BSCI 170 Exam 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Properties of life
-consume energy
-reproduce
-generate order
-self regulate
-sense and respond to the environment
-evolve
Amphipathic
Polar phosphate head; Nonpolar tails
Emergent properties (Big Idea In Biology)
-As you increase level of organization, new properties appear
-Put small things together to make big things
- Big thing has a different function
Cell Theory (Big Idea In Biology)
-All cells come from other cells
-All life is made of cells (continuity of life)
Regulatory mechanisms (Big Idea In Biology)
-Processes are regulated
-So we don't reach equilibrum&die
- e.g: response to environment, growth,homestasis, development
Evolution (Big Idea In Biology)
-All organisms evolve from other organisms
-All organisms have a single common ancestor
Energy transformation (thermodynamics)
-Energy cannot be created nor destroyed
-Energy can only be moved around or transformed from one form into another (solar energy -> to chemical energy)
Structure-Function relationship (Big Idea In Biology)
-Function requires a structure to do stuff (e.g-we have enzymes that do what they do)
-Changes in structure=changes in function
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis
Mitochondria
Power house of the cell (energy)
Chloroplast
Enables photosynthesis because of the presence of chlorophyl.
Lysosome
Waste removal
Prokaryotes
Bacteria (no shape)
-Cell membrane
-Cytosol
-Ribosomes
- Nucleoid body (DNA is in here)
Eukaryotes
Animals, fungi, plants (Has shape)
- nucleus- DNA is in here
-Membrane-bound organelles
-Cytoskeleton
Advantage of Endomembrane system
Compartmentalization- Gives opportunity to create compartments, giving our body the ability to multitask
Membrane-bound organelles
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts(not part of endomembrane)
- Resemble prokaryotes: own DNA; own ribosomes; self replicating
Endosymbiotic theory
-Organelles evolved from prokaryotic cells living symbiotically within early eukaryotic cells
Element
Substance that cannot be broken down to other substances
- We are mostly oxygen, hydrogen, carbon
Particles of atom
-Protons: positive
-Neutrons: neutral
-Electrons: negative
Atomic # = # protons = #electrons
P+N = Mass #
Electronegativity
How much an electron wants another electron
- There are different types of bond because elements differ in electronegativity
Cohesion
Water molecules stick to other water molecules
Adhesion
Attraction between water and a different thing
Surface tension
- Force that causes the molecules on the surface of a liquid to be pushed together and form a layer
- Cause of cohesion
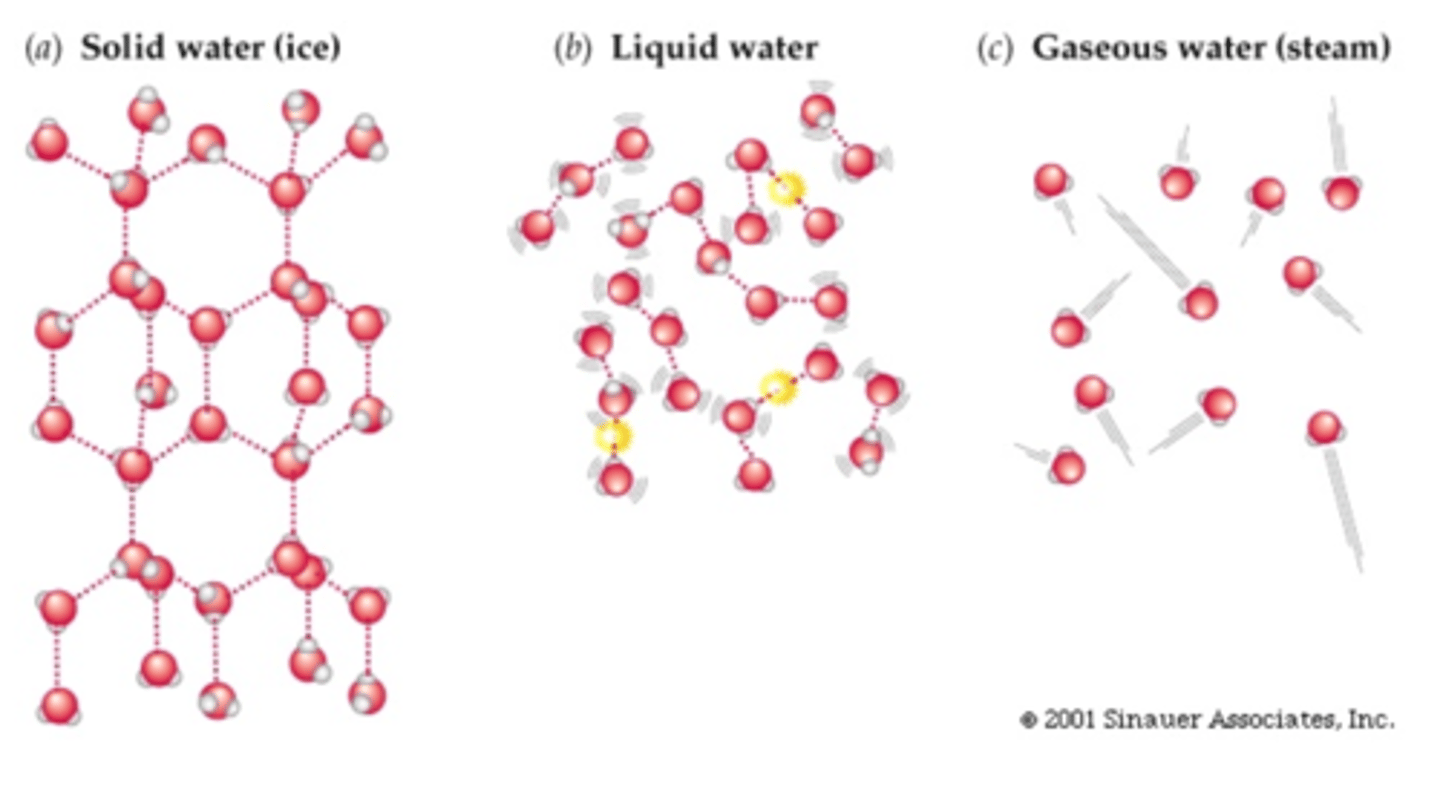
Ice is less dense
- A lattice is formed in Ice bond and because the lattice is spacious, ice haas fewer molecules than liquid water.
