Chemistry - Chapter 16 - Amines and Amides - Nitrogen Chemistry
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
OBJ: Course Objectives Chapter 16

INFO: Amines and Amides - Nitrogen Chemistry

INFO: Amines and Amides - Continued
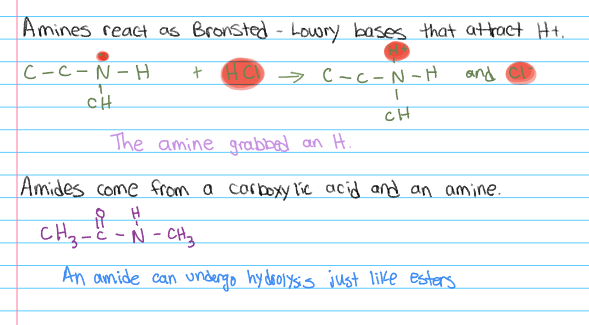
0: general formula for a primary amine
RNH2, where R is an alkyl group
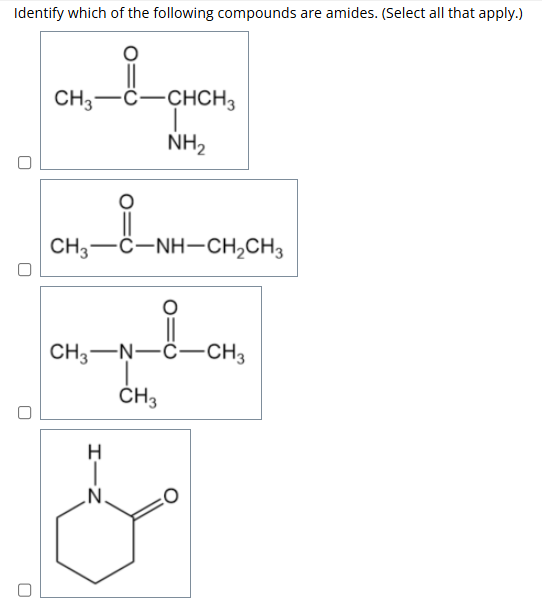
0: Identify which of the following compounds are amides.
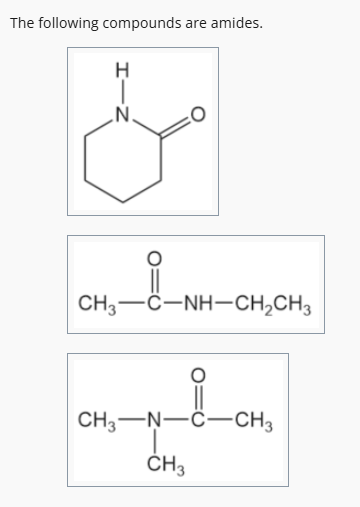
A compound is an amide if it contains a carbonyl group (C=O) directly attached to a nitrogen atom (N).
structure:
R–CONH₂
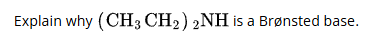
0:
(CH3CH2)2NH is a Bronsted base because it can accept a proton from a proton donor. The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is available to form a bond to hydrogen ions.
A bronsted base is a substance that can accept protons (H+) from acids, thereby increasing the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution.
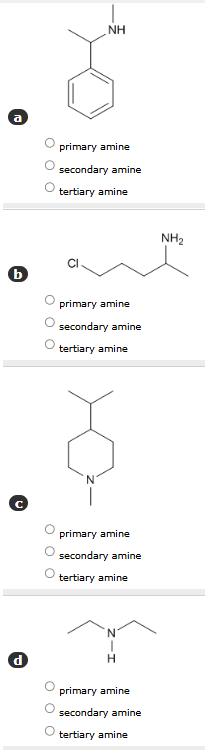
1: Classify each of the following as a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine:
a) There is 1 bonded hydrogen atom, secondary amine
b) There are 2 bonded hydrogen atoms, primary amine
c) There is 0 bonded hydrogen atoms, tertiary amine
d) There is 1 bonded hydrogen atom, secondary amine
Remember:
Primary amine: 2 bonded H
Secondary: 1 bonded H
Tertiary: 0 bonded H
1: Which of the following represents the general formula for a primary amine?
R2NH
R3N
RNH2
The general formula for a primary amine is RNH2, where R is a hydrocarbon chain or alkyl group.
