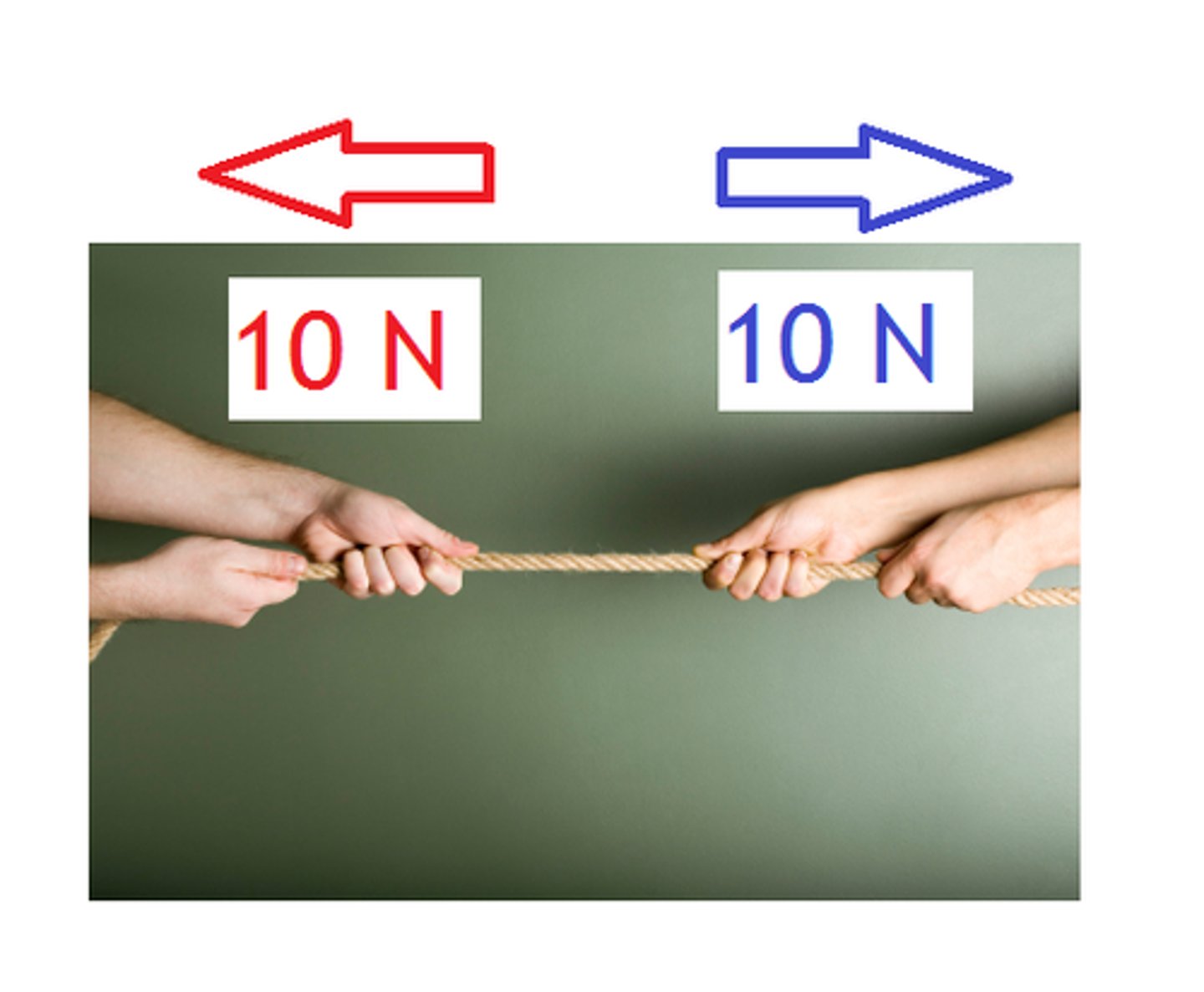
P8 - Forces in Balance
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
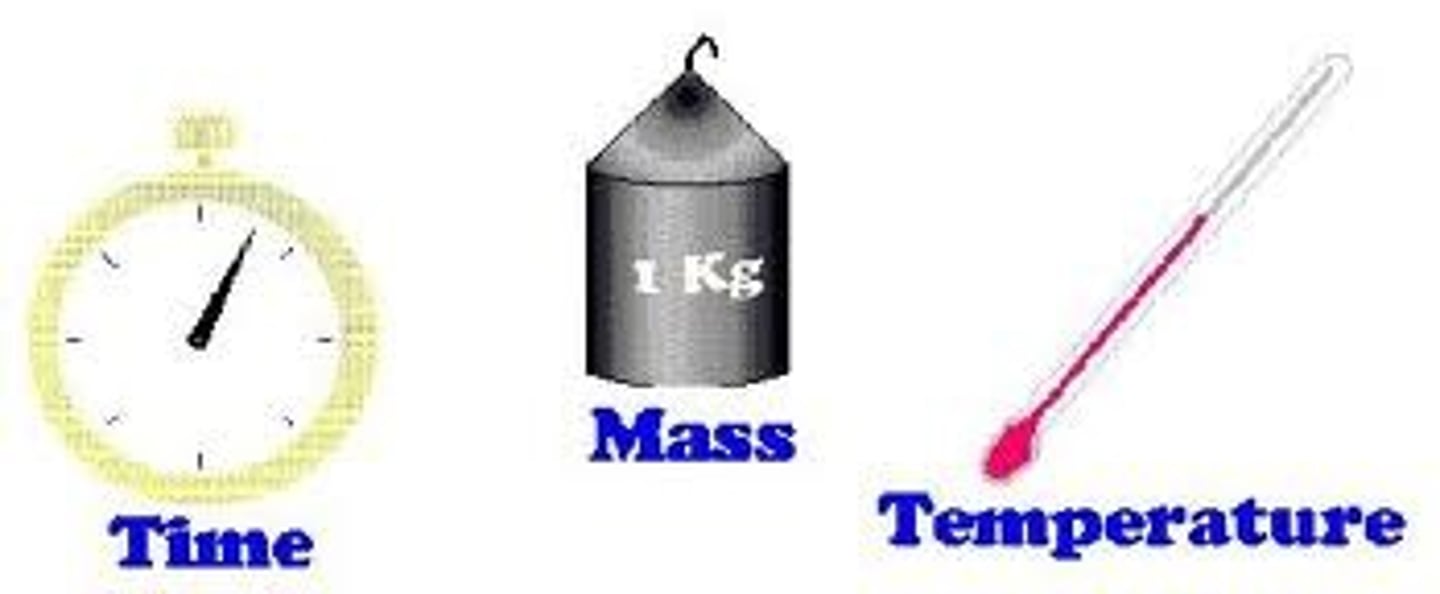
Scalar Quantity
- something with magnitude only
- has a size
- speed
- distance
- mass
- temperature
- time
- energy
Vector Quantity
something that has both magnitude and direction
- the length of the arrow is the magnitude
- the direction pointing to of the arrow shows direction
- displacement: a distance at specific
- velocity
- weight
- momentum
- acceleration
- force

A Force
a push or pull that acts in an object
- due to the interaction or exertion with another object
- in newtons
- have magnitude and direction: so is a vector quality
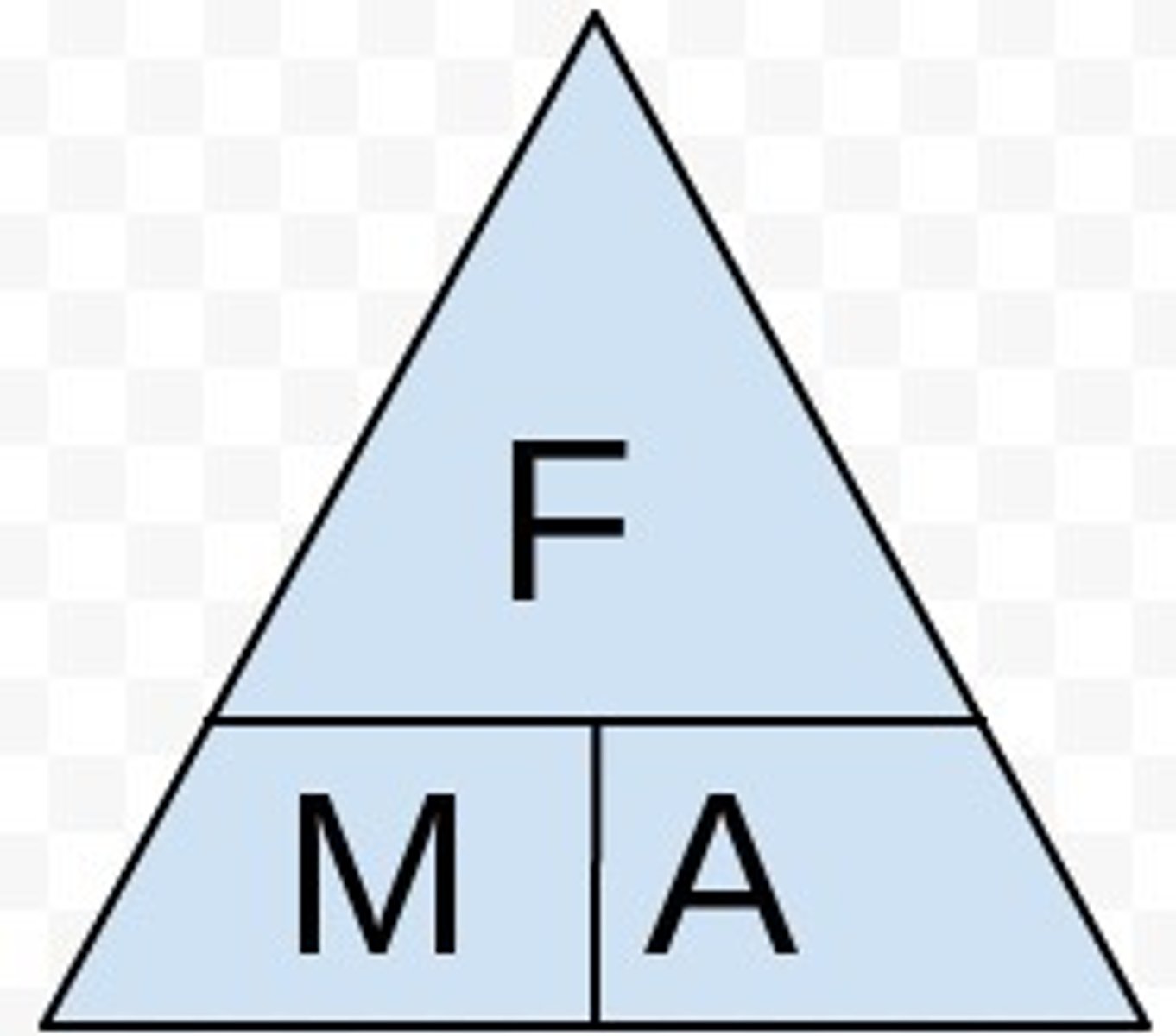
Force =
mass x acceleration
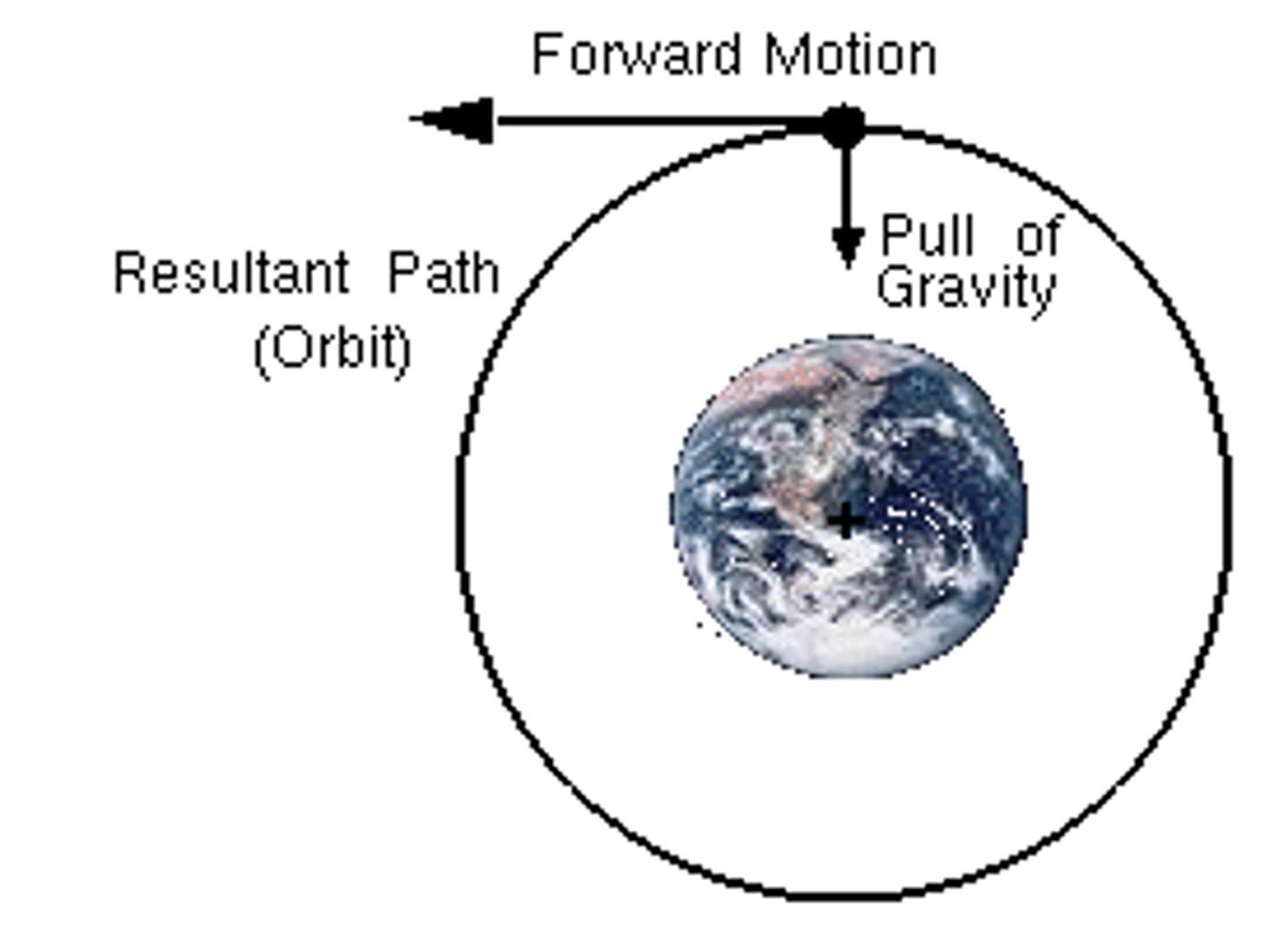
Why does a Satellite in a Circular Orbit Travel at a Constant Speed?
