theme 1- Micro - Introduction into markets and market failure
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
the basic economic problem
problem of scarcity,limited rescources and infinite wants
positive statements
objective statements which can be proven or disproven
normative statemnents
subjective statements which express opinions or judgements
needs
minimum necessary to survive, limited
types of needs
water
food
shelter
clothes
warmth
wants
desires for consumption of goods and services, not necessary to survive, unlimited
rescources
inputs we use to produce goods and services
social science
economics is a social science which focus on theories and problems relating to the production of goods, distribution of goods and the consumption of wealth
natural science
studies the natural world
ceterus paribus
the effect of one economic variable has on another while all other variables remain the same
renewable resource
resource of economic value that can be replenished on a level equal to its consumption
non-renewable resource
a resource of economic value that cannot be readilly replaced by natural means on a level equal to consumption
opportunity cost
the value of the next best alternative foregone
factors of production
resources are split up into 4 factors of production
land
labour
capital
entrepreneurship
land
all natural resources used in production i.e raw materials
owners receive rent from land or money from the sale of land
labour
the mental and physcial human effort
labourers receive wages
capital
man-made resources which are used to produce goods and services e.g equipment
owners of capital receive interest on their land
enterpreneurship
the willingness and ability to take the risks of combining the other factors of production in order to make a product
enterpreneurs receive profit
circular flow of income
a model of the economy which describes how money flows
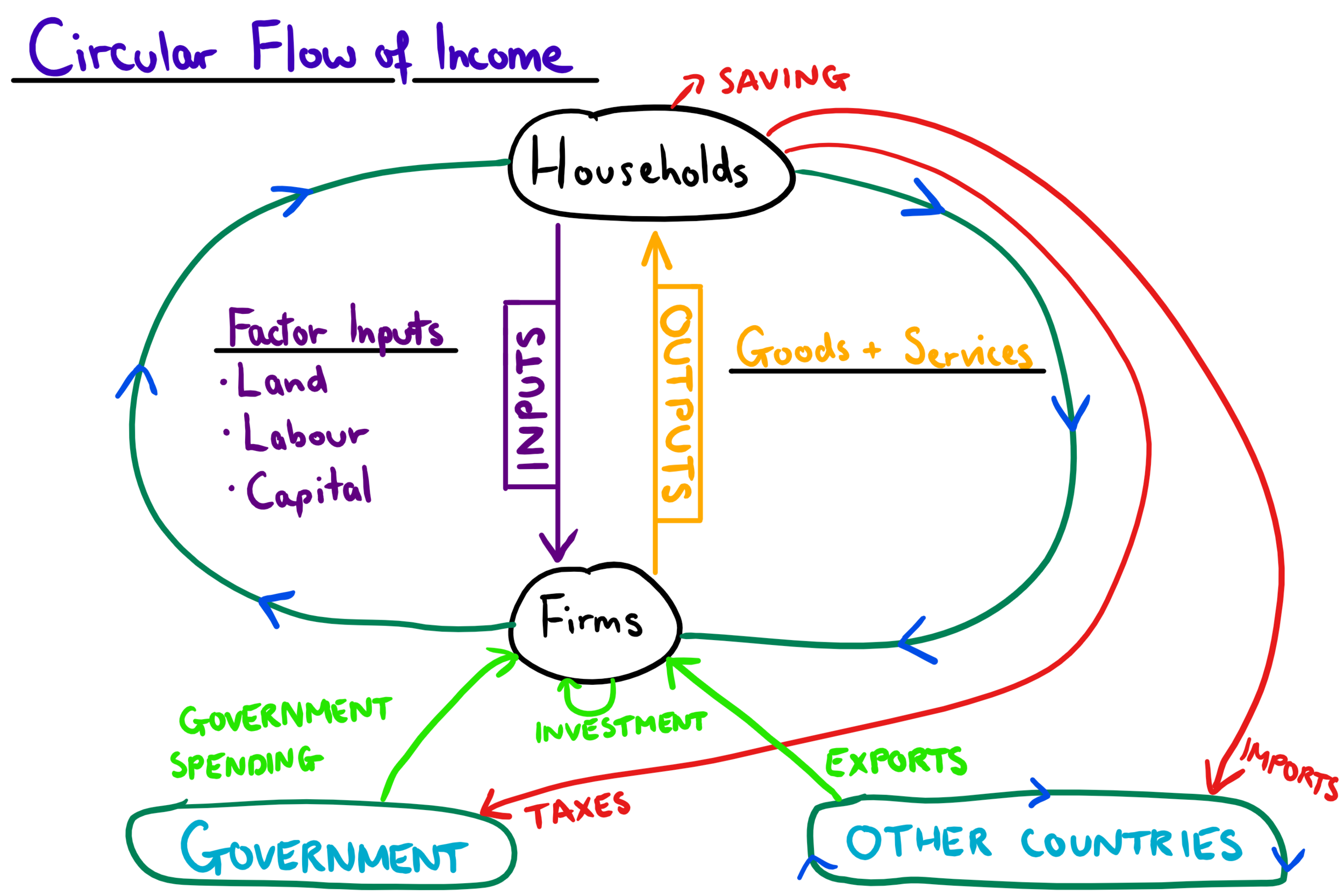
injection
variables that add to the circular flow of income
governments spending + investment+exports
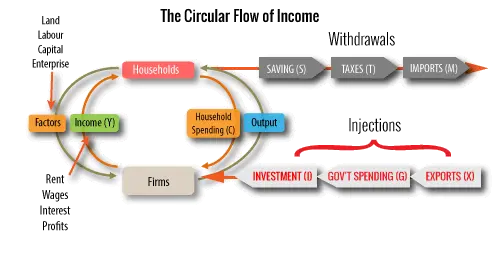
withdrawal
variables leaking out of the circular flow of income and reducing the size of the national income
taxation+saving+import
measures of economic performances
output
income
employment/unemployment
economic growth
inflation
CPI/RPI
PPF
product possibility frontiers -
shows the maximum possible combinations of 2 products or capital and consumer goods that the economy can achieve with its current resources and technology
why is PPF normally a curve
because the opportunity cost of producing the combinations of the 2 products changes when a certain amount of each product is produced
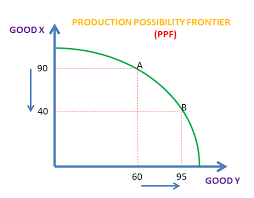
what does it mean when the point is on the curve of a ppf
maximum potential of an economy, its economically efficient
opportunity cost on a ppf
how many of one good is lost in order to produce more of the other good
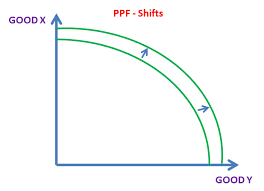
what happens to the PPF when the economy grows
it shifts outwards
done by increasing the quantity/quality of resources
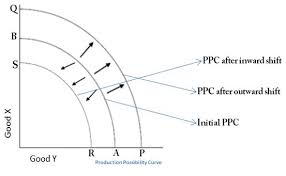
what happens to the PPF when the economy declines
it shifts inwards
caused by natural disasters,natural resources running out,decrease in quantity or quality of labour
specialisation
concentration of workers,firms,areas or countries on a paticular task or narrow range of products
pros of specialisation
quality
quantity
allows countries to concentrate output which increases standard of living
cons of specialisation
what if demand falls
competitors
wages+raw materials
division of labour
production is broken down into many seperate tasks
pros of division of labour
workers highly productive
lower costs of production
improved skills
saves time
quality
cons of division of labour
demoralisation
reduced flexibility
finding alternative work