Dermatology 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the least cancerogenic serotypes of HPV?
6, 11, 42, 43, 44
What are the diagnostic hallmarks of psoriasis on dermoscopy?
Red dotted vessels (due to dilation of capillaries within the dermal papillae)
White scales (due to proliferation of keratinocytes and cornified cells leading to thickening of the stratum corneum)
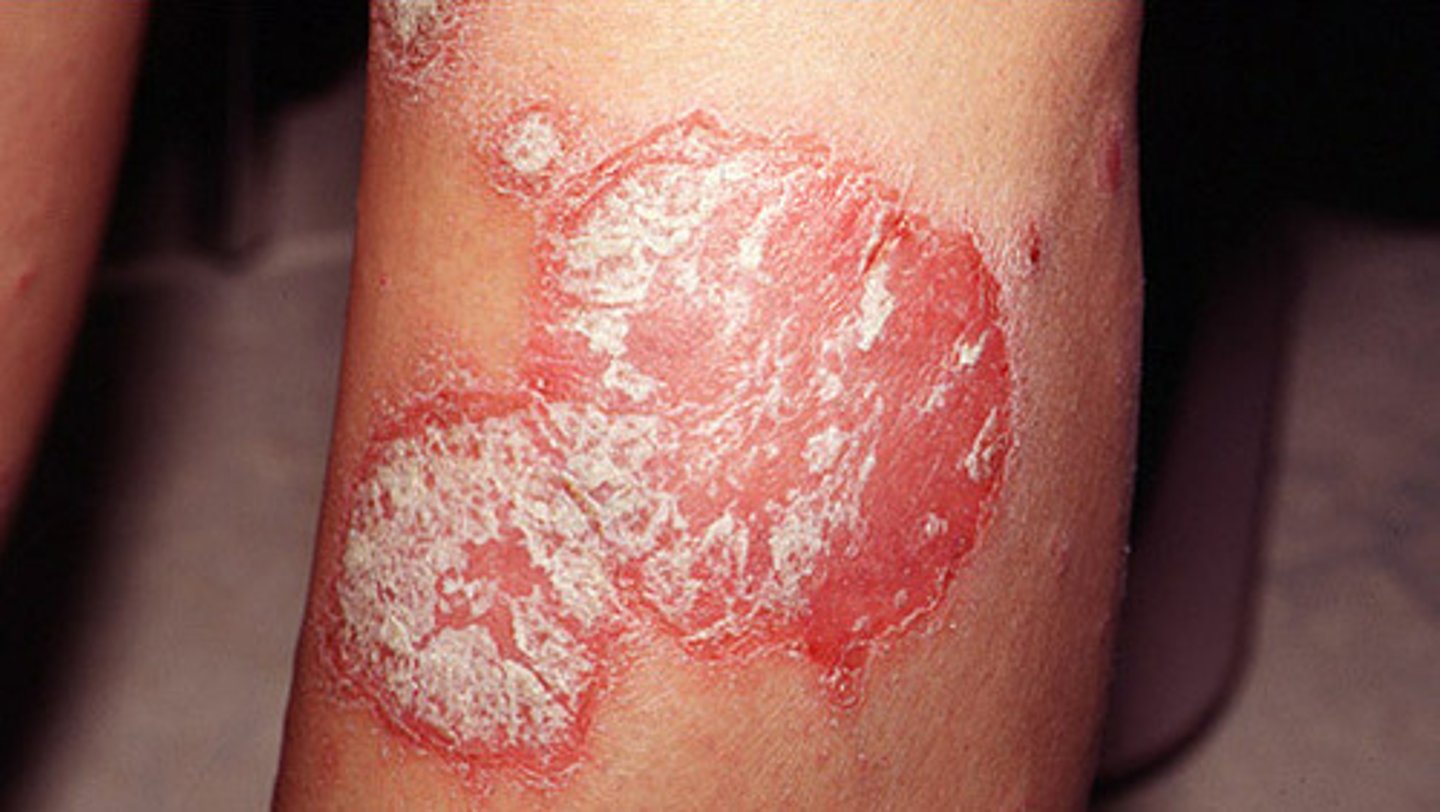
A 16-year-old male complains of itching of the face. He has a personal and family history of atopy (allergic rhinitis and asthma). The dermatologic examination revealed an erythema with small vesicles at the level of the armpit, consistent with eczema. A previous treatment with topical corticosteroids had temporary results. The patient is otherwise fine and has no other complaints.
Which is the most plausible diagnosis in this patient?
Atopic dermatitis
Name at least 3 different types of acne.
