Ch8 Pt.1: Genetic analysis and mapping in E. coli and Bacteriophages
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part I: What are bacteria again, and how do bacteria exchange alleles in conjugation? Chapter 8: Genetic Analysis and Mapping in Bacteria and Bacteriophages
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Why do modern prokaryotes appear to be simple but are actually in every sense
modern
theyre well-adapted to changing environments
provide basic info about prokaryotes
-Single celled organisms, circular chromosome, associated extrachromosomal DNA called plasmids
-generally lack internal membranes or organelles:
→modern free-living relatives of chloroplasts and
mitochondria have extensive membranes
→Agrobacterium: organelle like structure for sequestration of cations.
-often have a cell wall; variable and complex. very tiny in size
Domain Eubacteria: metabolically diverse
what is known about them
-heterotrophic, and autotrophic (photo- & chemosynthetic)
-thermophiles (Thermus aquaticus)
Define Cyanobacteria and Proteobacteria
Cyanobacteria: cousin of the chloroplast
Proteobacteria: cousin of the mitochondrion
Go in detail of Bacteria as pathogens
Bacteria as pathogens: tuberculosis, typhoid fever, diptheria, cholera, leprosy, Lyme disease, syphilis.
Go in detail of E. coli
-model organism, wild-type from lower intestine of mammals
-Chromosome of 4.6 million bases (human genome = 3 billion bases)
-Grows rapidly and in simple medium.
Culturing bacteria: the basics
define medium, what does minimal medium contain
define Titer
Medium: material containing nutrients in which bacteria can be grown
-liquid medium (Luria broth)
-solid medium (agar)
Minimal medium contains sugar, salts, minerals
Titer: concentration of bacterial cells in liquid medium colony forming units/ml culture (cfu*/ml)
How do you obtain titer from a sample
1. Dilute liquid medium containing bacteria
2. Plate known quantity on agar
3. Incubate at 37°C and count colonies
4. Each colony represents a single cfu. Using dilution factor, calculate cfus in solution
What kinds of phenotypes can be observed in bacteria?
-Useful phenotypes based on metabolic capability
-Wild-type: prototrophic, can grow on minimal medium
-Nutritional mutant: auxotrophic, lacks ability to synthesize an essential
nutrient and therefore must be cultured on augmented medium
Example of observing phenotypes in bacteria
Strain trp ade thi+ can synthesize thiamine (wild-type = +) but not tryptophan or adenine, which must be included in the medium
Prokaryotes are effectively haploid, having only one copy of
the chromosome
so what does not apply?
Homozygosity, heterozygosity, and dominance relationships do not apply!
How are mutant strains detected?
Provide steps of replica plating
1. Grow bacteria on complete medium
→contains essential and nonessential nutrients
2. Transfer colonies to minimal media using sterile velveteen
3. Compare original plate to replica plate.
→Missing colonies indicate nutritional mutants.
4. Grow nutritional mutants on plates containing minimal medium + one other nutrient.
What process is required for genome mapping in prokaryotes? go in detail
what warning should I be aware of regarding knowledge of inheritance
Recombination: Even though bacteria do not undergo meiosis or sexual reproduction, genes may be exchanged through conjugation.
→Unidirectional transfer of genetic material through direct cell-cell contact
→Donor and recipient
→Recipient also called the transconjugant
Warning: Most of what we know about inheritance in prokaryotes is from E. coli.
Discovery of Genetic Exchange in E. coli
what is in Strain A and Strain B
what can they not grow in
what happens if grown together
-Strain A: met bio thr+ leu+ thi+
-Strain B: met+ bio+ thr leu thi
-Neither can grow on minimal medium
-Grown together, some progeny are able to grow on minimal media; prototrophic (met+ bio+ thr+ leu+ thi+)
Explain the Discovery of Conjugation
why do you load Strain A and Strain B into a U-shaped tube?
what must be in contact to effect conjugation
Strain A and B loaded into U-shaped tube:
-Separated by filter that allowed exchange of media but did not allow cells to pass
-Plated cells yielded no prototrophic colonies
-Cells must be in contact to effect conjugation!