- Hydrogen bonds are more stable in ice, therefore they move way less than liquid water
Hydrogen bonds state
FIXED LENGTH!! (Same length)
Gas- everywhere (no bond)
Liquid - breaks & reform (some together, some out)
Solid- Little bit apart(dashed line bond)
Polar Covalent bonds
Unequal sharing (One atom spends more time with the shared electron than the other)
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
Equal sharing
Ionic bonds
No sharing. Either donate or accept (gain a charge by accepting or receiving electrons). Gain = - charge, Lose=+ charge
Hydrophobic
Fearful of water
Hydrophillic
Loves water
Heat capacity
- Water absorbs a lot of heat-->takes a while to try and break the hydrogen bonds in order to boil the water
pH balance
Water forms certain amounts of H+ and OH- ions
Polar functional groups
-Hydroxyl
-Carbonyl
-Carboxyl
-Amino
-Phosphate
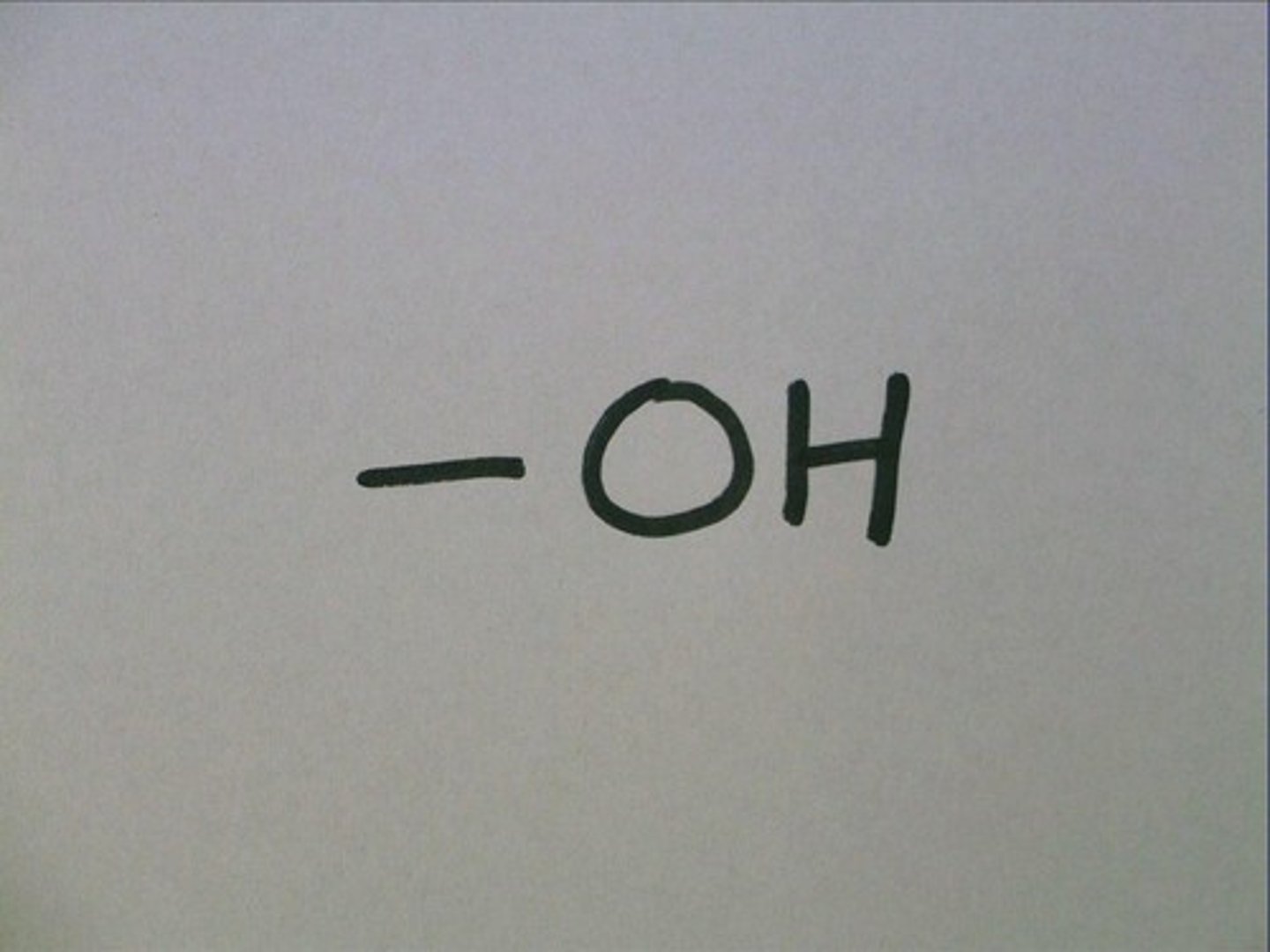
Hydroxyl group (OH-)
- Adds polarity when added to a molcule
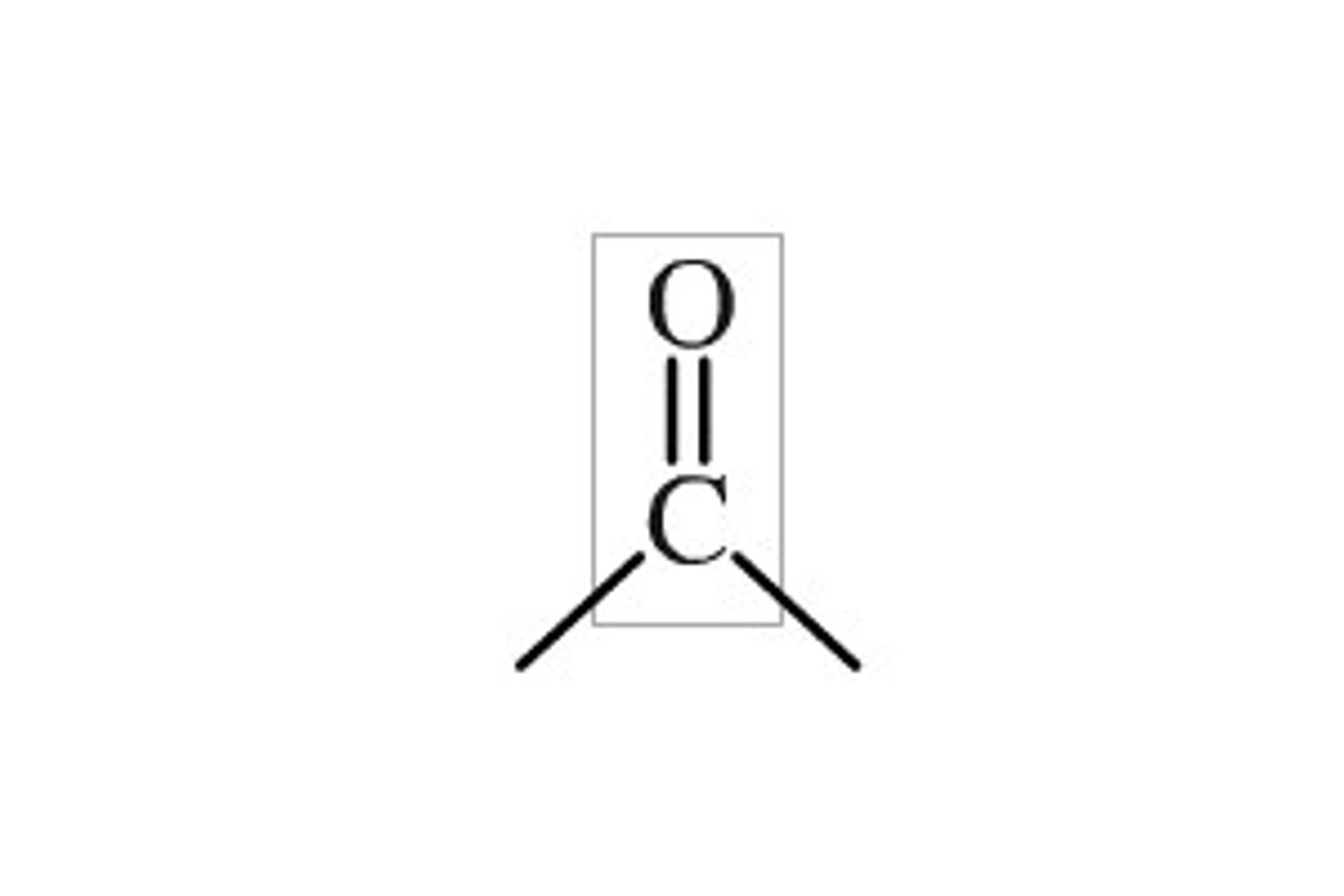
Carbonyl group
-Can alter shape of molecules when added
-Polar
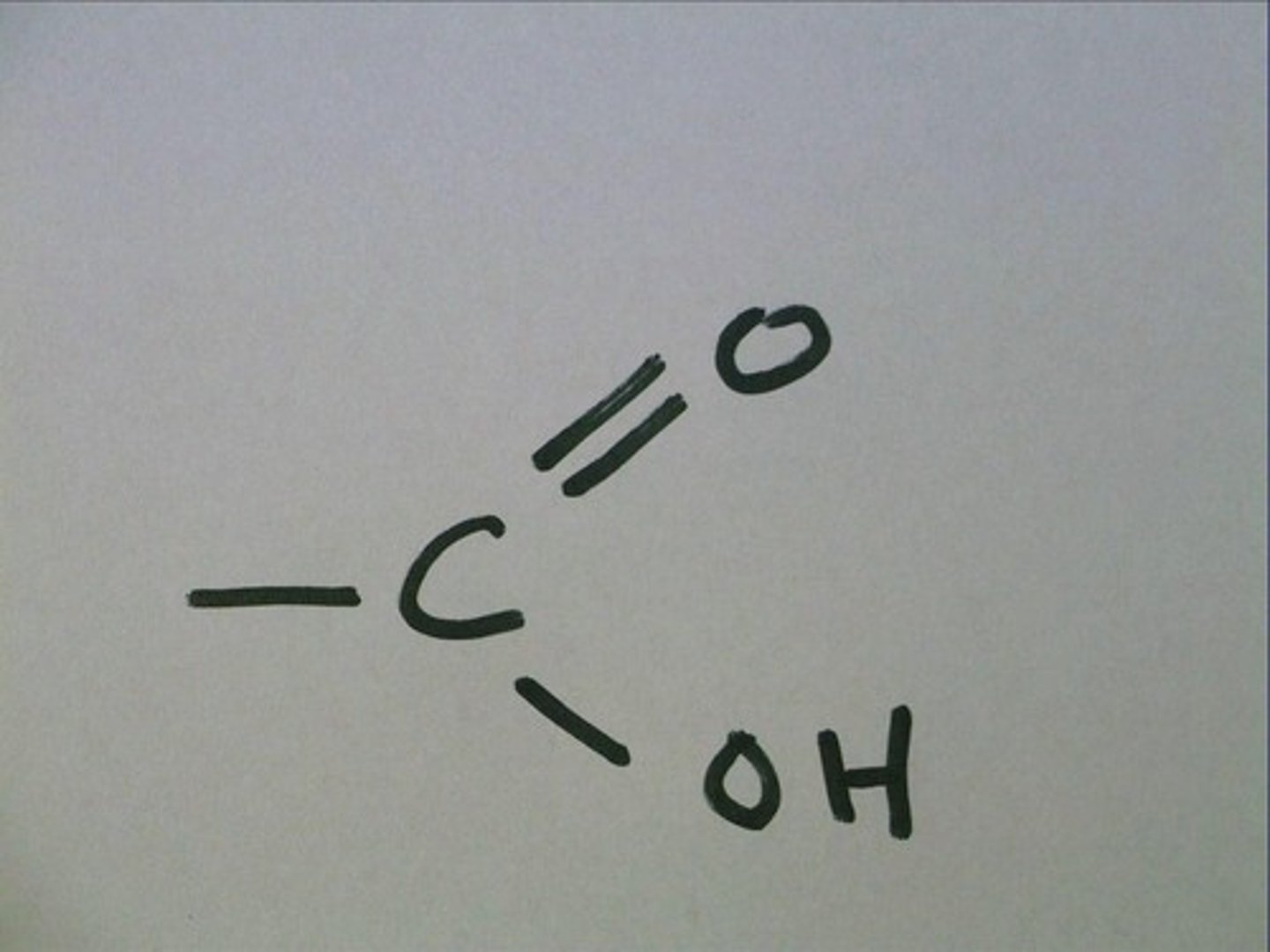
Carboxyl group
Act as acids bc they drop a H+ in solution
-Polar
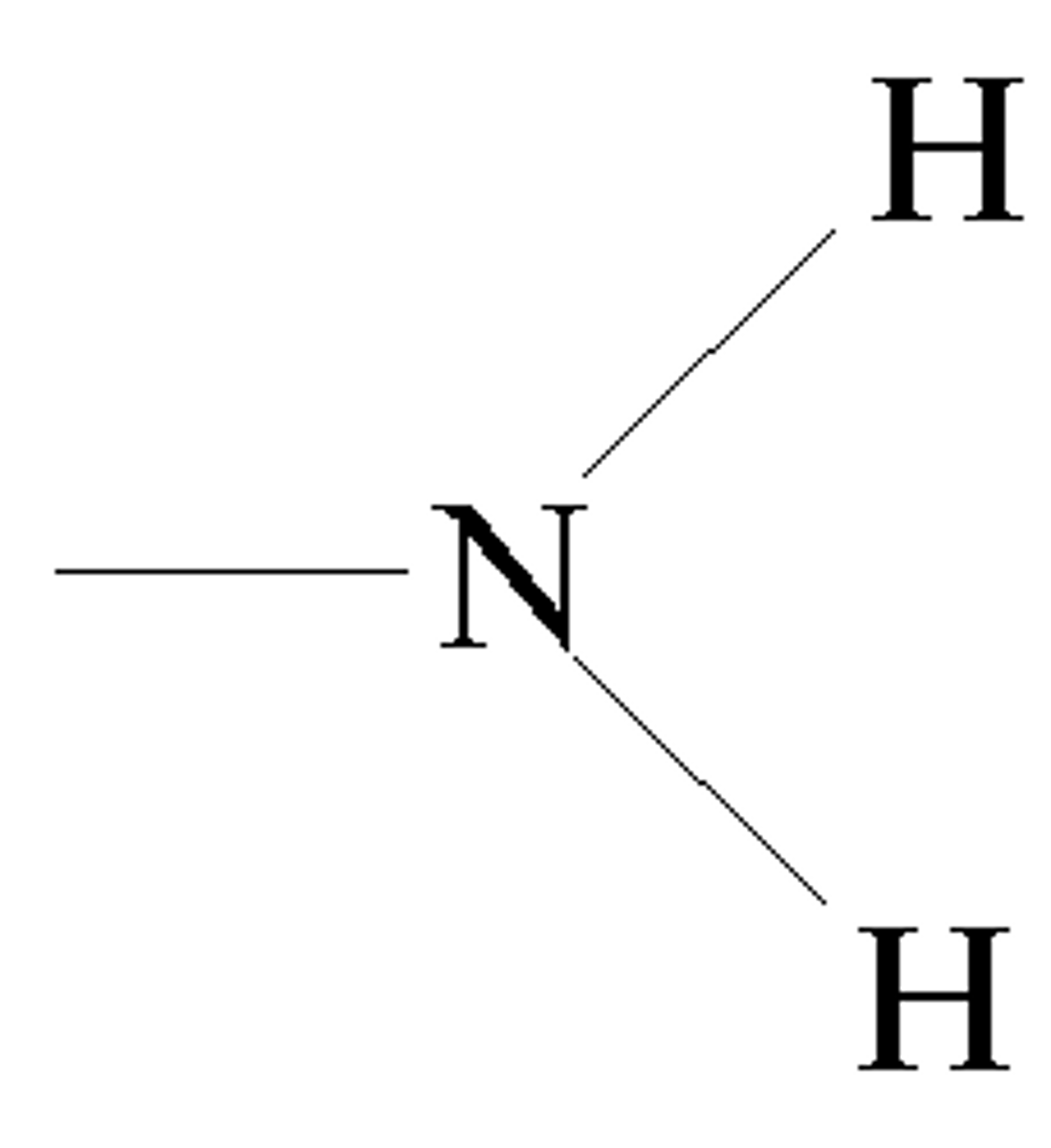
Amino group
- Act as bases bc they take an extra H+
-Polar
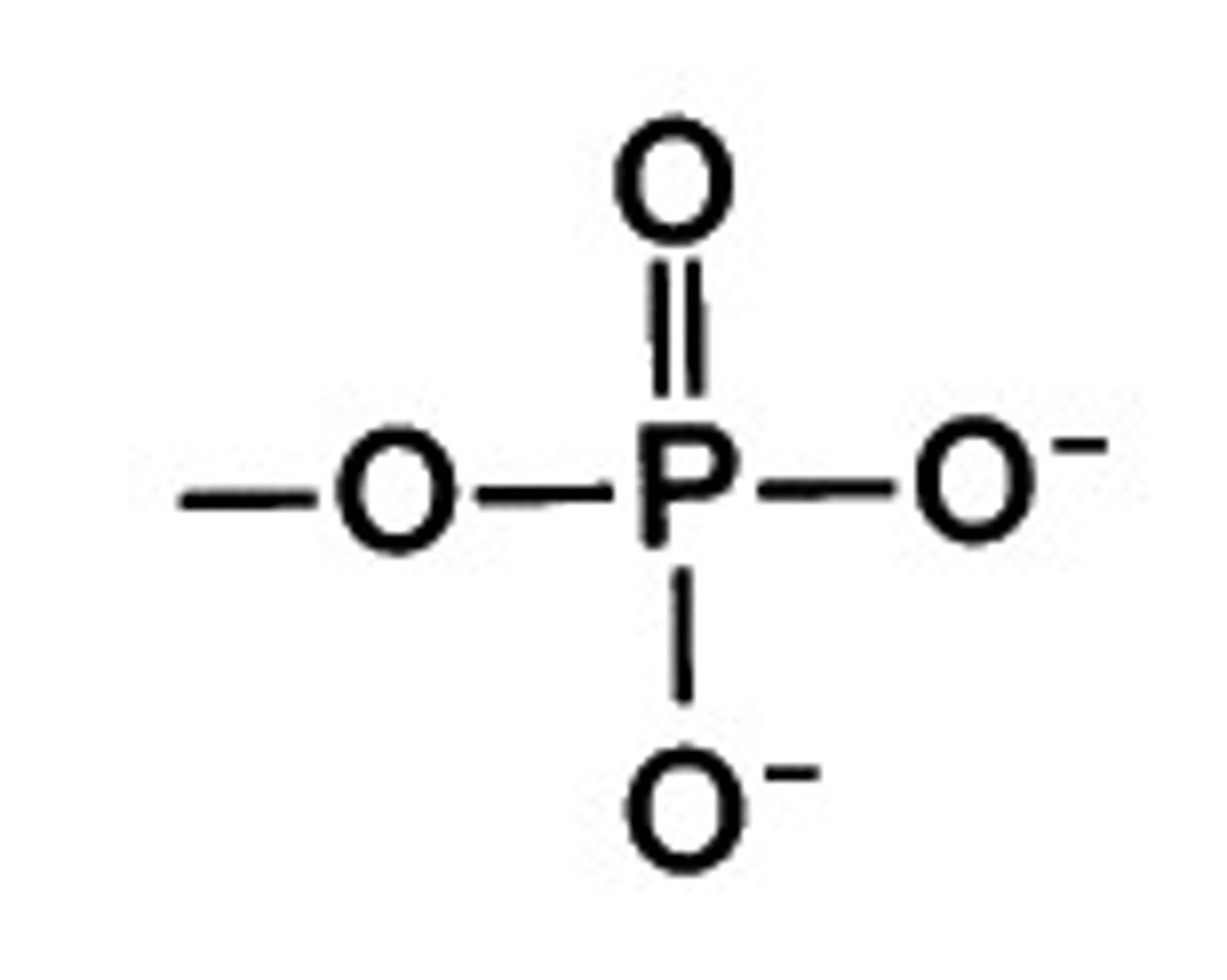
