Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (copy)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
tectonic plate
a massive, irregularly shaped slab of lithosphere usually composed of both oceanic and continental lithosphere; AKA lithospheric plate
lithosphere
outermost layer of the Earth containing the crust and uppermost rigid part of the mantle
asthenosphere
"plastic" or putty-like layer directly underneath the lithosphere; plates ride on this layer
continental drift
idea proposed by Alfred Wegener that the continents move; explained why the same fossils and rock formations were found on now widely-separated continents
oceanic crust
crust underneath the oceans; thinner and more dense than continental crust
continental crust
crust making up the continents; thicker and less dense than oceanic crust
magnetic reversal
a change in Earth's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged
seafloor spreading
process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge
Theory of Plate Tectonics
scientific theory that explains how volcano formation, earthquakes, mountain formation, and the changing positions of continents is caused by the movements of lithospheric plates
subduction
process where one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate and sinks into the mantle as they converge
subduction zone
a boundary where two plates converge, and because of differences in density, one dives beneath the other
slab pull
the pulling action exerted by the sinking (subducted) edge of a plate on the rest of the plate
convection
heat transfer by the motion of a fluid away from the heat source
deep-ocean trench
a long, narrow trench in oceanic crust usually lying above a subduction zone
mid-ocean ridge
underwater mountain chain formed as tectonic plates spread apart; wraps around the globe like the seam of a baseball
fault
a crack in the Earth's crust along which rocks have shifted
earthquake
what happens when two slabs of lithosphere suddenly slip past each other
volcano
a place where molten rock makes its way to the surface
lava
molten rock above the surface
magma
molten rock below the surface
Pangaea
a famous supercontinent that existed about 225 million years ago and has since broken up
supercontinent
a large landmass formed by the convergence of multiple continents
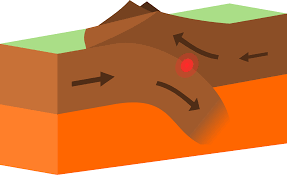
What type of boundary is this?
Convergent Plate Boundary (with subduction)
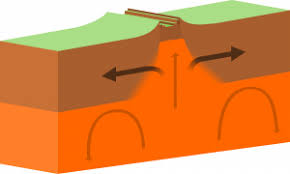
What type of plate boundary is this?
Divergent Plate Boundary (where two plates move apart)
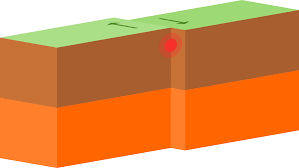
What type of boundary is this?
Transform plate boundary (Plate move past each other)
What are the three types of Convergent plate boundaries?
Oceanic- Oceanic , Continental-Continental, Oceanic-Continental