- the direction is constantly changing as it's going in a circle as it orbits: in circular motion
- this causes the velocity to constantly change
- acceleration is the rate of change of velocity
- therefore it's constantly accelerating
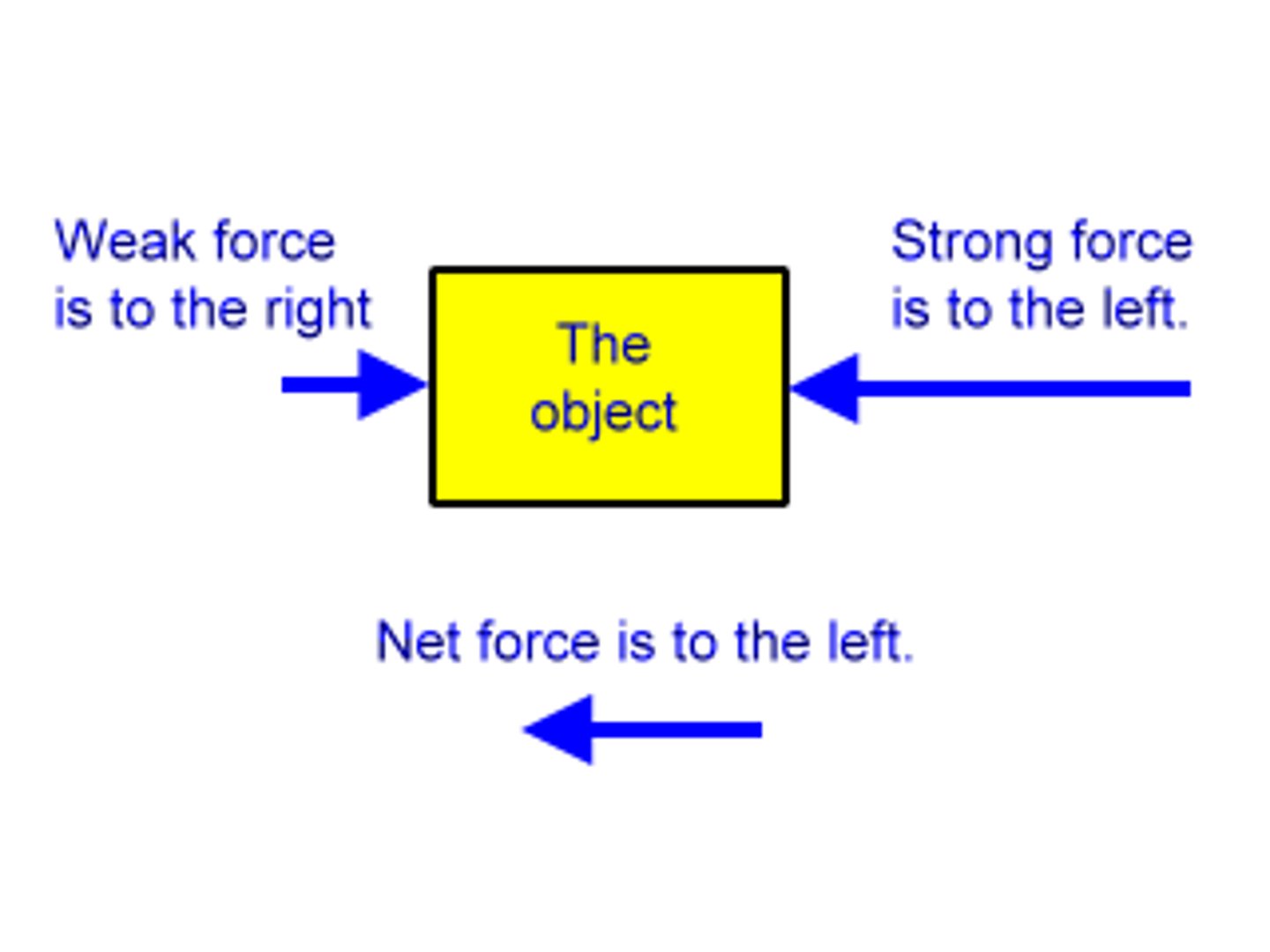
Resultant Force
a single force that has the same effect as all the original forces acting on the object
- the net-force
- when there's two forces in opposite directions then subtract the smaller force from the larger force: the direction is to the larger force
Examples of Force
- friction
- gravity (weight)
- resistance
- up thrust
- normal contact reaction
- drag/air resistance
- magnetic
When a Force is Applied to an Object it Can
- change size
- change motion
- change shape

Contact Force
a force that is exerted only when two objects are physically touching
- friction
- tension: in a rope
- air resistance: a skydiver
- normal contact force
Non-Contact Force
a force that one object can apply to another object without touching it or is physically separated
- gravity: the earth and moon
- an electrostatic force: as opposites attract and alike repulses
- magnetism
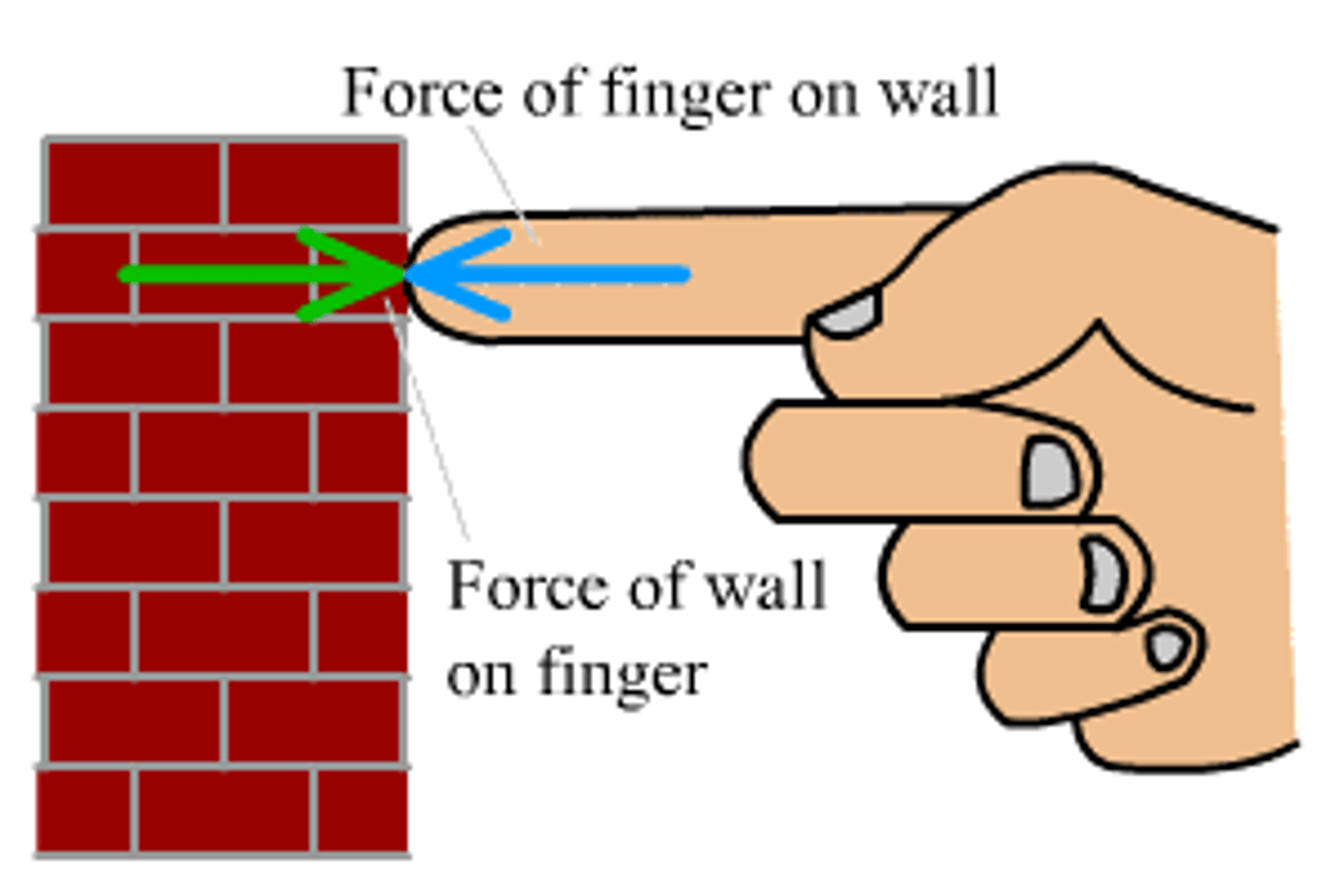
Newton's Third Law
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction

