5.5ab Causes of flooding
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
types of flooding
flash flooding, coastal flooding, river flooding, groundwater flooding, surface water flooding
physical causes of flooding
snow/glacial melt, intense rainfall, monsoon, drainage basin characteristics, prolonged rainfall
what causes prolonged rainfall in the uk
jet streams
label the jet stream
where does the jet stream more in the winter
south
where does the jet stream move in the summer
north
what can sometimes happen to the jet stream
can get stuck further south in the summer causing low pressure and wet summers
what does the prevailing wind cause
comes from south west over warm Atlantic Ocean so more evaporation and vapour
what flooding is causes in York
rapid snowmelt
what flooding is caused in Asia and America
snowmelt
what flooding is caused in Iceland
glacial outburst floods due to volcanic activity generating melt water
what flooding is caused in Russia
annual flooding in Siberia as quick transition from winter to summer so ice melt
what flooding is caused in South Africa
get tropical cyclones e.g. in 2019 from cyclones idea and Kenneth major flooding
what flooding is caused in Pakistan
disastrous floods in 2010, 9000mm of water in one week (10x yearly av)
what flooding is caused in Nepal
catastrophic draining of glacial lakes in Himalayas
why is Bangladesh so at risk of flooding
80% people exposed to flood risk, half country less than 12.5m above sea level
why is china and Vietnam at risk of flooding
most at risk due to low lying plains of large rivers
what does southern and eastern Asia experience
intense seasonal monsoonal rainfall
what is annual rainfall like today
70% of av annual rainfall occurs in 100 days
how can human actions exacerbate (worsen) flooding
changing lands, mismanagement of rivers
what are the types of changing lands
plant other forests e.g. palm oil, deforestation, urbanisation, agriculture
what are the types of mismanagement of rivers
dams, embankment, channelising rivers
what is an example of planting other forests increasing flooding
flooding increased by 20% in Malaysia
what is an example of agriculture increasing flooding
in India they went from forest to pastoral farming and flooding risk increased by 50%
what does deforestation then lead to
agriculture
what are the types of agriculture
arable(crops) and pastoral(animals)
how does arable(crops) agriculture increase flooding risk
down contour plough, bare soil for part of the year
how does pastoral(animal) agriculture increase flooding risk
overgrazing leading to compaction
how does urbanisation increase flood risk
impermeable surfaces, blocked bridges by debris (cars/trees), drains and sewers
what is an example of impermeable surfaces due to urbanisation
5% of surfaces in London is tarmac for parking
what is an example of blocked bridges due to debris
boscastle 2004
what is an example of embankments increasing flood risk
2015 Keswick, 5m embankment overtopped by 5.9m flood
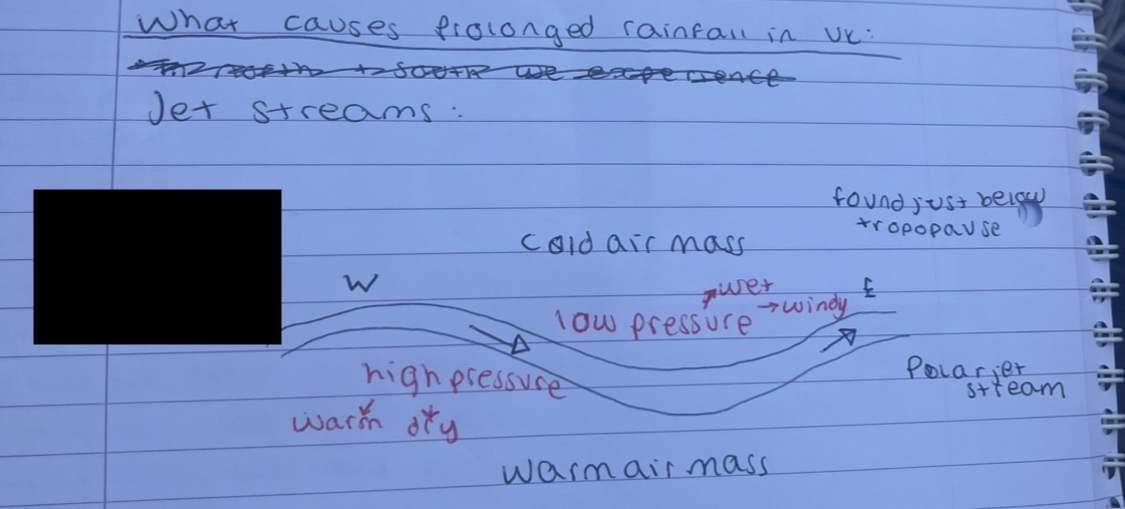
what is the wind in a jet stream
ribbon of strong winds aprox 200km

what is the air mass here
warm air mass

what is the pressure here
high pressure, warm and dry

what is the air mass here
cold air mass

what is the pressure here
low pressure, wet and windy
where is the jet stream found
just below tropopause
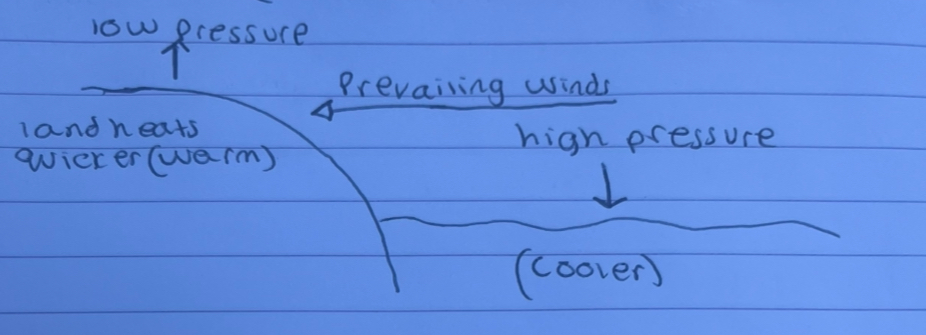
what season is this and why
summer so more monsoons as hotter land so more evaporation
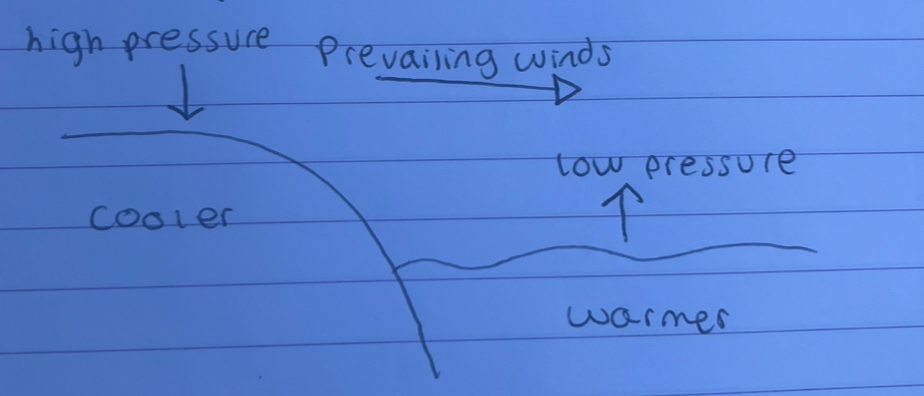
what season is this and why
winter so drier as cooler land and warmer seas