OB Lecture Exam 1
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ch. 4 (assessment and health promotion), ch. 12 (conception and fetal development), ch. 10 (problems of the breast), ch. 9 (infertility), ch. 8 (contraception and abortion), ch. 7 (sexually transmitted and other infections), ch. 6 (reproductive system concerns), ch. 11 (structural disorders and neoplasms of the reproductive system)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
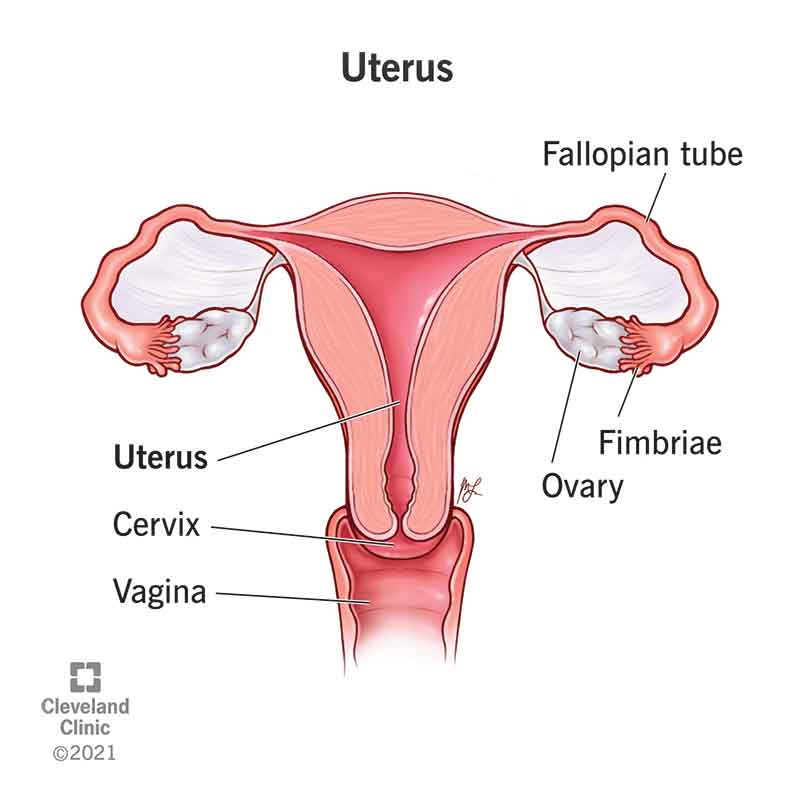
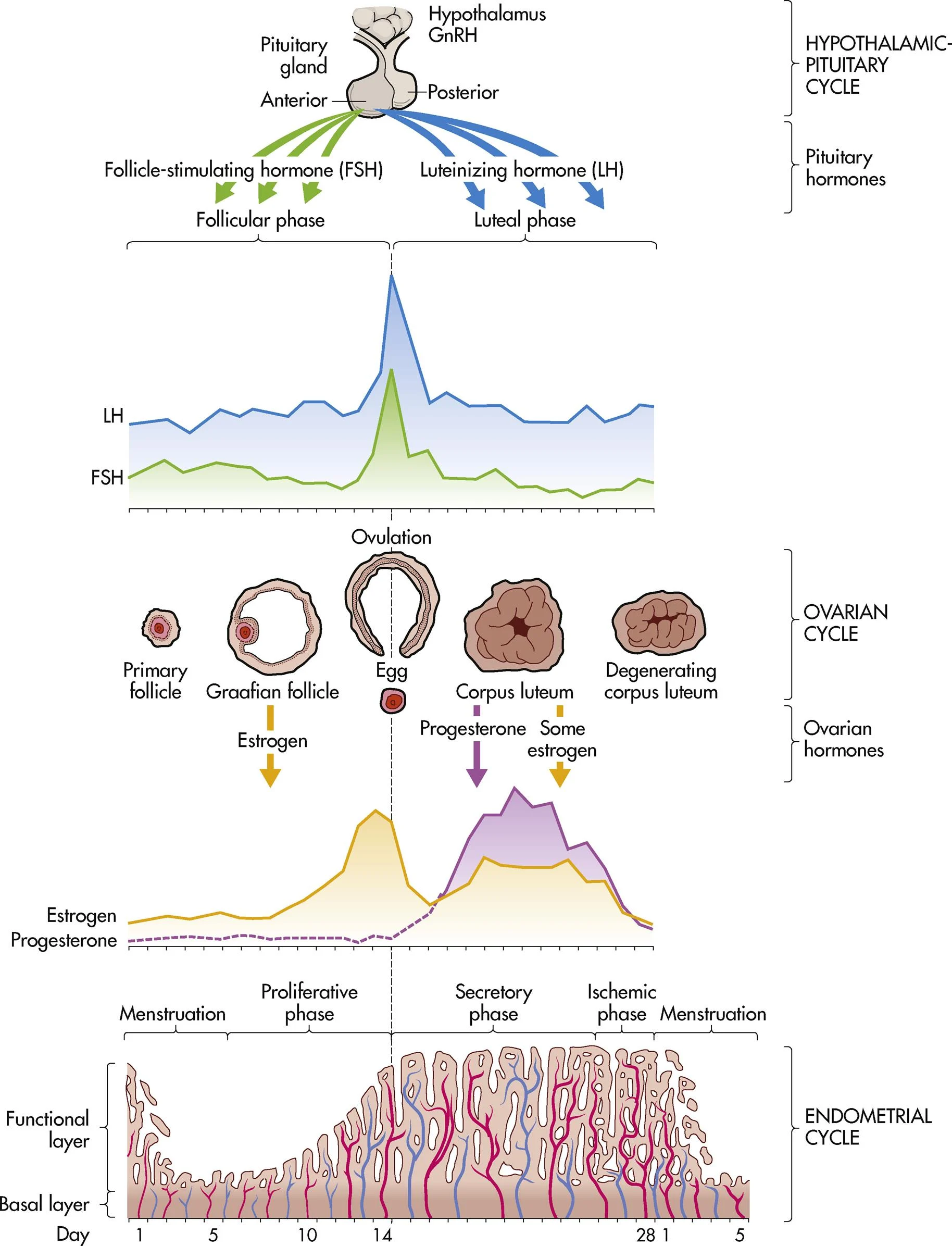
ch. 4 - what are the functions of the uterus?
