8A- nutrition in pregnancy, lactation, infancy, and childhood
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
zygote path
zygote= fertilized egg
travels through fallopian tube to uterus where it implants into uterine lining
implantation complete after about 14 days
embryonic stage of development
2-8 weeks
cells of embryo begin to differentiate, arrange themselves and begin organ development
fetal stage of development
9 weeks until birth
fetus continues to grow
develops internal and external organ structures
length is approximately equal to weeks gestation
fertilization location and timing
in oviduct
12-24 hours after ovulation
when does egg compete first cell division
after about 30 hours
becomes 100 cells after about 3-4 days
where does nutrient and waste transfer occur
placenta
placenta
organ that develops during pregnancy to facilitate transfer of nutrients to the growing fetus and the removal of waste products
made of maternal and fetal tissue
maternal and fetal blood supply do NOT mix
brings blood close enough to allow for nutrient transfer
releases hormones that are needed to maintain pregnancy
why does maternal body change
to support pregnancy, fetal development, birth, and lactation
weight gain during pregnancy
purpose: fetal growth and development, additional energy stores
how much weight is gained during pregnancy and what makes up this number
11.5-16 kg
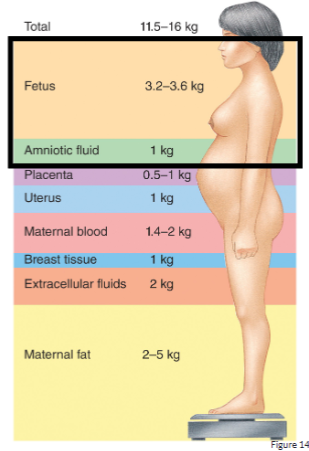
how much weight is lost immediately after giving birth
around 5 kg (10 lbs)
fetus and amniotic fluid
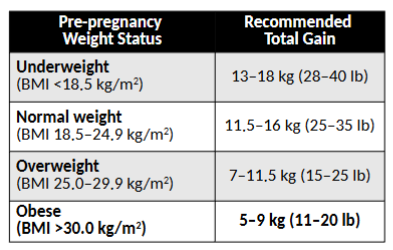
how much weight should be gained during pregnancy based on pre pregnancy BMI
overall: the heavier pre gestation, the less weight to gain so if underweight before pregnancy, need to gain more weight
*memorize these numbers
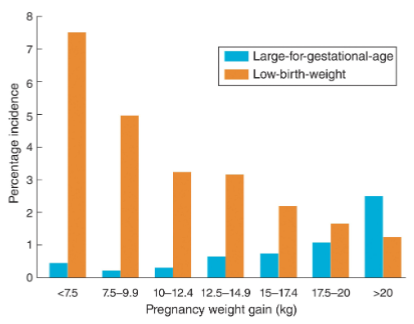
what happens if you gain too little weight
low birth weight or pre term birth
increases in child’s risk of heart disease or diabetes later in life
what happens if you gain too much weight
high BP
diabetes
difficult delivery: C-section
infants large for gestational age
correlation between weight gain and size of infant when born
hypertensive disorders of pregnancy stats
5-10% of pregnant person experience high BP during pregnancy
30% are related to -re-existing chronic HTN
gestational HTN
abnormal rise in BP that occurs after 20th week of pregnancy
may be a signal of a more serious condition (preeclampsia: high BP and loss of protein in urine → organ damage)
spiral uterine artery changes in pregnancy
non pregnant: longer and more spiraling
normal pregnancy:
runs in spiral shape within functional layer
forms capillary network and blood sinuses when it reaches the superficial layer of the functional layer
then merges into small veins and merges through muscular layer to form uterine artery
pre-eclampsia
spiral artery recasting disorder: shallow implantation of placenta vessels
gestational diabetes mellitus
consistently elevated glucose level during pregnancy in a person without previously diagnosed DM
in 3-20% of all pregnancies
who is at higher risk of GDM
obese
family hx of T2DM
what are the long term consequences of GDM
increased risk for T2DM later in life
patho of GDM
risk factors: obesity, inflammatory cytokines
results in excessive peripheral insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production
excessive endogenous glucose production, excessive peripheral insulin resistance
also caused be placental related hormones
results in increased glucose production decreased uptake, resulting in hyperglycemia
