8.3 AI Learning objectives answered
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
General structural feature of β2 agonists
Phenylethanolamine core with β-hydroxylamine and substituted aromatic ring
Predominant receptor in the heart
B1
Predominant receptor in smooth muscle
b2
How does epinephrine bind to b2 receptors?
Hydrogen bonding of catechol OH groups to 2 Ser residues
How is norepinephrine metabolized?
COMT transfers a methyl
MAO replaces CH2NH2 with aldehyde
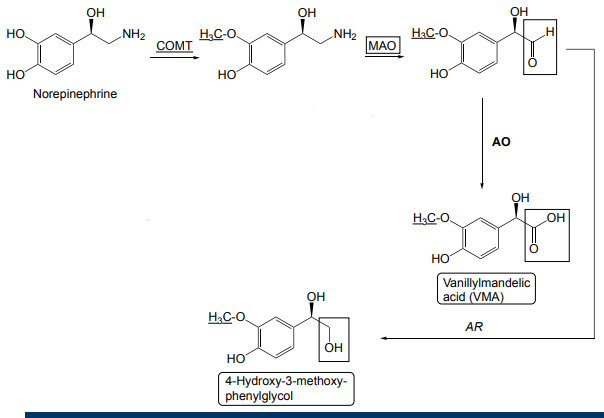
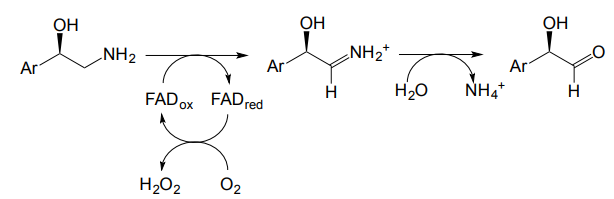
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) is dependent on what enzymes and yields what?
Dependent on flavin enzymes (ie FAD) and the reaction yields aldehyde +amine
Effect of bulky N-substituents on β2 agonists
Increase β receptor selectivity and reduce α activity
Blocks or decreases MAO activity
What do aromatic ring substitutions do?
Can make resistant to COMT but still be capable of interacting with receptor
Ring substitutions that resist COMT metabolism
Salicyl alcohol and resorcinol patterns
COMT-resistant example with β2 selectivity
Albuterol with salicyl alcohol and tert‑butyl amine (bulky N group)
Albuterol S isomer may be associated with ______
bronchial hyperresponsiveness
Structural feature increasing duration for salmeterol
Long lipophilic chain on amine holds drug near receptor
Salmeterol is resistant to metabolism by what?
COMT and MAO
Salmeterol duration of action
12 hours
Salmeterol is combined with corticosteroid in what product?
Advair, T
Fluticasone propionate/Salmeterol
Formoterol feature affecting onset
More hydrophilic than salmeterol, faster receptor access and rapid onset
N substituent ends with phenyl-OCCH3
Phenyl substituents replaces CH2OH w/ N-aldehyde
Formoterol contains how many possible stereoisomers?
4
What formoterol racemic is active and which is inactive?
Active: RR (Arformoterol)
Inactive: SS
Formoterol is use in combo with corticosteroid in what product?
Symbicort (Budesonide/Formoterol)
What are examples of Ultra long acting beta2 agonists (3)
Vilanterol, Olodaterol, Indacaterol
Vilanterol is only available in what combo products
Corticosteroid (Breo), antimuscarinic (Anoro), antimuscarinic +corticosteroid (Trelegy)
How many times a day are ultra long acting b2 agonists taken for COPD?