1. Acne vulgaris
2. Acne keloidalis
3. Acne conglobata
4. Adult acne
5. Acne fulminans
6. Acne excoriée
7. Infantile acne
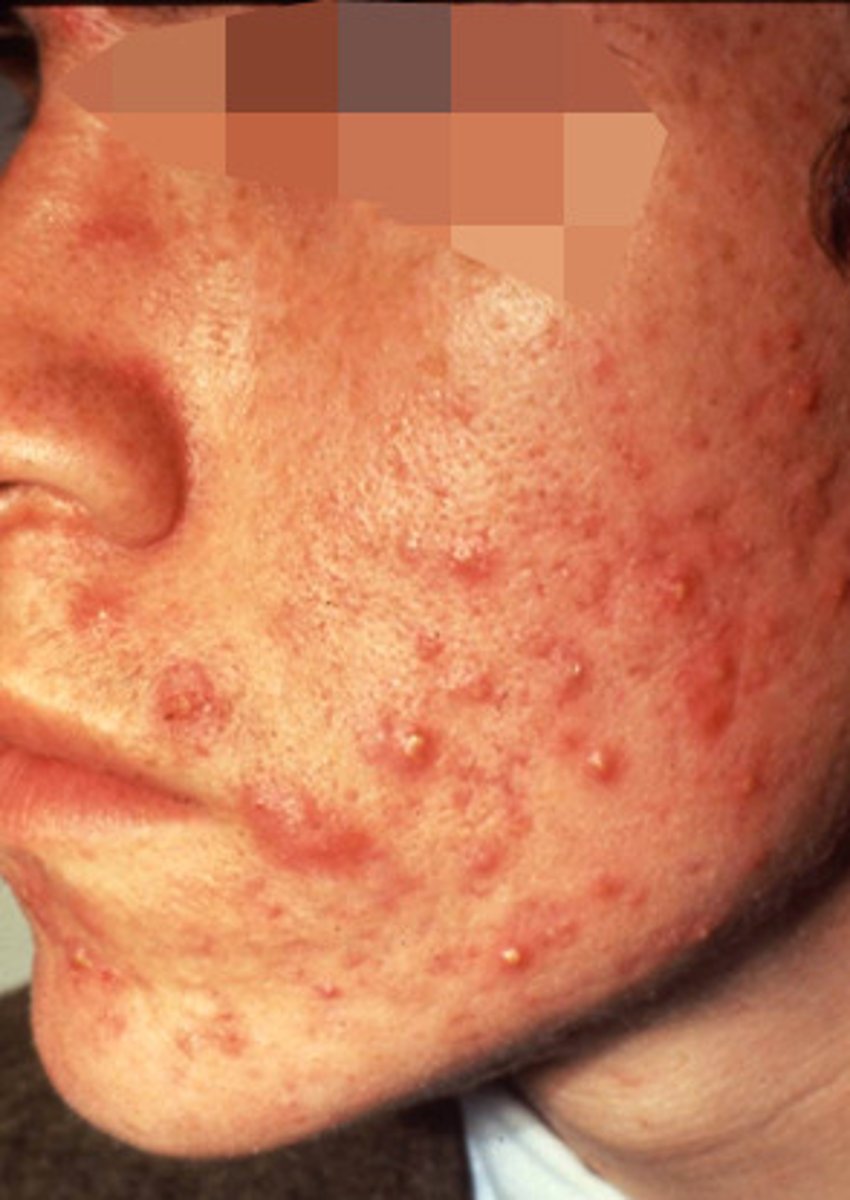
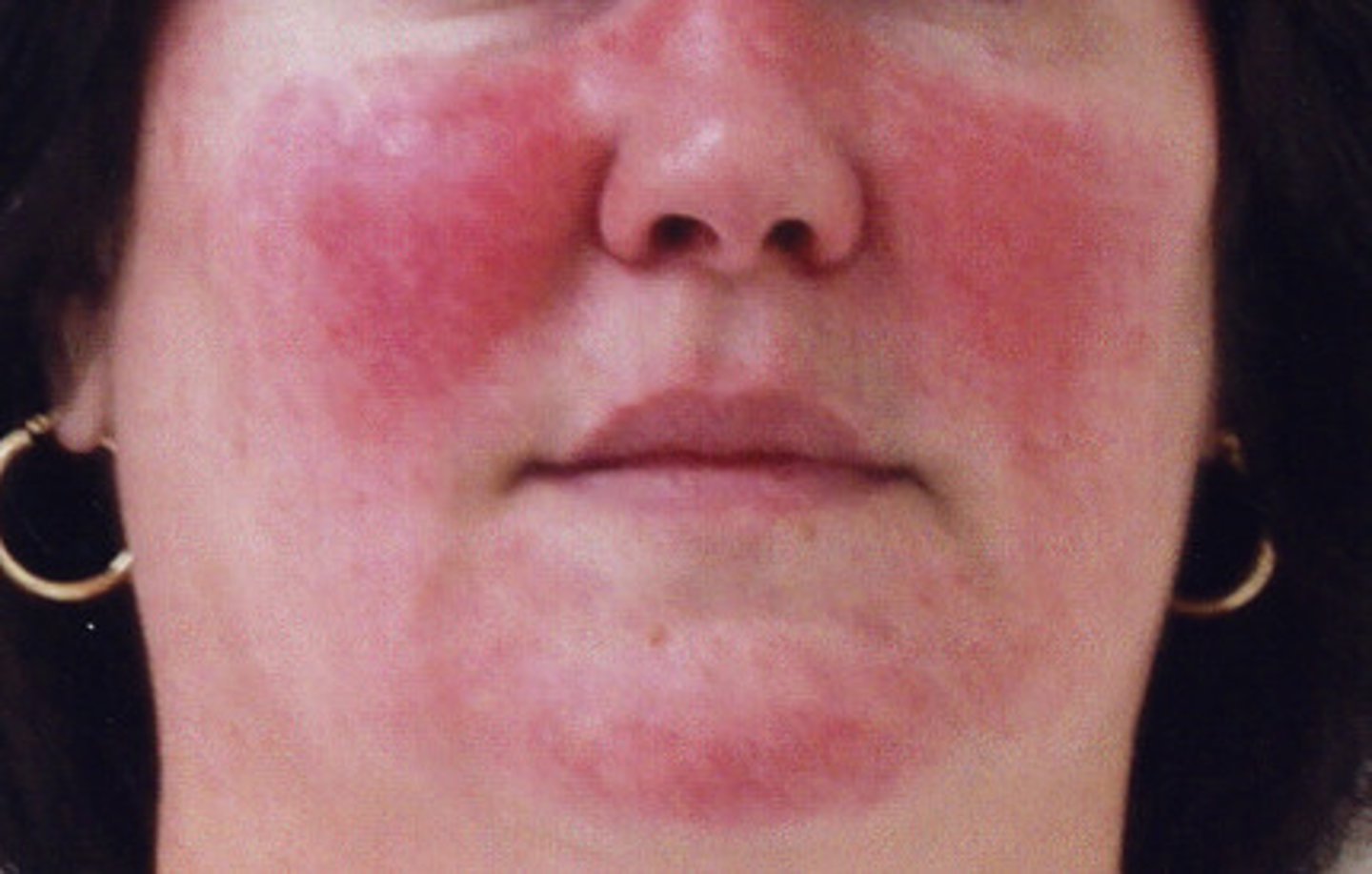
What are the main areas of presentation of rosacea?
