1.2.7 Price mechanism, 1.2.8 Consumer & producer surplus
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Definition of consumer surplus
The difference between the price a consumer is prepared to pay for a good/service & the market price paid
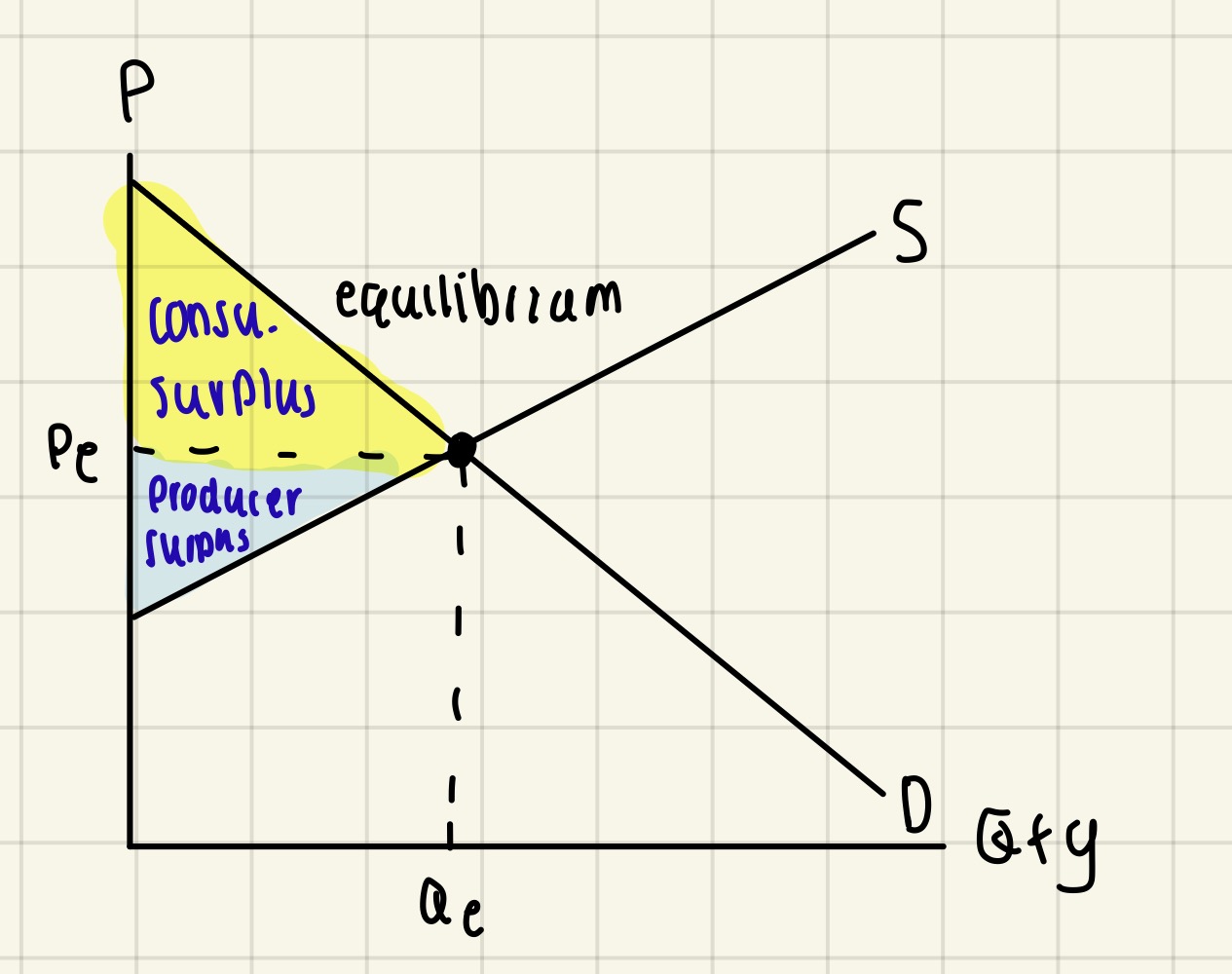
Definition of a producer surplus
Difference between the price the producers is prepared to supply the good/service at & the actual market price
What are the three functions of the price mechanism to allocate resources? (in order to restore market equilibrium)
1) Rationing
2) Incentive
3) Signalling
What is a rationing function
Shift out in demand curve - causes an increase in price - rations consumer out to avoid excess demand - making it available only for those who can afford to purchase it
What is incentive function
The higher price incentivises producers to allocate more factors of production to meet the new demand - extension along supply curve from Q1 to Q2
What is signalling
Shifts out in demand curve signals to other producers that demand for the good is strong & the increase in price maximise profit - they should consider entering the market/switching some of their production from the old good to this new good
As a result, new equilibrium + excess demand is eradicated
Evaluation for rationing
Price increase not significant - many consumers still remain in the market - so rationing not as effective
Evaluation for signalling
Shift in demand not significant - signalling not as effective