Example of Newton's Third Law
if you push on a wall, it will push back on you as hard as you are pushing on it
Newton's First Law
objects continue to move in a state of constant velocity when in balance
- only unless a resultant force acts upon it
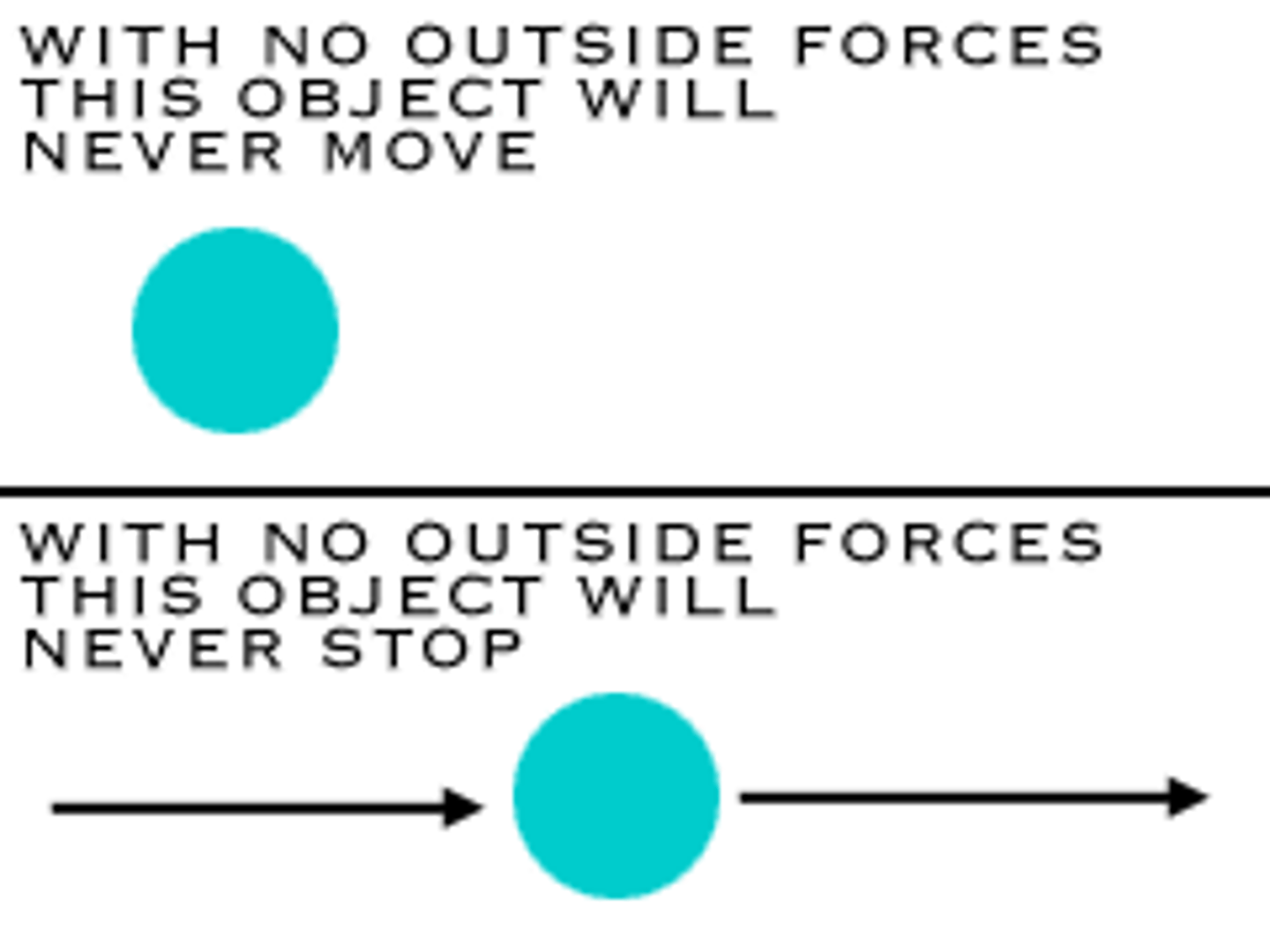
If the Forces Acting on an Object are NOT Balanced they Will:
- speed up
- slow down
- change direction
- change its shape
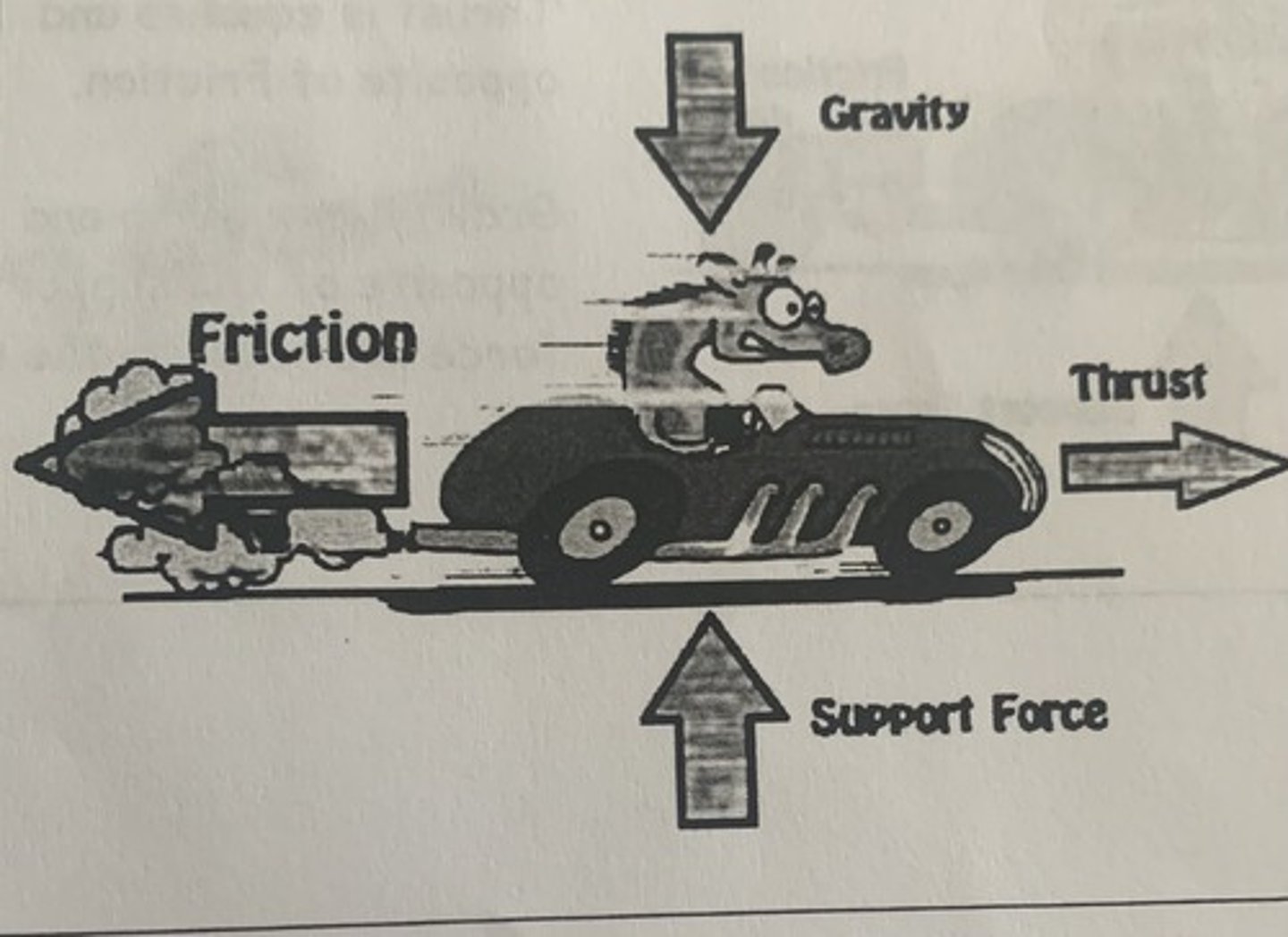
If Forces of a Car are Unbalanced Against the Thrust
- drive force or thrust is smaller then the effects of friction and air resistance
- the car decelerates
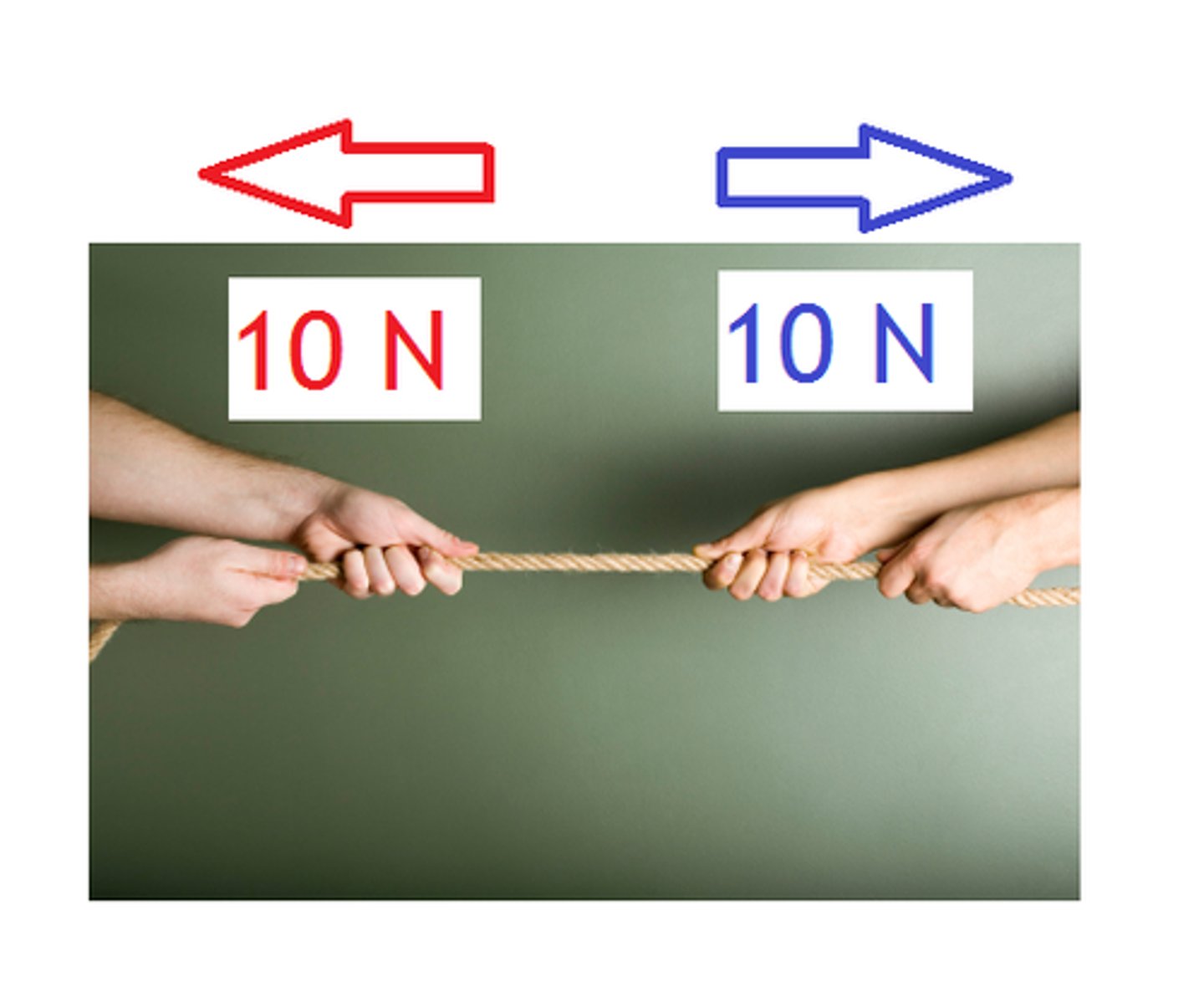
When 2 Forces are in Equilibrium
the forces are equal in size and opposite direction
Example of Newton's First Law
a ball rolling down a hill will continue to roll unless friction or another force stops it

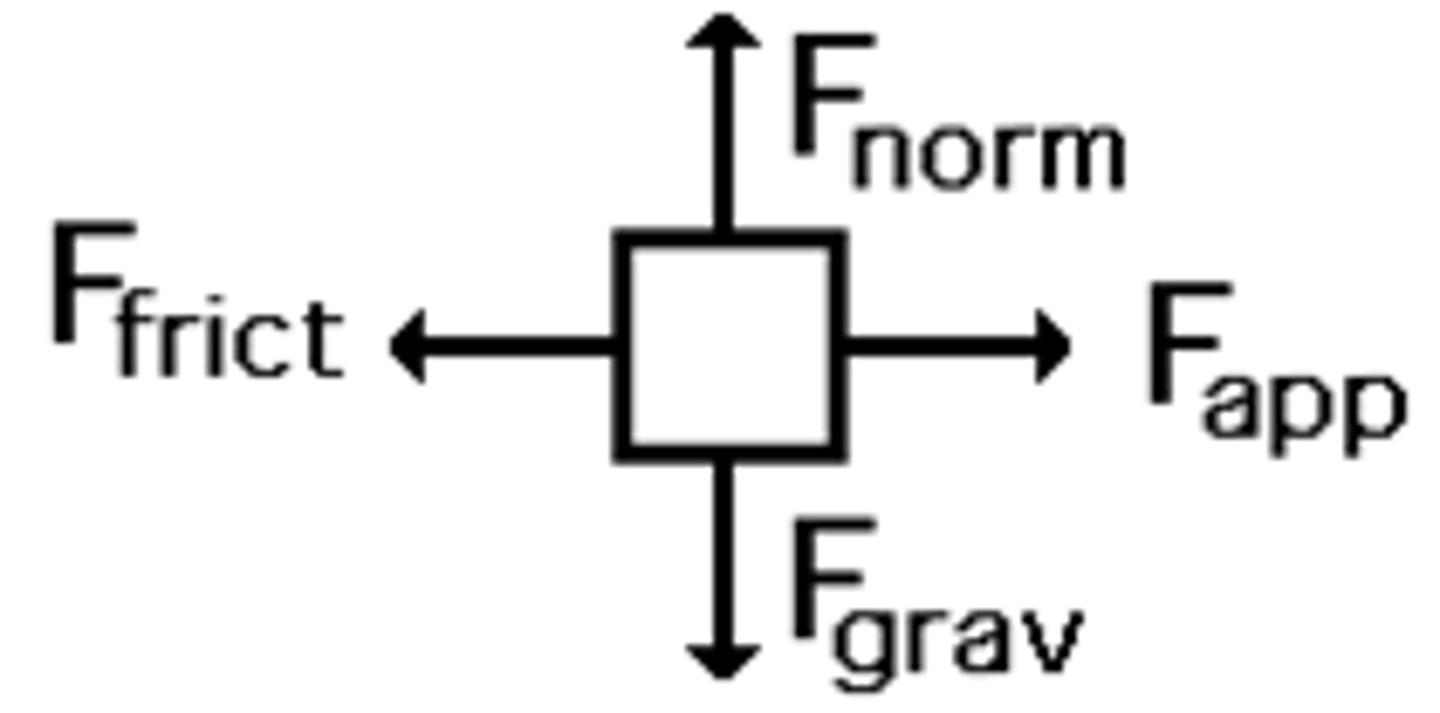
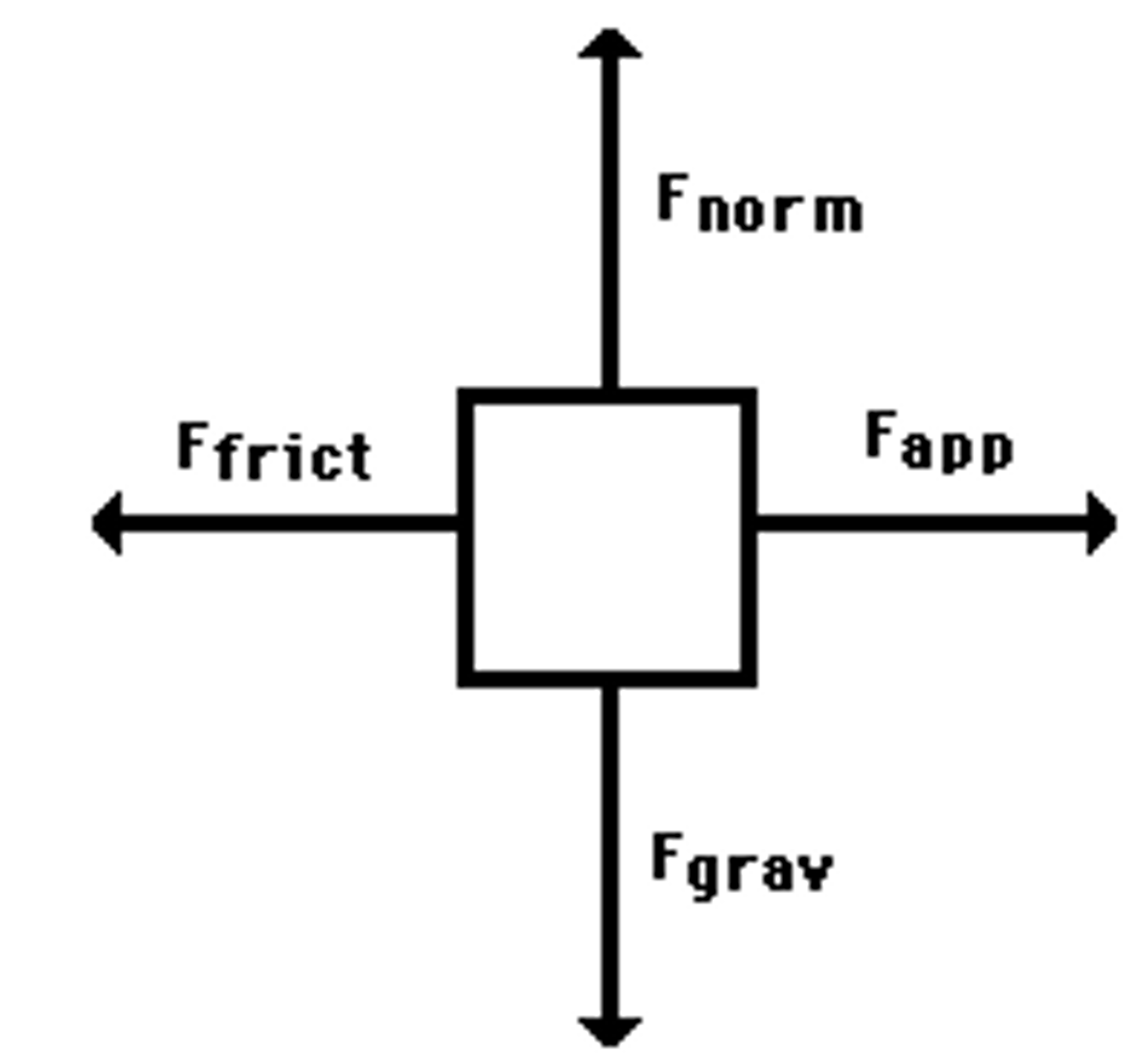
Free Body Force Diagrams
- the length of the arrow is the magnitude of the force
- the direction pointing to of the arrow shows direction of the force
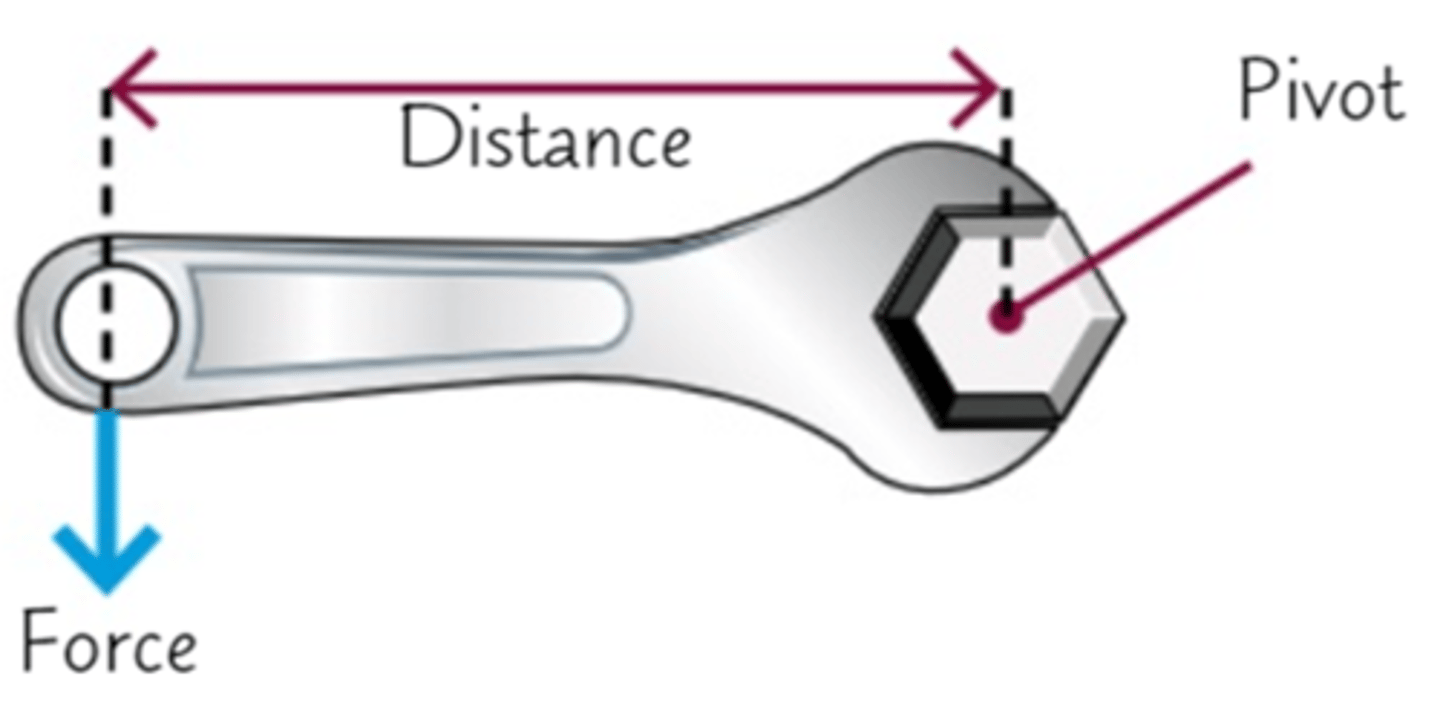
A Moment
- the turning effect of a force
- caused by force
- about a point equal to the magnitude of the force x the perpendicular distance from the point to the line of action from the force
