UD1: Digestive System
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
homeostasis
The process by which the body maintains a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions, crucial for proper functioning of the digestive system.
Our body maintains homeostasis through a 3 part mechanism
Sensor: detects change in the external environment
Effector: brings internal temp back to normal
Control Centre: activates effector based on info from sensor
6 essential nutrients
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Vitamins
Minerals
Carbohydrates subunits
composed of monosaccharide subunits (monomers)
Lipids subunits
composed of Glycerol & Fatty Acid subunits
Proteins subunits
composed of amino acid subunits
Nucleic Acids subunits
composed of Nucleotide subunits
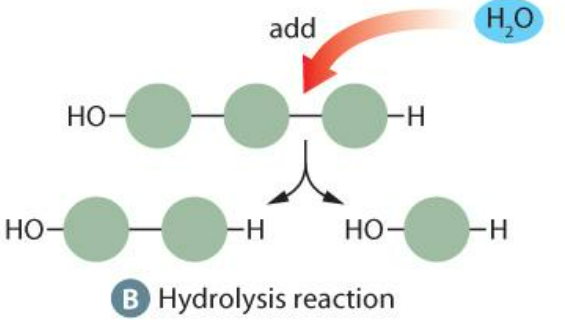
Assembling Macromolecules
Dehydration synthesis - removal of a water molecule (Needs enzymes)
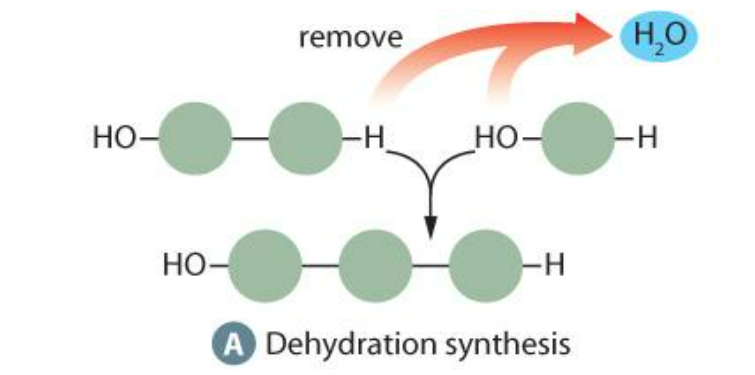
Disassembling of Macromolecules
Hydrolysis - addition of a water molecule (Needs enzymes)
Carbohydrates
(C + H + O)
Main source of Energy
Monosaccharides
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Disaccharides
Maltose = Glucose + Glucose
Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose
Lactose = Glucose + Galactose
Polysaccharides
Cellulose - forms structural material of plants
Starch - storage form of carbs in plants
Glycogen - storage form of carbs in animals
Lipids
(C+H+O)
Long term energy storage, forming cell membrane, protection of internal organs, insulation, and formation of hormones
NON POLAR & insoluble in water
Composed of glycerol molecule bonded to fatty acids (ex. monoglycerides = 1 fatty acid)
Saturated Fatty Acids
contain only single bonds between carbon atoms
usually from animal sources and solid at room temp
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
have 1 or more double bonds between carbon atoms
usually from plant sources and are liquid at room temp
Proteins
(C+H+O+N)
Transport, Blood clotting, immunity, enzymes, for chemical reactions, structure and support
Composed of chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
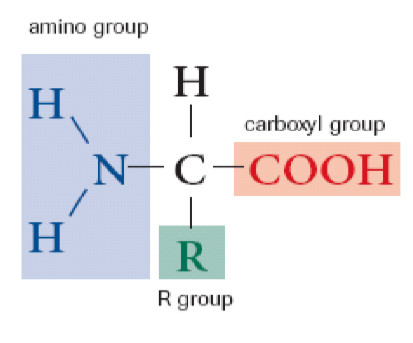
Amino acids
(C-H) + (Amino Group with Nitrogen) + (Acid group) + (R group 20 types)
body can synthesize 11 amino acids the other 9 are called essential amino acids that come from food
Peptide
chain of several amino acids bonded together
Polypeptide
chain of peptides
Nucleic Acids
(C+H+O+N+P)
makes chemical code for DNA & RNA
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid: codes for production of proteins