Amines are designated as primary, secondary, or tertiary by the number of carbon groups (R groups) attached directly to the nitrogen atom.
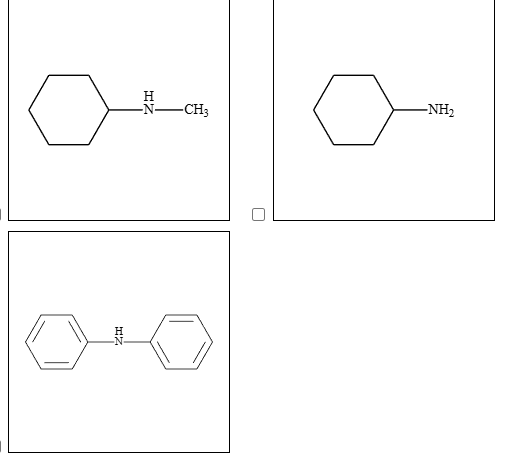
1: Identify which of the following compounds has an amine functional group in it
by checking for the presence of an amino group (-NH2) attached to a carbon atom in the compound.
All of the given compounds contain an amine functional group
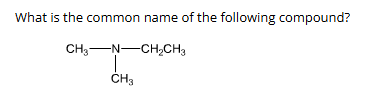
2:
ethyldimethylamine
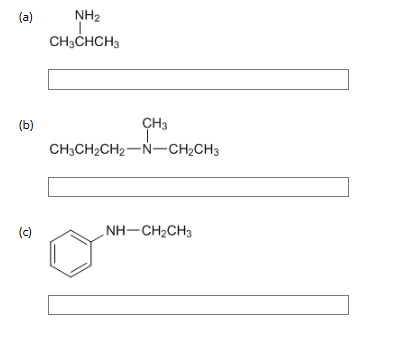
2: Give the common name for each of the following amines by adding the ending -amine to the alkyl group name.
a) isopropylamine
(it is called isopropyl and not propyl because the molecule features a 3-carbon chan attached to the amine group rather than a straight-chain propyl group)
b) N-ethyl-N-methylpropylamine
(parent structure is propyl, the N prefix denotes that they are attached to the Nitrogen)
c) N-ethyl-N-phenylamine
(parent structure is phenyl attached to the nitrogen(C6H5 benzene ring), with an ethyl group attached to the Nitrogen)
3: What are the most likely products of a reaction between CH3CH2NH2 and H2O?
Amines act as weak bases in water. Thus, a hydrogen atom will be donated from the water to the amine nitrogen atom.
The products are hydroxide ion and ethylammonium ion.
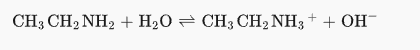
3: Explain why all classes of low molecular weight amines are water soluble.
All low molecular weight amines are water soluble because all amines can form hydrogen bonds with water. Low molecular weight amines have small aliphatic portions, thus the hydrogen bonds to water are strong enough to allow the amines to dissolve.
water solube means that it is able to be dissolved in water.
3: Why are the boiling points of amines lower than those of corresponding alcohols?
The boiling points of amines are lower than those of the corresponding alcohols because the hydrogen bonds formed between nitrogen and hydrogen are weaker than the hydrogen bonds formed between oxygen and hydrogen.
Boiling points:
alcohol > amine > alkane
Small amines are water-soluble
3: Why are the boiling points of tertiary amines lower than those of corresponding primary and secondary amines?
The boiling points of tertiary amines are lower than the boiling points of primary and secondary amines because tertiary amines cannot form a hydrogen bond to each other, while primary and secondary amines can. The weaker intermolecular forces in tertiary amines allow them to boil at a lower temperature.
Tertiary has no hydrogen bonded to the nitrogen.
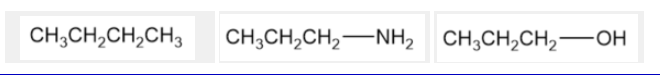
3: Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing boiling point.
In order of INCREASING boiling point:
Highest boiling point: CH3CH2CH2 - OH
CH3CH2CH2 - NH2
CH3CH2CH2CH3
Since the molecular weights of these three compounds are comparable, they experience comparable dispersion forces. The order of their boiling points is determined by the nature of the other intermolecular forces they experience. Alkanes have the lowest boiling point because they are unable to form hydrogen bonds with other alkanes. Primary amines have an intermediate boiling point because they are capable of forming hydrogen bonds between their molecules but these hydrogen bonds are not as strong as the hydrogen bonds between the molecules of primary alcohols, which have the highest boiling point.
