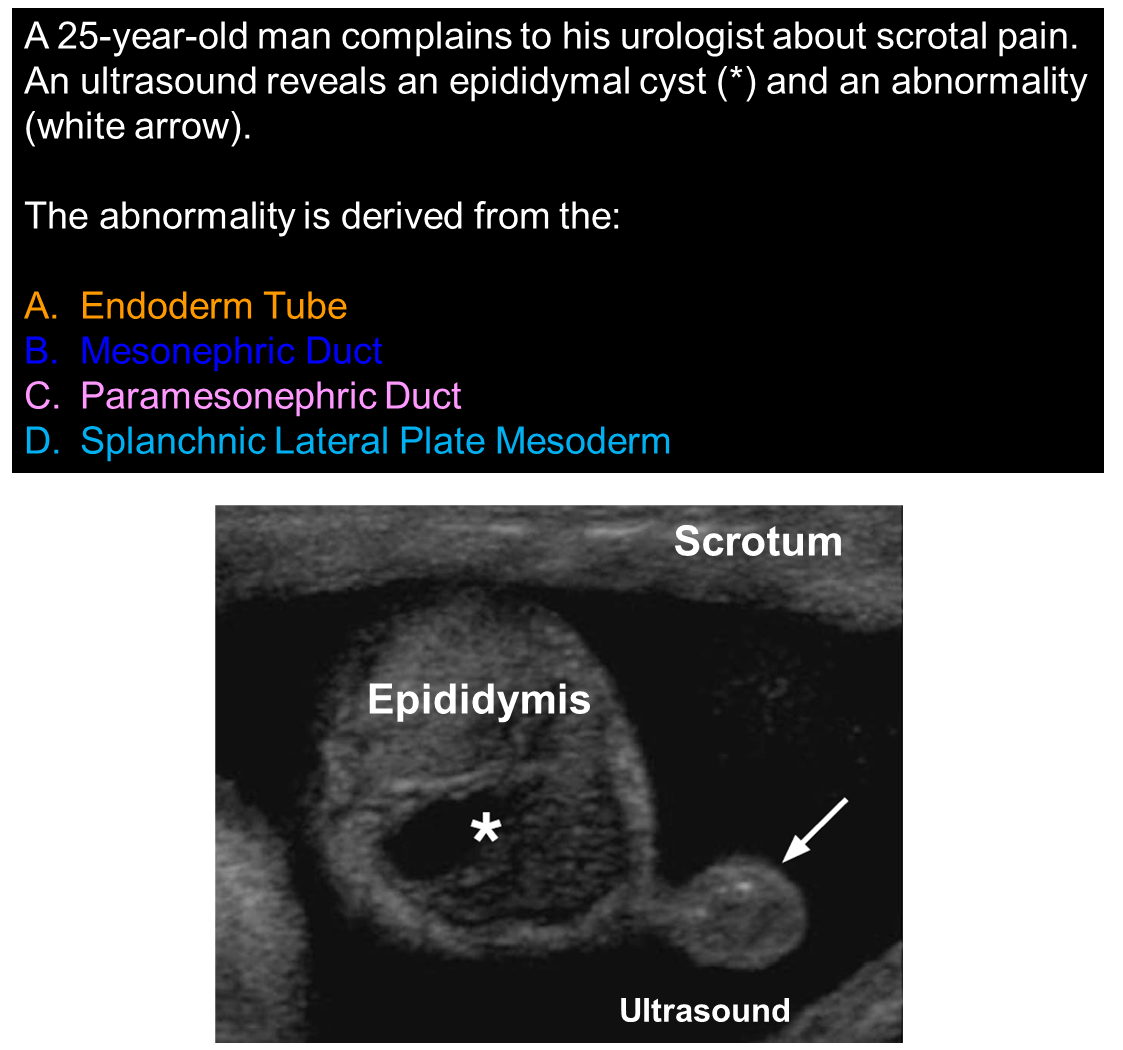
Mesonephric/ Wolffian ducts
Responsible for female reproductive organs
Paramesonephric/ Mullerian duct
Remnants of paramesonephric/Mullerian duct
Appendix testis (hydatid of Morgagni)
Prostatic utricle (blind sac)
Appendix testis (hydatid of Morgagni) is a remnant of the
Mullerian duct
Prostatic utricle (blind sac) is a remnant of the
Mullerian duct
Mesonephric and paramesonephric ducts (Wolffian and Mullerian) develop from
Intermediate mesoderm
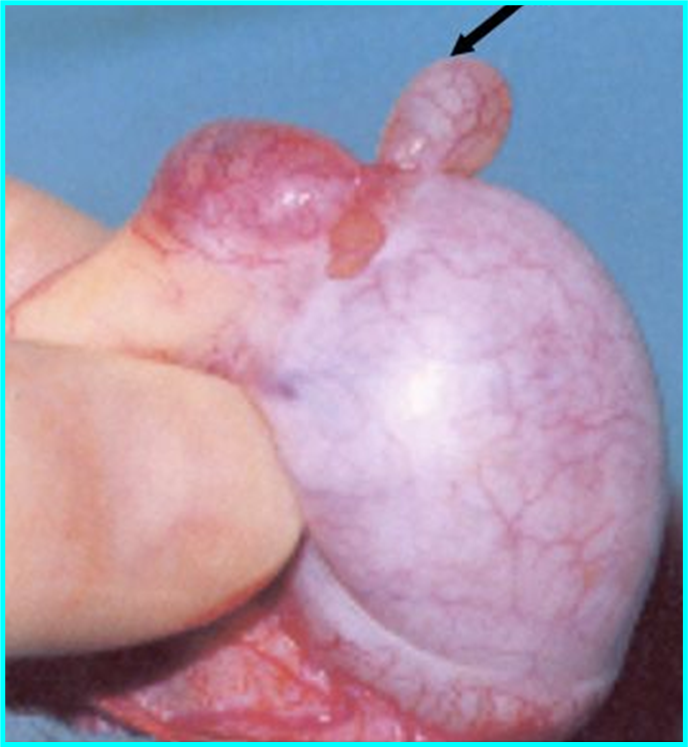
