Physio module 5 & 6
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
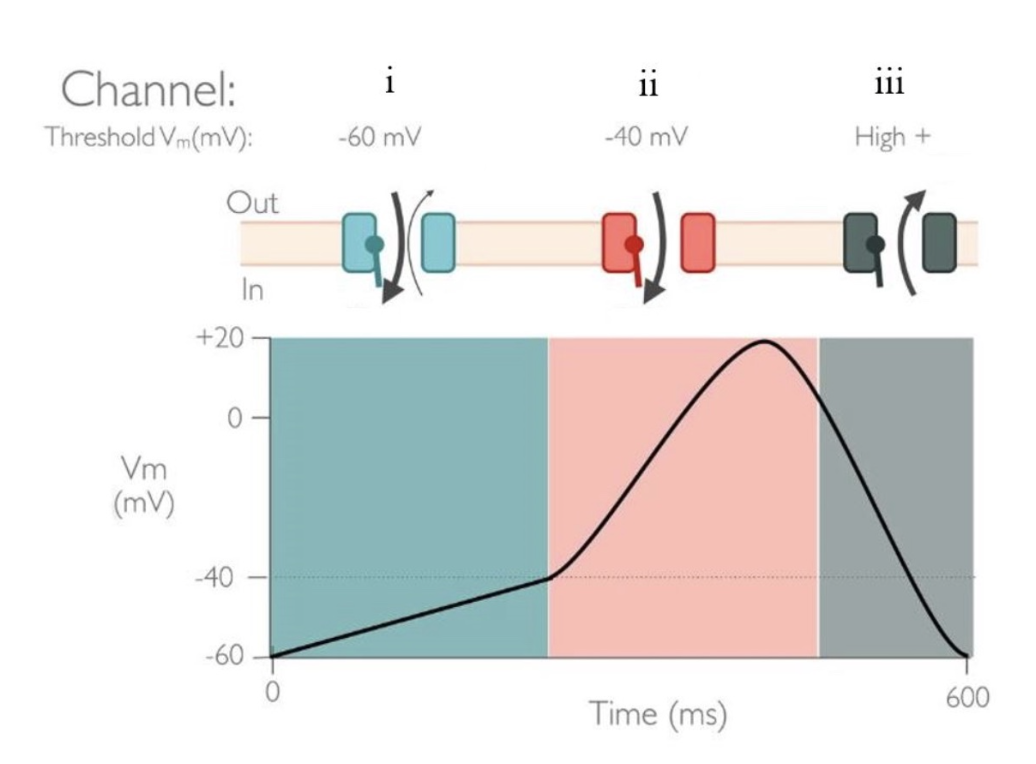
Choose the answer that correctly labels all three channels as well as their associated ions.
Channel i: Funny (IF) channel; Na+ in K+ out
Channel ii: Voltage-gated Calcium channel; Ca2+
Channel iii: Potassium Leak Channel; K+
Select all of the following that are reasons cardiac muscle is resistant to fatigue.
The anatomic range of the heart is limited to avoid hyperextension.
Action potentials from pacemaker cells are limited in the frequency at which they can fire.
Your friend who works in a lab on campus is doing research that compares the contractile properties of cardiac and skeletal muscle. One day, she accidentally forgot to label a cell culture.
What experiments could you suggest to determine whether the culture is cardiac or skeletal muscle?
Measure refractory period of muscle cell, because cardiac cells have longer refractory periods.
Use high frequency stimulation to see if the muscle undergo tetanus because cardiac cells do not fuse twitches.
Measure the duration of a muscle twitch, since cardiac muscles have a longer twitch duration.
The duration of cardiac contractile cells is much longer (on the order of 250ms or 0.25 seconds) than skeletal muscle fibers (generally on the order of 100ms or 0.1 seconds).
Cardiac contractile cells do have a longer refractory period, which also relates to them not being able to fuse twitches to achieve tetanus.