Forehead, nose, upper cheeks, chin.
Most often symmetric presentation
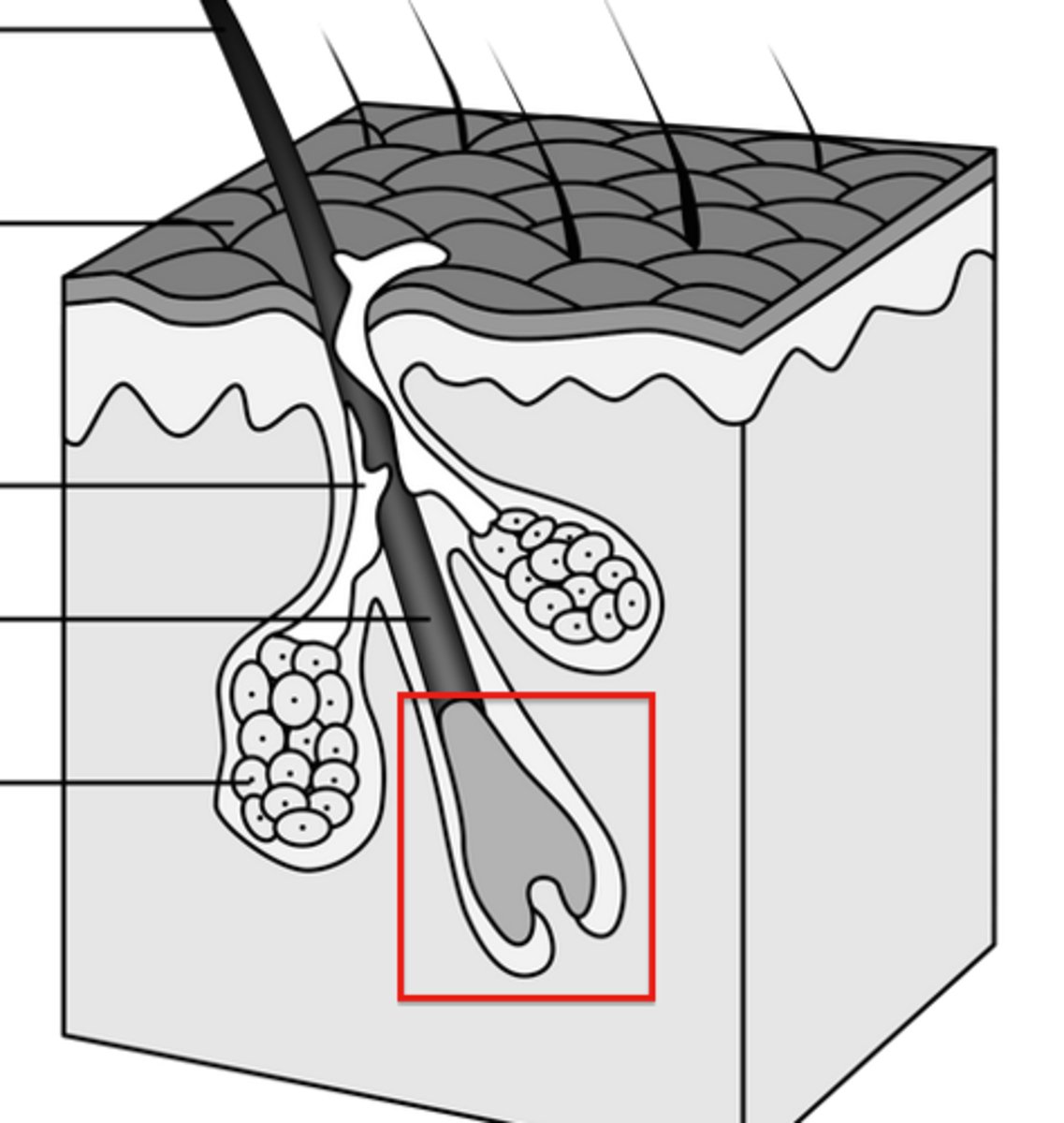
Which structure of the hair follicle contains matrix cells responsible for hair shaft production?
