intro + molecular orbitals
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what is an organometallic
a compound containing a metal-carbon (M-C) bond
what is a particle
a small, localised object to which can be ascribed several physical or chemical properties such as volume, density, charge or mass
what do particles have and what do they obey
particles have position and momentum
they obey classical particle physics
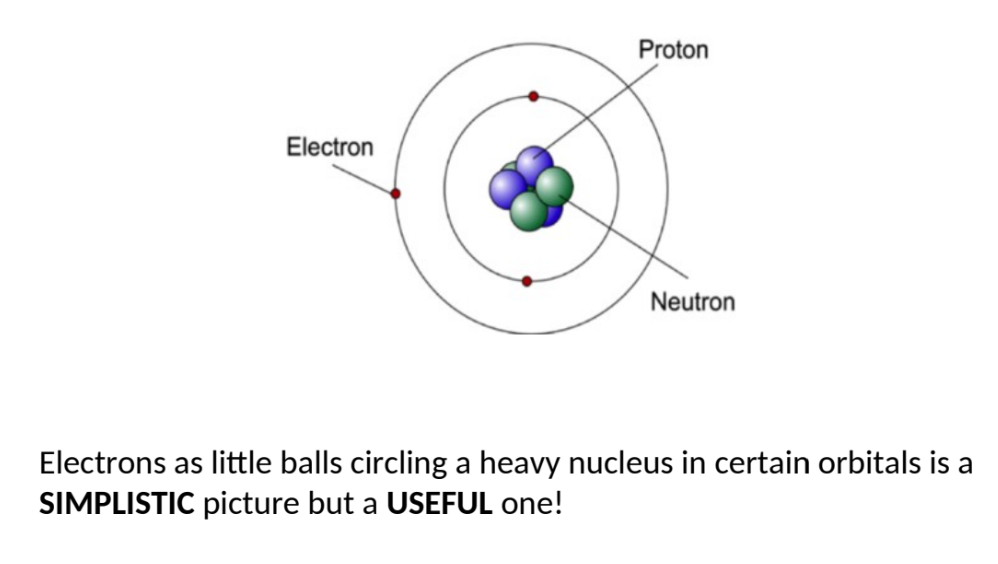
how else are particles thought of
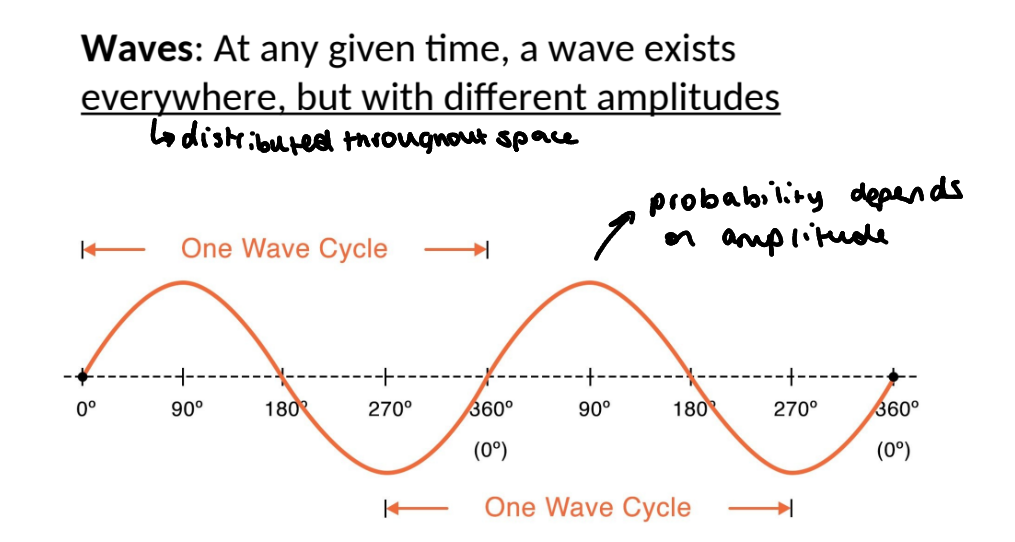
ball view of electrons
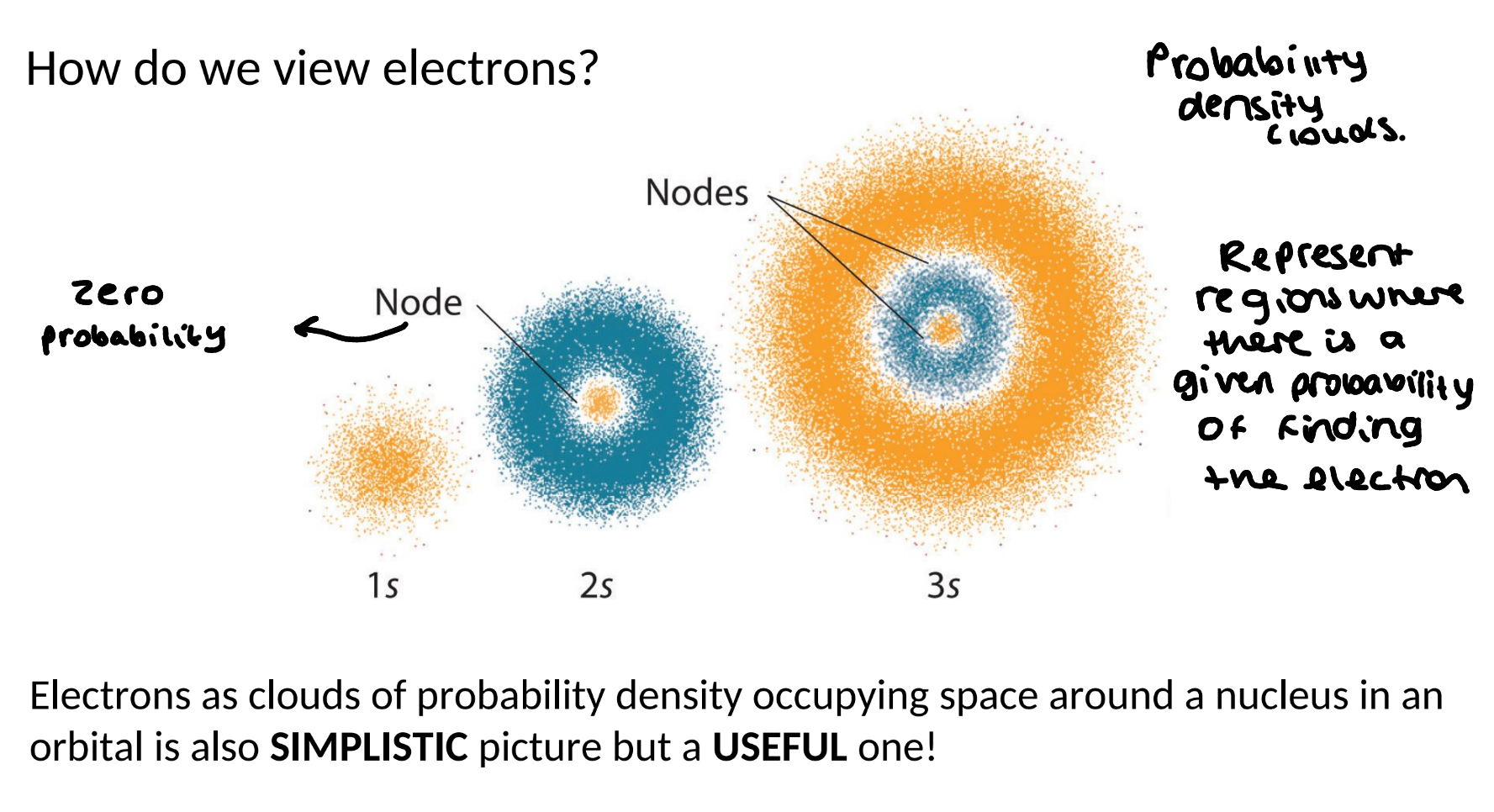
cloud view of electrons
how can atoms be expressed and what information does this give
every system which contains sub-atomic particles such as an atom can be expressed as a mathematical equation - a wavefunction
this tells us about the behaviour of all the components of the atom
how are wavefunctions used for electrons
we can set up a wavefunction just for the electrons in the atom and then calculate what happens to that wavefunction (the electrons) when they interact with the nuclear charge
Schrodinger equation