contraction during labor, menstrual bleeding, & location of sperm cells
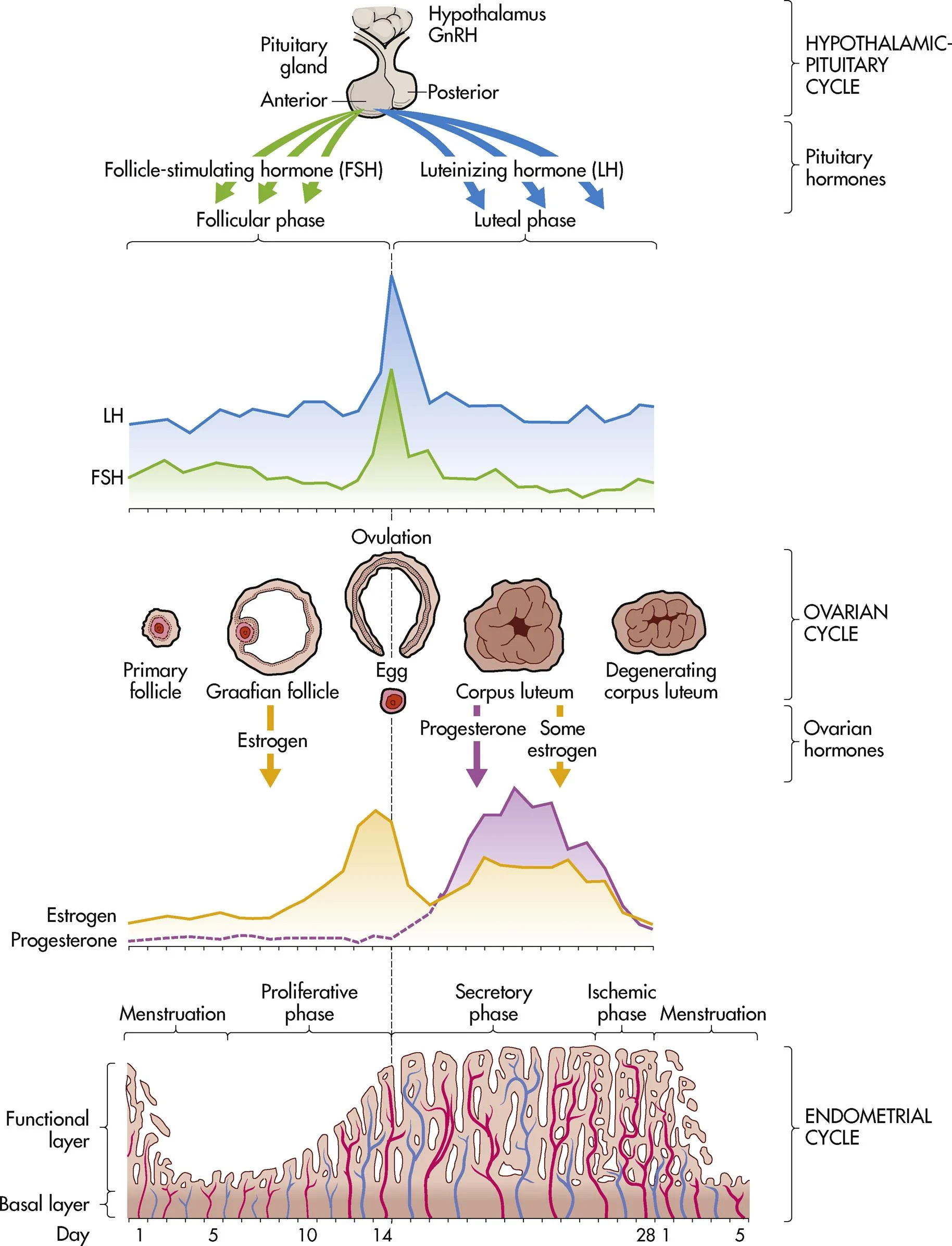
ch. 4 - at the end of the menstrual cycle, what low levels of hormones stimulate the hypothalamus to secrete GnRH?
estrogen and progesterone
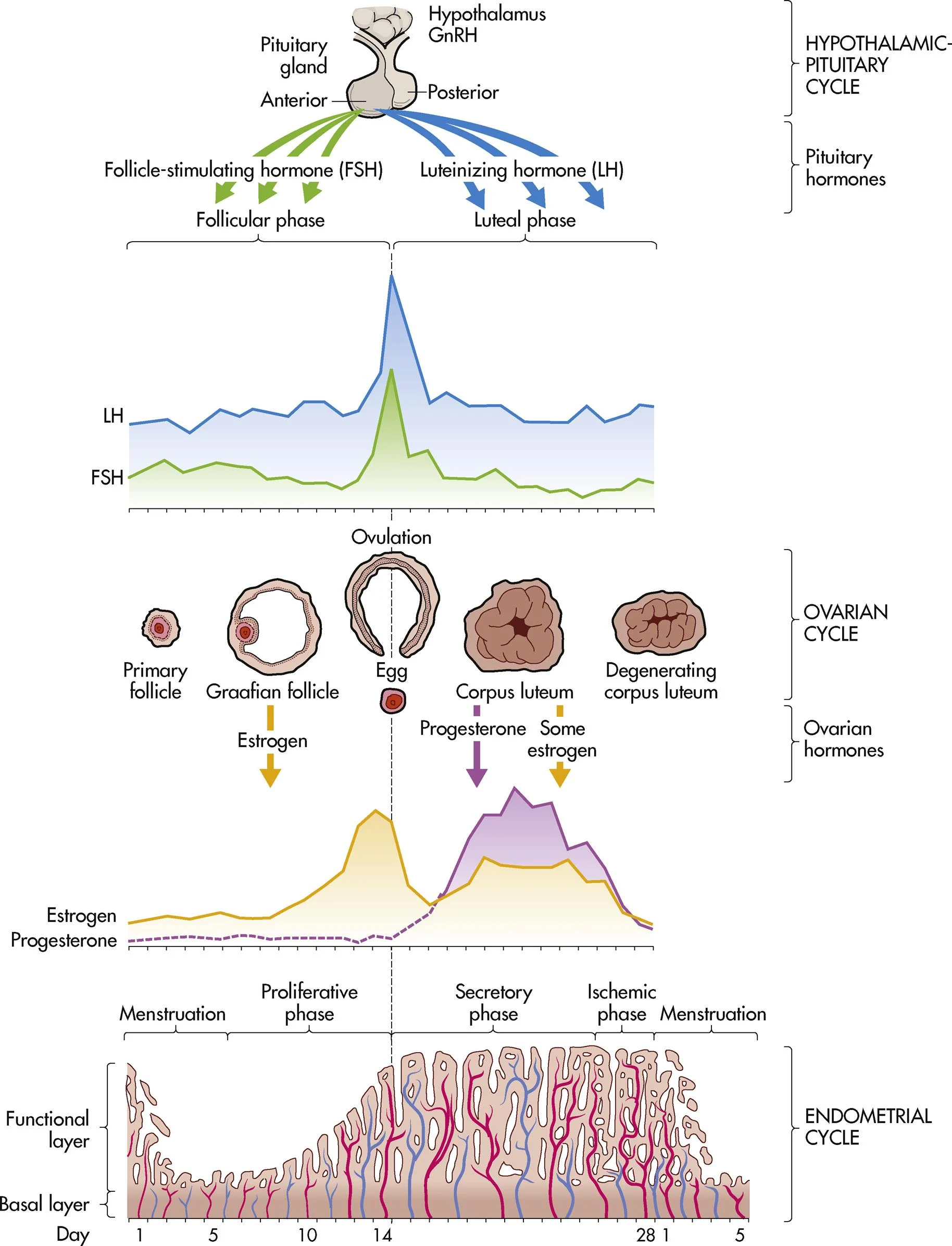
ch. 4 - a marked surge in what hormone precedes the release of the ovum from the Graafian follicle (ovulation in ovarian cycle)?
