Gas exchange and homeostasis
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
upcoming biology test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
gas exchange surfaces must be…
permeable
thin
moist
large surface area
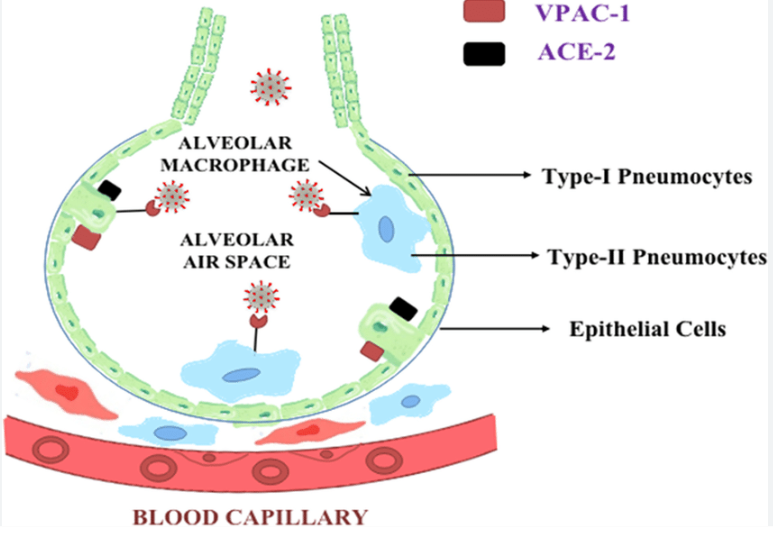
alveoli
the sight of gas exchange in the lungs
small branching chambers that increase surface area
have extensive capillary beds
Alveolar epithelium cells have two types
Type 1 Pneumocytes- very thin to facilitate gas exchange
Type 2 Pneumocytes- secrete fluid for gas exchange and surfactant to prevent collapse due to cohesion of water
ventilation
a concentration gradient of gases must be maintained by moving air in and out of the lungs
airways
Trachea branches into two large tubes (bronchi)
Bronchi branch into little bronchioles
bronchioles go to little alveoli
can you name:
the arteriole and venule blood flow directions
Type 1 and 2 Alveolar epithelium cells
where o2 and co2 enter and exit
capilaries
inspiration (breathing in)
diaphragm contracts
external intercostal muscles contract pulling the rib cage up and outwards
internal intercostal muscles relax and are pulled back into their elongated state
all of these movements increase volume and decrease pressure think a syringe
Expiration (exhale)
the diaphragm relaxes
ab muscles contract
internal intercostal muscles contract pulling ribcage in and down
external intercostal muscles relax and are pulled back into their elongated state
antagonistic pair
work in pairs to preform related but opposite movements (intercostal muscles)
hemologbin
oxygen binding protein in red blood cells
composed of 4 polypeptide chains each with an iron containing heme group that reversibly binds oxygen
prosethetic group
non protein molecule that is tightly bound to a protein and helps it function
and example of this is the heme group
as each O2 binds…
it alters the confirmation (shape) of hemoglobin (very slight change)
the altered confirmation makes subsequent binding easier this is called cooperative binding (this means hemoglobin has a higher affinity for O2 in oxygen rich areas like the lungs )
this results in sigmoid curve
oxygen loading
is promoted in oxygen starved areas like muscles
where hemoglobin has a lower affinity for O2
fetal arteries have a lower pressure hence hemoglobin….
must have a higher affinity at lower pressures
myoglobin
oxygen bonding molecule found in skeletal muscles
not capable of cooperative (therefore not a sigmoid curve)
holds onto O2 longer than hemoglobin
slows the onset of anaerobic respiration
CO2 in the picture
tissue with high metabolic rate release more CO2
hemoglobin has an allosteric site for CO2
when co2 binds hemoglobin changes it shape thus the O2 affinity is lowered
red blood cells release O2 in the presence of CO2
muscle cells have high metabolic activity means more co2 and Bhor shift
6.4 homeostasis
kidney plays a role in
osmoregulation and excretion in humans
Osmoregulation
maintenance of internal solute concentration (water and solute concentration)
regulation of osmotic concentration
units= osmoles per liter (OsmolL-1)
excretion
removal of waste
Renal artery
brings blood to the kidney
renal vein
carries blood away from the kidney
where does filtration occur?