epigenetics of GDM and offspring health: the time for action is in early stages of life article → what are the key highlights
intrauterine hyperglycemia is not only associated with increased perinatal morbidity and mortality, but also with increased lifelong risks of the exposed offspring for obesity, metabolic, CV and malignant disease
fetal overnutrition (and undernutrition) lead to persistent epigenetic changes in developmentally important genes, influencing neuroendocrine functions, energy homeostasis and metabolism
what are vital nutrients during pregnancy
zinc
rapid growth and enzymes
iron
blood vessels, avoid anemia
folate
neural tube development
neural tube closure done by day 28
how much extra energy is needed during different trimesters and lactation
1st trimester
0 kcal/day
2nd trimester
350 kcal/day
3rd trimester
450 kcal/day
lactation
300-400 kcal/day
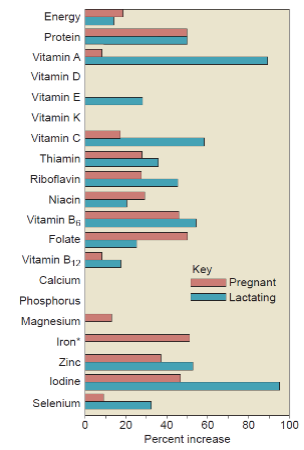
nutrition needs during pregnancy and lactation
pregnancy:
protein
folate
IRON
zinc
iodine
B6
lactation:
protein
vitamin A, E, C
B6
iodine
selenium
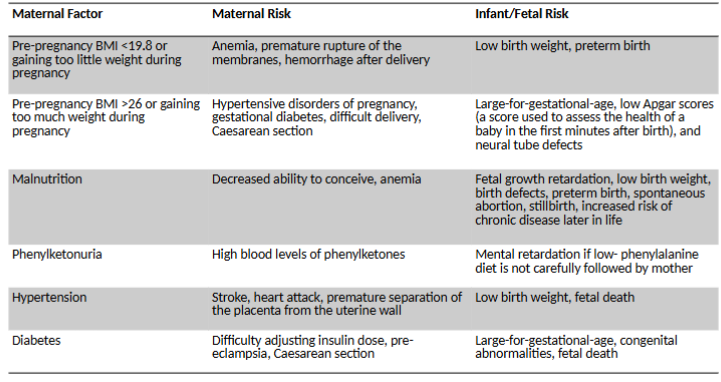
maternal factors risk for mother and infant/fetus
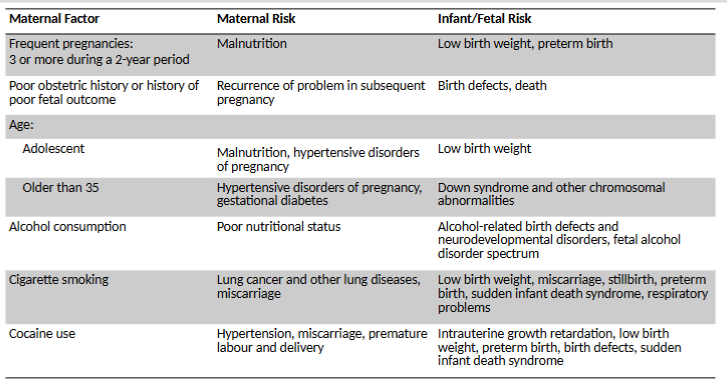
maternal factors risk for mother and infant/fetus pt. 2
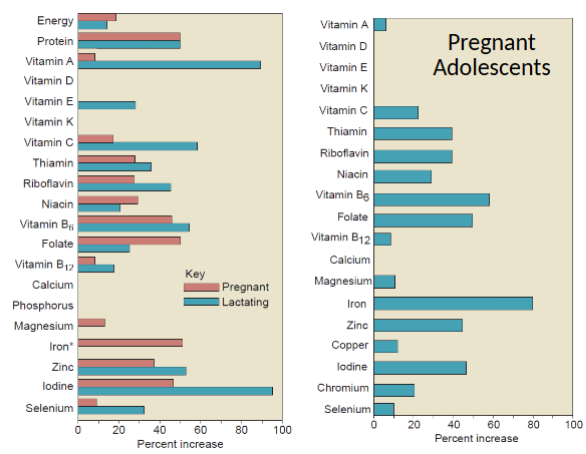
why does a pregnant adolescent need different nutrient requirements
adolescent girls continue to grow and mature physically for about 4-7 years after menstruation begins
diet of pregnant teen must provide both for her growth and that is baby
pregnant adolescent nutrient requirements
niacin
B6
iron
copper
teratogens
substances of chemical or biological origin that can cause birth defects
critical periods
time when different organ systems are particularly susceptible at different times
when are most critical periods
embryonic development (3-8 weeks)
Canadian Prenatal Nutrition Program (CPNP)
provides funding to community groups to hep to improve the health of pregnant women, new mothers, and their babies who face challenges that put their health at risk such as;
poverty
teen pregnancy
social and geographic isolation
substance use
family violence
lactation
involved the synthesis of milk components, including protein, lactose adn lipids, and the movement of the milk through the milk ducts to the nipple
let-down
the release of milk from the glands through the ducts
triggered by the hormone oxytocin
colostrum
immature milk
secreted during first days after delivery
rich in protein and immune factors
iron needs during lactation
decrease by ½
because not menstruating
do lactating individual need more fluid
yes- not certain amount though just in general
where does energy come from for lactation
fat stores created during pregnancy
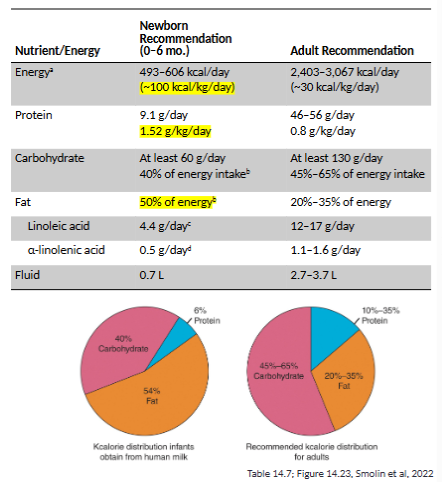
infant nutritional needs
higher percent of fats than adults
almost double amount of protein relative to adult
water intake is critical (high surface area: volume ratio)
most common cause of infant mortality
dehydration due to diarrhea
breastmilk nutrition
includes most nutrients needed for infant growth except vitamin D and K
poor source of iron
fluoride supplementation recommended at 6 months in breast fed infants
infants following vegan diet
may need B12 supplementation
infant iron supplementation
iron rich foods needed at 6 months
after 6 months iron stores are depleted
health canada breast feeding recommendations
exclusive breastfeeding for first 6 months
sustained for up to 2 years or longer with appropriate complementary feeding to support nutrition needs
benefits of breastfeeding
nutrients and protection
perfect amount of nutrition and antibodies for disease prevention
brain power