LH
ch. 4 - what happens if fertilization and implantation does not occur (menstrual cycle)?
progesterone and estrogen levels drop, menstruation, & hypothalamus secretes GnRH
ch. 4 - menstrual phase (endometrial/uterine cycle)
shedding of the endometrium (1-5 days)
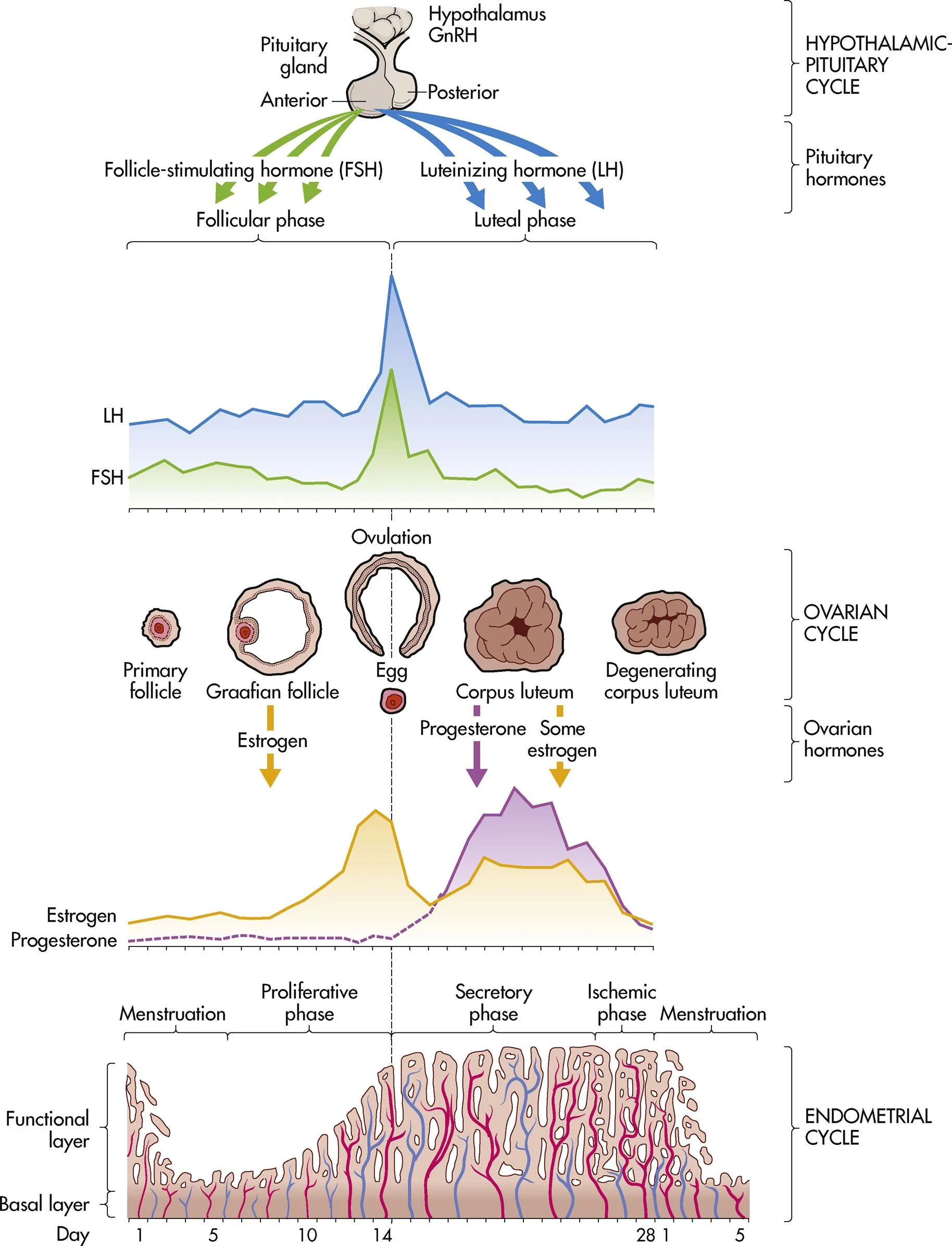
ch. 4 - proliferative phase (endometrial/uterine cycle)
building of the endometrium under the influence estrogen; “the builder” (days 6-14)