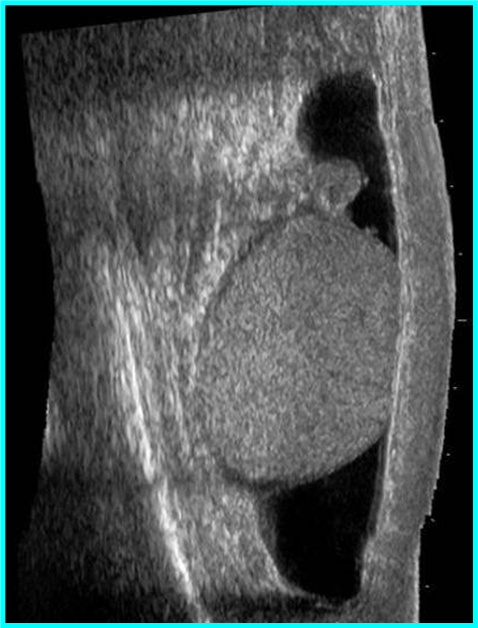
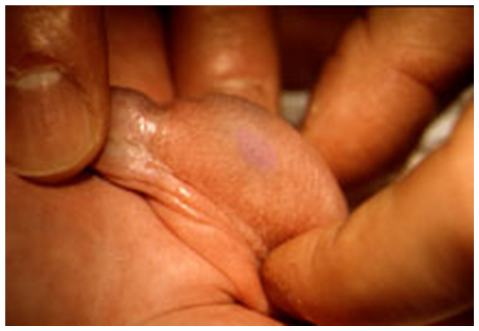
Appendix testis
remnant of Mullerian duct
Patients will usually have tenderness over the upper pole
Early torsion of the appendix testis may present with a pathognomonic “blue dot sign” (bluish discoloration seen through the scrotal skin)
Appendix testis
ASSOCIATED WITH: Downs syndrome, Hypospadias, Low Mullerian Inhibiting Factor (MIF) from Sertoli cells, Resistance to MIF
Can cause urine backup, damaging the kidney.