Phosphate group
-It changes shape to a molecule when added
- Makes the molecule unstable
-Transfers energy between molecules
-Reacts with water, releasing energy
-Polar
Sulfhydryl group (-SH)
-Bonds to other sulfhydryl groups
-Polar
- Important when looking@protein structure
- S-----H
Methyl group
-Carbon is temporary
- When added it changes identity of molecule
-Additon to DNA affects expression of genes
- Non polar
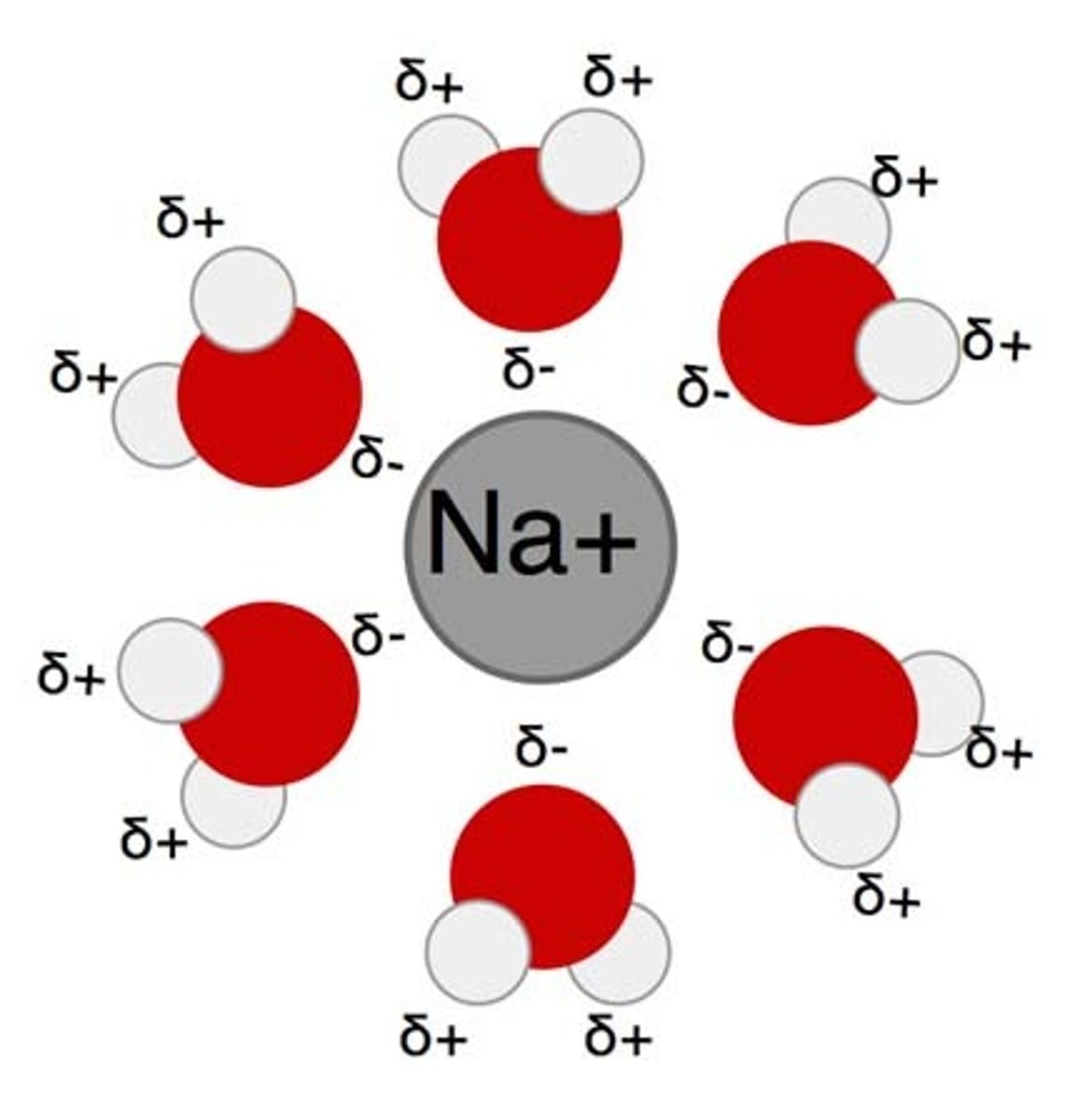
hydration shell
Shells form when they go into water and you have the charges around them
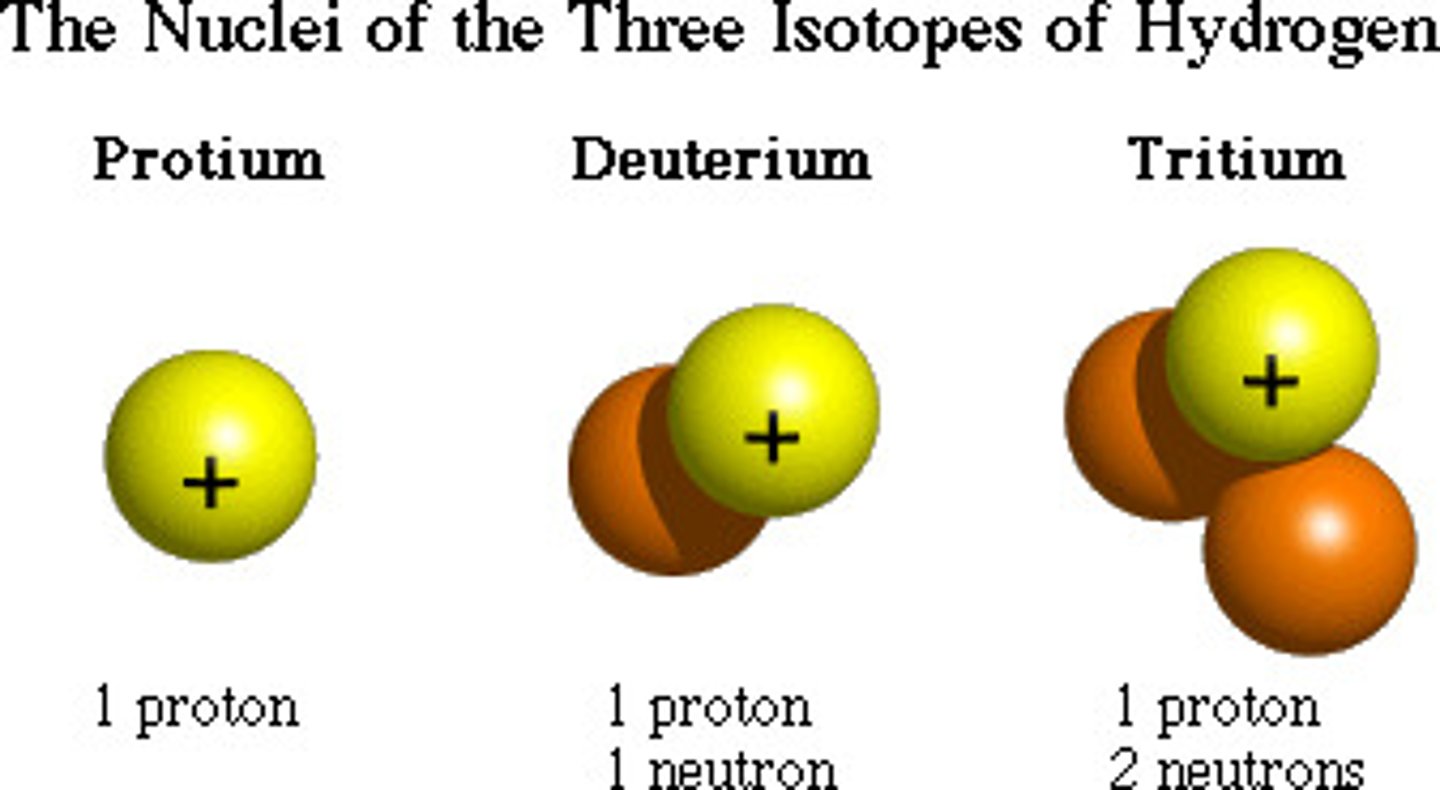
Isotope
Elements with extra neutrons
Components all cells have
-DNA
-RNA
-ribosomes
-limiting membrane
-cytosol/cytoplasm
Integral membrane proteins
- Stick into the hydrophobic region of a membrane
Membrane most fluid when
high temperature, short tails, very unsaturated fatty acids