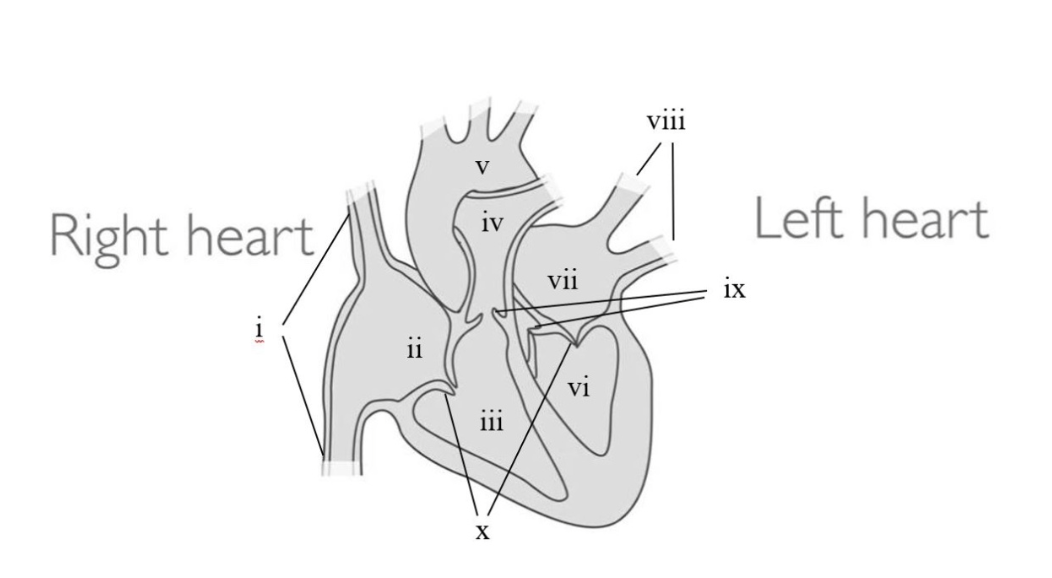
Using the above image of the heart's anatomy, correctly match the name to the anatomical structure's Roman numeral.
x: atrioventircular (AV valves)
iii: right ventricle
v: aorta
vi: left ventricle
vii: left atrium
ix: semilunar valves
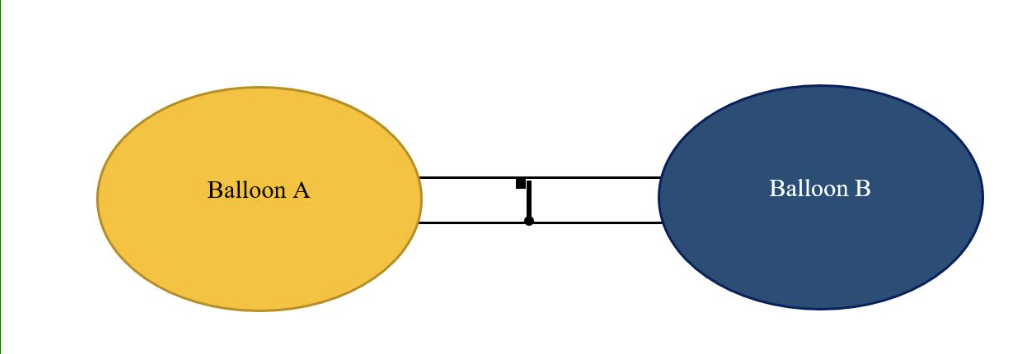
The above illustration shows Balloon A (yellow) and Balloon B (blue), which are connected by a vessle that has a valve with a latch (black square).
What do you expect to happen if you only squeezed on Balloon A?
Increased pressure from the left (balloon A) side will open the valve.
Balloon B will expand.
Because of the position of the valve and latch/stopping mechanism the fluid inside the tube can only flow from Balloon A to Balloon B (to the right) but not the other direction.
If pressure is applied to Balloon A, it will decrease in volume, and thus increase pressure from the left side (Balloon A) will cause the valve to open ultimately leading to the expansion (increase in volume) of Balloon B.
Choose the answers that best complete the following sentence.
When the left ventricle relaxes during diastole, the left AV valve will open due to a higher pressure within the atrium and lower pressure in the ventricle, while the left semilunar valve remains closed because of lower pressure in the left ventricle.
When the left atrium contracts it will open the left AV valve because of the pressure gradient between the left atrium and left ventricle where the left atrium is highly pressurized due to contracting and the ventricle will have a relatively lower pressure since it is relaxed.
The left semilunar valve will remain closed because of the relatively low pressure within the left ventricle
How is it that the sinoatrial (SA) node controls the beat rate of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
The AV node has a lower autorhythmic frequency.
