FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:10 AM on 2/3/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
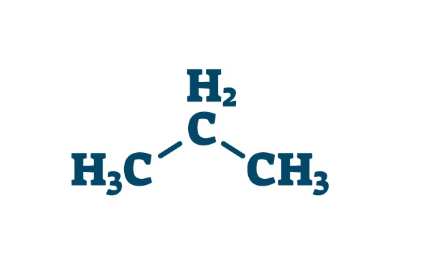
-ANE
Alkane
2
New cards
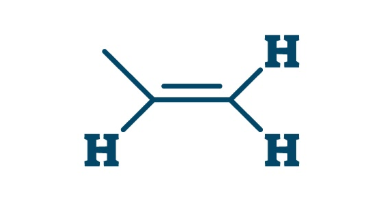
Ene
alkene
3
New cards

Yne
alkyne
4
New cards
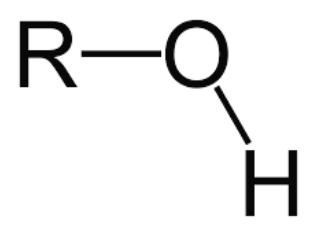
OH
alcohol
5
New cards
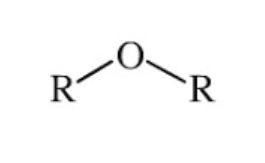
ROR
ether
6
New cards
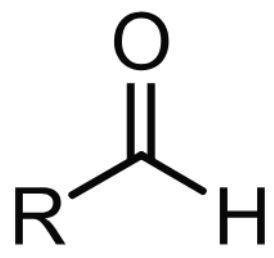
RCHO
aldehyde
7
New cards
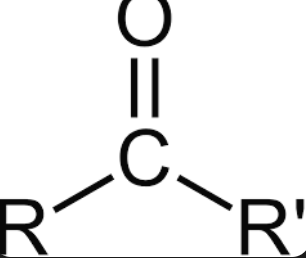
RCOR
ketone
8
New cards
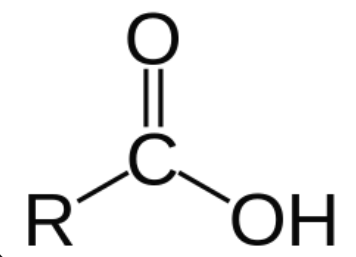
C-OOH
carboxylic acid
9
New cards
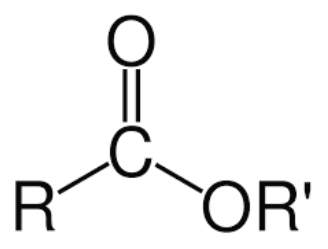
R-COO-R
ester
10
New cards
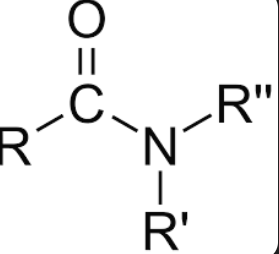
RCONH2
Amide
11
New cards
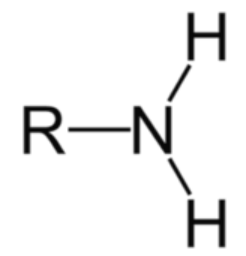
NH2
amine
12
New cards
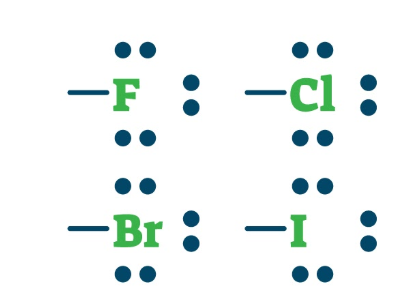
R-X (X: Br, Cl, F, I, At)
haloalkane or alkyl halide
13
New cards
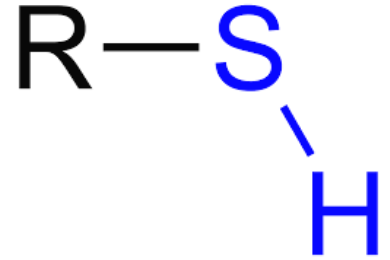
SH
thiol
14
New cards
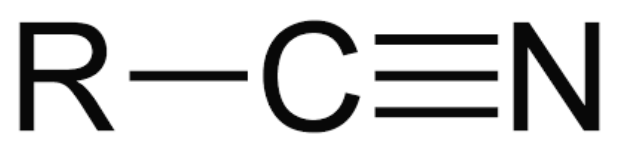
C≡N
nitrile
15
New cards
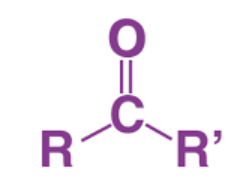
R-C=O
carbonyl
16
New cards
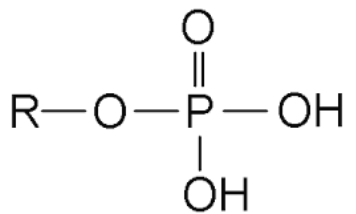
R–PO₄³⁻
phosphate