Hair bulb
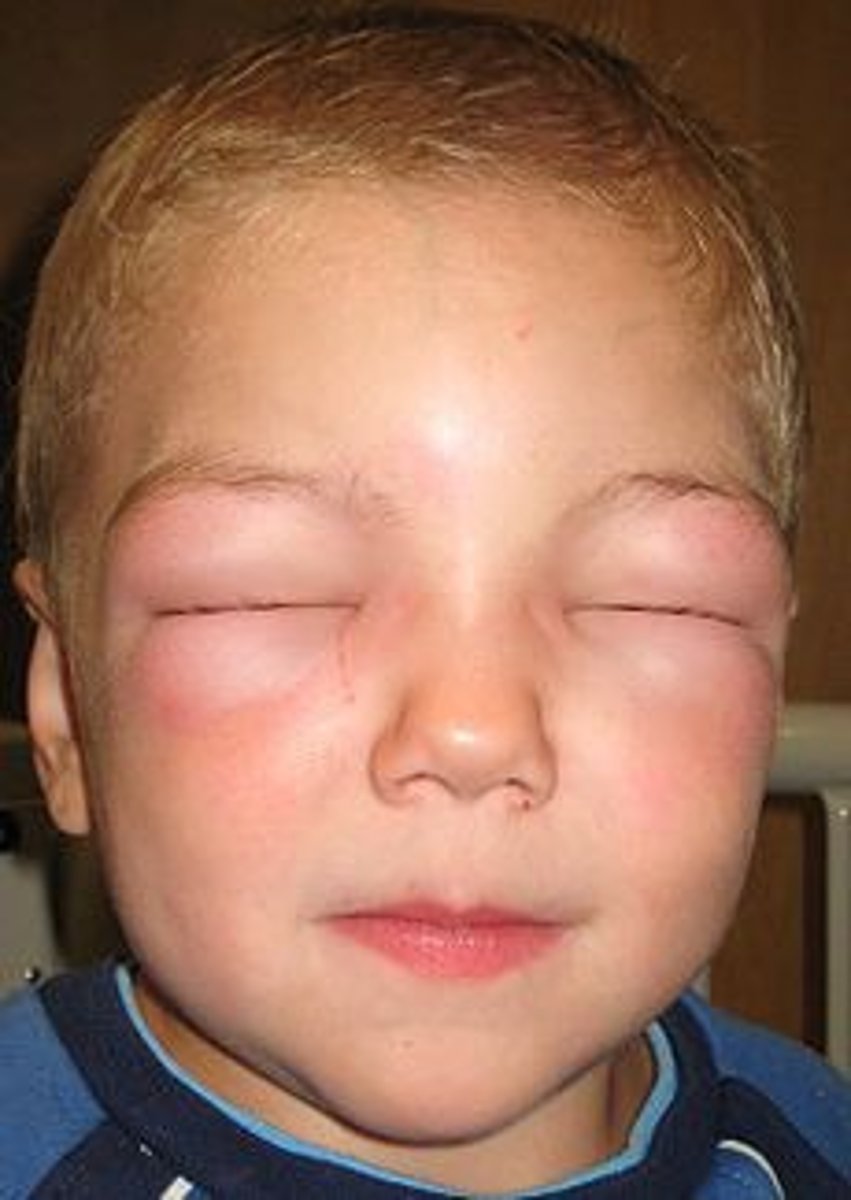
List at least 3 cutaneous diseases associated with type I hypersensitivity reactions
Urticaria; Angioedema; Anaphylaxis
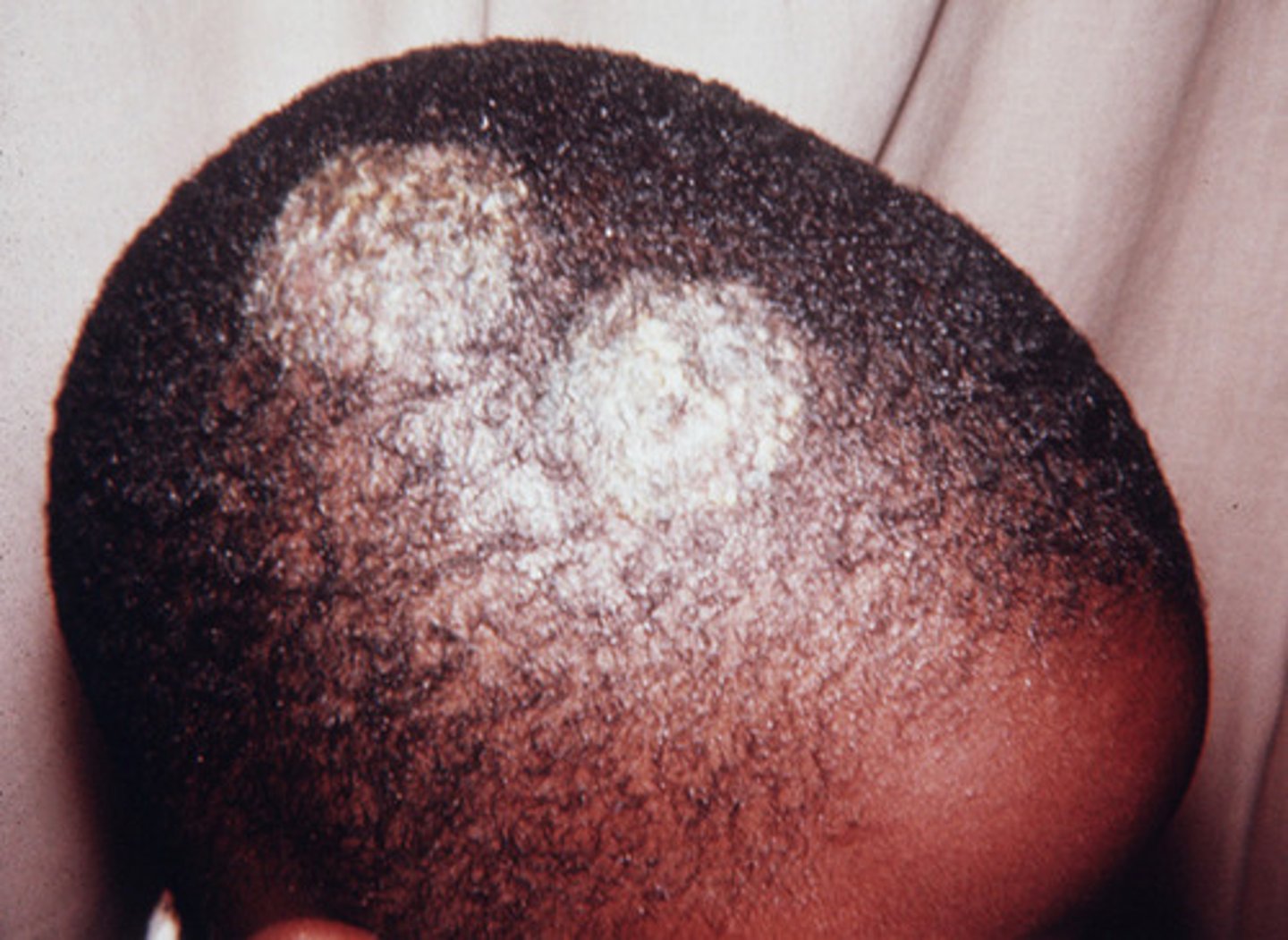
An 18-year-old male presents to the emergency department with a skin lesion that he has noticed for about two weeks. He describes the lesion as a red, scaly area on his scalp, with well-defined edges. On physical examination, the lesion has a "ring-like" shape with a clear center and red borders. No signs of enlarged lymph nodes or fever. The patient has no other symptoms but reports itching in the affected area. He has no significant history of skin diseases, although he has recently engaged in sports and shared equipment with other teammates. What is your diagnosis? Which kind of test would you use to confirm the diagnosis?
TINEA CAPITIS;
Gold standard: fungal culture and microscopic examination
State one form of a NON autoimmune pemphigus and explain why
Hailey Hailey disease is a form of a non-autoimmune pemphigus caused by an autosomal dominant mutation in the ATP2C1 gene which codes for a calcium channel.
List the exogenous risk factors of melanoma
1. UV radiation exposure
2. Sunburns
3. Geographical and environmental factors
4. Iatrogenic immunosuppression (e.g. organ-transplanted patients)
5. Artificial UV sources

What is the 4-step model of melanoma progression?
1. A driver mutation (i.e. BRAF mutation) makes the cell hyperactive in growth signaling
2. Escaping primary senescense (i.e. CDKN2A loss). Loss of CDKN2A allows cells to escape the natural aging stop signals
3. Overcoming apoptosis (i.e. TP53 mutation)
4. Immortalization (i.e. TERT-p mutation): mutations in TERT-promoter switch on telomerase, making the cell immortal
What is the main clinical distinguishing point between acne and rosacea?
The absence of comedones and presence of facial flushing in Rosacea.