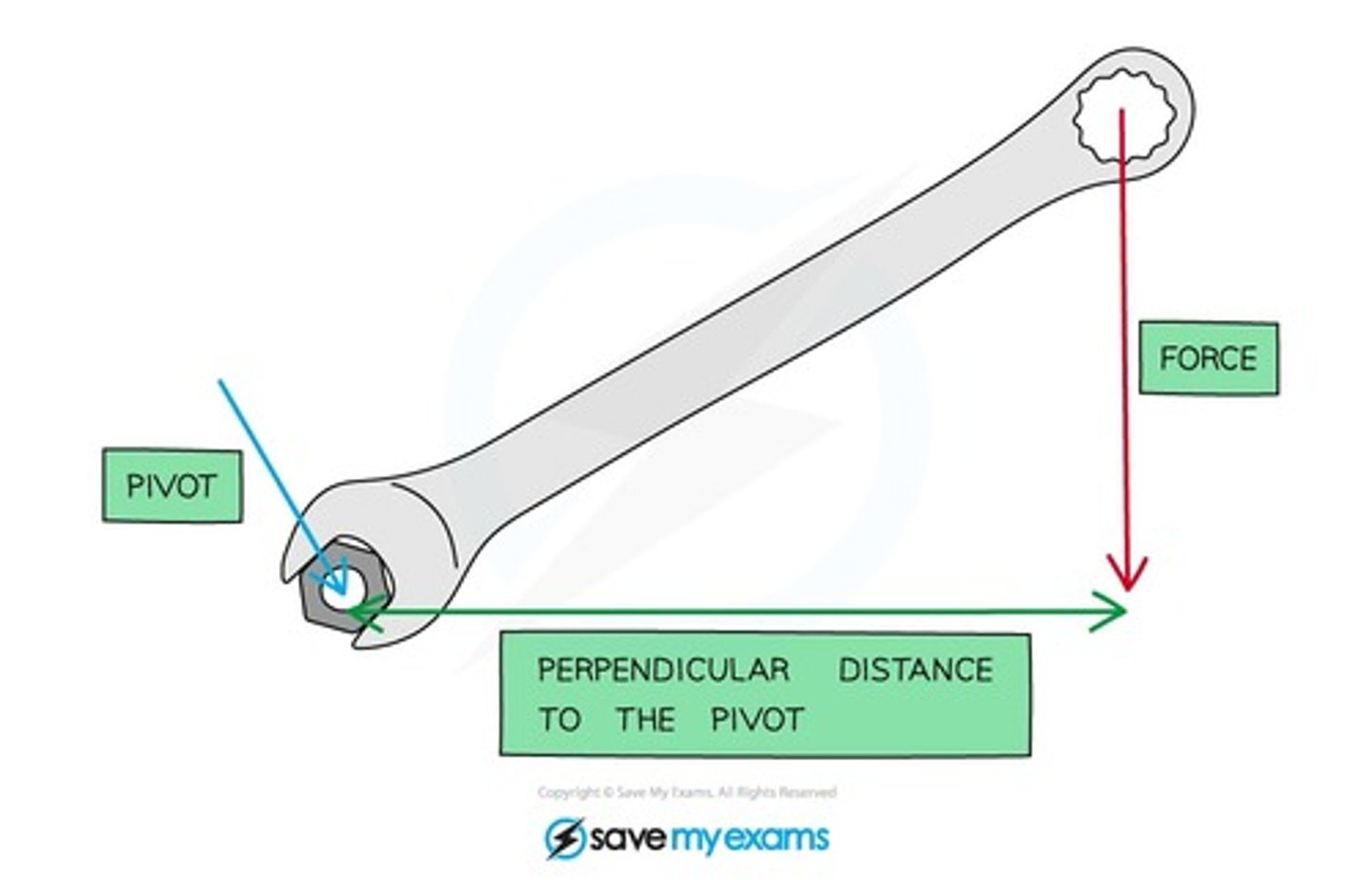
The Larger the Turning effect
- the bigger the force
- the larger the perpendicular distance from the pivot to the point where force is applied
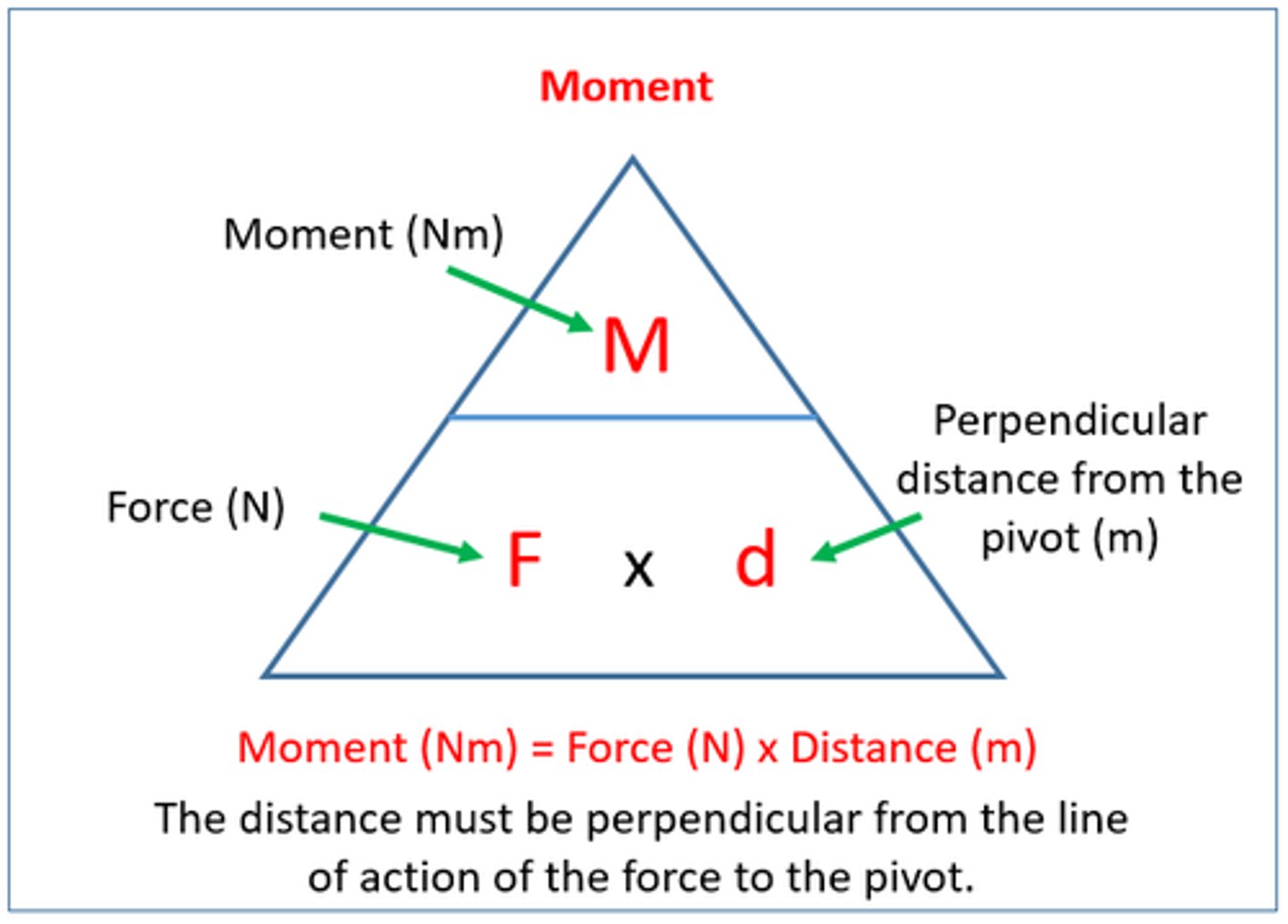
Moment (Nm) =
force x perpendicular distance from pivot
N x m
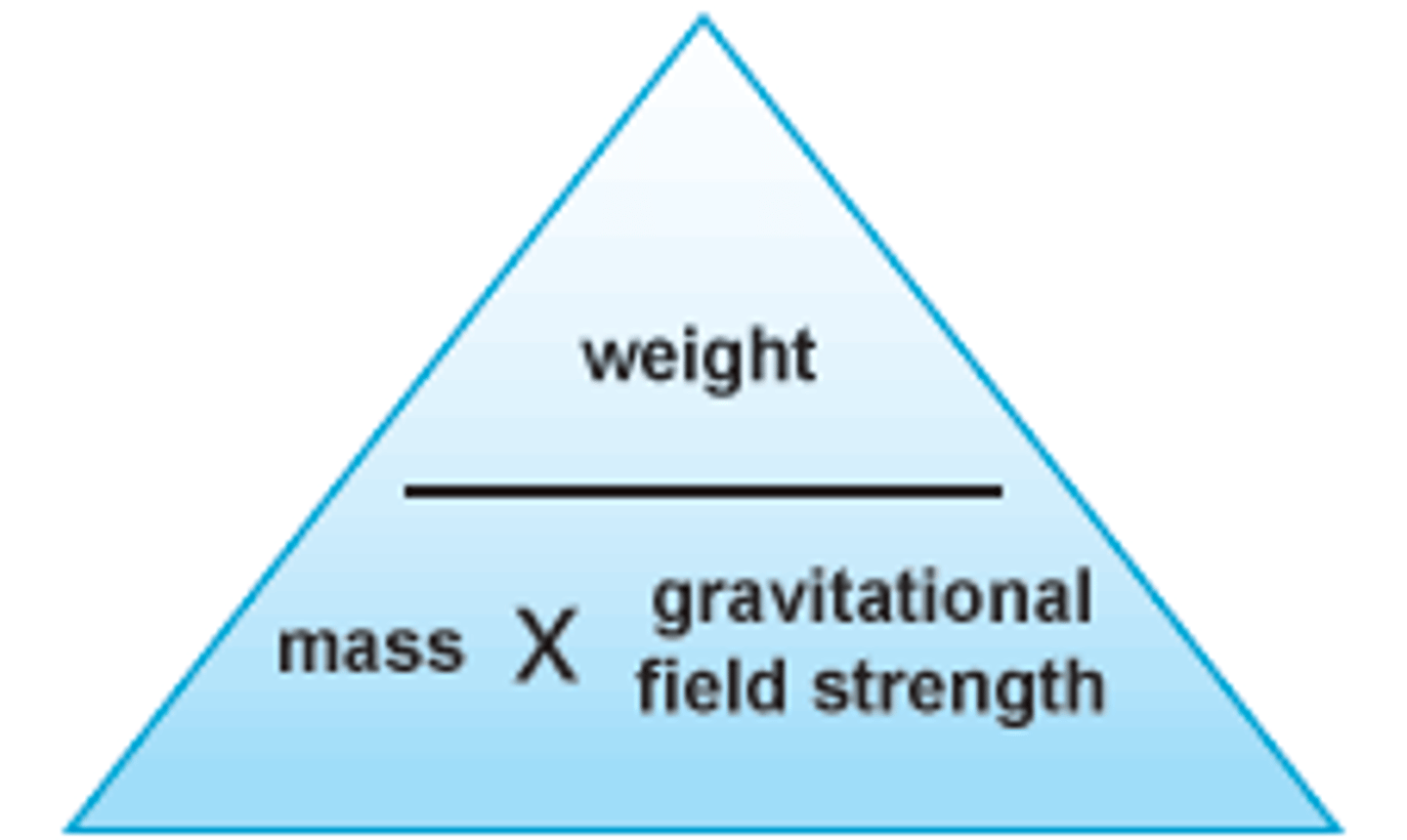
Weight =
mass x gravity
kg x N/kg
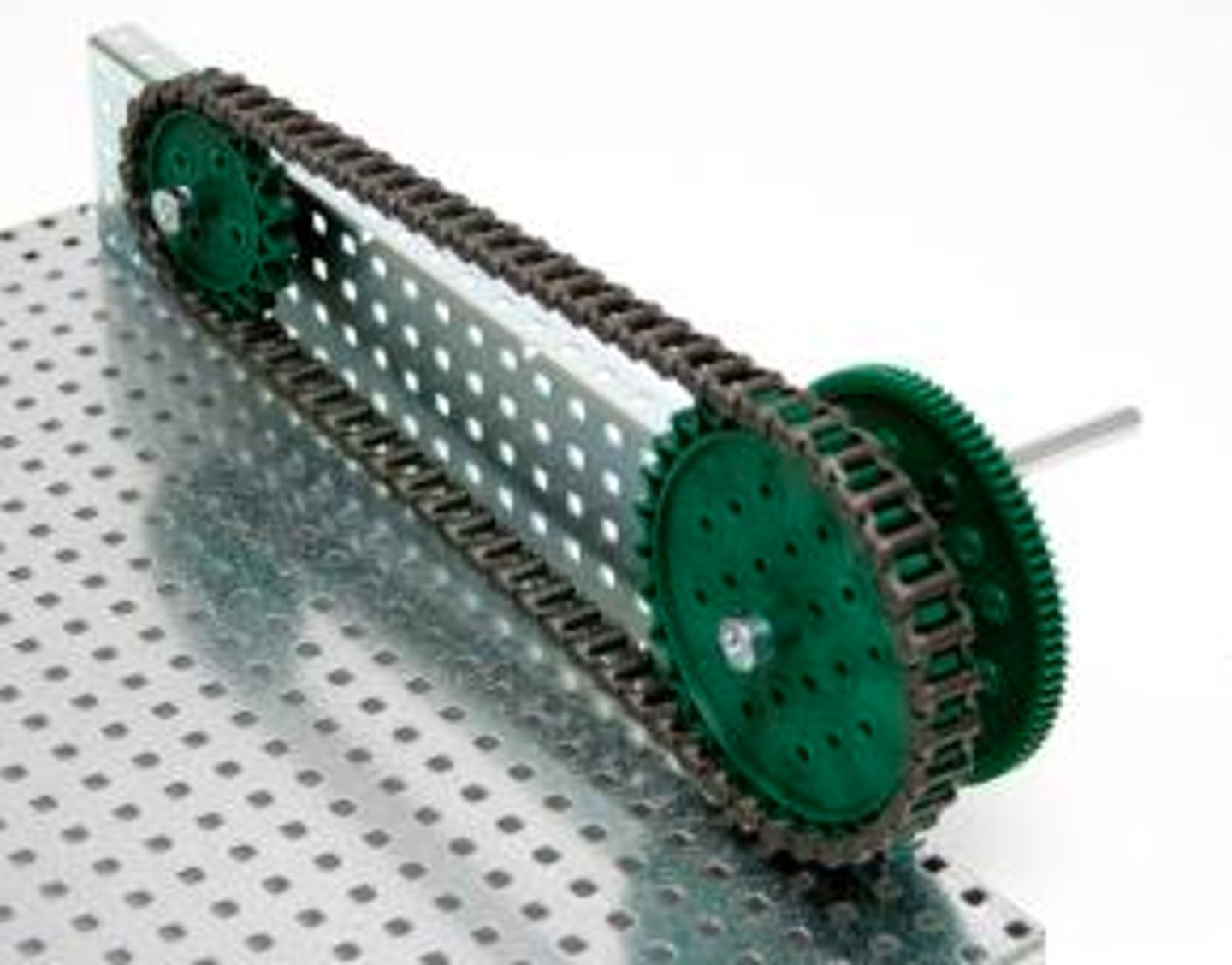
Gears
two or more wheels linked together by interlocking teeth
- turning in opposite directions
- can multiply a turning effect
- used to transmit the rotational effect of a force from one place to another
Gears are Used to
- increase speed
- increase force
- change direction
Cars at a Low Gear
- the engine turns a small gear quickly
- the wheels with the large gear turn more slowly, but with more force
Cars at a High Gear
- the engine turns a large gear slowly
- the wheels with a small gear turn more quickly but with less force
Disadvantages of Gears
- if a gear gives you more force, it must give you less speed at the same time
- if it gives you more speed, it has to give you less force
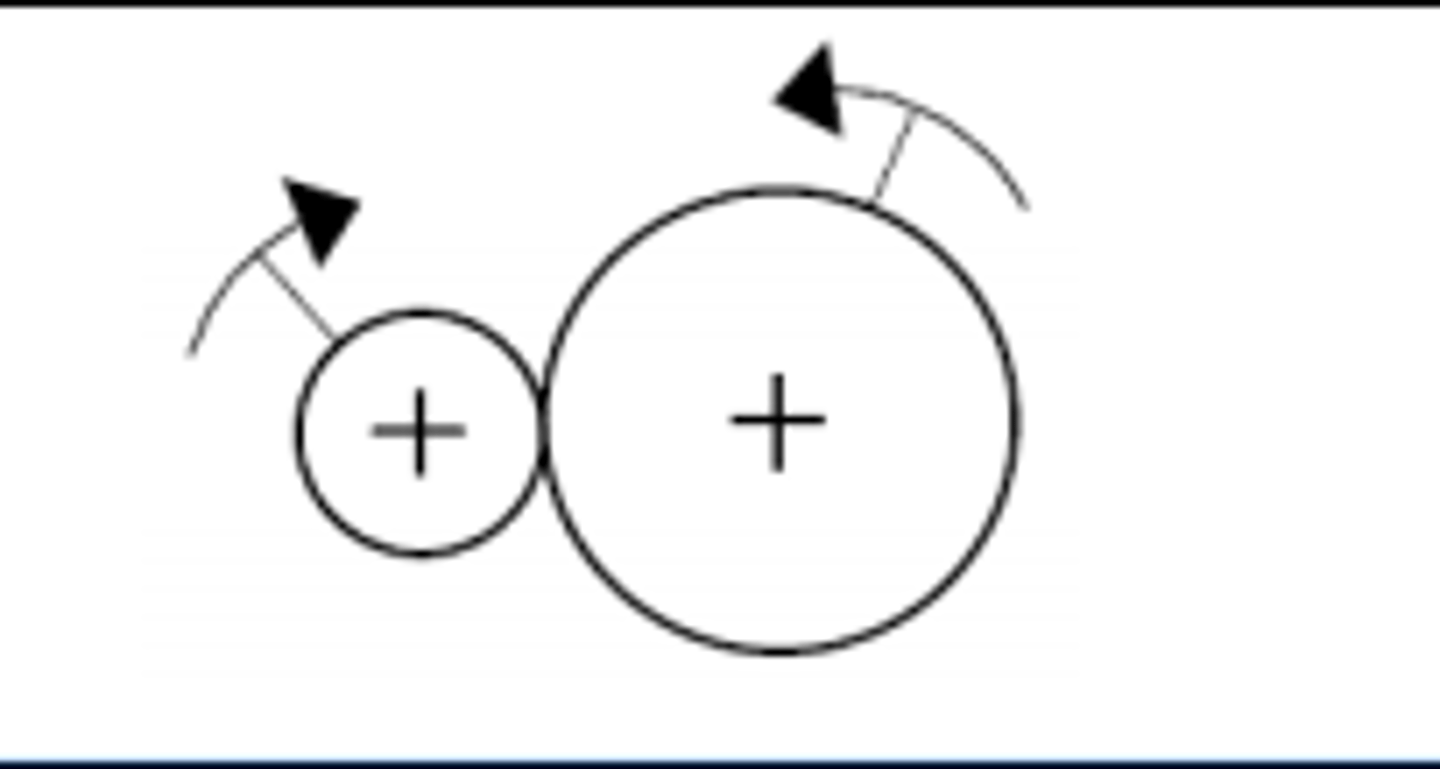
A Low Speed Engine
- engine turns a small gear quickly