Go in detail about the Sex Factor: F
1953- Wm. Hayes demonstrates that conjugation is always unidirectional
F-factor: plasmid that is transferred [plasmids are extrachromosomal, self-replicating DNA]
F factor: 1/40th the size of a chromosome
→transferred from F+ donor to F- recipient
→replication begins at sequence called the origin
→Genes for construction of F-pili (F-pilus, sing.): (hair-like extensions of the cell membrane through which genetic material can pass)
![<p><span><strong><u><span>1953- </span></u><span>Wm. Hayes demonstrates that conjugation is always unidirectional</span></strong><span><br></span><strong><u><span>F-factor: </span></u></strong><span>plasmid that is transferred [plasmids are extrachromosomal, self-replicating DNA]</span></span></p><p></p><p><span><strong><u><span>F factor: </span></u></strong><span>1/40th the size of a chromosome<br>→transferred from F+ donor to F- recipient<br>→replication begins at sequence called the origin<br>→Genes for construction of F-pili (F-pilus, sing.): (hair-like extensions of the cell membrane through which genetic material can pass)</span></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bd51c4b3-9052-42a6-b2de-366f6c2168f7.png)
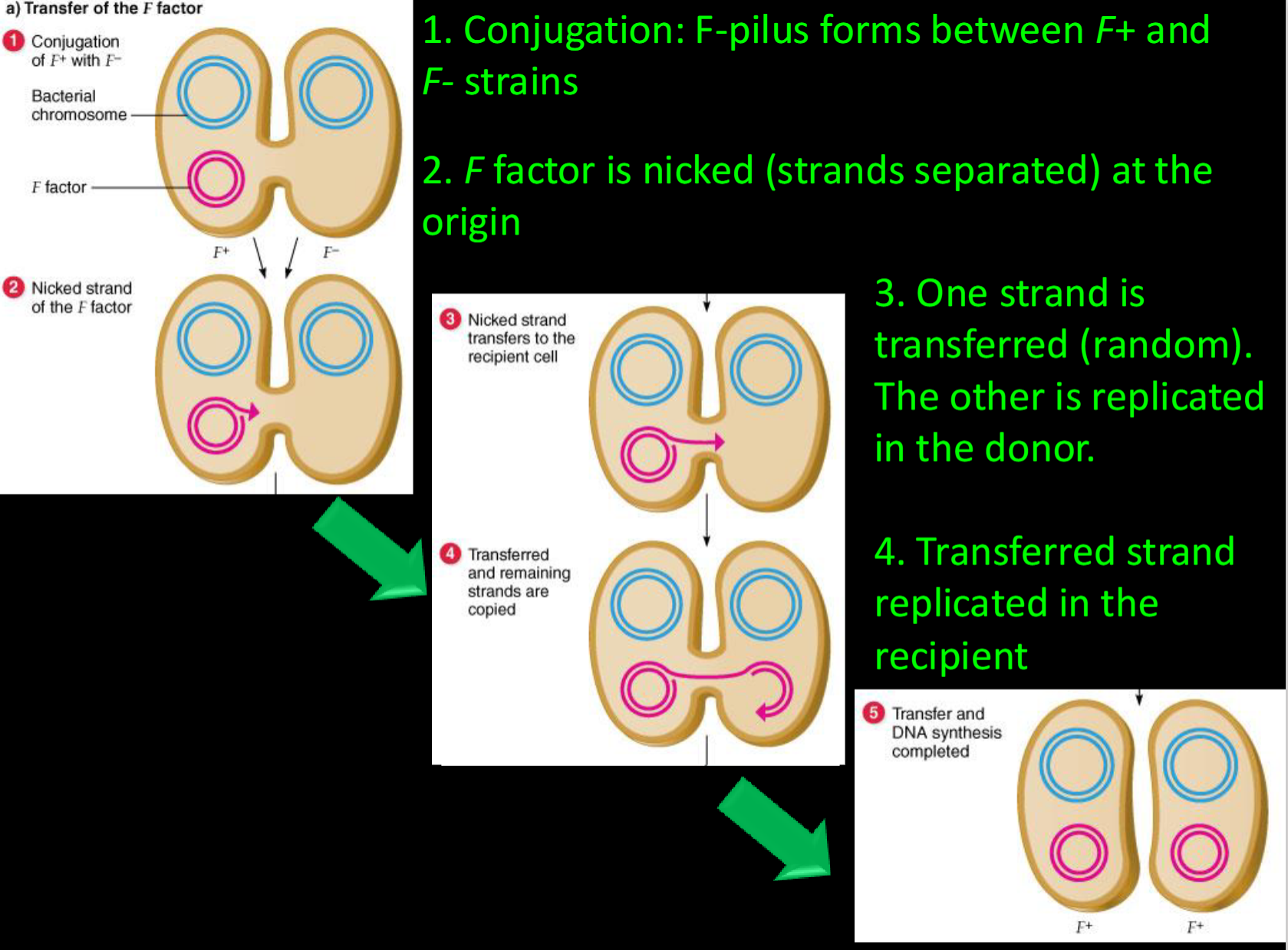
Describe the transfer of the F factor
1. Conjugation: F-pilus forms between F+ and F- strains
2. F factor is nicked (strands separated) at the origin
3. One strand is transferred (random). The other is replicated in the donor.
4. Transferred strand replicated in the recipient
No metabolic genes on the F-factor: How is recombination
achieved?
