Lecture 11: Hemolytic Disease of Fetus and Newborn
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
blood problem found in newborns
fast rate of red cell breakdown due to mother having clinically significant antibody
mother forms IgG antibodies from previous transfusion or pregnancy
IgG antibodies in mother circulation can cross placenta during pregnancy
Corresponding antigen present on baby RBCs
antibody in fetal circulation binds to antigens on baby RBCs
baby must get antigen from father
mother has to lack the antigen to form antibody
Severity HDN varies
antibody ID, titer
greatest danger to fetus while still in utero in anemia
greatest danger to newborn is build up of unconjugated bilirubin
Antibodies causing HDN
most severe: D, K, c
other: E, C, e, Fya, Fyb, Jka, Jkb, S
mild HDN can be caused by ABO antibodies
most commonly IgG anti-A,B
Prenatal studies
ABO grouping and Rh typing
Antibody screen
antibodies to low incidence antigens typically not detected with antibody screens but can still cause HDN
Presence of antibodies doesn’t mean HDN will occur
baby needs to have antigen to corresponding antibody
phenotype of father for likelihood of babying being +
father -: 0%
father heterozygous: 50%
father homozygous: 100%
Antibody titer
done for any clinically significant antibodies detected
can help clinicians decide to do more invasive procedure
amniotic fluid analysis
intrauterine transfusions
serum is serial diluted to determine titer of antibody
titer is highest dilution at which agglutination occurs
current titer result run in parallel with previous frozen sample
an increase in titer could indicate HDN
Amniocentesis
can help in prediction of severity of fetal anemia
measures the level of bilirubin pigment in amniotic fluid
does spectrophotometrically
concentration of bilirubin correlates with degree of fetal anemia
Cordocentesis
also known as percutaneous umbilical blood sampling
fetal blood sample is withdrawn for testing
direct indicator for severity of HDN
HCT
phenotyping
Assessment of values obtained
HCT and bilirubin values given an idea of how much RBC destruction is occurring in fetus
clinical team determines if medical intervention is needed to reduce fetal anemia
intrauterine transfusion
Intrauterine transfusion
used in cases of severe fetal anemia
provides fetus with RBCs that will survive normally
blood is transfused through fetus’s abdomen or an umbilical cord vein
transfused cells must be compatible with maternal antibodies
Characteristics of blood used
freshest unit available
usually no older than 5 days after collection
group O RBCs
typically Rh - RBCs
negative for antigens corresponding to maternal antibodies
CMV -
hemoglobin S negative
irradiated
crossmatch compatible at AHG with maternal serum
infant eluate or serum can be used if maternal sample unavail
Plasma reduced blood
citrate phosphate dextrose (CPD) anticoagulant
no additive solutions
if unit had additive solutions, must be washed
crossmatch compatible at AHG with maternal serum
Postpartum testing
cord blood should be contained for newborns with:
Type O mothers
could have IgG anti-A,B
mothers with allo-antibodies
Rh negative mothers
Cord blood testing - ABO group
only forward type can be performed
serum testing not performed
newborns don’t develop antibodies until 4-6 months old
any ABO antibodies present in cord blood sample are from mother
Cord blood testing - Rh type
immediate spin test and weak D test performed on newborns
especially important to do weak D for newborns of Rh negative mothers
used to assess the mother’s Rh immune globulin candidacy
Cord blood testing - DAT
determines presence of antibodies on surface of RBCs in vivo
antibodies present on newborn RBCs will have + result and are from mother
these RBCs will be destroyed
strength of DAT doesn’t correlate to severity of HDN
HDN due to ABO incompatibilities typically have weak DAT reactions
stronger + DAT found in HDN due to anti-D, anti-K, anti-c and other non-ABO blood group antibodies
cord blood testing - Elution
if DAT is +, elution can remove maternal antibodies bound to newborn RBCs
a panel can be performed with eluate to determine specificity of antibodies
only necessary if mother has multiple antibodies
Mom: O +, - antibody screen/Newborn: A pos, weak positive DAT
ABO HDN
can occur in any pregnancy
most commonly seen in O mother and AB or B newborn
DAT is weak
anti A or anti B or anti A,B can be eluated
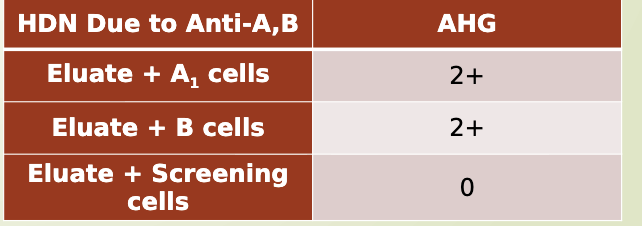
Mom: O +, - antibody screen Newborn: O +, 2+ positive DAT
HDN due to low incidence antibody
antigen to maternal antibody is not present on screening cells
example: Kpa, Jsa