higher IQ
convenient and portable
breast milk always safe, fresh, exactly right temp
size does not matter
breast will produce enough milk for baby regardless of size
benefits mothers too
helps lose weight and reduce risk of some cancers
continues the special relationship
helps with bonding
benefits don’t stop
all additional time continues to help more in child
easy on budget
no buying formula
works for working mothers
can be expressed with pump so that others can help with feedings
good for environment
no waste, pollution, packaging
who is most likely to breastfeed for first 6 months
those who:
have partners
do not smoke during pregnancy
deliver in their home
do not work
formula composition regulation
Canadian Food and Drug Regulations and enforced by Canadian Food Inspection Agency
growth
measurable change in body size due to 2 underlying cellular processes
hyperplasia: increase in cell number
hypertrophy: increase in cell size
accretion: increase in intercellular substances
what do growth charts identify
malnutrition
undernutrition (weight for age)
stunting (length for age)
wasting (weight for length, BMI for age)
overnutrition (weight for length, BMI for age)
how is children’s growth compared
compared to growth charts of average growth during checkups
99th percentile: larger (higher BMI) than 99% of other children= very large for age
50th percentile: larger than 50% of other children
3rd percentile: larger than 3% of other children (= very small for age, “abnormal”)
when is BMI used
after 2 years of age to account for body changes due to puberty
birth to 6 months developmental milestones and foods
milestones:
takes milk by sucking
solid food placed in mouth usually pushed out because tongue is thrust forward during sucking
by 6 months tongue action diminished that baby can accept solid food
foods
exclusively breast milk
infant formula if breastfeeding is not possible
vitamin D supplement if breastfed
6-12 months developmental milestones and foods
milestones
infant can hold head up, sit, chew, hold food, move hand to mouth
progresses to drinking from cup and feeding self
foods
breast milk or formula (cows milk after 9 months)
iron-fortified infant cereal
pureed or drained vegetables
fruits
finger foods like cooked pasta or cooked and cut vegetables
12-18 months developmental milestones and foods
milestones
feed self
drink from cup, use spoon, bite food well, eat ground or chopped table food
foods
breast milk or cow’s milk
meats and beans
iron-fortified cereal
chopped veg
soft fruit
finger foods
move towards following Canada’s food guide
nutrition and health concerns in children
dental cavities
food allergies
diet and hyperactivity
evidence is mixed and weak overall
childhood obesity
impact of screen time
advertising (ex. sat morning cartoon ads favour unhealthy food cereal, snacks, candy..)
food allergy
more common in infants than adults
exposure to allergen for first time causes immune system to produce antibodies to that allergen
allergy symptoms
sneezing, rash, eczema, hives, cramps, aches, vomiting, asthma, diarrhea
may be immediate or take up to 24 hours to appear
may range from mild to life-threatening
food intolerances
do NOT cause antibody production
create problems during DIGESTION
ex. lactose intolerance
top 8 food allergens
milk
eggs
fish
shellfish
peanuts
tree nuts
wheat
soy
*must be indicated on food labels
5-4-3-2-1 GO! initiative
5 servicing of fruit and veg per day
4 serving of water per day
3 servings of low fat dairy a day
2 hours or less of screen time per day
1 hour or more of physical activity per day
0 sugar sweetened beverages
*to combat obesity