Episome: a plasmid that can be integrated into the bacterial
chromosome
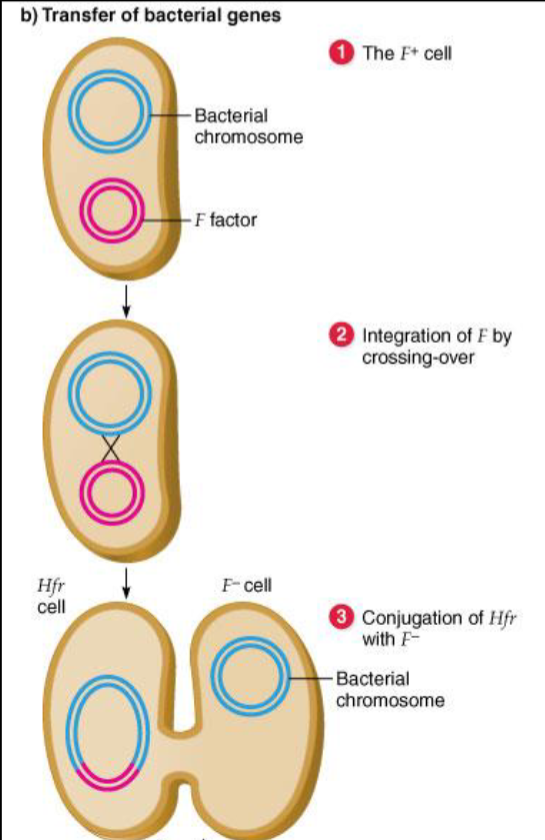
Describe the transfer of bacterial genes (steps 1-3)
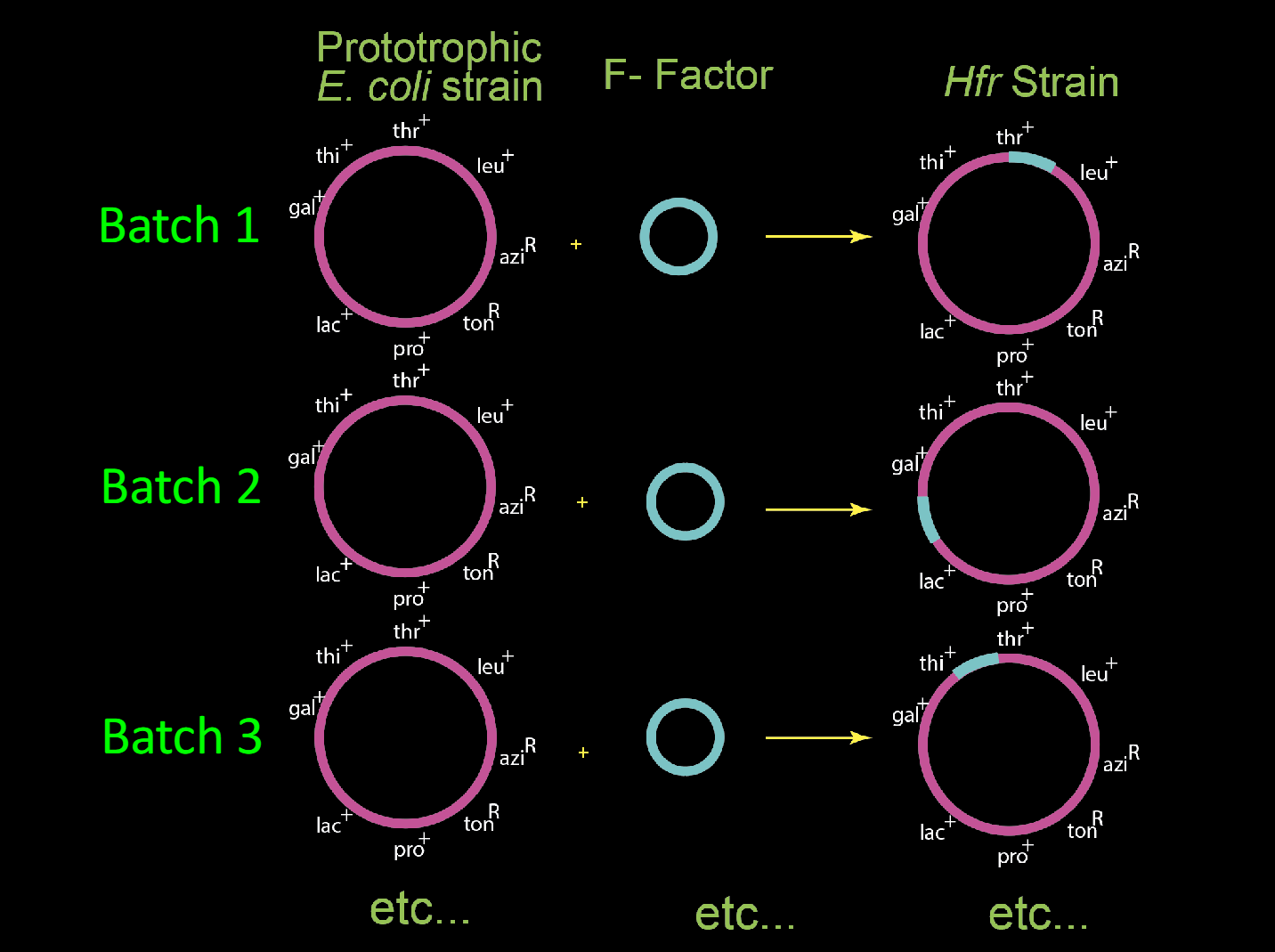
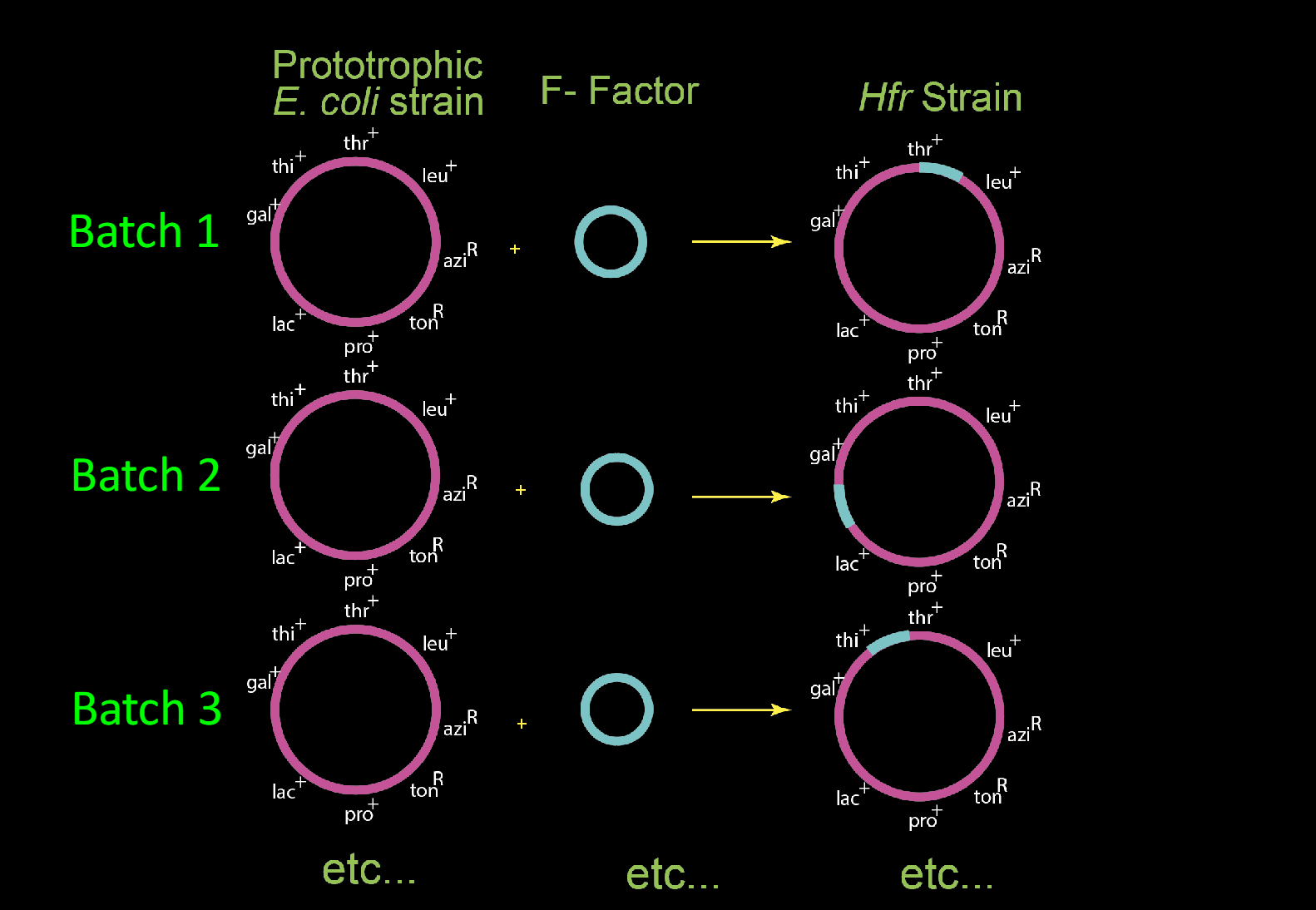
What is Hfr?
-strains with integrated F factor are Hfr (High Frequency of Recombination)
-1 in 10,000 F+ cells