eluate will not react with A cells, B cells, or screening cells
eluate would react against newborn cells and paternal RBCs
Mom: O +, + antibody Newborn: A +, 3+ positive DAT
HDN due to other blood group antibodies
eluated antibody will react with screening cells
Wharton’s Jelly
gelatinous substance within umbilical cord
causes false positive reactions in cord blood testing
avoid by washing forward type several times before testing RBCs
Intrauterine transfusion
following an intrauterine transfusion, recipient circulating blood could contain up to 90% of donor cells
cause weak or mixed field reactions
could type exactly as donor cells (O-)
will have to wait until donor cells are out of patient’s system to know true blood type
Newborn’s cells heavily coated with IgG antibodies
maternal antibodies cross placenta and bind a significant portion of newborn antigen binding sites
strong positive DAT
RBCs tested with antisera
antisera has reduced or no place to bind
false negative
Suspect fetus in Rh + but types as Rh -
maternal anti-D: coating the Rh + newborn cells
reagent anti-D has no place to bind
known as blocked D

Resolution of blocked D
a gentle heat elution will remove the maternal anti-D
cord RBCs can now be re-tested with reagent anti-D
Rh + binding sites are available for reagent anti-D to react and agglutinate
Used in cases of severe HDN
remove aliquots of neonatal blood and replaces it with donor blood in order to
reduce bilirubin levels
remove antibody coated RBCs that will be destroyed
lower concentration of maternal antibodies in newborn circulation
maintain adequate blood in circulation to deliver O2 to tissues
Rh immune Globulin
common brand RhoGAM
RhD immune contains mostly IgG anti-D from pools of human plasma
used to prevent Rh - mothers from developing anti-D
thought to block immune system from recognizing foreign D antigen (ie from baby)
important in preventing HDN in future pregnancies due to anti-D
When is RhoGAM given
Rh negative woman may come into contact with Rh positive RBCs
When Rh - woman is pregnant:
must be given within 72 hours of bleeding event
abortion
miscarriage
amniocentesis
antepartum hemorrhage
Rh negative women at 28th week of gestation
must be given 72 hours of giving birth to Rh + newborn
immediate spin or weak D +
When mother received RhIG during pregnancy
neonate may have + DAT
weak, doesn’t cause hemolysis
RhIG can still be present and cause + antibody screen at time of delivery
can sty detectable at 3-4 months
What testing is performed prior to administration of RhIg
ABORh typing
Antibody screen and ID
ABORh type
given to Rh - women
given to women with partial D mutations
can develop anti-D to missing epitopes
Antibody screen and identification
women who already developed anti-D don’t need Rh immune globulin
careful about presence of anti-D from dose at 28th week still + at delivery
don’t want to miss-ID anti-D RhIG as real anti-D
women with all other antibodies are a candidate
Rh immune globulin given circumstances
Rh - women pregnant and experiences:
abortion
miscarriage
amniocentesis
Rh negative women at 28th week of gestation
Rh negative women gives birth to Rh positive baby
women with partial D mutations
Rh immune globulin not given circumstances
Rh positive women
Rh negative women with anti-D
Rh negative women gives birth to Rh negative baby
Determining RhIG dose
full dose of Rh immune globulin protects against 15 mL of Rh + packed RBCs
equates to 30 mL of whole blood
antepartum administration
usually 1 dose given
postpartum administration
# of doses given is determined by presence and volume of fetal blood cells in maternal circulation
Determining RhIG dose - fetal blood screen
determines if there is any Rh + fetal blood in Rh - mother
Anti-D is added to post-partum maternal sample to coat any Rh positive fetal RBCs
enzyme treated Rh + RBCs are added
clumps will form around the anti-D coated, Rh positive fetal cells
- result: 1 dose of RhIG
+ result: detects FMH> ~10mL; needs a quantitative test to determine dose
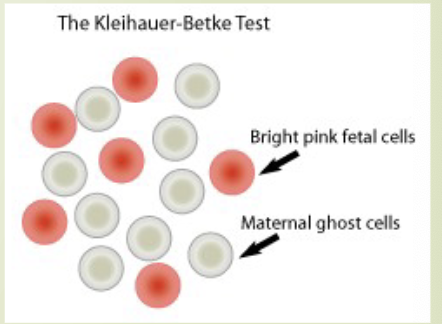
Kleihauer-Betke test used to quantify FMH
maternal blood is treated with acid
fetal cells have higher HGB F and are more resistance to acid elution
fetal cells remain intact and are red
maternal cells lose hgb and appear as ghost cells
KB test calculation
[% Fetal cells x 50mL] / 30mL
KB test gives % of fetal cells
calculation gives volume of fetal cells in maternal circulation
Round up if >.5 Round down if <.5
an extra vial is given for safety
if KB is 0.3%, volume of fetal cells in circulation is 15%mL, which divided by 30mL is 0.5. Rounded up to 1 and give an extra to make 2 vials of RhIg