Enlarged prostatic utricle
Remnant of Mullerian duct
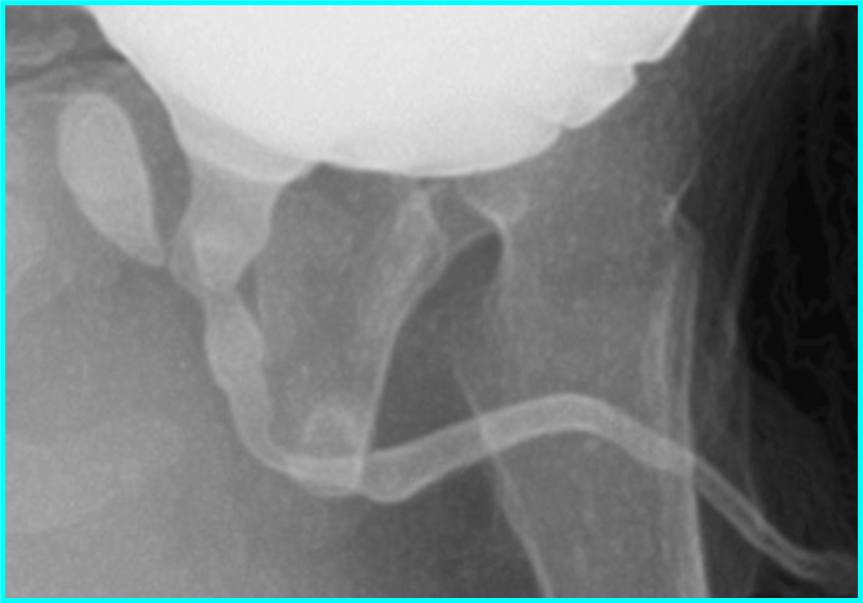
Enlarged prostatic utricle
Remnant of Mullerian duct / paramesonephric
B
Testosterone is responsible for development of ______
Mesonephric duct/ Wolffian duct
What is formed by the Mesonephric duct?
Efferent ducts
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicles
Ejaculatory duct
Remnant of the Wolffian duct may present as
cysts
Epigenital tubules of mesonephric duct remnant causes
Appendix epididymis
Paragenital tubules from mesonephric duct remnant causes
Paradidymis cysts aka Giraldis organ
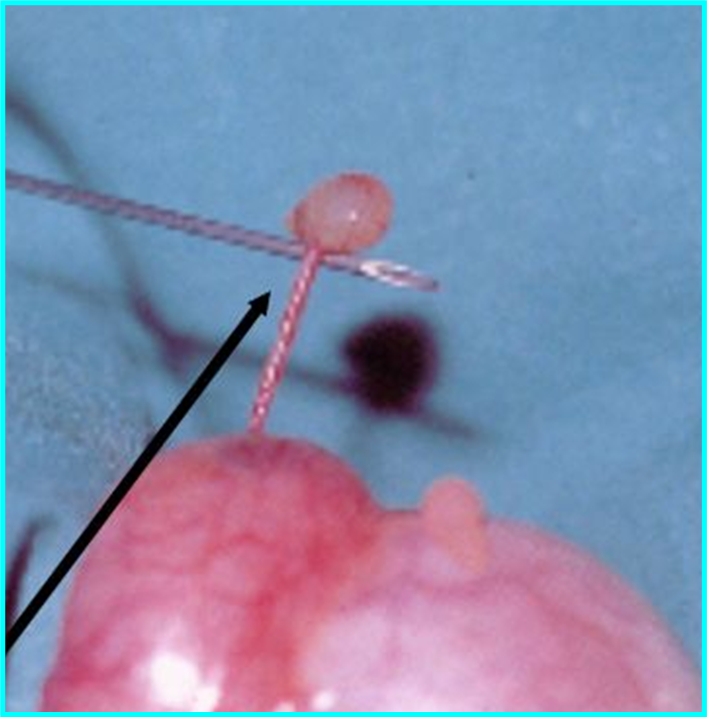
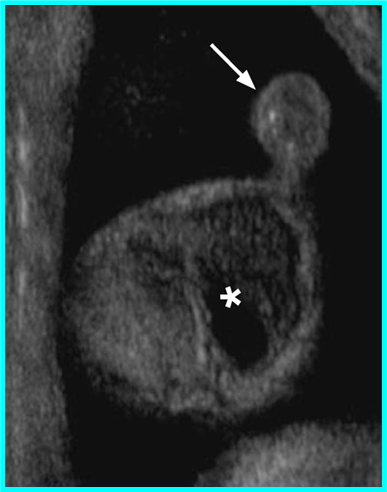
Black arrow in top
white arrow in bottom
Appendix epididymis
remnant of wolffian duct
With volvulus (twisting). Most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubertal males
Appendix epididymis (remnant of wolffian duct)
Usually have tenderness over the upper pole of the testis. Early torsion of the ______ _______may present with a pathognomonic “blue dot sign” (bluish discoloration seen through the scrotal skin).