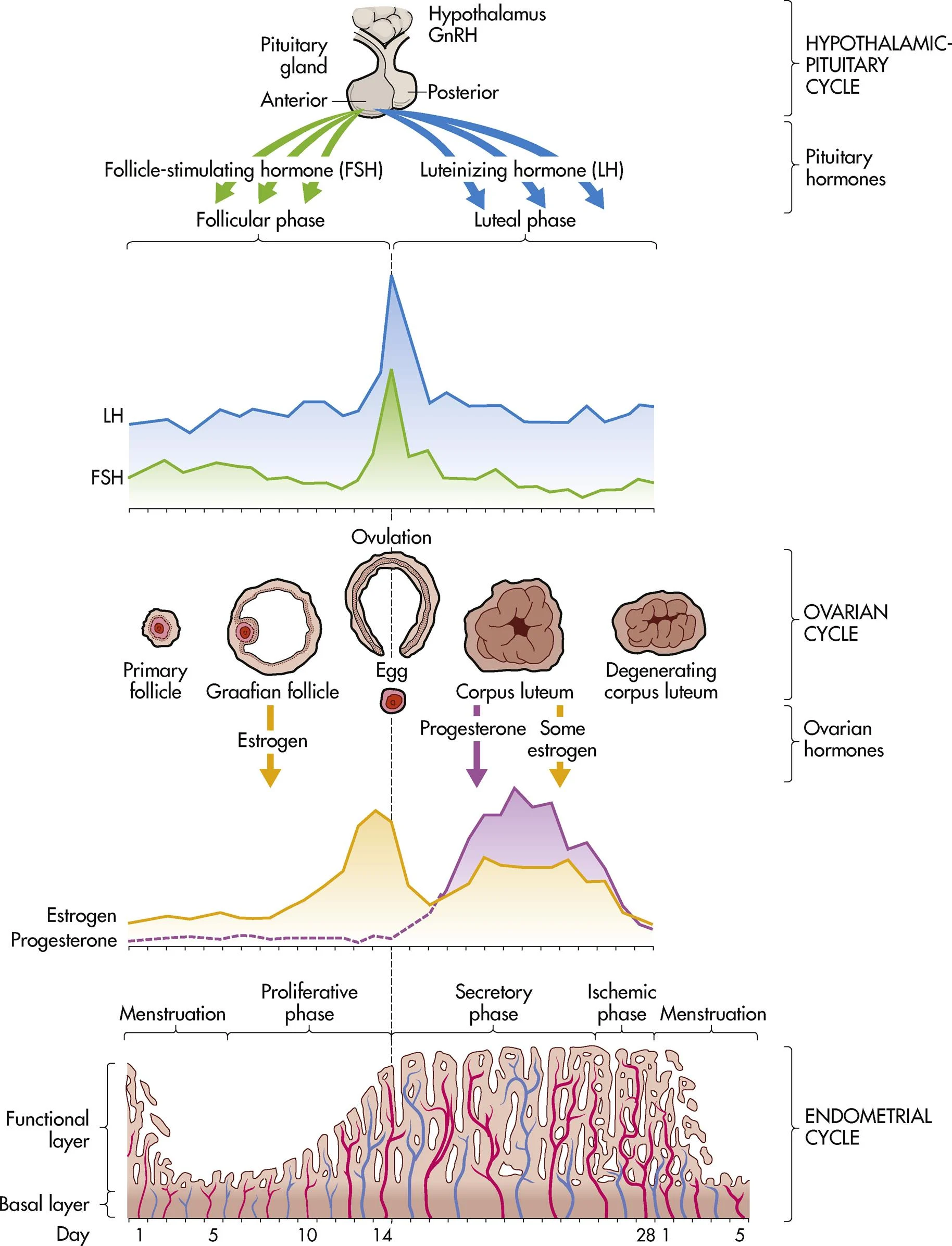
ch. 4 - secretory phase (endometrial/uterine cycle)
marked swelling and growth due to progesterone; “the maintainer” (days 15-28)
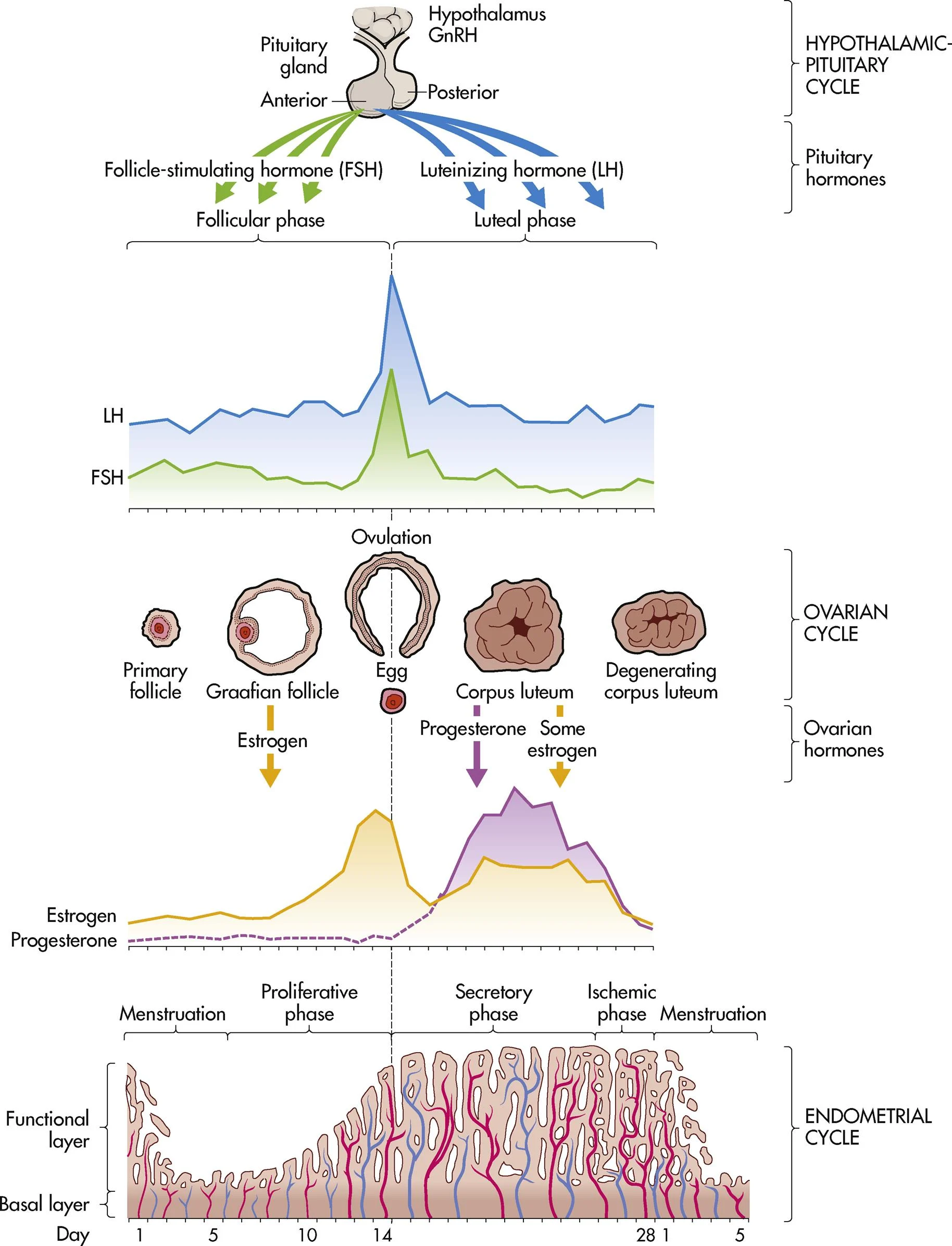
ch. 4 - ischemic phase (endometrial/uterine cycle)
blood supply to endometrium is blocked and necrosis occurs (phase right before menses)
ch. 4 - what are two possible things that occur at the end of the menstrual cycle?