-integration results from double crossover at random site in host genome
-once integrated, F factor still mediates conjugation, but drags the whole genome with it.
Describe the transfer of bacterial genes (steps 3-5)
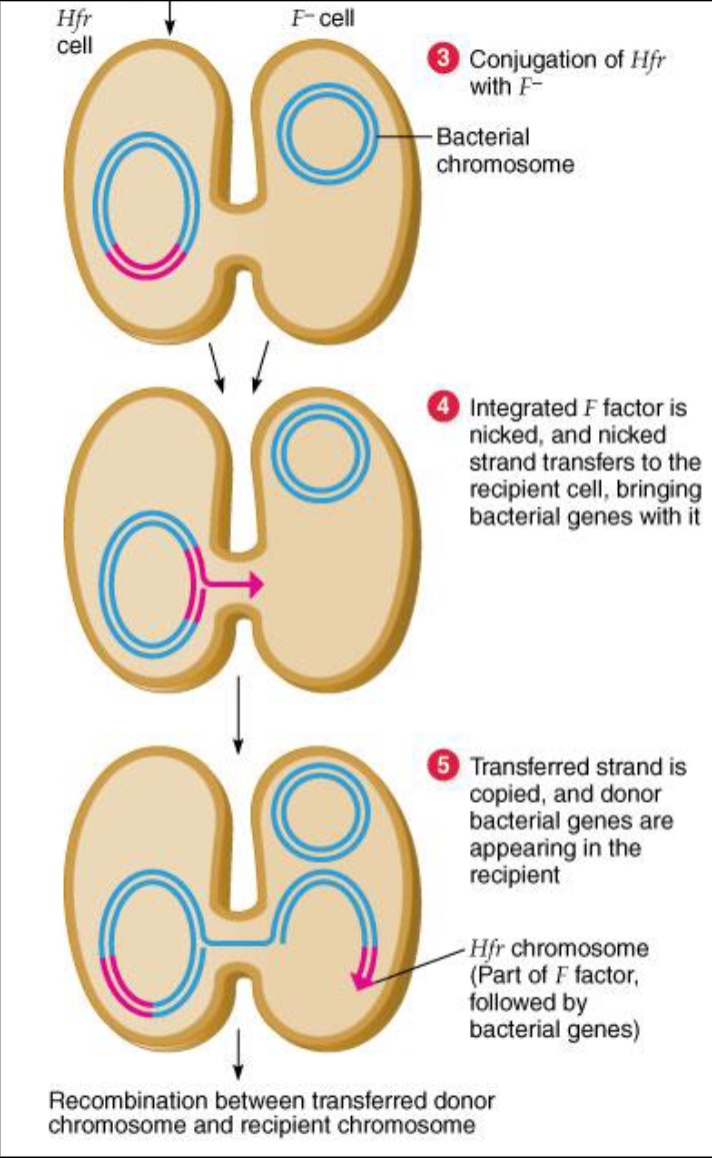
describe Conjugation with Hfr cells:
-Parts of donor chromosome are inserted into recipient chromosome.