once
Olodaterol half life
18 hours
Olodaterol has _____B2 selectivity compared to salmeterol and formoterol
higher
The N substituent on Indacaterol is _____
hydrophobic
cyclopentyl +phenyl w/ 2 ch3 branches
How catechol analogs are metabolized
COMT methylation and MAO oxidative deamination
Structural change reducing MAO metabolism
β‑substitution and bulky amines
Carbon and ring number of corticosteroids
21‑carbon steroid with four fused rings
Cortisone acts as a ______
prodrug
Active endogenous glucocorticoid
Cortisol
Enzyme converting cortisone to active form Cortisol
11β‑hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
Ketone on position 11 becomes OH
Cortisol interacts with _______receptor, resulting in salt retention
mineralocorticoid
What hydroxyls enhance salt retention
17a and 21
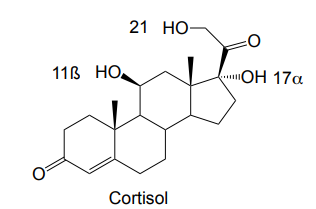
11ß-OH only enhances ______ activity
glucocorticoid
How is aldosterone structurally different from cotisol
Addition of aldehyde on C18 and no hydroxy on 17a

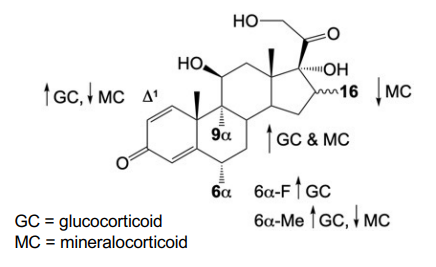
Effect of 9α‑F or 9α‑Cl on corticosteroids
Increase glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity and slow 11β‑OH oxidation
Glucocorticoid receptor mechanism
Steroid diffuses passively into cell and binds receptor. Receptor dimerizes, enters nucleus and binds to DNA to inhibit cytokine production
Corticosteroid metabolism
Reduction of A ring and cleavage of side chain
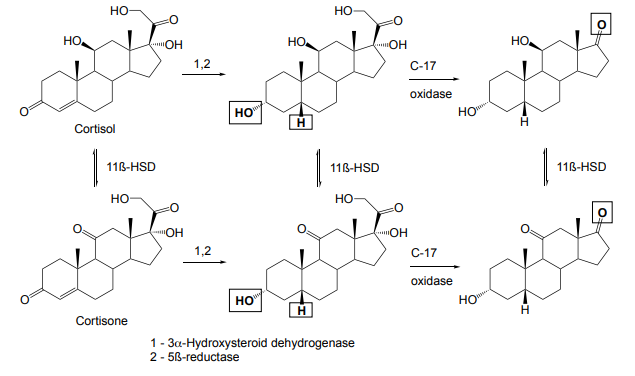
Effect of Δ1 double bond
Increases glucocorticoid activity and decreases mineralocorticoid activity
Effect of 6α‑methyl
Increases glucocorticoid activity and decreases mineralocorticoid activity
Effects of 6a- F
Increases glucocorticoid activity
Effects of 9a- F or Cl
Increase both anti-inflammatory (GC) and mineralocorticoid activity
Slows oxidation of 11ß-OH by 11ß-HSD
Effect of 16α,17α‑acetonide
16a-OH
16a- and 16B methyl
Decreases mineralocorticoid activity
Esters w/ ionizables groups has what effects?
increased water solubility and can be used in injectible products
Lipophillic esters have effects/
local activity w/ less systemic absorption
Esters are readily hydrolyzed by what?
plasma esterases
Hydroxyl at what position is a requirement for corticosteroid receptor binding and makes it a prodrug?
Free C21 hydroxyl
What position esters are active w/o hydrolysis?
C17

Example of corticosteroid prodrug
Prednisone or beclomethasone dipropionate
How is prednisone converted to prednisolone?
11 ketone converted to alcohol by 11ß-HSD to give prednisolone
Prednisolone (T) 4-fold higher potency than hydrocortisone due to what reason?
Double bond between C1 and C2
Slows metabolism and increases duration
Example of active corticosteroid
Prednisolone or flunisolide
Beclomethasone diproproprionate is a prodrug with what features?
9a-Chloro increases both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity, 16ß-methyl decreases mineralocorticoid activity
Fluticasone has what structural features?