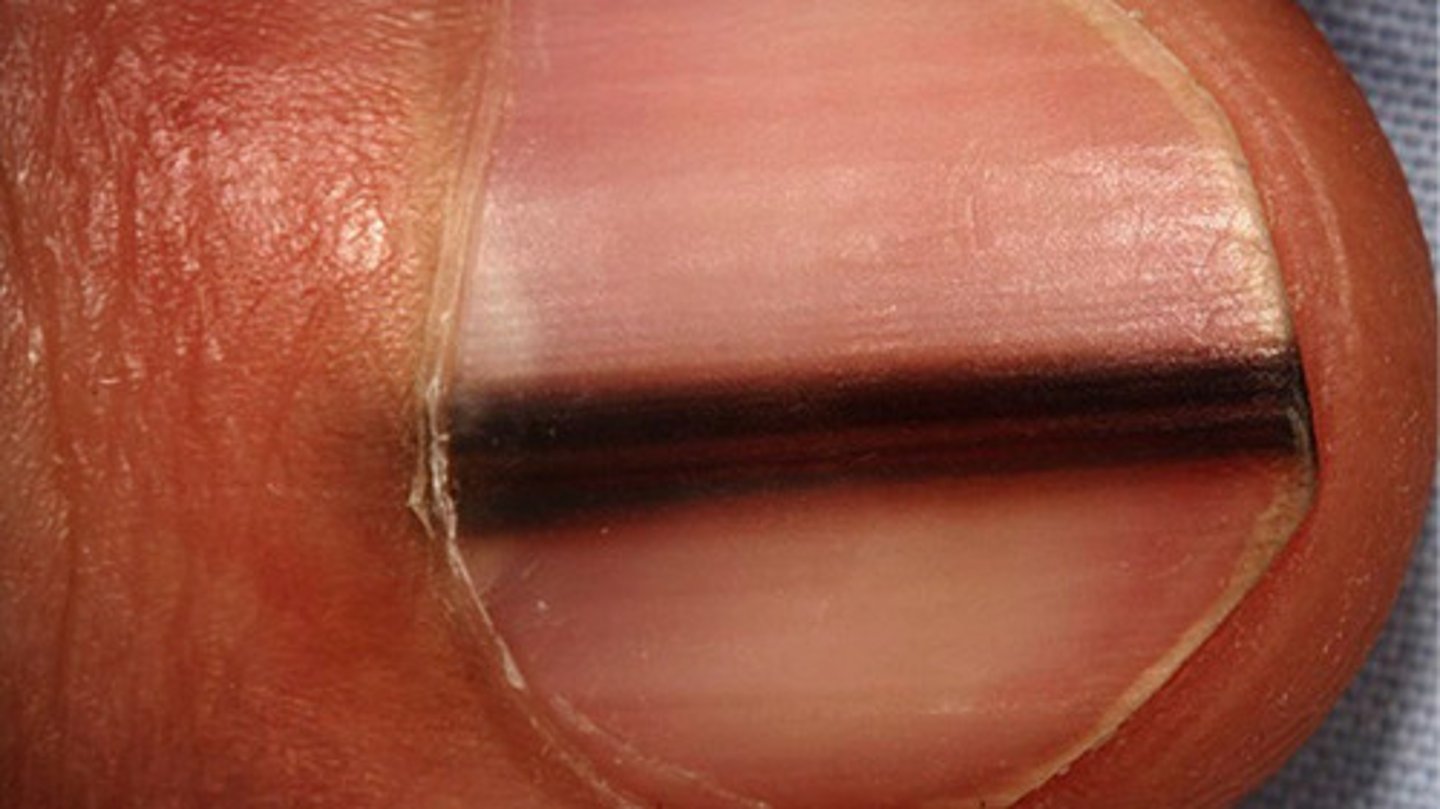
Which patients most commonly present with Muehrcke's lines?
Patients with hypoalbuminemia / liver cirrhosis.
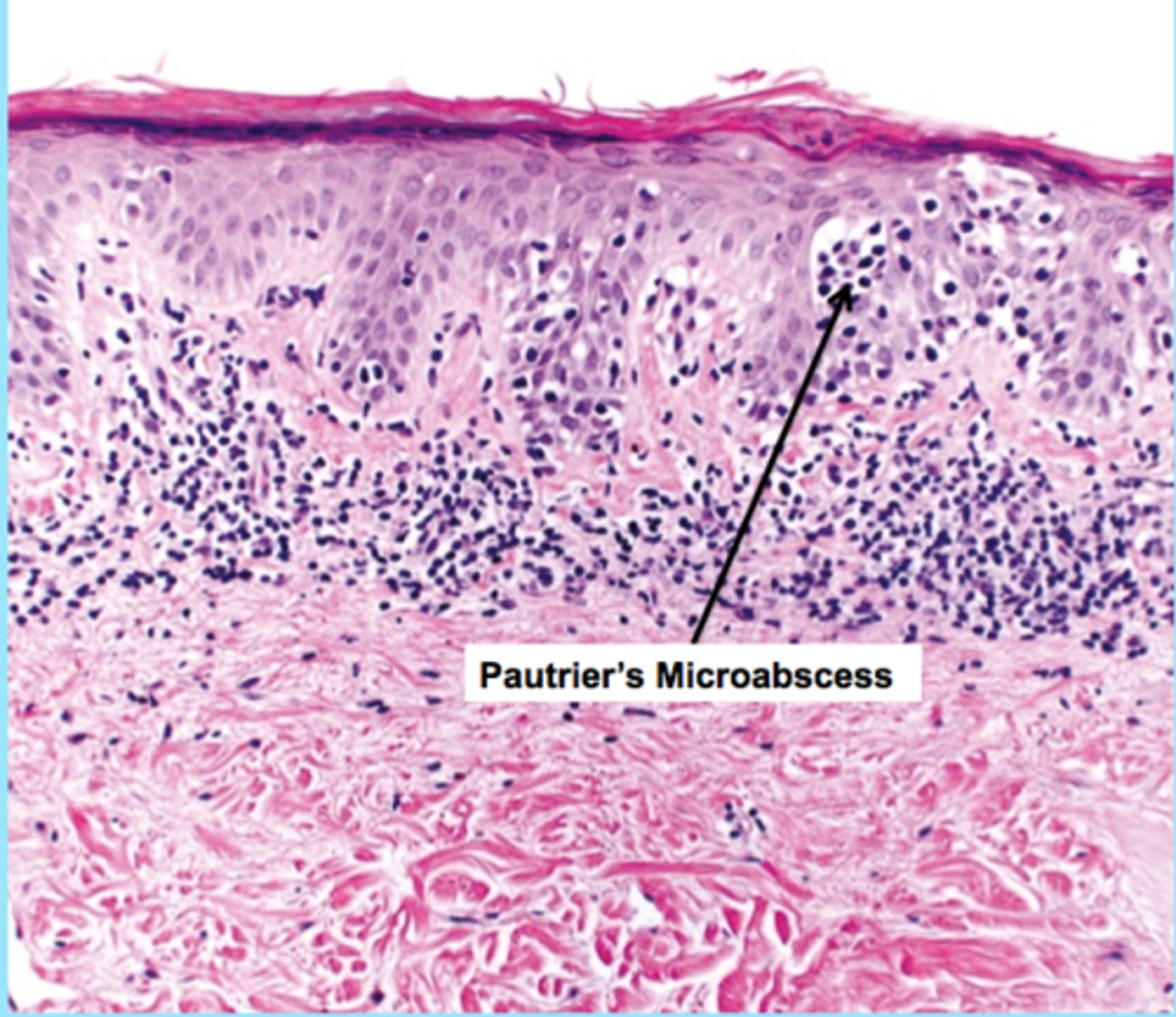
In which condition can Pautrier microabscesses be observed?