-Recombinants detectable
describe why Hfr phenotype rarely transferred
-Origin is within F-factor
-Entire chromosome must be transferred for F-factor to be complete in the recipient
-conjugation usually ends before this can take place
Intro of Conjugation mapping by interrupted mating…
how long does Hfr conjugation require for complete transfer
what does the order that recombinant alleles appear indicate
- Hfr conjugation requires ~100 minutes for complete transfer.
-The order in which recombinant alleles appear indicates the order of genes on
the Hfr chromosome.
1. Make Hfr strains starting with prototrophic E. coli
(Conjugation mapping by interrupted mating)
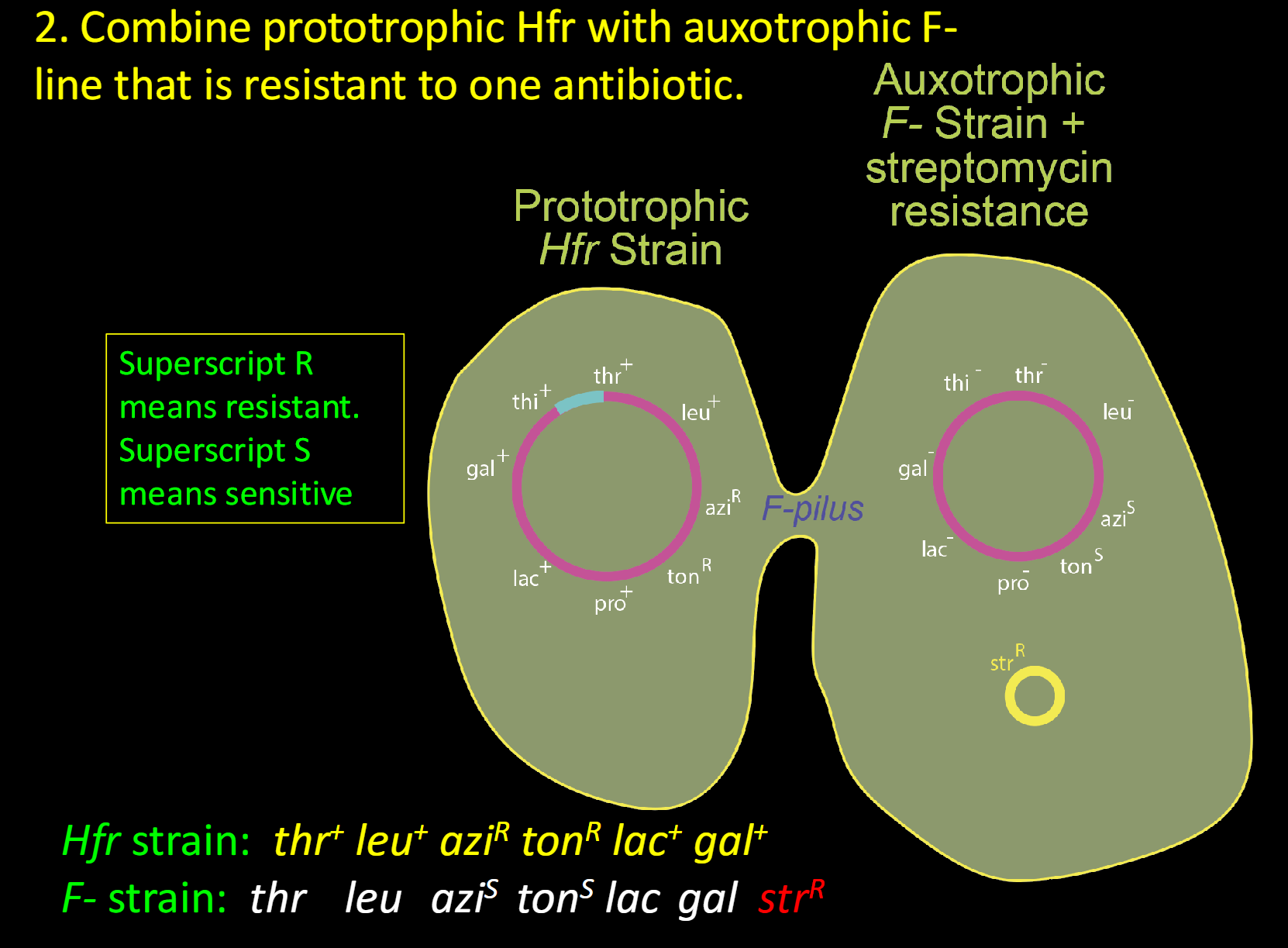