9a-F increases both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity, 6a-F enhances only glucocorticoid activity
What has a higher glucocorticoid receptor affinity: fluticasone proprionate or beclomethasone
fluticasone proprionate
Mometasone structural featues
9a-Cl increases both glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activity, 16a-methyl decreases mineralocorticoid activity
How are cyclic ketals formed?
formed with 16a plus 17a alcohols
How do ketals/acetals affect mineralocorticoid activity?
decreases
Flunisolide is used to treat ______
allergies
Flunisolide has what structural features?
6a-F increases glucocorticoid activity
not a prodrug
Why does flunisolide have minimal systemic adverse effects?
40% of inhaled dose is systemically bioavailable, but it is rapidly metabolized to the minimally active 6ß-hydroxy metabolite
Budesonide is an acetal devired from _____
butanal
what causes Budesonide 2 fold decrease in potency?
Chiral center at acetal carbon
Budesonide is metabolized to what?
minimally active metabolites
Ciclesonide is both _______
ester and acetal
Prodrug that requires activation
Ciclesonide acetal is formed from what?
cyclohexylcarbonaldehyde
________is an endogenous neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine
What 2 receptor classes stimulate acetylcholine?
nicotinic and muscarinic receptors
M1, M3, and M5 GPCR utilize what?
Gq/G11
Hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate in Gq/G11 leads to what?
diacyl glycerol + inositol triphosphate
Activation of M3 receptors causes what?
bronchoconstriction
M2 and M4 couple through _____ and inhibit ______
Gi /Go
adenyl cyclase
Core structure of antimuscarinics
Aminoalcohol esters related to tropine
Structurally related to tertiary amines atropine and scopolamine
quaternary amine
Structural feature limiting CNS penetration
Permanent quaternary amine
What is a short acting antimuscurinic?
Ipratropium bromide
How is Ipratropium bromide administered?
inhalation; bronchodilator effects
is Ipratropium bromide selective or nonselective?
non-selective
Side effects common to antimuscarinics
dry mouth, blurred vision
Examples of LAMA
Tiotropium bromide (T), Aclidinium bromide, Umeclidinium bromide
What is the only antimuscurinic that binds preferentially to M3 over M2 muscarinic receptors?
Glycopyrrolate (glycopyrronium bromide)
How is Glycopyrrolate (glycopyrronium bromide) excreted?
Rapidly excreted by kidney, largely in unchanged form (hydrolysis in plasma slow)
How is Revenefacin 1,2 very structurally different than other antimuscarinics?
Has carbamate, not esters, and also shows kinetic selectivity for M3 over M2 receptors
How does Rivenfacine minimize side effects?
Terminal amide stable in lungs, but hydrolyzed to carboxylic acid in circulation
Roflumilast and Ensifentrine are examples of what?
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
Reaction inhibited by PDE inhibitors
Hydrolysis of cAMP (leads to anti-inflammation)
Effect of PDE3 inhibition
Bronchodilation
Effect of PDE4 inhibition
Anti‑inflammatory by increasing cAMP in inflammatory cells
Example of selective PDE4 inhibitor
Roflumilast
Roflumilast duration and administration technique
10 hour half life
administered orally
What metabolite is also a PDE4 inhibitor?
N-Oxide metabolite
What limits use of Roflumilast?
systemic side effects
Example of selective PDE3 inhibitor
Ensifentrine
3000 times more potent PDE3 inihibition vs PDE4
How is Ensifentrine administered?
inhalation
Two mechanisms decreasing leukotriene effects
Inhibit biosynthesis or block cysteinyl leukotriene receptors
Enzyme inhibited by zileuton
5‑lipoxygenase. Can’t convert arachnidonic acid to leukotrine
What group is essential for zileuton activity?
N-Hydroxyl group
O- glucuronide metabolite is inactive
zileuton is administered _____
orally
cysLT receptor endogenous agonist
Glutathione- adducts LD4 and its metabolites to cysLT 1 receptors
Antagonists used clinically to block inflammatory activity of leukotrienes is selective for what?
cysLT 1 receptors
Functional group in leukotriene antagonists mimicks what?
Acidic functionality mimics C1 acid of leukotrienes in agonists