Biology: Genetics 2
5.0(1)Studied by 9 people
Card Sorting
1/35
Last updated 10:35 PM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Somatic Cells
diploid body cells (skin cells, muscle cells, etc.)
2
New cards
germ line cells
Diploid cells that undergo meiosis to form haploid gametes
3
New cards
Gametes
sex cells
4
New cards
Chromosome
threadlike structure within the nucleus that contains genetic
information that is passed on from one generation to the next
information that is passed on from one generation to the next
5
New cards
Homologous Chromosomes
term used to refer to chromosomes in which one
set comes from the male parent and one set comes from the female parent
set comes from the male parent and one set comes from the female parent
6
New cards
Sister Chromatids
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
7
New cards
Autosome
chromosome that is not a sex chromosome; also called autosomal
chromosome
chromosome
8
New cards
Sex chromosome
one of two chromosomes that determines an individual's
sex
sex
9
New cards
sexual reproduction
type of reproduction in which cells from two parents unite
to form the first cell of a new organism
to form the first cell of a new organism
10
New cards
asexual reproduction
process of reproduction involving a single parent that
results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
11
New cards
Fertilization
process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells join to form a new cell
12
New cards
Linked genes
genes that are typically inherited together because they are
located close to each other on the same chromosome
located close to each other on the same chromosome
13
New cards
Diploid
term used to refer to a cell that contains two sets of homologous
chromosomes
chromosomes
14
New cards
Haploid
term used to refer to a cell that contains only a single set of genes
15
New cards
Meiosis
process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half
through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell
through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell
16
New cards
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
17
New cards
Zygote
a fertilized egg
18
New cards
independent assortment
one of Mendel's principles that states that genes
for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
19
New cards
crossing over
process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis
20
New cards
Nondisjunction
error in meiosis in which the homologous chromosomes fail
to separate properly
to separate properly
21
New cards
locus
location of where a gene is located on a chromosome
22
New cards
gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait;
factor that is passed from parent to offspring
factor that is passed from parent to offspring
23
New cards
Allele
one of a number of different forms of a gen
24
New cards
when does crossing over take place
prophase 1
25
New cards
when does independent assortment take place
metaphase 1
26
New cards
what is Mendel famous for
he learned that traits are passed from parent to child
27
New cards
Homozygous dominant
2 dominant alleles ex HH
28
New cards
Heterozygous
one dominant and one recessive allele ex Hh
29
New cards
Homozygous recessive
2 recessive alleles
30
New cards
sex linked traits
traits located on sex chromosmes
31
New cards
codominance
2 alleles are expressed separately ex spotted animal
32
New cards
incomplete dominance
2 alleles are expressed together, a blend of the 2 alleles
33
New cards
pedigrees
A way to model the inheritance of a specific trait through a family to track a specific disorder or identify an pattern of inheritance.
34
New cards
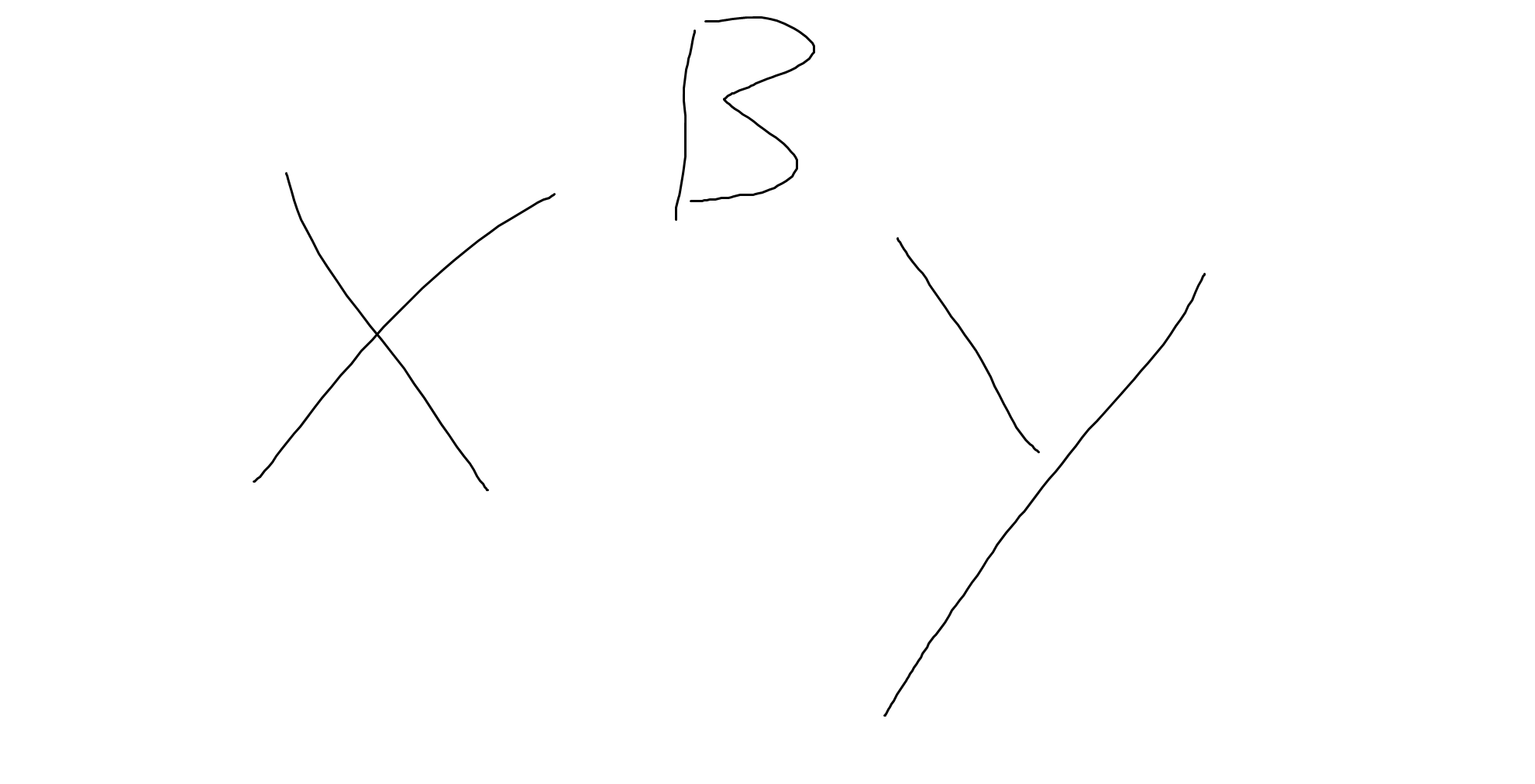
what is the phenotype of this child? B = brown eyes b = blue eyes
brown eyed boy
35
New cards
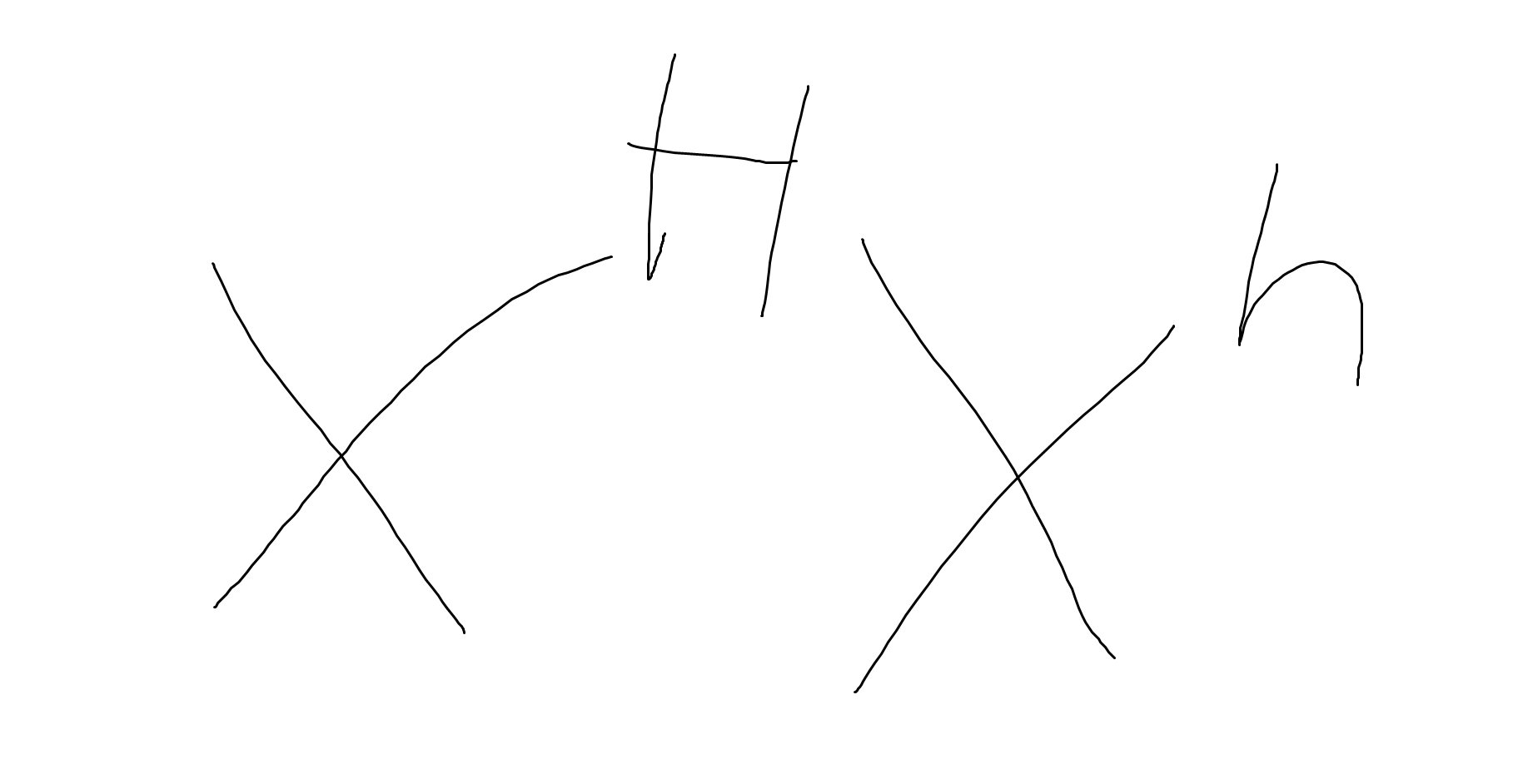
what is true about this child
girl who is a hemophilia carrier
36
New cards
why CANT men be hemophilia carriers
because they only have 1 x chromosome