2. Combine prototrophic Hfr with auxotrophic F- line that is resistant to one antibiotic.
(Conjugation mapping by interrupted mating)
Hfr strain: thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac+ gal+
F- strain: thr leu aziS tonS lac gal strR
3. At short intervals, disrupt mating and take samples
(Conjugation mapping by interrupted mating)
multiple trials
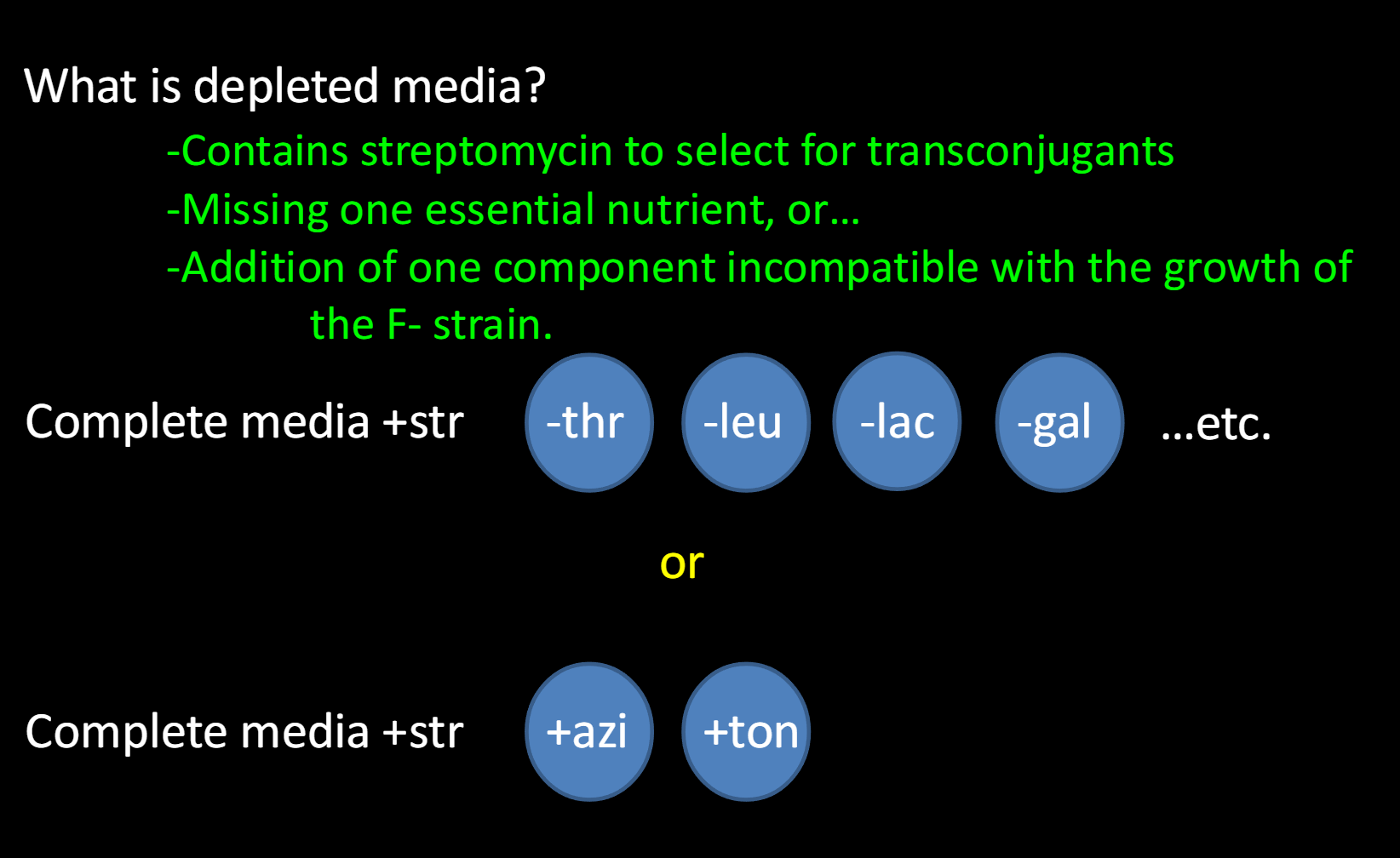
Plate cells on depleted media to observe recombinant
phenotypes
(Conjugation mapping by interrupted mating)
depleted and complete media
Depleted media:
-Contains streptomycin to select for transconjugants
-Missing one essential nutrient, or…
-Addition of one component incompatible with the growth of
