Enzyme Regulation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the 2 main strategies that cells use to regulate enzyme activity
Change the number/amount of enzymes
Change the activity of existing enzyme molecules
What are the 2 methods used to change the number/amount of enzymes
Increase/decrease the production of enzyme
Increase/decrease the degradation of enzyme
What are the 2 methods used to change the activity of existing enzymes
Allosteric regulation
Covalent modification
Describe allosteric regulation
A molecule binds to a site other than the active site (the allosteric site).
This changes the enzyme’s shape and either activates or inhibits it.
Often used in feedback loops.
Describe covalent modification
Chemical groups (e.g., phosphates) are added or removed from the enzyme.
These changes can activate or deactivate the enzyme.
Common modifications: phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation
What is an example of allosteric regulation?
Aspartate transcarbomylase
What reaction is catalyzed by aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase)?
It catalyzes the first step in pyrimidine biosynthesis, combining aspartate and carbamoyl phosphate to form carbamoyl aspartate.
What biosynthetic pathway is ATCase involved in?
Pyrimidine biosynthesis (e.g., CTP, TTP, UTP).
What molecule inhibits ATCase? What is this an example of?
CTP — this is an example of feedback inhibition.
What molecule activates ATCase?
ATP — it promotes enzyme activity.
What kind of cooperativity does ATCase show?
It shows cooperative binding of aspartate and carbamoyl phosphate.
What does cooperative binding mean in the context of ATCase?
The binding of one substrate molecule increases the likelihood that additional substrates will bind.
What does the ATCase velocity vs. [aspartate] graph look like?
The graph typically exhibits a sigmoidal curve, indicating cooperative binding and a gradual increase in velocity with rising aspartate concentrations.
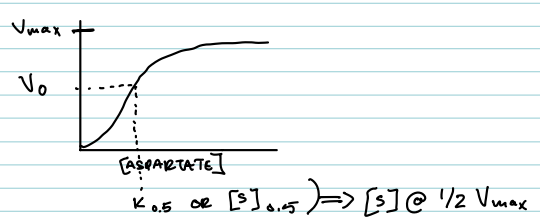
![<p>What does K₀.₅ or [S]₀.₅ mean for ATCase?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dc2c2059-a9b5-4af1-8254-f1448c3fe503.png)
What does K₀.₅ or [S]₀.₅ mean for ATCase?
It is the substrate concentration at which V₀ = ½ Vmax (analogous to Km, but for cooperative enzymes).
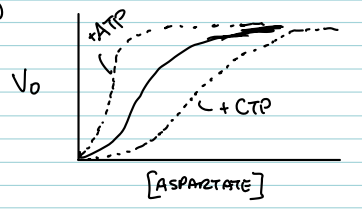
What effect does CTP have on the ATCase curve?
It shifts the curve to the right, indicating inhibition (more substrate is needed to reach ½ Vmax).
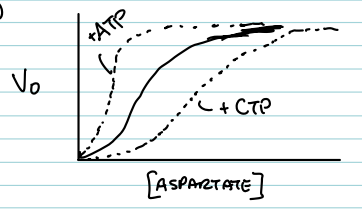
What effect does ATP have on the ATCase curve?
It shifts the curve to the left, indicating activation (less substrate is needed to reach ½ Vmax).
What is an example of covalent modification?
Phosphorylation
What happens during phosphorylation?
A phosphate group is transferred from ATP to the side chain of serine, threonine, or tyrosine (S, T, Y)
Which enzymes catalyze phosphorylation?
Kinases
Which enzymes remove phosphate groups from proteins?
Phosphatases
What can phosphorylation do to an enzyme?
It may cause subtle or significant structural changes, altering its activity
What enzyme is regulated by both phosphorylation and allosteric control?
Glycogen phosphorylase
What reaction does glycogen phosphorylase catalyze?
It releases glucose from glycogen
What are the two allosteric modulators of glycogen phosphorylase?
ATP (negative modulator) and AMP (positive modulator)
Where is glycogen phosphorylase phosphorylated?
At Ser14
(also regulated by phosphorylation here)