Glycoprotein
-Found on the outside surface of a membrane but NOT on the inside
Peripheral protein
May be inside/outside membrane
Transmembrane
Goes through bilayer (Inside)
Molecular Diversity
-Allows change in molecules
1. Changing carbon strcutures(carbon cn form double bonds)
2. Variation in functional groups
Isomers
Same chemical formula but different structure
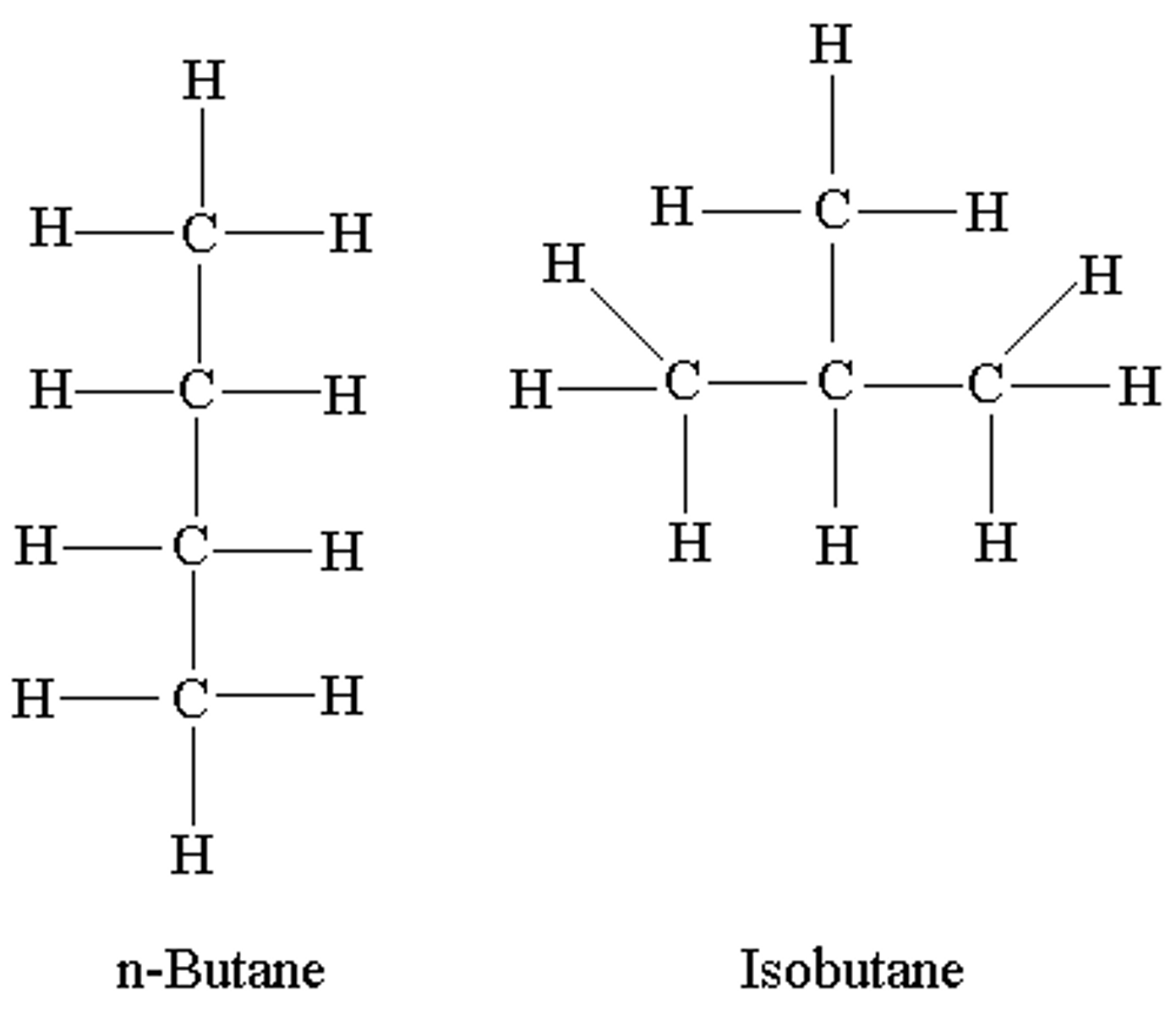