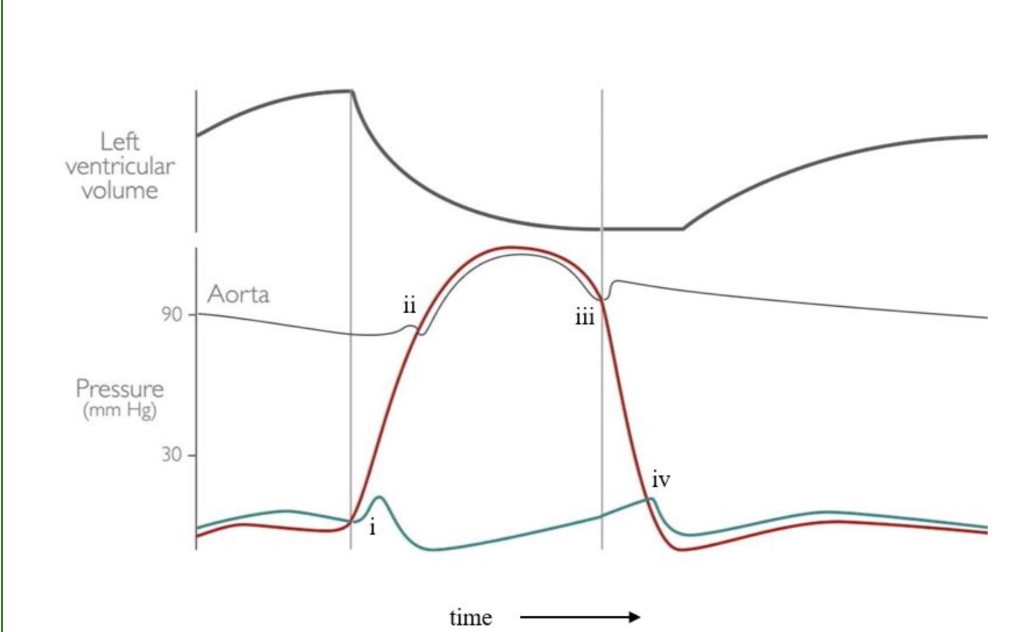
Using the above Wigger's diagram, match the corresponding event in the cardiac cycle to the correct Roman numeral.
i: AV valve closes
ii: Semilunar valve opens
iii: Semilunar valve closes
iv: AV valve opens
Select all that apply during the Q-R-S Complex of an electromyocardiogram (ECG) recording.
Atrial repolarization.
Ventricular depolarization.
What causes the sound associated with a heart beat?
Closing of AV valves and semilunar vavles
It is the closing of the two different valves during the course of a heart beat that causes the sound. Remember from lecture the video of the two valves clapping together like hands.
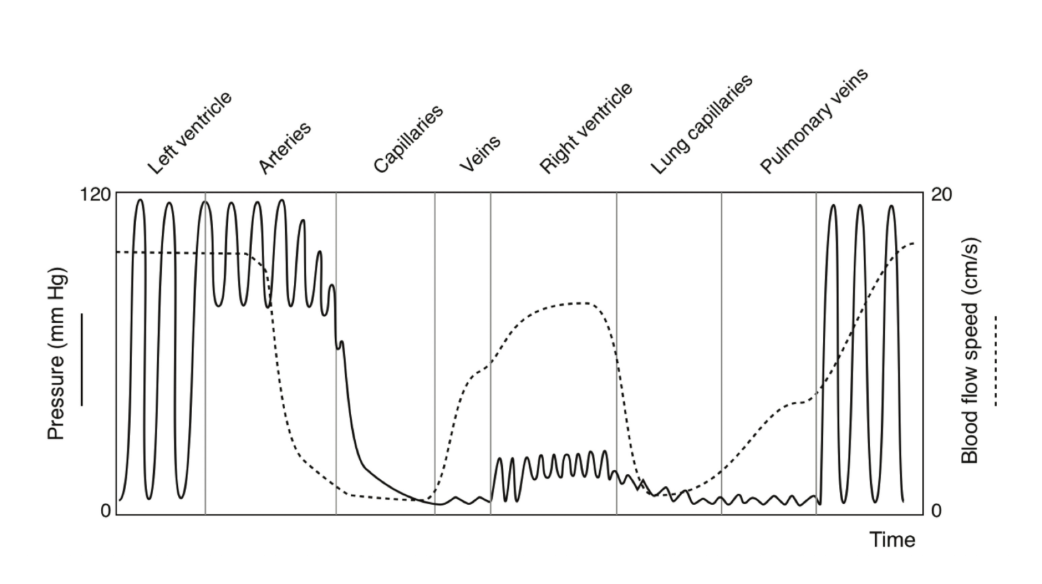
Refer to the above figure for the following question:
Why is the flow speed (cm/s) in the right ventricle less than the left ventricle?