menses or pregnancy
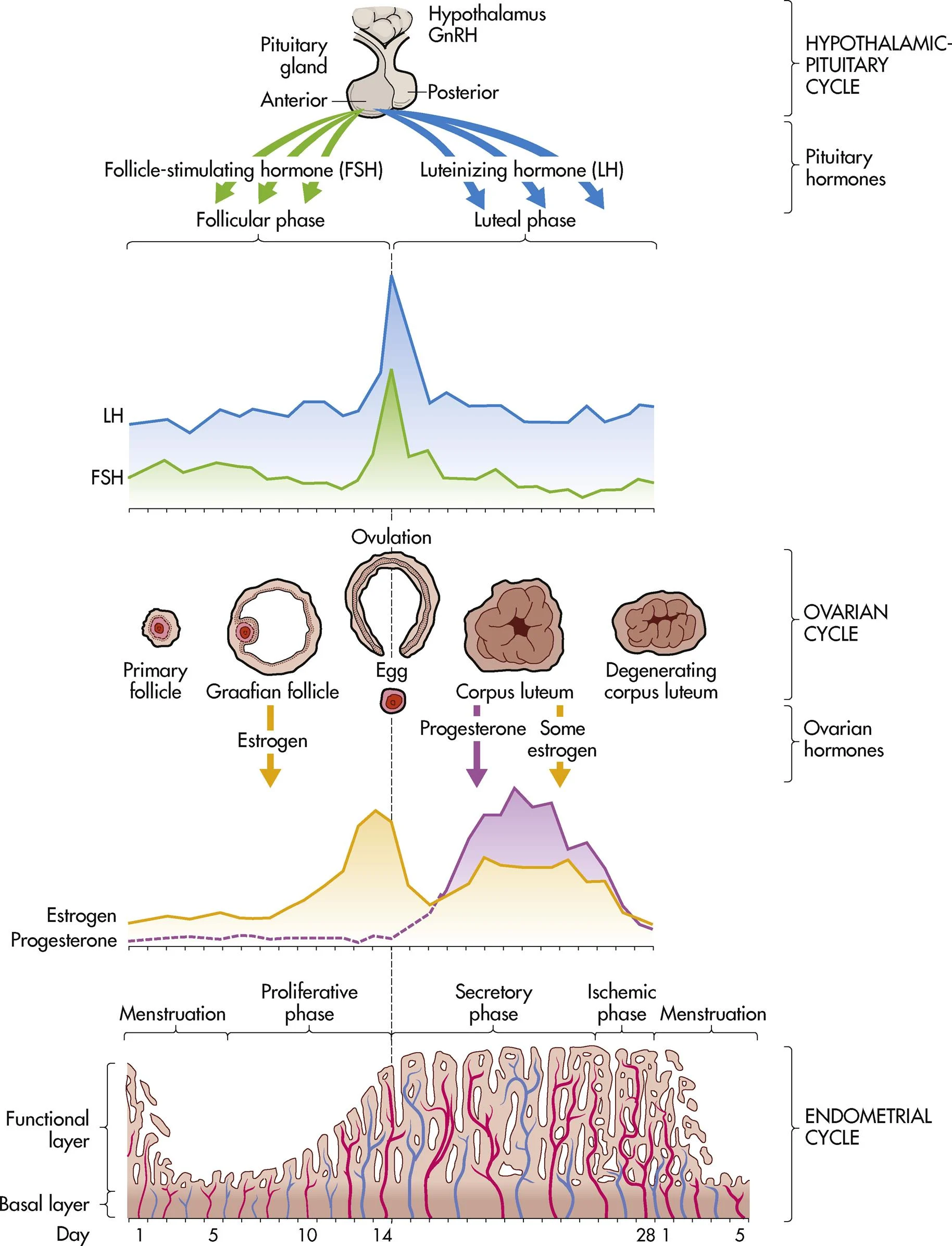
ch. 4 - follicular phase (ovarian cycle)
days 1-14 (can vary in length)
ch. 4 - ovulation (ovarian cycle)
occurs on day 14 in length of cycle, midcycle bleeding, mittelschmerz, & thin cervical mucus
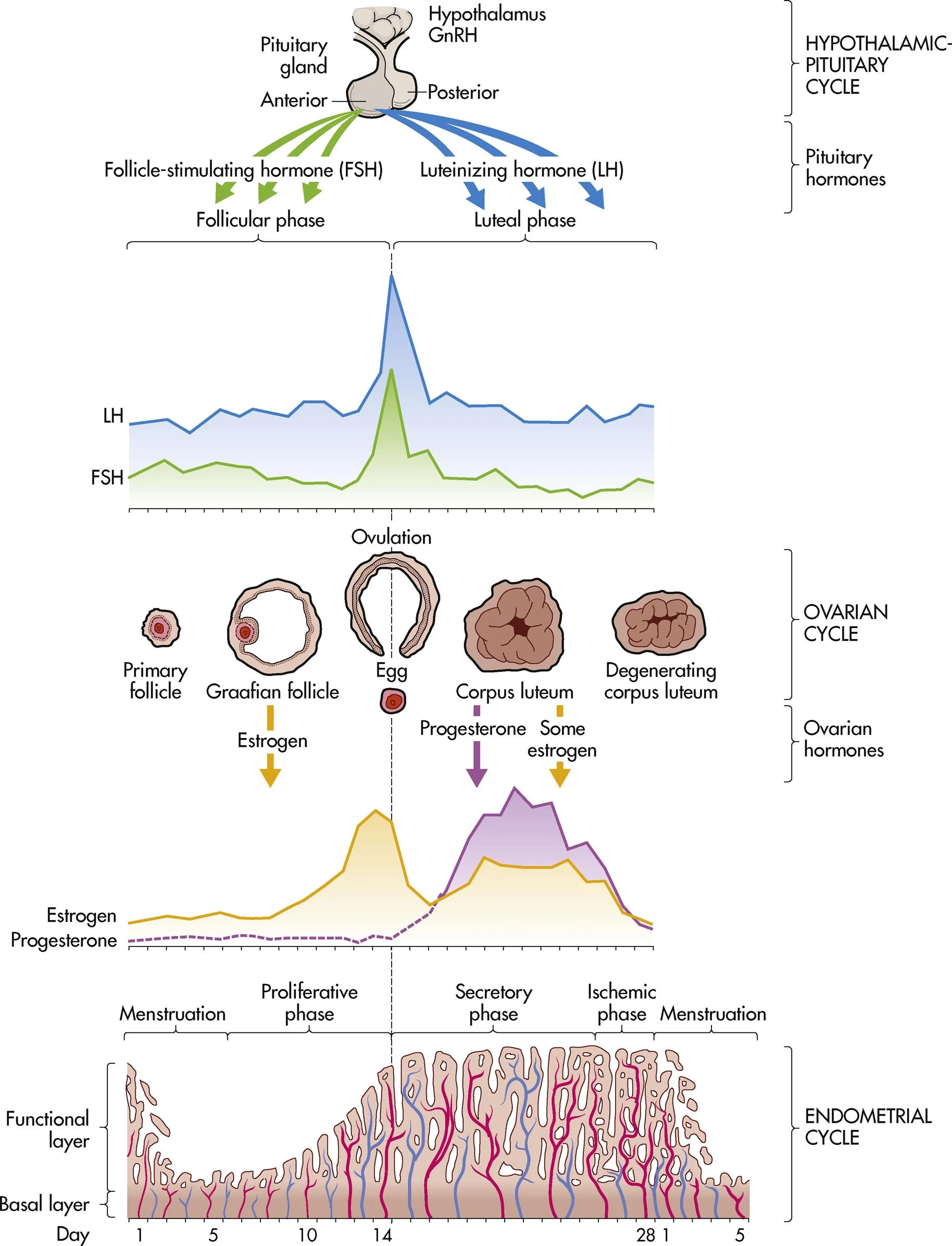
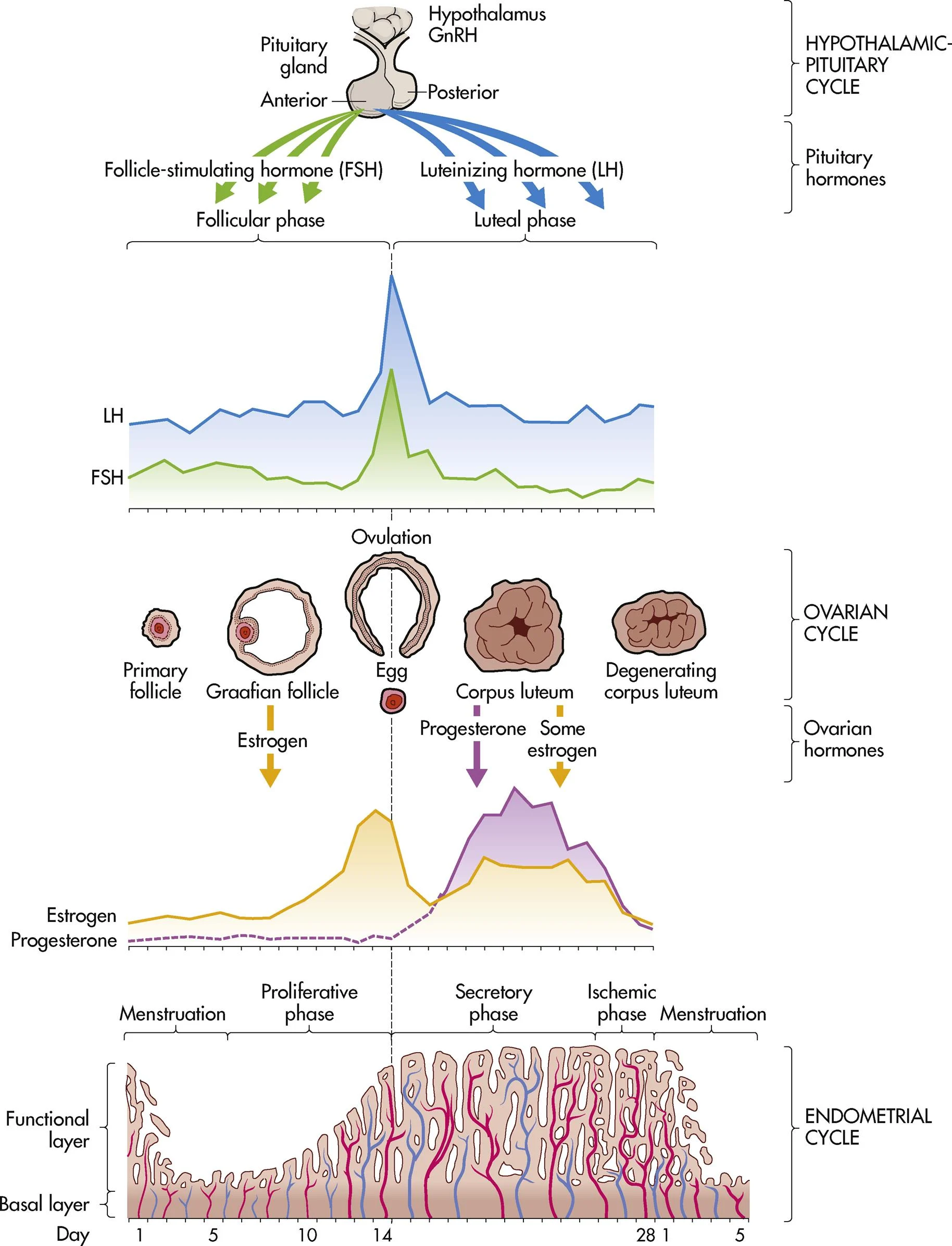
ch. 4 - luteal phase (ovarian cycle)
days 15-28 ends with onset of menses
ch. 12 - conception
one egg and one sperm join, starting pregnancy; creates a cell with 46 chromosomes
ch. 12 - mitosis
how body cells grow, repair, and replace themselves; creates two identical cells
ch. 12 - meiosis
how sex cells are made; it cuts the number of chromosomes in half, from 46 to 23
ch. 12 - oogenesis
the process of making eggs; it starts before birth
ch. 12 - spermatogenesis
the process in males where sperm cells grow and mature into sperm
ch. 12 - scrotum
each part (two parts) holds a testis, an epididymis, and part of the spermatic cord
ch. 12 - testes
the main male reproductive organs; they make testosterone and produce sperm
ch. 12 - epididymis
on the back of each testis; carries sperm from the testes to the vas deferens
ch. 12 - ductus (vans) deferens
a tube that continues from the epididymis and carries sperm to the ejaculatory ducts
ch. 12 - ejaculatory ducts
carry sperm into the urethra and add fluids from the prostate to help sperm work properly
ch. 12 - seminal vesicle
responsible for producing most of the components that make up semen
ch. 12 - prostate
it makes fluid that mixes with sperm and other fluids to form semen
ch. 12 - urethra
runs from the bladder to the penis; it carries semen and sperm out of the body during sex
ch. 12 - how long is ova fertile?
12-24 hours
ch. 12 - how long does sperm survive for?
24-72 hours
ch. 12 - capacitation
the process that makes sperm able to fertilize an egg after entering the female body
ch. 12 - acrosome reaction
when the tip of the sperm releases enzymes to break through the outer layer of the egg