- engine turns a large gear slowly but with a large moment
Distance Multiplier
- the larger gear is the drive
- there's a lower turning force
- the small gear goes fast
Moment Multipler
- the smaller gear is the drive
- there's a larger turning force
- the smaller gear goes slowly
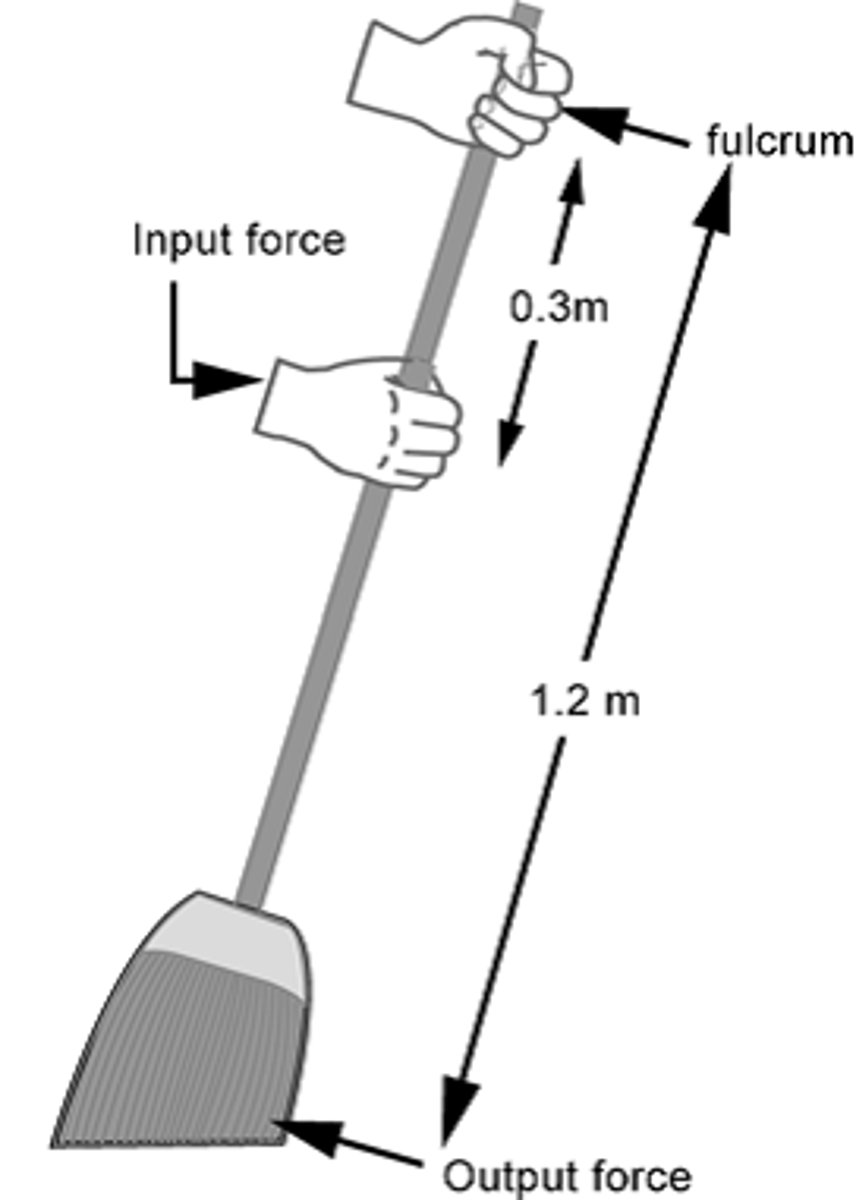
How does the Force on the Pedal cause a Moment about the Rear Axle
- the force on the pedal causes a moment on the axle
- the moment causes a force on the chain

It's Easier to have a Large Back Wheel Riding up a Hill as
- the large wheel acts as a moment multiplier
- so you don't need a strong force to cause a moment
- as there's a large distance from the pivot

It's Easier to have a Small Gear to Ride Fast as
- the smaller gear would act as a distance multiplier
- as it would spin faster
- meaning you wouldn't need to pedal as fast to go the same speed
Output Force
the force exerted on an object by a machine
- generally closer to the pivot
- larger
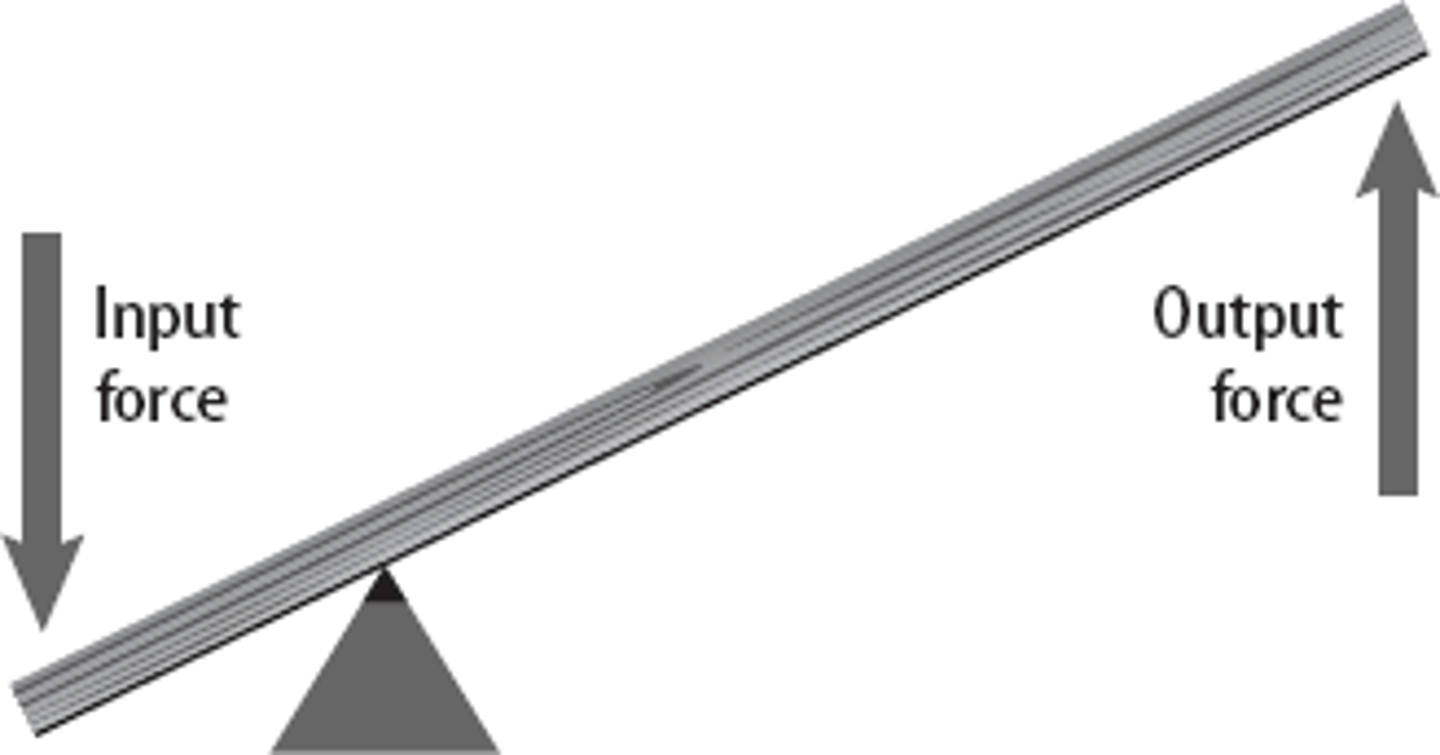
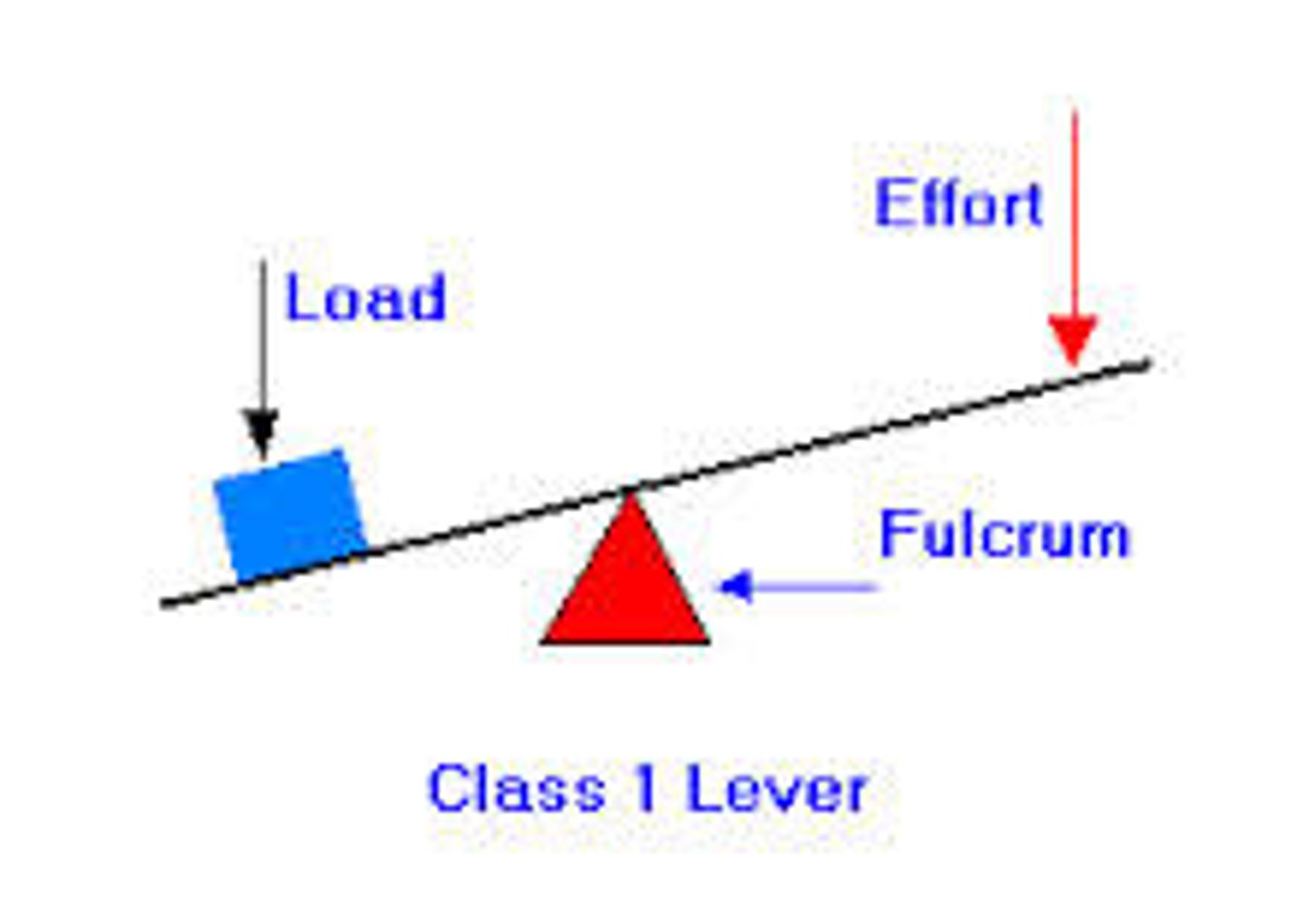
Levers
simple machines with an arm that moves around a fulcrum
- make it easier to do work
- helps to lift loads
- force multiplier
Why do Levers Work
you have to move the effort force through a greater distance than the load force generated moves