Appendix epididymis

Paradidymal cyst (mesonephric duct remnant)
torsion & swelling
_______ _________ with torsion & swelling. Causes a back up of fluid in the epididymis & testis.
Paradidymal cyst (mesonephric duct remnant)
Blind tube remnant from mesonephric duct
Vas aberrans
Epididymal appendix, vas aberrans, paradidymis remnant of?
Mesonephric duct / Wolffian duct
Testicular appendix, prostatic utricle remnants of?
Paramesonephric/ Mullerian duct
Blocked efferent ducts with sperm
Spermatocele
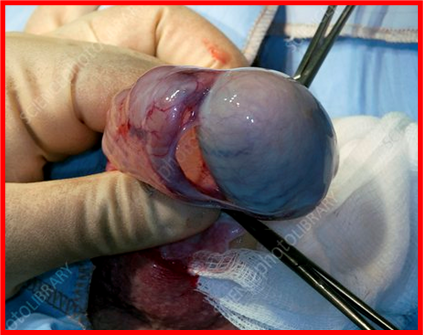
Spermatocele
Blocked efferent ducts. With clear fluid
Epididymal cyst
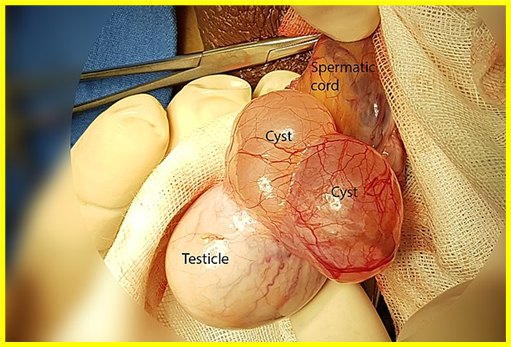
Epididymal cyst
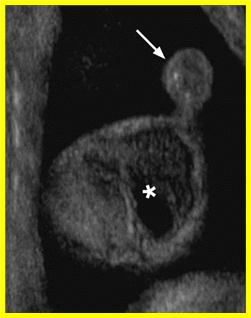
No connection between the efferent ducts and rete ducts.
Ectasia rete testis
Ectasia rete testis
Dilation of rete ducts & seminiferous tubules. They contain clear fluid & sperm.