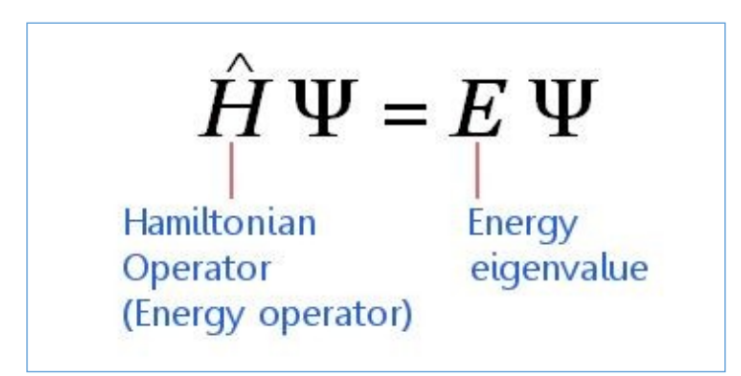
how can the Schrodinger equation be applied in molecules
is applies for not only electrons interacting with a single nucleus but also for more than one nucleus as in molecules - electrons occupying molecular orbitals
valence bond theory
atomic orbitals mix together in one atom to form new orbitals that are combinations, or hybrids, of the original atomic orbitals
why does molecular orbital theory contain more ionformation than valence bond theory
it tells us about both bonding and antibonding orbitals (VB only bonding)
7 rules of MO theory
number of MOs is always equal to the number of combining AOs
bonding MOs are lower in energy than the parent AOs and antibonding MOs are higher in energy
electrons of the molecule are assigned to orbitals from lowest to successively higher energy
AOs combine to form MOs most effectively when the AOs are of similar energy
the closer an MO is to a constituent AO in energy, the more of that AO character the MO has
the more nodes an MO has the higher in energy it tends to be
LUMOs have significant roles to play in reaction mechanisms