ch. 12 - the process of fertilization
blastomere is divided: embryoblast (becomes baby) and trophoblast (becomes placenta)
ch. 12 - pre-embryonic
days 1-14
ch. 12 - embryo
the stage from the 2nd or 3rd week after fertilization up to the 8th week
ch. 12 - fetus
9th week until 40th week
ch. 12 - what is the order of embryonic development?
cellular multiplication, cellular differentiation, and development of organ systems
ch. 12 - ectoderm (top layer)
makes skin, glands, hair, and nails
ch. 12 - mesoderm (middle layer)
forms bones, teeth, and muscles
ch. 12 - endoderm (bottom layer)
becomes the lining of the lungs and digestive system
ch. 12 - what are the two membranes that surround the fetus?
chorion and amnion
ch. 12 - chorion
outer membrane that comes from trophoblast; the first layer reached during amniotomy
ch. 12 - amnion
the inner membrane that forms from the blastocyst and is closest to the baby
ch. 12 - what are the functions of the amniotic fluid?
maintain temperature, protects fetus, and medium for movement
ch. 12 - what are the functions of the placenta?
endocrine gland function, metabolic functions, and adequate circulation
ch. 12 - fetal maturation
the baby is called a fetus from 9 weeks to the end of pregnancy
ch. 12 - viability
the point when a baby can survive outside the womb
ch. 12 - what is viability age in Texas?
20 weeks or 350 grams
ch. 12 - placental blood circulation is blood that flows between the mother and baby. the umbilical cord contains how many vessels and what kinds?
3 vessels; AVA = artery, vein, artery
ch. 12 - what three shunts does fetal circulation use to move blood?
ductus venosus, foramen ovale, and ductus arteriosus
ch. 12 - ductus venosus
sends blood from the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava
ch. 12 - foramen ovale
lets blood flow from the right atrium to the left atrium
ch. 12 - ductus arteriosus
connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta, skipping the lungs
ch. 12 - dizygotic (fraternal) twins
2 eggs + 2 sperm, 2 placentas, and 2 amnions and 2 chorions