Structural Isomers
Same elements but different arrangement
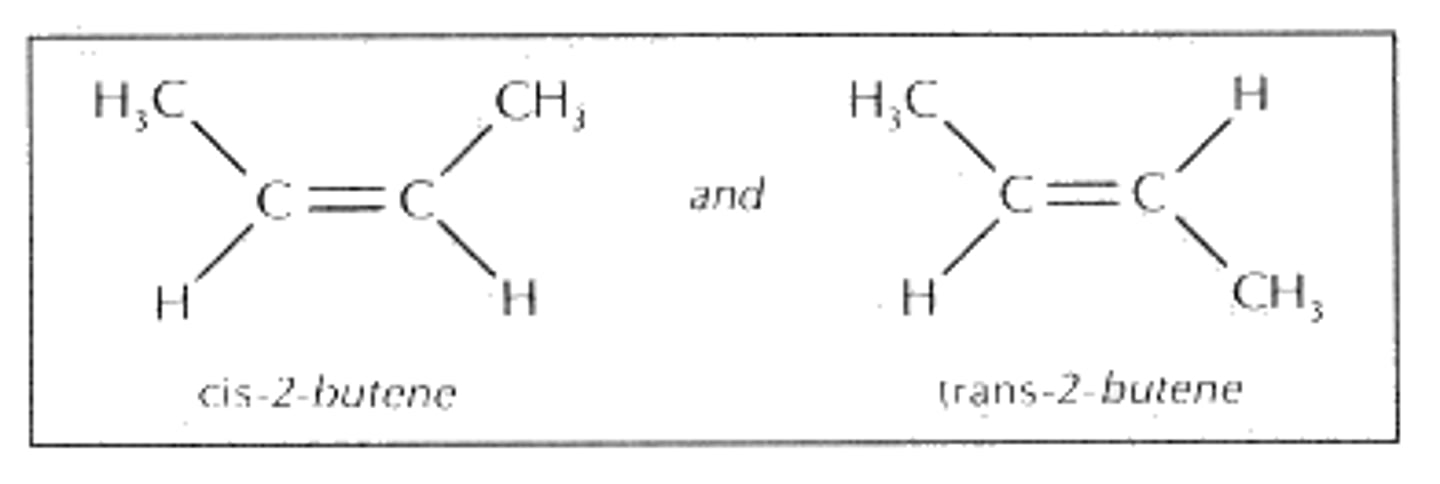
Geometric Isomers
- Needs a double bond.
- Differ in spatial arrangements
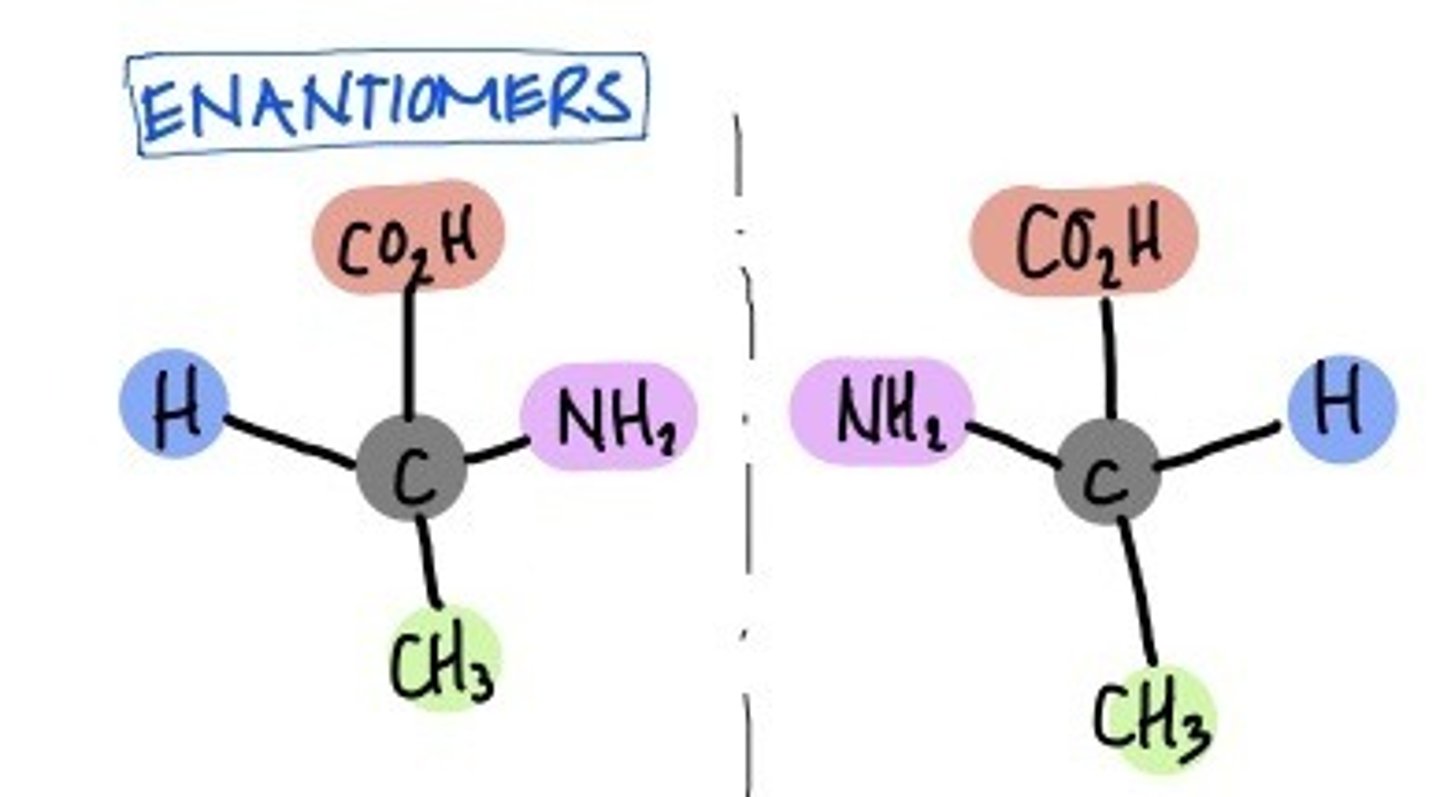
Enantiomer
Mirror Images of each other
Bonds
Bonds are formed because of ELECTRONEGATIVITY-how bad an atom wants an electron
Electrostatic interaction
Oppositely charged groups attract, same charged groups repel each other