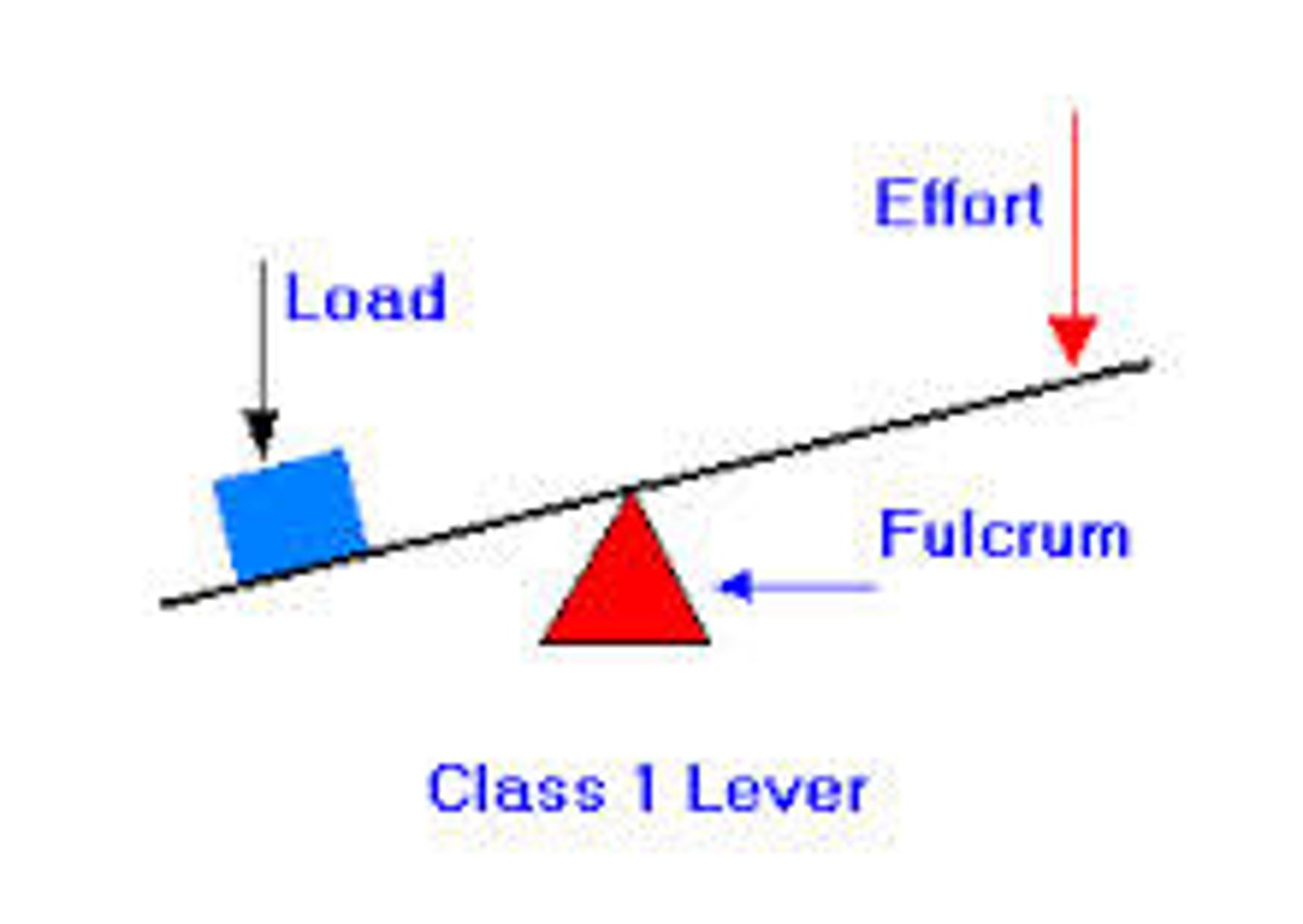
Increasing the Distance Between Pivot and Applied Force
- means less force is required to get to the same moment
- so less work needs to be done
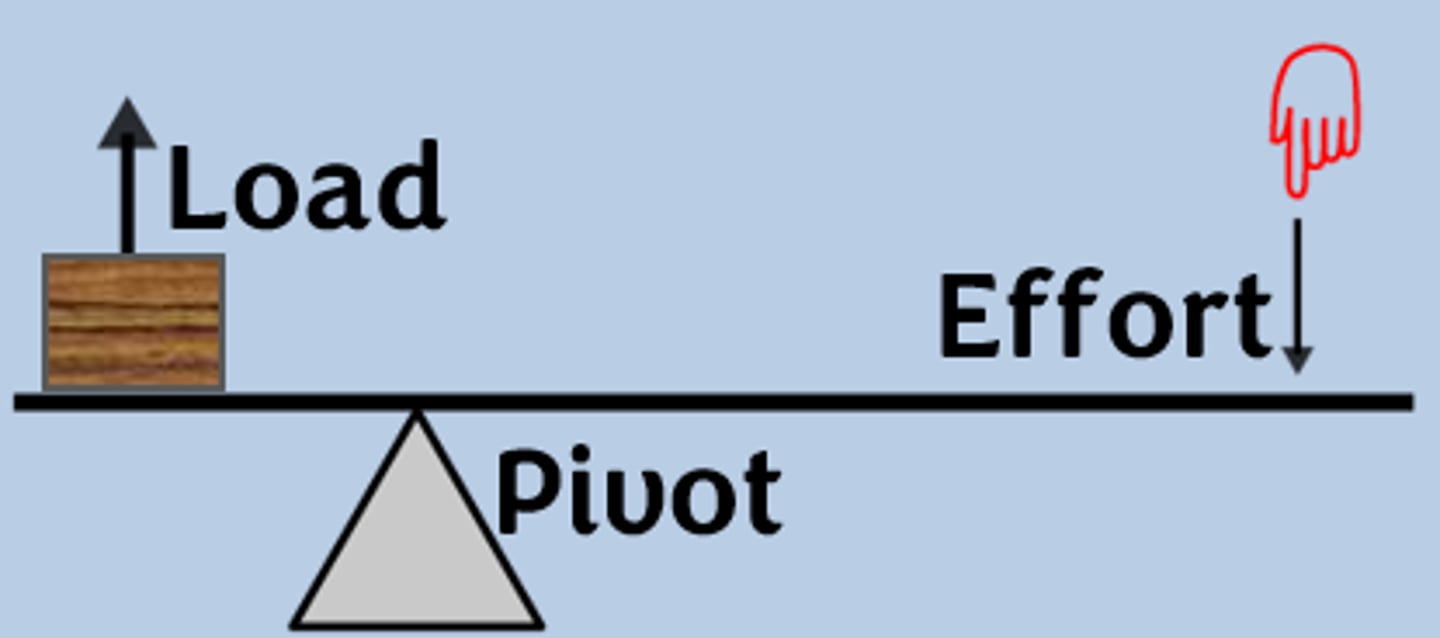
Levers and Gears can be Seen as Simple Machines as
- it only has 2 parts with different functions
- you only need to move one thing with mechanical power to achieve the goal
The Centre of Mass of an Object
the centre point where it's mass can be considered of as being concentrated
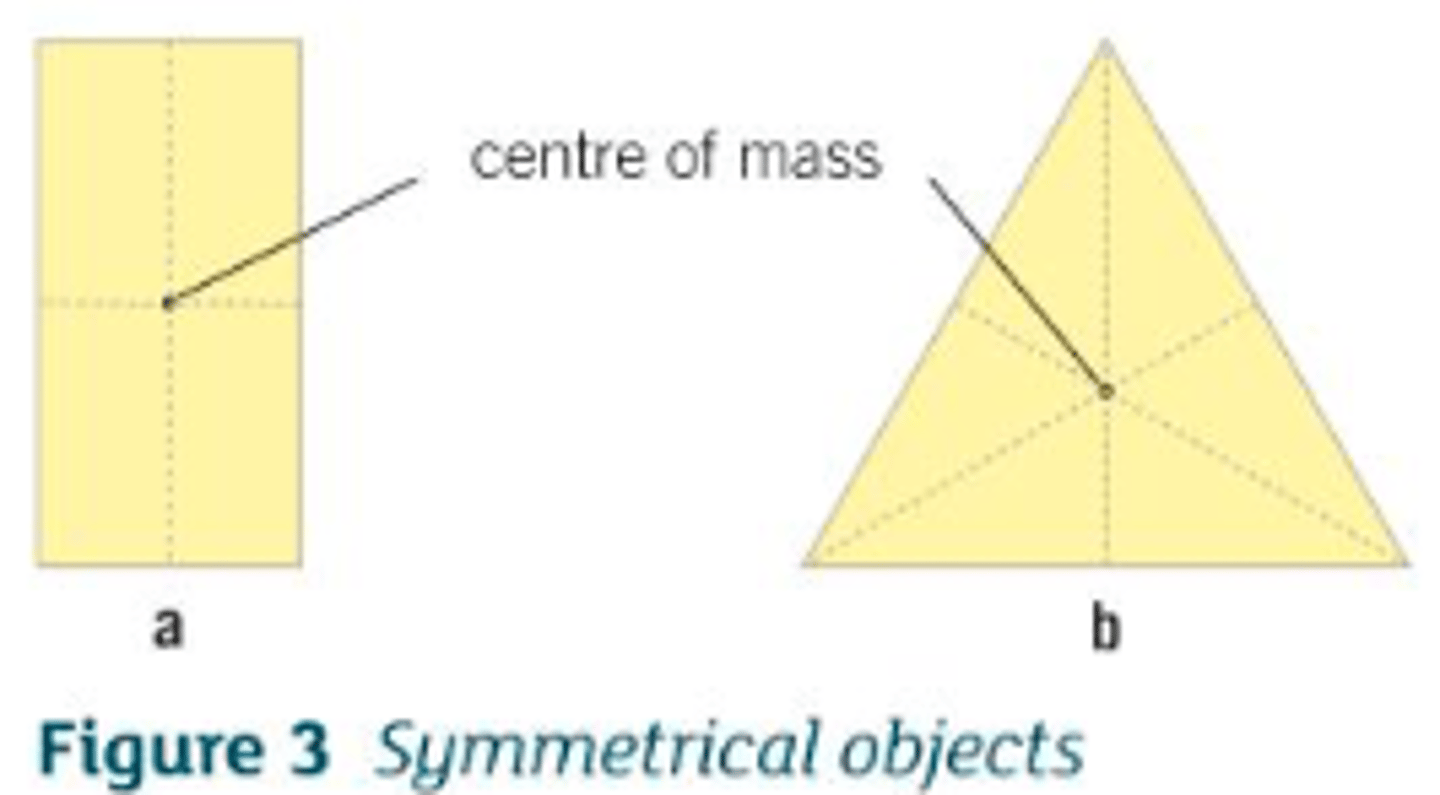
The Centre of Mass in 2D Shapes
the point where all the lines of symmetry meet
- the exact middle
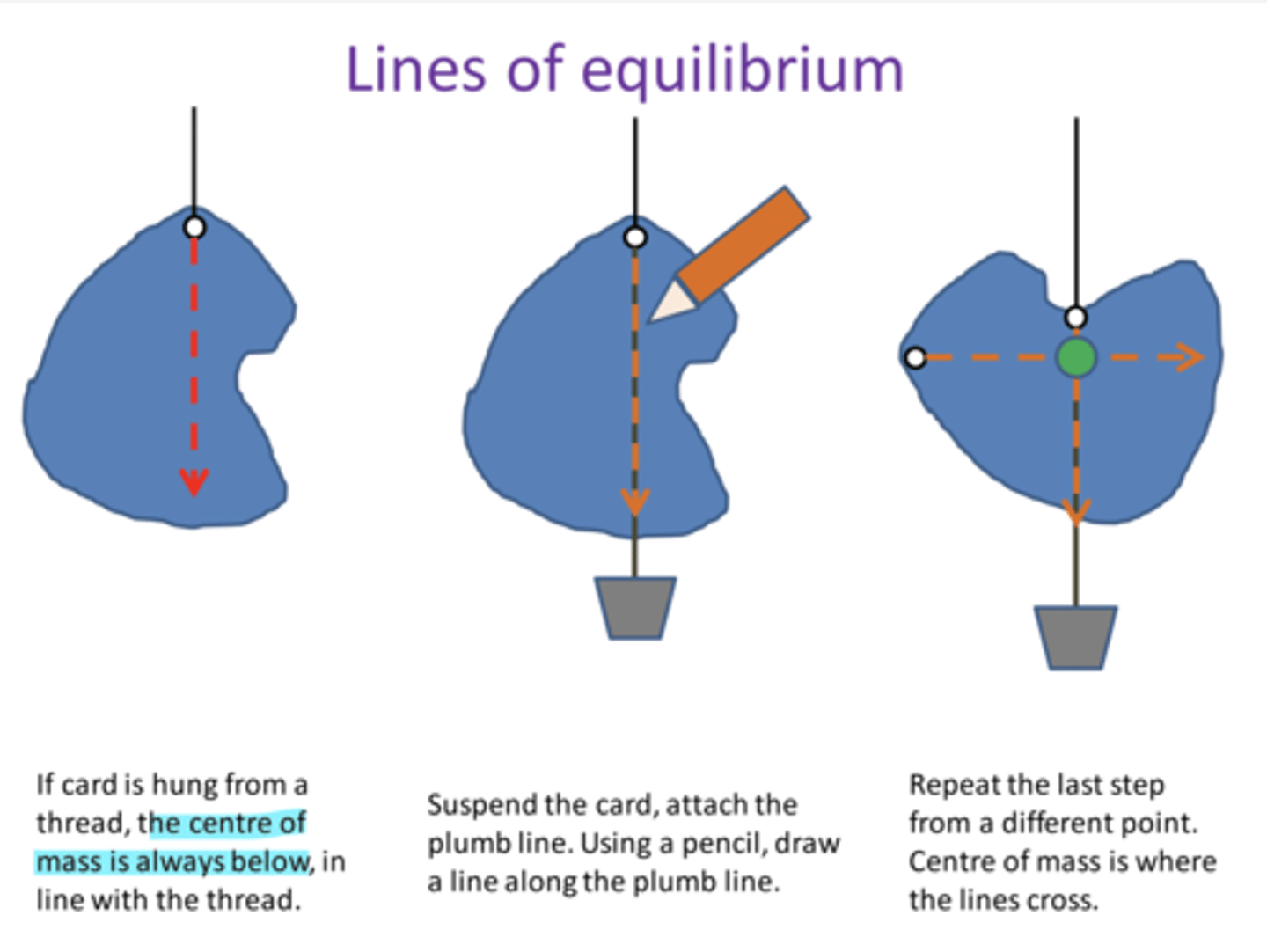
How to Find the Centre of Mass in Irregular Objects
- cut an irregular shape out of paper
- punch 2 holes in the shape
- hang from a clamp stand using string
- hang a weighted piece of string from the same point
- draw a straight line along your weighted string on the paper
- repeat after you have rotated your paper by 90⁰
- where the lines cross in the centre of mass
- try and balance the paper on the end of a pencil
As Every Particle has a Small Gravitational Force Acting on it
these forces act like a single one pulling at just one point
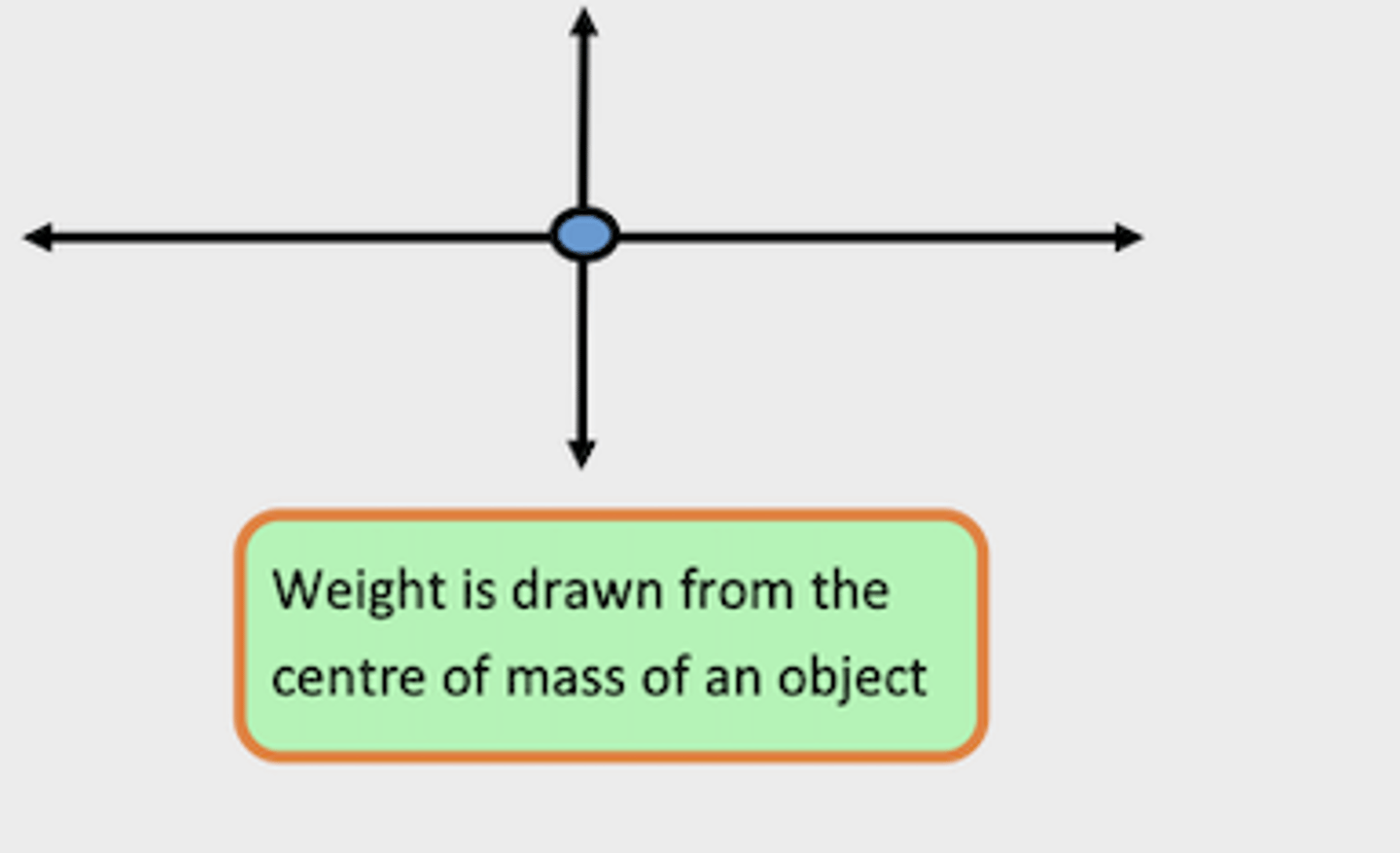