the nephrons
about 1 million per kidney
functional unit of the kidney
only the plasma is filtered through the kidneys
ultrafiltration
occurs in the glomerulus
blood flowing in the capillaries of the glomerulus is under very high pressure
the glomerulus has fenestrated capillaries which allows fluid (non-blood cells) no escape
filtrate
is the fluid forced through the capillary walls
anything that goes through the three barriers of the glomerulus becomes a part of the glomerular filtrate
after the glomerulus, filtration flows through….
the proximal convoluted tubule
the PCT selectively reabsorbs glucose, amino acids, and salts by active transport (microvilli increases its surface area)
the loop of Henle
allows the reabsorption of water
starts in the cortex of the kidney then dips down into the medulla (medulla must be hypertonic)
what allows a high solute concentration in the ascending part of the loop of Henle?
the active pumping of salts
the water that is reabsorbed in the loop does one of two things…..
the water from the loop is reabsorbed back into the blood
water that stays in the loop becomes urine
DIstal convoluted tubule
ions are exchanged (more active transport)
there is less absorption than the PCT due to no microvilli being present
Finally the filtration enters….
the collecting duct for final water adjustments
the collecting ducts permeability to water varies
the hormone ADH controls this permeability
ADH
promotes the formation of aquaporins in the walls of the collecting duct
the aquaporins are membrane channels that are permeable to water
if ADH is present…
more water is reabsorbed into the blood creating a small volume of concentrated urine
if ADH is not present …..
a large volume of urine is produced
Finished urine
leaves the kidneys through the ureters
stored in the bladder
and exits the body through the urethra
Homeostasis
maintenance of the internal environment of an organism, variables are kept within preset limits, despite fluctuations in the external environment
an example of this is Osmoregulation and blood sugar regulation
the inner workings of homeostasis are
control centers receive inputs from receptors and generate outputs to send to effectors
homeostasis relies on
a negative feedback cycle to maintain set conditions
the feedback loop reduces the effects of change and helps maintain balance
Blood Sugar regulation
two hormones regulate blood glucose levels (insulin and glucagon)
glucose is regulated by building up or breaking down glycogen
Alpha cells
synthesize and secrete glucagon when glucose levels in the blood are too low
glycogen is hydrolyzed to glucose in the liver and released into the bloodstream
blood sugar rises as a result
Beta cells
synthesize and secrete insulin when glucose levels in the blood are too high
stimulated uptake of gluecose by skeletal muscle and liver tissues
stimulates formation of glycogen from gluecose in the liver
type 2 diabetes (late onset)
deficiency in glucose receptors or glucose transporters on target cells
the body may not produce or respond to insulin
the cause in unknown but is associated with sugary, fatty diets, prolonged obesity, lack of exercise and genetic factors
Treatments
diet must be adjusted to avoid “peaks and throughs” in blood glucose levels
small frequent meals with low sugar content
exercise increases insulin uptake and action
Thermoregulation
peripheral thermoreceptors detect temperature changes and send signals to the brain
the brain initiates several different reponses
Potential responses for thermoregulation
shivers- small muscle twitches generate warmth
vasodilation/ vasoconstriction- increased blood flow for heat retention (heat lost through the skin)
sweating for cooling
goosebumps for warmth (rising hair traps)
Brown adipose tissue
specialized “fat cells”
more in infants but also found in adults
metabolized for heat production
uncoupled respiration- where energy produced by respiration is dissipated instead of being used to perform work
Thyroxin
regulates metabolic rate and therefore body temperature; secreted by thyroid gland
osmoregulation
the maintenance of constant osmotic pressure in the fluids of an organism by the control of water and salt concentrations
Osmo regulators
maintain a constant internal solute concentration
ex: most terrestrial animals, freshwater animals and some marine organisms
Osmo conformers
tend to have internal solute concentrations that are isotonic to their external environment
(many marine invertebrates)