MYCOSIS FUNGOIDES
What is the key sign that allows us to distinguish between subungual melanoma vs. a benign melanocytic nevus of the nail matrix? (define in 1 sentence)
Hutchinson's sign = melanonychia with a necessary extension into the perionychium
A 52-year-old man presents with sudden, painless tongue and facial swelling without urticaria. He has been on ramipril for hypertension for 3 years. C4 is low. What is the diagnosis?
ACE-I INDUCED ANGIOEDEMA
How to differentiate Urticaria from Urticarial Vasculitis?
Based on the DURATION OF THE LESIONS:
- Urticaria: <24h
- Urticarial vasculitis >24h
List the 6 clinical main subtypes of basal cell carcinoma
1. Nodular BCC
2. Pigmented BCC
3. Superficial BCC
4. Morpheaform (sclerodermiform) BCC
5. Uncus rodens (ulcerated BCC)
6. Pinkus tumor
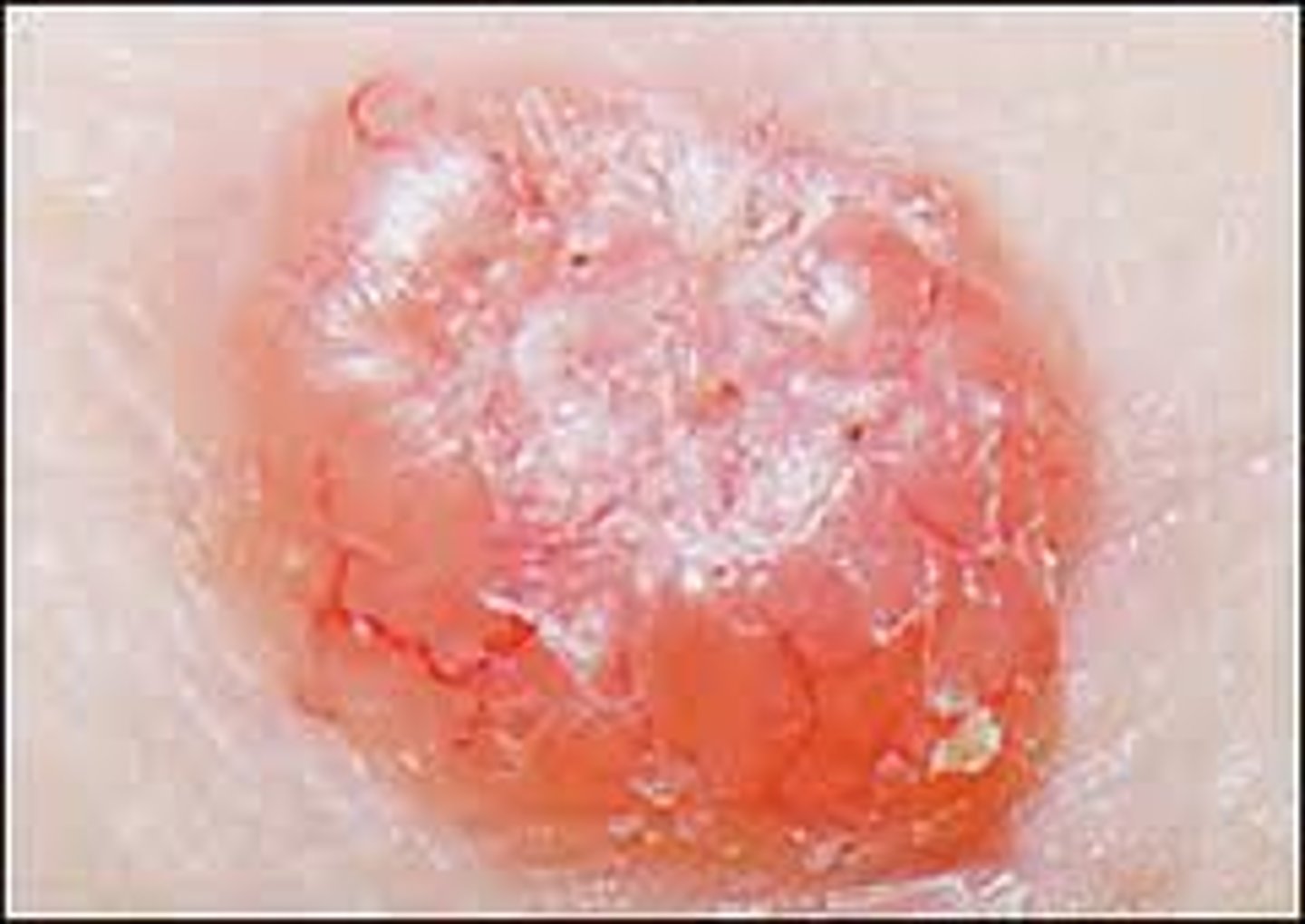
List at least 3 cutaneous diseases associated with type III hypersensitivity reactions
1. SLE
2. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
3. IgA vasculitis

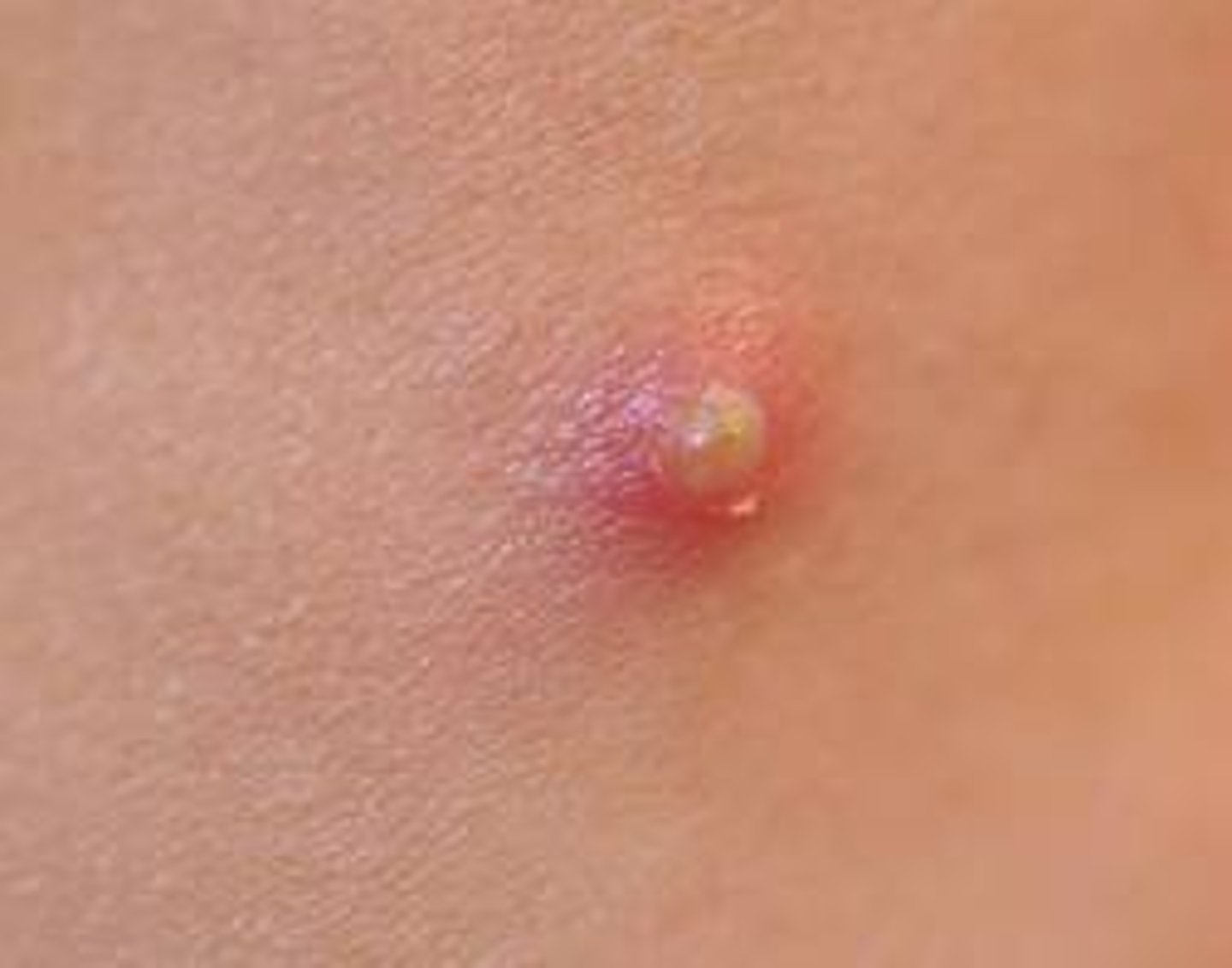
Define Pustule and list the names of 4 diseases that appear with this lesion
PUSTULE: circumscribed, raised papule containing visible pus.
1) Acne vulgaris
2) Acne fulminans
3) Palmoplantar pustular psoriasis
4) Impetigo