Centre of Mass: Weight
weight acts straight down from the centre of mass
The More Stable an Object
- the lower the centre the of mass
- the wider the base
- the line of action is above the base

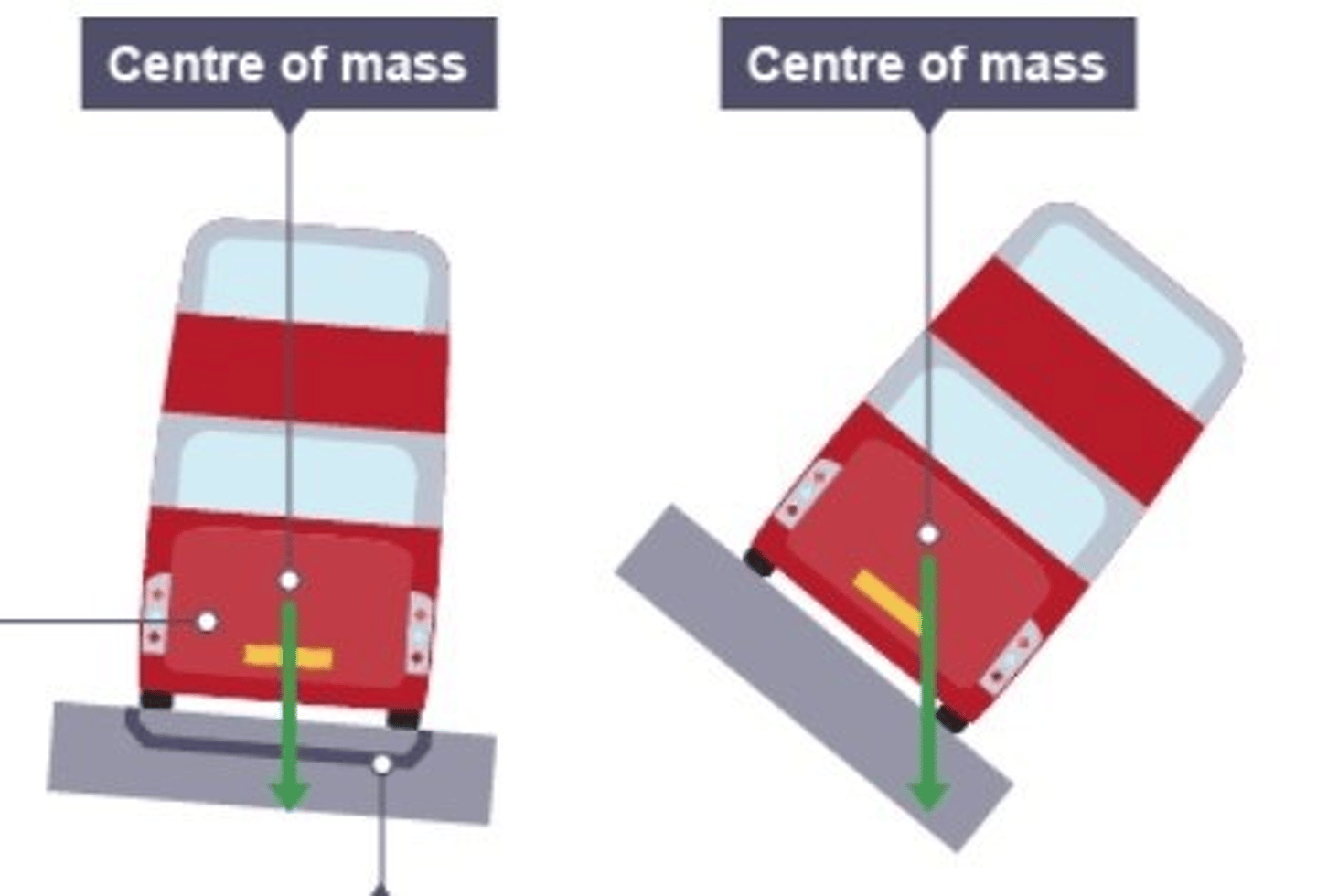
The Stability of a Double Decker Bus Compared with a Racing Car
- the bus is less stable than the race car
- as the centre of mass is much higher
- with a shorter base
- this means the car is less likely to topple going around corners quickly
- to improve the stability of the bus, you could increase the wheel base (make it wider)

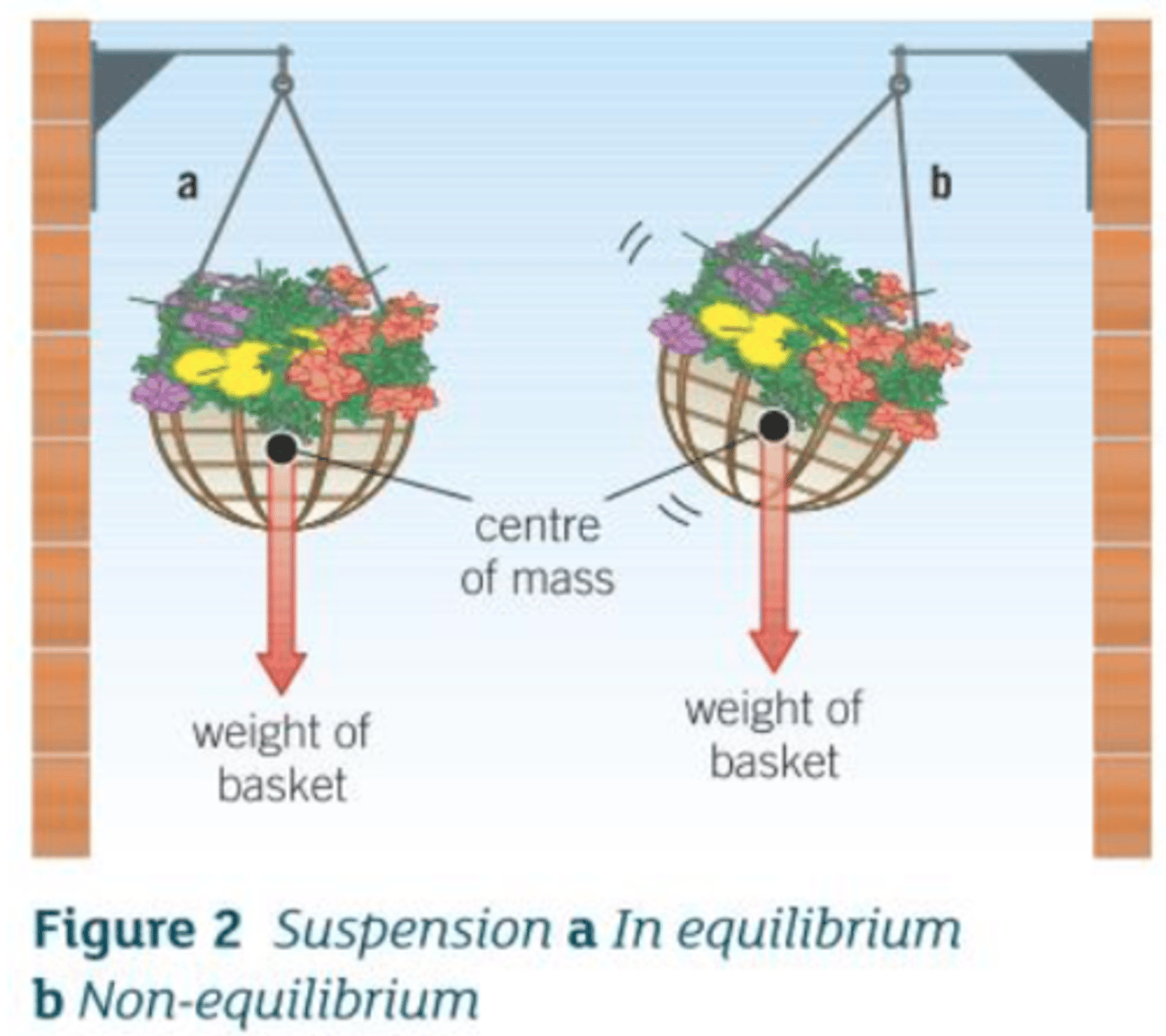
If you Suspend an Object and then Release it
- it will eventually come to rest
- with it's centre of mass directly below the point of suspension
Principal of Moments
moments must stay balanced
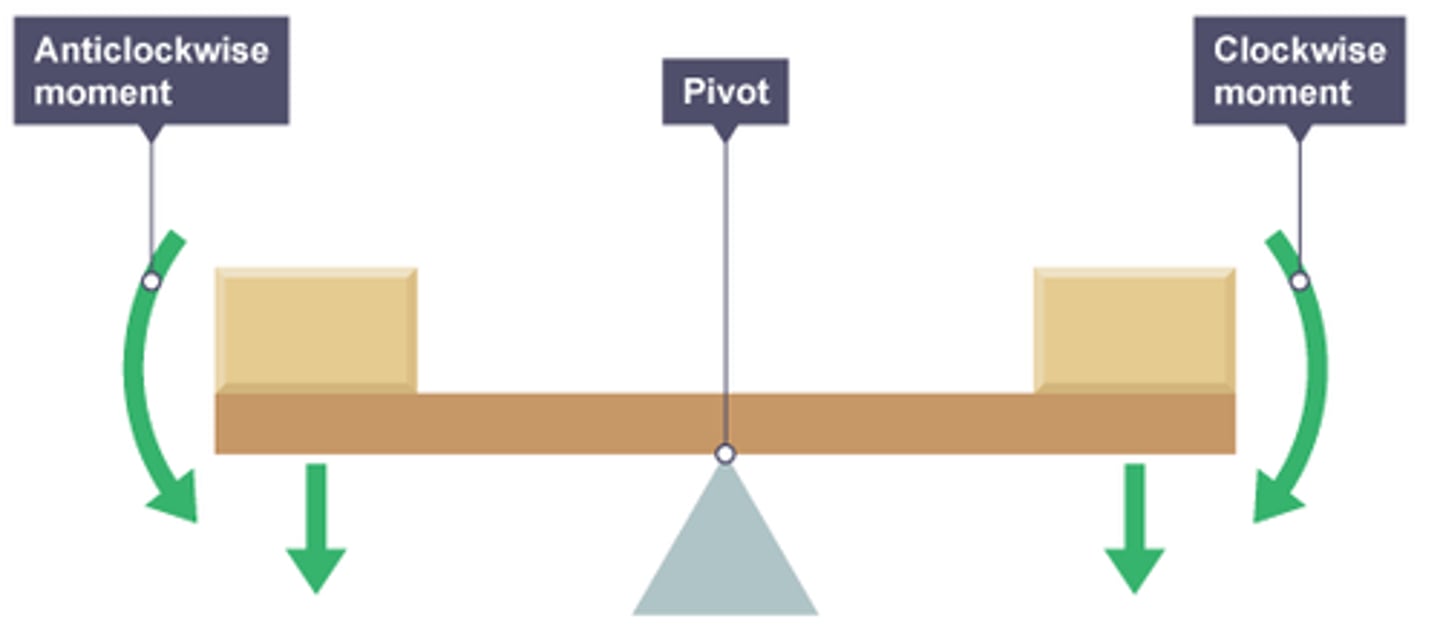
The Sum of Anti-clockwise Moments =
the sum of clockwise moments
How to See if Something is Balanced
- calculate the clockwise moments
- calculate the anti-clockwise moments
- see if they're balanced
If the Sum of Moments is Unequal
the object will spin in the direction of the larger force

The Parallelogram of Forces
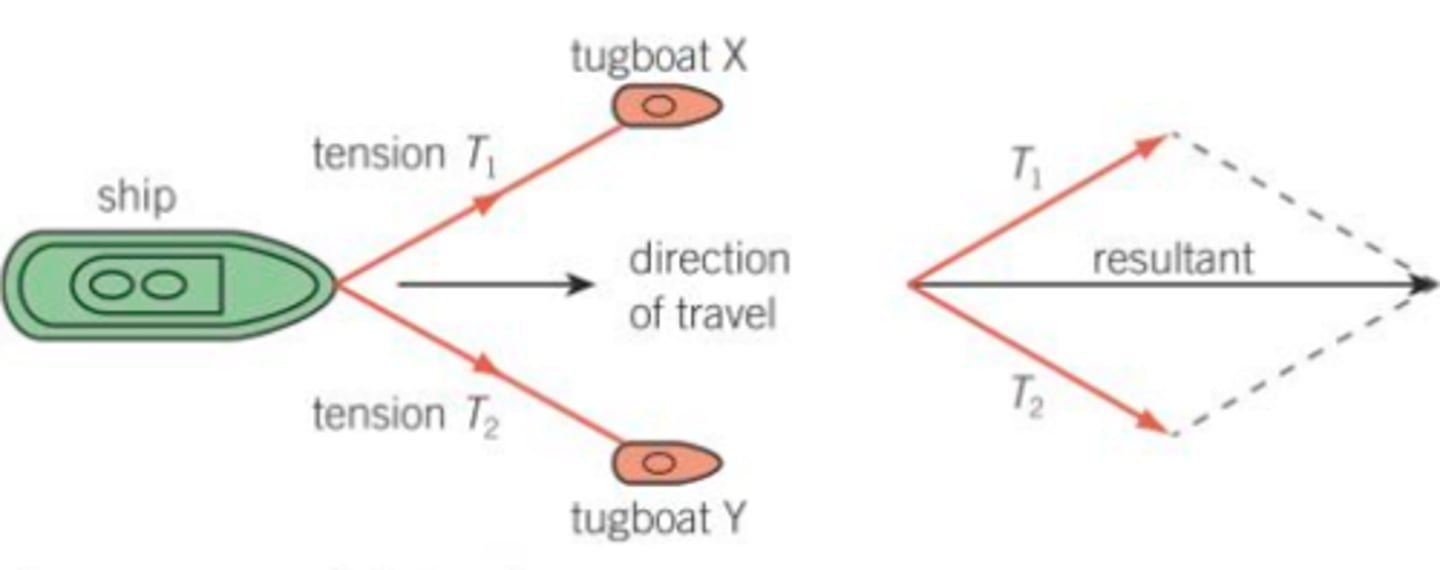
How to Draw the Parallelogram of Forces