the F- strain.
what does Superscript R and Superscript S mean
Superscript R: resistant
Superscript S: sensitive
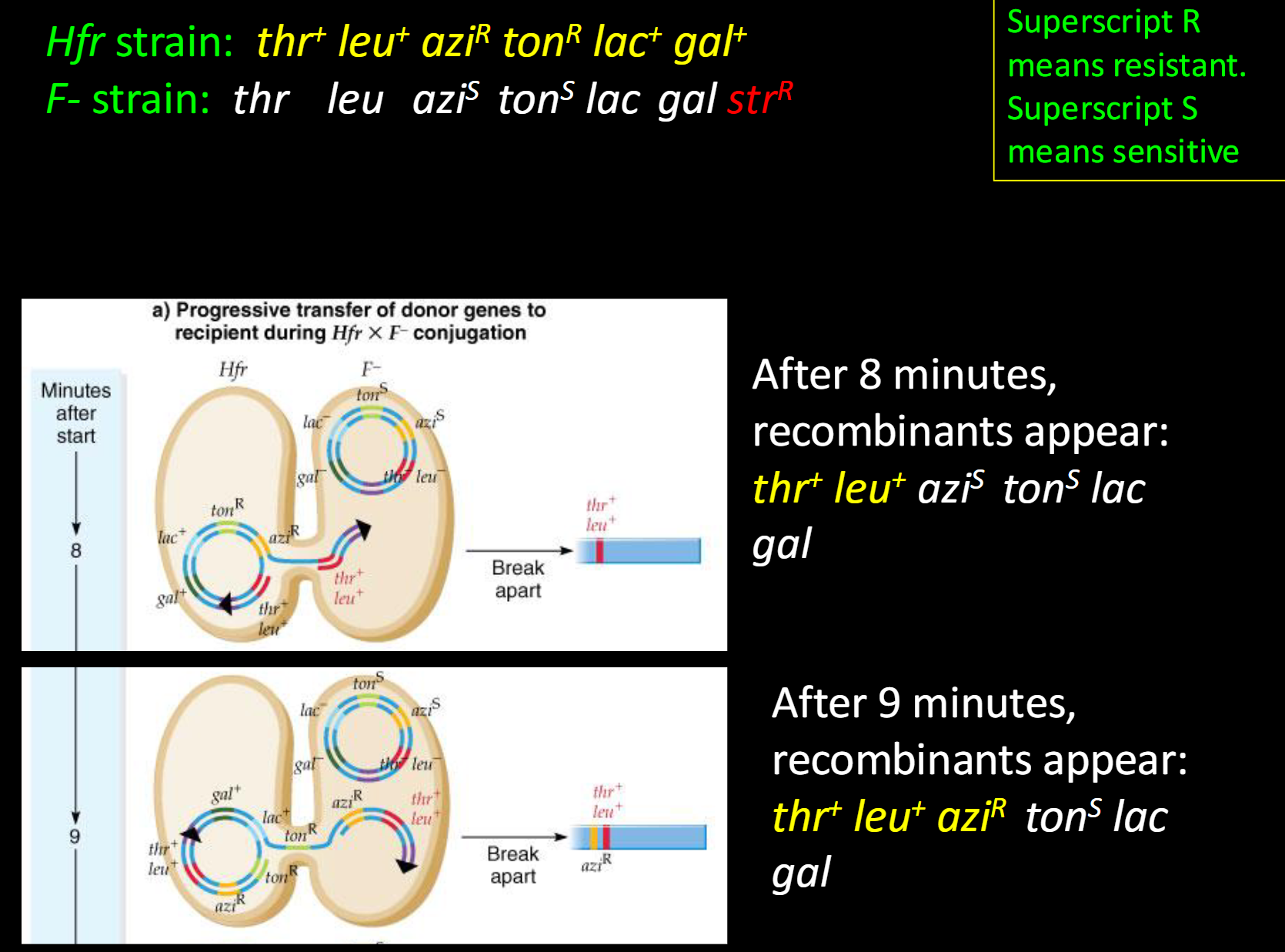
what is the first Hfr Strain and F- Strain
what recombinants appear after 8 and 9 minutes.
Hfr strain: thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac+ gal+
F- strain: thr leu aziS tonS lac gal strR
-After 8 minutes, recombinants appear:
(thr+ leu+ aziS tonS lac gal)
-After 9 minutes, recombinants appear:
(thr+ leu+ aziR tonS lac gal)
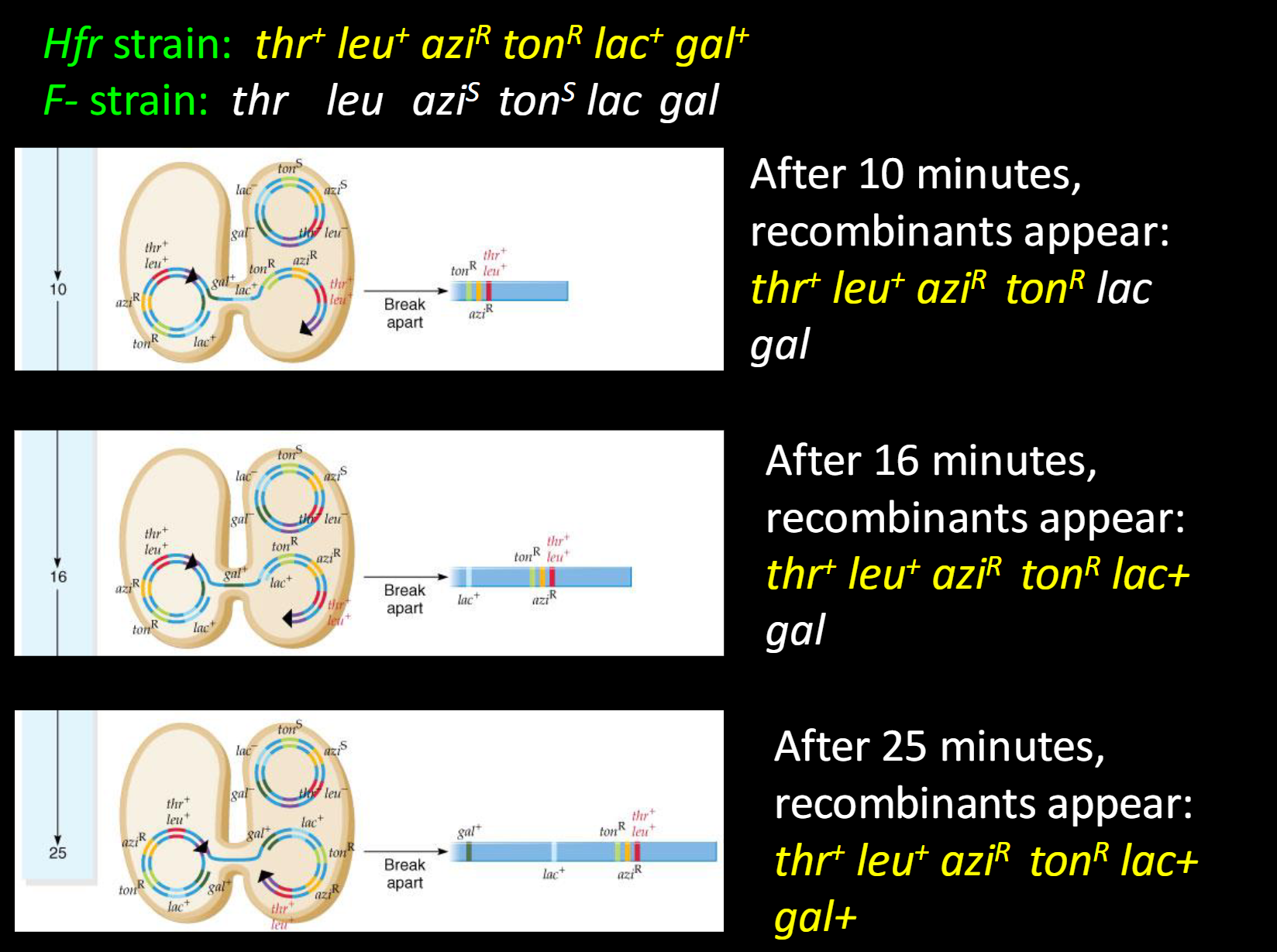
what is the second Hfr Strain and F- Strain
what recombinants appear after 10, 16, and 25 minutes
