AP Biology - Unit 4
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/53
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
4 types of karyotypes
* Metacentric
* Submetacentric
* Acrocentric
* Telocentric
* Submetacentric
* Acrocentric
* Telocentric
2
New cards
How to differentiate karyotypes
According to the length of sister chromatids
3
New cards
How many somatic cells do humans have?
22 pairs
4
New cards
How many sex cells do humans have?
1 pair
5
New cards
How many chromatids in total do humans have?
46
6
New cards
Cell cycle
Life of a cell from its formation until it divides into 2 cells
7
New cards
Function of cell cycle
Reproduction, growth & tissue repair
8
New cards
Genome
All of a cell’s genetic info (DNA)
9
New cards
Prokaryote
Single, circular chromosome
10
New cards
Eukaryote
More than one linear chromosome
11
New cards
What kind of cells are created through mitosis?
Somatic cells
12
New cards
What kind of cells are created through meiosis?
Gametes
13
New cards
What are three steps of interphase?
G1, S phase, G2
14
New cards
G1 Phase
Cell grows & carries out normal functions
15
New cards
S Phase
Duplicates chromosomes (DNA replication)
16
New cards
G2 Phase
Prepares for cell division
17
New cards
4 steps of mitosis
Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
18
New cards
Prophase
Spindle fibers become visible
19
New cards
Metaphase
Alignment at the equator
20
New cards
Anaphase
Separation of sister chromatids
21
New cards
Telophase
Form two identical daughter cells
22
New cards
Cytokinesis
* Cytoplasm divides
* Animal cells: Cleavage furrow
* Plant cells: Cell plate forms
* Animal cells: Cleavage furrow
* Plant cells: Cell plate forms
23
New cards
Prometaphase
Chromosomes are lined up and each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber.
24
New cards
How do bacterial cells divide?
Binary fission
25
New cards
Checkpoint
Control point where stop/go signals regulate the cell cycle
26
New cards
What’s the most important checkpoint?
G1 checkpoint
27
New cards
How is G1 checkpoint controlled?
Cell size, growth factors, env’t
28
New cards
What happens during G1 checkpoint “Go?”
Completes whole cell cycle
29
New cards
What happens during G1 checkpoint “stop?”
* Cell enters nondividing state (G0 Phase)
* Nerve, muscle cells stay at G0
* Liver cels called back from G0
* Nerve, muscle cells stay at G0
* Liver cels called back from G0
30
New cards
How is G2 checkpoint controlled?
DNA replication completion, DNA mutations, cell size
31
New cards
M-spindle (Metaphase) checkpoint
Check spindle fiber (microtubule) attachment to chromosomes at kinetochores (anchor sites)
32
New cards
Kinases (Cdk)
Protein enzyme controls cell cycle; active when connected to cyclin
33
New cards
Cyclins
Proteins which attach to kinases to activate them; levels fluctuate in the cell cycle
34
New cards
MPF is short for?
Maturation-promoting factor
35
New cards
MPF function
Specific cyclin-Cdk complex which allows cells to pass G2 and go to M(mitosis) phase
36
New cards
Checkpoint function
Cell-cell communication to check for abnomalities
* Without this, high possibility of cancer
* Without this, high possibility of cancer
37
New cards
Growth factor
Proteins released by other cells to stimulate cell division
38
New cards
Density-Dependent Inhibition
Crowded cells normally stop dividing; cell-surface protein binds to adjoining cell to inhibit growth
39
New cards
Anchorage Dependence
Cells must be attached to another cell or ECM (extracellular matrix) to divide
40
New cards
Cancer
Disorder in which cells lose the ability to control growth by not responding to regulation
41
New cards
Transformation
Process that converts a normal cell to a cancer cell
42
New cards
Tumors
Mass of abnormal cells
43
New cards
Benign tumor
Lump of cells remain at original site
44
New cards
Malignant tumor
Invasive - impairs functions of 1+ organs (is cancer)
45
New cards
Metastasis
Cells separate from tumor & travel to other parts of body
46
New cards
Cancer treatment
* Surgery
* Radiation
* Chemotherapy
* Personalized medicine (ex. Breast cancer uses Herceptin to block HER2 protein)
* Radiation
* Chemotherapy
* Personalized medicine (ex. Breast cancer uses Herceptin to block HER2 protein)
47
New cards
Cancer prevention
* Don’t smoke, legal or illegal (includes hookahs, chew, 2nd-hand smoke)
* Use sun protection
* Exercise & keep weight at ideal level
* Eat 5-7 servings of fruit & veggies a day
* Use screening/preventative measures-breast/testicle/mole checks
* Practice abstinence or use condoms
* Vaccines (eg.HPV)
* Use sun protection
* Exercise & keep weight at ideal level
* Eat 5-7 servings of fruit & veggies a day
* Use screening/preventative measures-breast/testicle/mole checks
* Practice abstinence or use condoms
* Vaccines (eg.HPV)
48
New cards
Characteristics of cancer cells
* Some have abnormal numbers of chromosomes
* Metabolism disabled
* Lose attachment to ECM → spread to other tissues
* Signaling molecules cause blood vessels to grow toward tumor
* Metabolism disabled
* Lose attachment to ECM → spread to other tissues
* Signaling molecules cause blood vessels to grow toward tumor
49
New cards
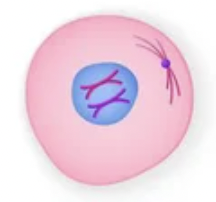
What phase is this?
Interphase
50
New cards
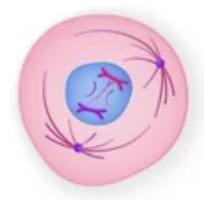
What phase is this?
Prophase
51
New cards
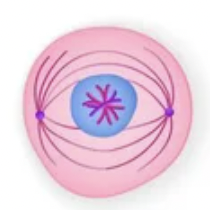
What phase is this?
Metaphase
52
New cards
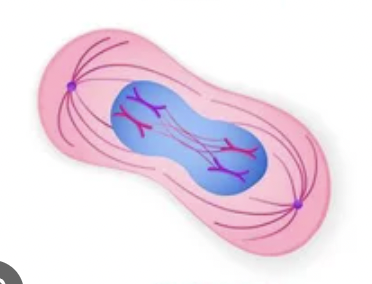
What phase is this?
Anaphase
53
New cards
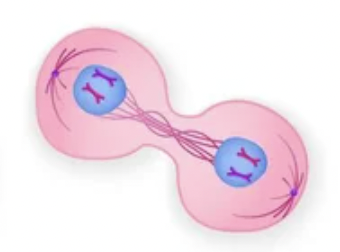
What phase is this?
Telophase
54
New cards
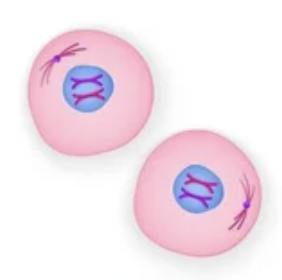
What phase is this?
Cytokinesis