It has a larger cross-sectional area.
If the heart pumps 5 Liters of blood per minute, what is the rate of flow of blood through the pulmonary veins?
5 L/min
Choose the answers that correctly complete the following statement.
Blood leaving the heart enters large vessels where the flow speed is relatively high, which ensures quick delivery of gases and nutrients.
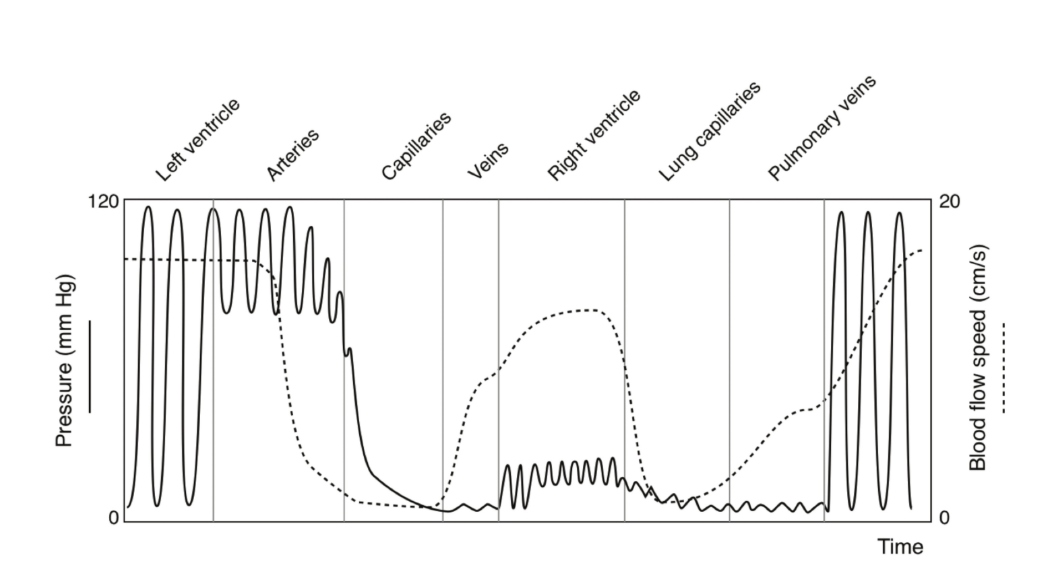
Refer to the above figure for the following question:
True or False: The diastolic pressure in the arteries is much greater than the diastolic pressure in the left ventricle.
True
During exercise your body shunts blood to muscles and away from digestive processes to better allow for gas and nutrient exchange where the demand is high. How does your body accomplish this?
Vasoconstriction of arterioles leading to digestive system.
You measure the blood pressure of an individual to be 150 / 90 mm Hg (systolic / diastolic). If the mean arterial pressure (MAP) of someone with hypertension is generally above 100 mm Hg, determine this individual's MAP and whether they have hypertension.
MAP is 110 mm Hg and they likely have hypertension.
Where are the baroreceptors and integration center for the body's sensing and control of blood pressure homeostasis located?
Receptors are in the walls of arteries and the integration center is in the brainstem.
Select all of the following ways which the sympathetic nervous system controls heart contractions.
Norepinepherine (NE) binds to receptors on pacemaker cells.
Increases Ca2+ concentration in contractile cells.
Increases duration of If (funny) channels shortening pacemaker potential phase.
Which of the following are NOT a property of a healthy heart?
The contractile cells operate on the ascending limb (i.e. left side) of the length-tension curve.
During exercise, sympathetic stimulation of the heart increases contractility.
Norepinephrine creates an increase in the twitch duration of contractile cells.
Stroke volume increases with increasing volume that enters during diastole.