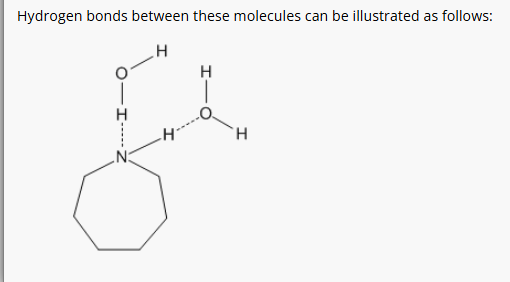
3: Draw diagrams to illustrate hydrogen bonding between the following molecules:
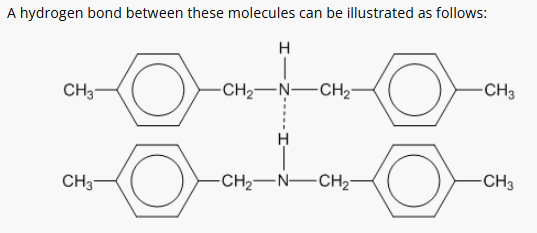
3: Draw diagrams to illustrate hydrogen bonding between the following molecules:
5: Define neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a substance that acts as a chemical bridge in nerve impulse transmission between nerve cells (neurons).
3: Draw diagrams to illustrate hydrogen bonding between the following molecules
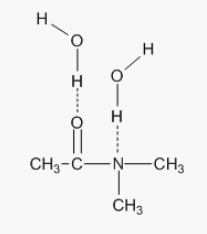
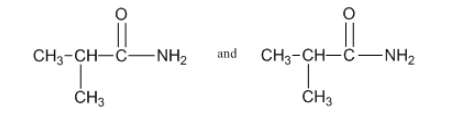
3: Draw diagrams to illustrate hydrogen bonding between the following molecules
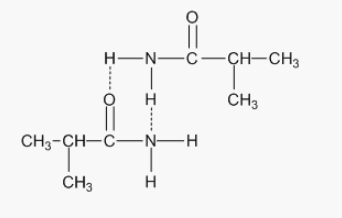
4: Important key Reactions of Amines?
Acid–Base Reaction
Amines are weak bases.
Amines + acid → ammonium salt
CH3NH2 + HCl → CH3NH3+ Cl–
5: What neurotransmiters are derived from Amines and what do they do?
Neurotransmitter | Derived From | Function |
|---|---|---|
Dopamine | Tyrosine | movement, pleasure |
Serotonin | Tryptophan | mood, sleep |
Norepinephrine | Tyrosine | alertness |
Epinephrine | Tyrosine | fight-or-flight |
Histamine | Histidine | immune response |
6: Amines with specific uses?
Benadryl → antihistamine
Amphetamine → stimulant
Nicotine → stimulant and addictive compound
Morphine → pain reliever
Anesthetics like Novocaine contain amine groups
7: How is amide formed?
Amide: Formed from Carboxylic acid + amine (or ammonia)
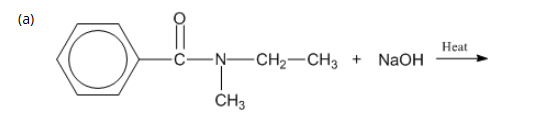
7: Complete the following reactions.
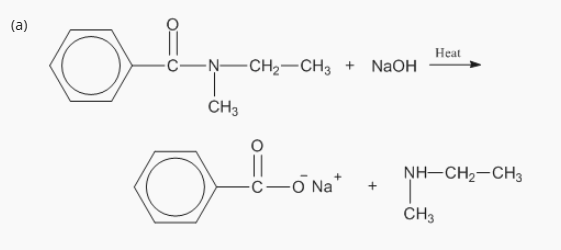
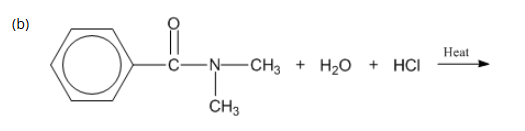
7: Complete the following reactions.