-Hfr strain: thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac+ gal+
-F- strain: thr leu aziS tonS lac gal
-After 10 minutes, recombinants appear: (thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac gal)
-After 16 minutes, recombinants appear: (thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac+ gal)
-After 25 minutes, recombinants appear: (thr+ leu+ aziR tonR lac+ gal+)
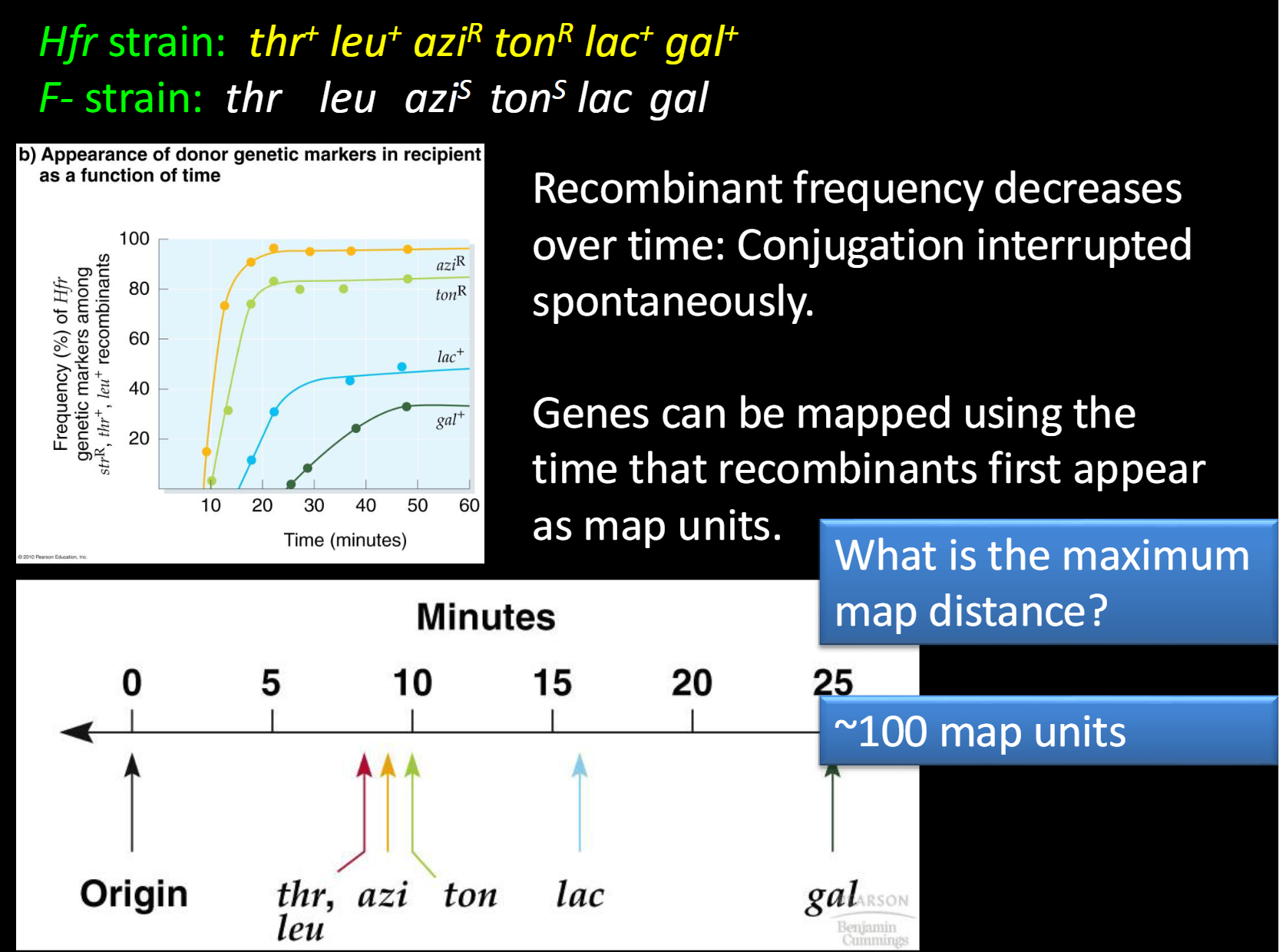
What does it mean if recombinant frequency decreases over time
conjugation interrupted spontaneously
How can genes be mapped
using the time that recombinants first appear as map units
How to map complete genome given limitations on conjugation?
Repeat experiment using different Hfr strains