RNA
ribonucleic acid: helps in the assembly process of proteins
Nucleotides
(5 Carbon sugar) + (Nitrogen base) + (Phosphate group)
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine
create base pairs for DNA
(c&g) (a&t)
Enzymes
protein molecule that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions
can be used over and over again
enzymes have a specific shape of which substrate it can bind to
4 factors that affect enzymes
Temp
pH
competitive inhibitors (molecules that attach to active site preventing substrate from binding)
non competitive inhibitors (molecules that bind to a regulatory site changing the shape of enzyme preventing substrate from binding to active site)
Factors that can DENATURE (loosing shape and function) the enzyme
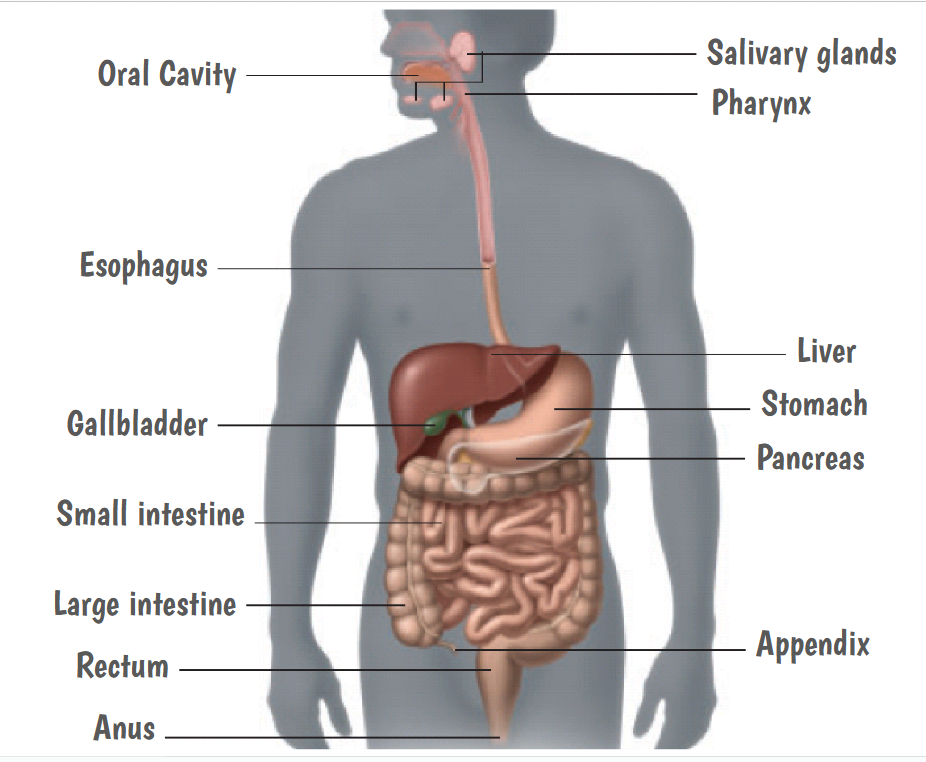
Digestive system
Mechanical Digestion
breaking down food into smaller pieces to increase surface area
ex. chewing, churning in stomach, segmentation in small intestine
Chemical deigestion
Enzymes are used to aid chemical breakdown of macromolecules to smallest subunits
Mouth
Mechanical Digestion: chewing food
Chemical Digestion: (CARBS only)
salivary amylase enzymes from salivary glands (pH-7)
breaks down complex carbs into polysaccharides
Esophagus
passage way from mouth to stomach
epiglottis covers trachea to prevent food and liquid from entering lungs
uvala prevents food entering nasal passages
peristalsis
a wave like series of muscular contractions that moves the bolus
esophageal sphincter
controls entry to stomach
Stomach
storage
pH of 2
mechanical digestion: churning
chemical digestion: Proteins
Gastric juices that contain pepsinogen and HCL combine with food to create chyme
pepsin (pepsinogen in active form) breaks down proteins into polypeptides
Ends with pyloric sphincter
Small Intestine
inner surface covered with villi which contains thousands of microvilli that increase surface area
Duodenum: ducts from the gall bladder and pancreas join to
Jejunum: food is broken down and some absorption of nutrients
Ileum: absorption of nutrients and pushes chyme into large intestine
Pancreas
secretes bicarbonate ions neutralizes HCL making pH of small intestine 8
Secretes enzymes
Carbohydrases: pancreatic amylase
Proteases: trypsin, chymotrypsin
Lipases
Nucleases
Liver
produces bile salts that emulsify fats that break lipids into tiny droplets (mechanical digestion)
Stores excess glucose in the form of glycogen
Gallbladder
Stores bile
Large intestine
pass through the ileocecal sphincter
water and salts are absorbed in the colon then feces is releaesd out da anuss hahahahah