Causes of Efferent Duct Blockage
Cystic fibrosis
Infections
Vasectomy
Trauma
Stones
Iatrogenic Injury (urethral manipulation)
The efferent duct is derived from the
mesonephric duct
Bacterial infection of epididymis
Epididymitis
Mesonephric duct makes
Seminal vesicle
Ejaculatory duct
Epididymis
Appendix epididymis
Epigenital and paragenital tubules
Vas deferens
efferent ductules
Peritoneum makes
Seminiferous tubules
Rete testes
Paramesonephric duct makes
Appendix testes
Prostatic utricle

Summary of male structures
The genital tubercle is formed by
Lateral plate mesoderm
The genital urogenital fold is formed by
Lateral plate mesoderm
The genital swelling is formed by
Lateral plate mesoderm
The urethra is formed by
Endoderm
The genital tubercle (lateral plate mesoderm) forms the
shaft, glans penis, and bulb
The genital folds/ urethral folds (lateral plate mesoderm) come together to enclose the
Urethra
The genital swellings/labioscrotal swellings (lateral plate mesoderm) comes together to form the
scrotum
The urogenital membrane and anal membrane is formed from
Ectoderm
Mesenchyme of the ventral shaft form the corpus ________ and the mesenchyme of the dorsal shaft form the corpus _______.
spongiosum
cavernosum
(genital tubercle lateral plate mesoderm)
The crus of the penis are attached to the _______ _____
Ischiopubic rami
The corpus spongiosum and cavernosum are developed from
Genital tubercle
lateral plate mesoderm
Skeletal muscle develop from
paraxial mesoderm
Bulbospongiousus muscle and ischicavernosus muscle develop from
paraxial mesoderm
Bulbospongiosus surrounds
corpus spongiosum around bulb
Ischiocavernosus surrounds the
Corpus cavernous around crus
Failure of genital folds to fuse ventrally
Hypospadias
Hypospadius is associated with
Chordee
Ventral bending of penis
Chordee
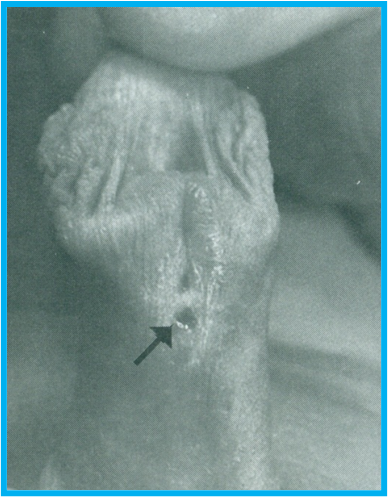
Hypospadius
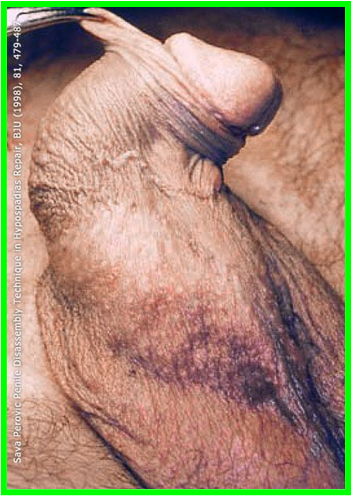
Chordee
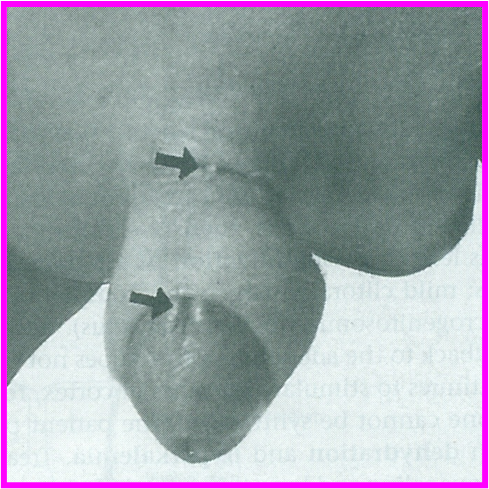
Epispadius
Failure of the dorsal mesenchyme of the shaft (genital tubercle) to properly fuse.
Epispadias
Shortens and guides the testes into the scrotum
Gubernaculum
Mesenchymal (connective tissue) cord that originates from the genital ridge
Gubernaculum
Peritoneum forms around the anterior and lateral sides of the gubernaculum this is the
Processus vaginalis
Processus vaginalis is made from
Peritoneum
The proximal portion of the vaginal process undergoes _____ leaving a sac with a parietal and visceral layer anterior to the testes and epididymis.
apoptosis