ch. 12 - monozygotic (identical) twins
1 egg + 1 sperm, share 1 placenta, and may have 1 or 2 amnions/chorions
ch. 12 - what infectious agents can cross the placenta?
rubella, cytomegalovirus, T. gondii (toxoplasmosis), and T. pallidum (syphilis)
ch. 10 - the two goals in the pathologic evaluation of a breast biopsy are to distinguish benign from malignant __________ tumors of the breast and to assess the risk of subsequent breast cancer associated with the lesion.
in situ or invasive
ch. 10 - __________ are dilated ducts with nipple inversion occurring during perimenopausal period and is an acquired condition.
mammary duct ectasia
ch. 10 - one form of nipple discharge not related to malignancy is __________, a bilateral spontaneous, milky, sticky discharge that occurs in women who are not pregnant or breastfeeding.
galactorrhea
ch. 10 - benign lumpiness in both breasts; related to menstrual cycle due to hormone changes; managed with dietary changes and vitamin supplementation
fibrocystic breast disease
ch. 10 - a benign, solid mass of the breast most common in women ages 20-30s; do not increase in size in response to the menstrual cycle; managed with surgery (if symptoms are severe)
fibroadenoma
ch. 10 - what are three risk factors included in the Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool?
age of woman, number of first-degree relatives affected, and age of woman at menarche
ch. 10 - current evidence and clinical guidelines suggest that women at increased risk for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer or carriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations can be offered __________ with either tamoxifen or raloxifene.
chemoprevention
ch. 10 - the rate of breast cancer growth depends on the effects of estrogen and progesterone and other prognostic factors such as __________ status and other variables. for purpose of prognosis, three subtypes are identified: hormone receptor positive, __________ positive, and triple negative.