- draw a straight horizontal line to scale with the force
- draw another force to scale from the left end of the first line
- draw a second arrow leaving from the first of the same size
- make sure this is at the same angle as before.
- connect the starting and ending points of the whole journey
- measure the lengths to find the force on the new arrow like before
- measure the angles as it is a vector
The Upwards, the Rightwards Force of One String =
equivalent to an upwards force and a rightwards force on two leads
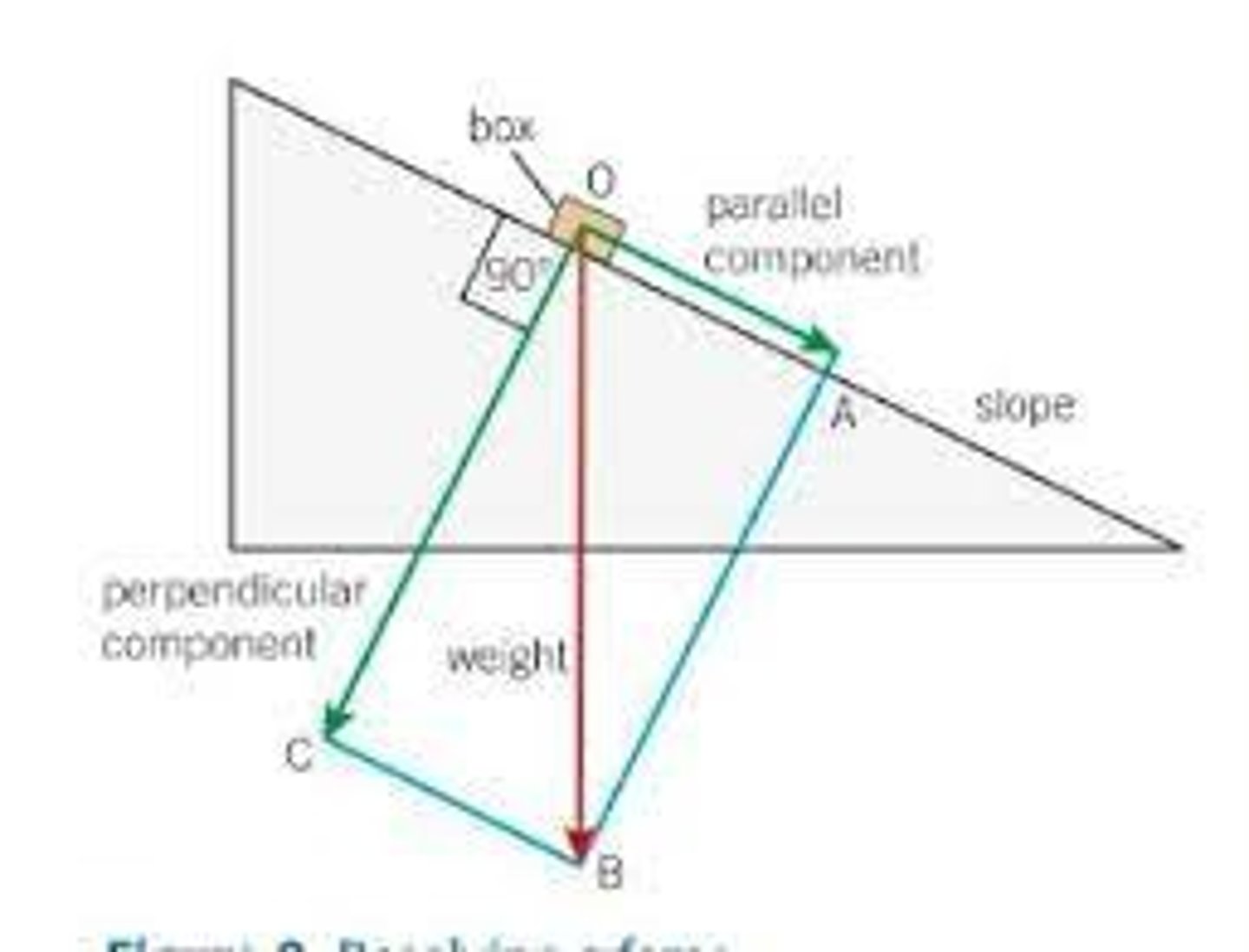
Why is it so Hard to Cycle Up a Hill
the weight of the cyclist and bicycle have an effect that acts downhill as well as down on the road
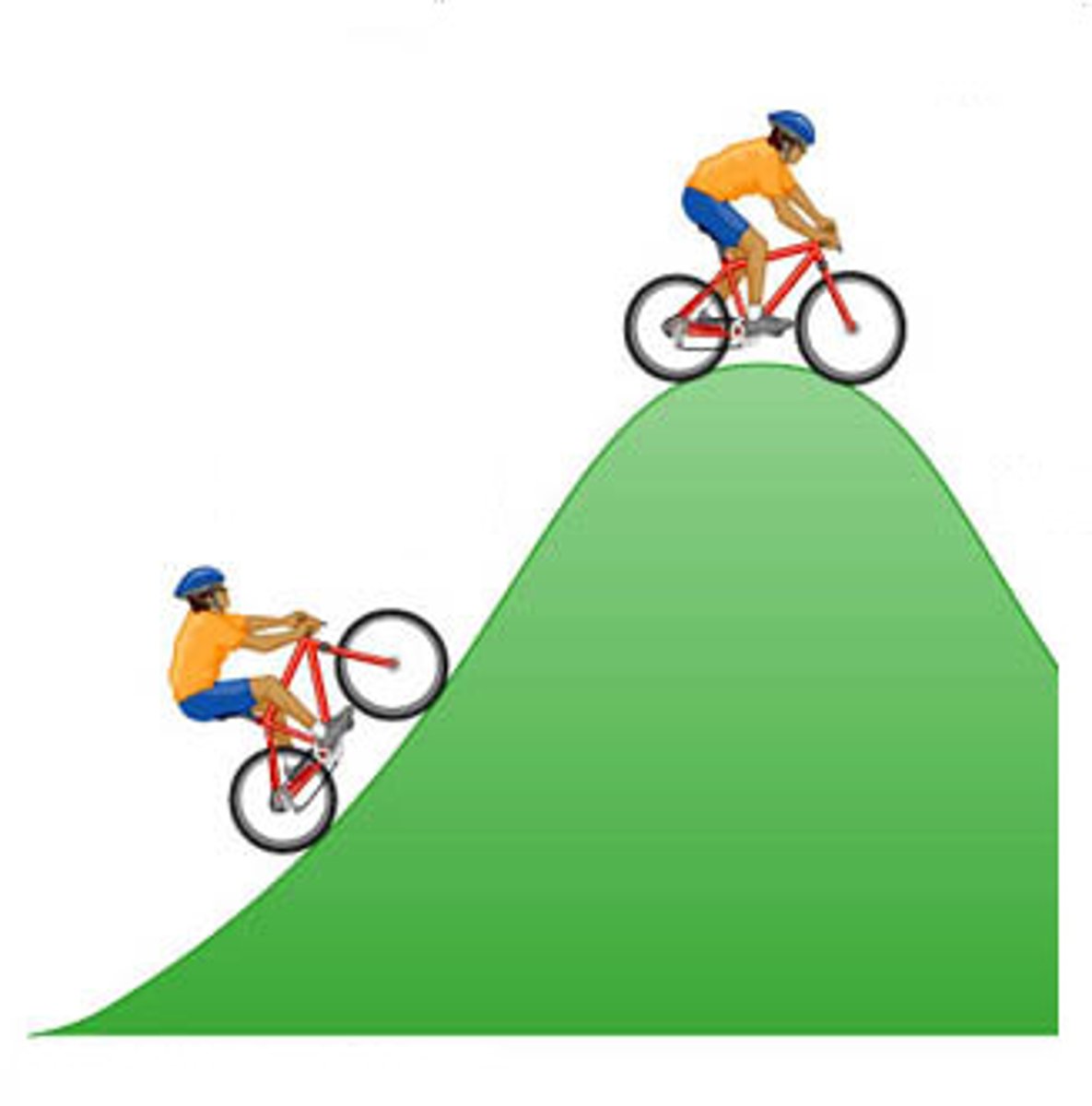

Free Body Diagram
the single force of gravity can be split into two parts
- one force acting down the slope
- the other at 90˚ to the slope.
- called resolving a force into two components
If the Slope of a Free Body Diagram was Steeper
- F gravity would not change
- FI: the downwards force PERPENDICUAR to the slope DECREASES
- FII: the force PARALLEL to the slope INCREASES
The Resolution of Forces Diagram
An Object is at Equilibrium if
- the resultant force on the object is zero
- the forces acting on the object have no overall turning effect