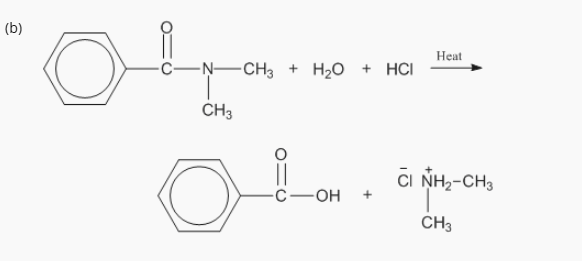
7: Products of acidic and basic hydrolysis of amides?
Remember: Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where water is used to break down a compound into two or more smaller parts
A. Acidic Hydrolysis (H+)
Amide + water → carboxylic acid + ammonium salt
RCONH2 + H2O + HCl → RCOOH + NH4+ Cl–
B. Basic Hydrolysis (OH⁻)
Amide + base → carboxylate salt + amine
RCONH2 + NaOH → RCOO− Na+ + NH3
Tip:
(Acidic Amide *ACID*)
Amide + H⁺ → carboxylic acid + ammonium salt
Amide + OH⁻ → carboxylate salt + amine
Can amines form stronger hydrogen bonding than carboxylic acids?
Amines form weaker hydrogen bonds than alcohols
Amines can hydrogen bond because nitrogen has a lone pair and an N–H bond.
BUT nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen, so the hydrogen bonds are weaker.
H-BONDING STRENGTH (strongest → weakest):
Carboxylic acids > alcohols > amines
Nitrogen < oxygen in electronegativity
a) Which statement is TRUE about amines?
A. They contain nitrogen bonded to a carbonyl group
B. They contain nitrogen bonded to alkyl or aryl groups
C. They have no hydrogen bonding capability
D. They are always insoluble in water
Correct answer: B. They contain nitrogen bonded to alkyl or aryl groups
Amines = N bonded to carbon chains, NOT carbonyls.
(A is for amides)
Which is a product of basic hydrolysis of an amide?
A. Carboxylate salt + ammonia
B. Carboxylic acid + ammonium salt
C. Alcohol + ammonium salt
D. Ester + alcohol
A. Carboxylate salt + ammonia
Remember: Products
Acidic hydrolysis → carboxylic acid + ammonium ion
Basic hydrolysis → carboxylate salt + ammonia
Which reaction produces an amide?
A. Carboxylic acid + amine → water + amide
B. Amine + water
C. Alcohol + carboxylic acid
D. Amide + base
A. Carboxylic acid + amine → water + amide
Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
A. Propanamide
B. Methylamine
C. Ethanol
D. Propanoic acid
Correct answer: B. Methylamine
Methylamine is the simplest amine and has lower intermolecular forces compared to the other compounds listed, resulting in a lower boiling point.
Which amine would be least water-soluble?
A. Methylamine
B. Ethylamine
C. Dipropylamine
D. Triethylamine
D. Triethylamine
NO N–H bond b/c tertiary→ cannot hydrogen bond with water
Most soluble → least soluble:
Primary amines (best H-bond donor)
Secondary amines (one N–H)
Tertiary amines (NO N–H → worst H-bonding)
Hydrogen bonding ability dominates solubility for small amines.
Which is formed by basic hydrolysis of an amide?
Type of hydrolysis | Products |
|---|---|
Acidic hydrolysis | carboxylic acid + ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) |
Basic hydrolysis | carboxylate salt + ammonia (NH₃) |
acidic → COOH + NH₄⁺
basic → COO⁻ + NH₃
Basic: CH₃COO⁻ + NH₃
Hydrolysis Reaction Outcomes
Amides + acid → COOH + NH₄⁺
Amides + base → COO⁻ + NH₃
Which compound will have the highest boiling point?
A. Propanamine
B. Propanamide
C. Triethylamine
D. Propanol
B. Propanamide
Boiling point ordering (strongest → weakest):
Amides (VERY strong hydrogen bonding; N–H and C=O both participate)
Carboxylic acids (dimers)
Alcohols
Amines
Hydrocarbons
So given the options:
Propanamide: strongest H-bonds
Propanol: strong, but not as strong as amides
Boiling point exam trick, always remember:
Amides > acids > alcohols > amines
Amides have two hydrogen bonding sites and the carbonyl oxygen is very electronegative and strongly polar.
Which is the correct common name for CH₃CH₂CH₂–NH₂?
A. Propanamine
B. Propylamine
C. Aminopropane
D. Dipropylamine
Propylamine