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)
ch. 10 - what are three clinical manifestations of breast cancer?
painless lump, skin dimpling changes to the nipple, and redness with edema
ch. 10 - the clinical stage helps providers decide how to proceed with treatment of the breast problem. this stage is determined by a combination of the TNM system, the grading system, and a biomarker determination. it sorts stage by size of __________, lymph __________, and whether __________ is involved.
tumor; node; metastasis
ch. 10 - where is the most common site for breast cancer lumps?
the upper outer quadrant of the breast
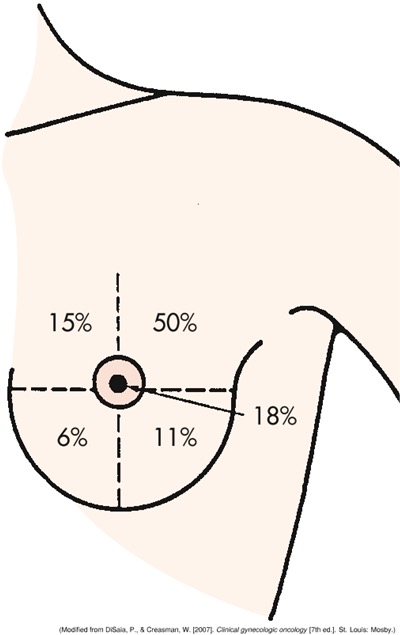
ch. 10 - includes lumpectomy and segmental or partial mastectomy, involving wide excision of the tumor and surrounding tissue
breast-conserving surgery (BCS)
ch. 10 - total (simple), modified radical, skin-sparing, and nipple-sparing mastectomies, including preventive/prophylactic procedures
mastectomy options
ch. 10 - aimed at restoring symmetry and preserving body image after surgery
breast reconstruction
ch. 10 - destroys remaining tumor cells after surgical manipulation; administered shortly after tumor removal to target micrometastatic disease
radiation therapy; adjuvant systemic therapy
ch. 10 - based on the presence and type of hormone receptors in the tumor; aims to icnrease and improve disease-free survival after initial treatment
hormonal therapy; chemotherapy
ch. 9 - infertility
not being able to get pregnant after one year of unprotected sex
ch. 9 - what are three hormonal and ovulatory female infertility factors?
anovulation, early menopause, and hyperprolactinemia
ch. 9 - what is one tubal and peritoneal female infertility factor?
loss of mobility and patency
ch. 9 - __________ infections and the pH of the __________ and cervix can increase the risk for female infertility.
uterine; vagina
ch. 9 - what are three other causes of female infertility?
obesity, amenorrhea, and cancer treatment
ch. 9 - what are three male infertility factors?
low testosterone levels, undescended testicles, and previous vasectomy
ch. 9 - what are other male infertility factors?
STIs, radiation, and alcohol
ch. 9 - what three factors are assessed when determining ovulation for female infertility?
ovulation kit, progesterone levels one week prior to menses, and basal body temperature
ch. 9 - besides determination of ovulation, how do you assess female infertility?
hormone analysis, imaging (hysterosalpingogram/HSG), and procedures
ch. 9 - a __________ is a radiographic film that allows visualization of the uterine cavity and uterine tubes after instillation of radiopaque contrast material via the cervix.
HSG
ch. 9 - semen analysis, ultrasonography of scrotum, genetic testing, hormonal analysis, and testicular biopsy if indicated
ways to assess male infertility
ch. 9 - psychosocial, nonmedical, and medical therapies are used for couples managing infertility. name an example of each.
provide emotional support, lifestyle changes, and use of fertility drugs
ch. 9 - intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT), and zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT)
examples of assisted reproductive technology (ART)
ch. 9 - woman must have at least one healthy fallopian tube; ova and sperm are deposited into the tube where fertilization takes place
GIFT
ch. 9 - fertilization takes place in vitro and then placed in fallopian tube during the zygote stage
ZIFT
ch. 9 - oocyte, sperm, and embryo donation; surrogate mothers and embryo hosts; therapeutic donor insemination
examples of ART
end of class review - the ultrasound report for a pregnant client confirms polyhydramnios. as the nurse, what does this data tell you about the fetus?
the fetus may have problems with the GI system
end of class review - what side effects of the combined oral contraceptive pill will you ask the client to report to her provider immediately?
headaches, blurred vision, and elevated BP
end of class review - the nurse assessed a client. which clinical finding indicates syphilis?
ulcer to genitalia
end of class review - a client is seen at the clinic with a vaginal infection. on clinical examination, the provider observes a frothy discharge, an inflamed vulva, and red spots on the cervix. what would the provider suspect?
trichomoniasis
end of class review - condoms protect against pregnancy and some STIs. the provider should not recommend the combined oral contraceptive for a woman with a medical history of DVT. when using the condom, __________ should not be used as a lubricant. a permanent method of contraception is a vasectomy. part of the pre-operative care for a woman scheduled for a bilateral tubal ligation is nothing by mouth for 6-8 hours.
petroleum jelly
end of class review - a client at 39 weeks pregnant is in labor. she was treated 10 weeks ago for herpes simplex. what would be the expected management of her labor and delivery?
a vaginal birth should be expected
ch. 8 - the device or practice used to decrease the risk of conceiving or bearing offspring
birth control
ch. 8 - informed consent is a vital component in educating a client about contraception or sterilization. the mnemonic BRAIDED may be useful. what does it stand for?
B - benefits
R - risks
A - alternatives
I - inquiries
D - decisions
E - explanations
D - documentation
ch. 8 - shallow dome-shaped latex or silicone device with a flexible rim that covers the cervix; available in 4 types and many sizes
diaphragm
ch. 8 - 3 sizes available; made of silicone and fits snugly around the base of the cervix
cervical cap
ch. 8 - small round polyurethane sponge that has N-9 spermicide that fits over the cervix; one size fits all
contraceptive sponge
ch. 8 - insufficient secretion of FSH and LH; ovulation is inhibited; endometrium becomes less favorable for implantation
actions of oral contraceptives (combined estrogen-progestin contraceptives)
ch. 8 - the ACHES mnemonic represents signs of potential complications of oral contraceptives. what does it stand for?
A - abdominal pain
C - chest pain or SOB
H - headaches
E - eye problems
S - severe leg pain
ch. 8 - combined oral contraceptives taken in 3-month cycles; the woman experiences fewer menstrual periods
oral contraceptive 91-day regime
ch. 8 - patch with combined progestin and estradiol; applied weekly on the same day for 3 weeks and then one week without
transdermal contraceptive system