Modern & Analytical Chemistry Ch 6.
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro to spectrometric methods
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Electromagnetic Radiation using wave/particle duality
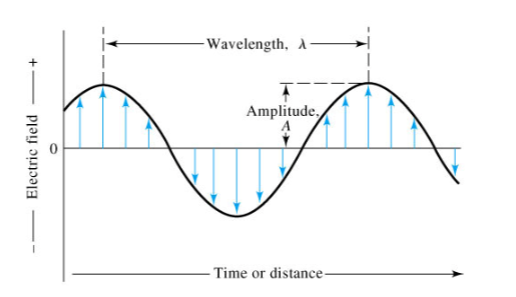
-We can describe electromagnetic radiation (EM) using a classical sinusoidal wave model with characteristics such as wavelength, frequency, velocity, and amplitude.
-We can describe EM radiation as a stream of discrete particles called photons where the energy of a photon is proportional to the frequency of the radiation.
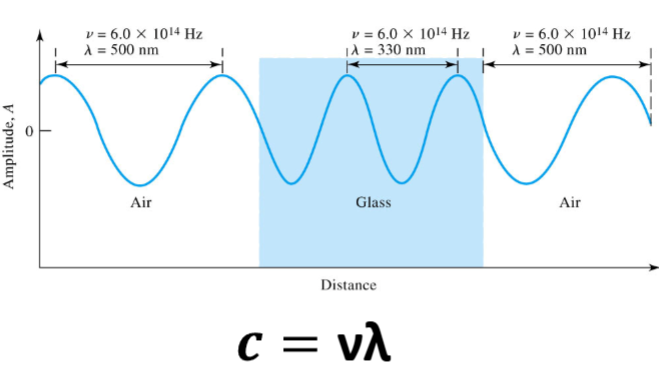
Frequency does
not change with the medium (Its invariant)
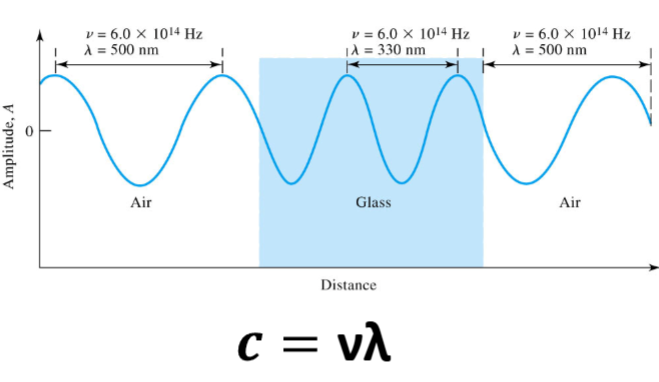
Wavelength and velocity of EM does
change with the medium
Two components of Electromagnetic Radiation
electric component & magnetic component
Electromagnetic Radiation
two components 90 degrees apart
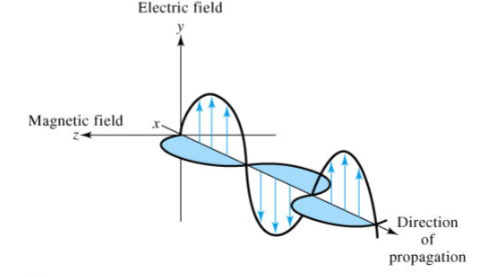
The electric component of radiation
is responsible for most phenomena of interest, i.e. transmission, reflection, refraction, and absorption. (Only consider electrical component for most instrumentation)
The magnetic component of radiation
is responsible for absorption of radio-frequency waves in nuclear magnetic resonance.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum and How it Interacts with Mater
Methods of Propagation of Radiation: Diffraction
Parallel beam of radiation is bent as it passes a sharp barrier or through a narrow opening
Diffraction
is a superposition of waves because of interference
Superposition
when two or more waves transverse the same space, a disturbance occurs that is the sum of the disturbances caused by the individual waves.
Constructive interference
results in an increase in amplitude because waves are in phase.
Deconstructive interference
results in a decrease in amplitude because waves are out of phase.
Methods of Propagation of Radiation: Transmission
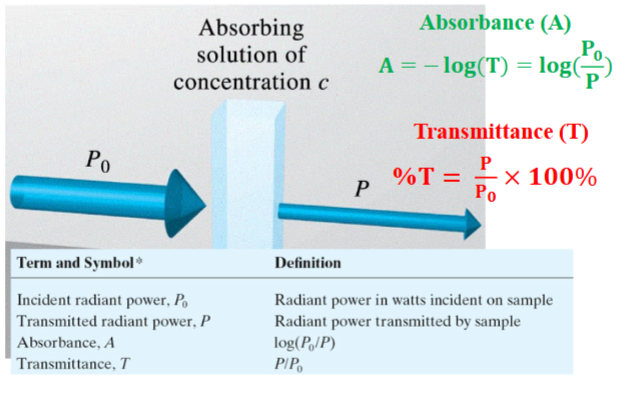
Transmission
the propagation of EM radiation through materials
Methods of Propagation of Radiation: Refraction
Abrupt change in a direction of a beam due to differences in velocity between two media of different densities
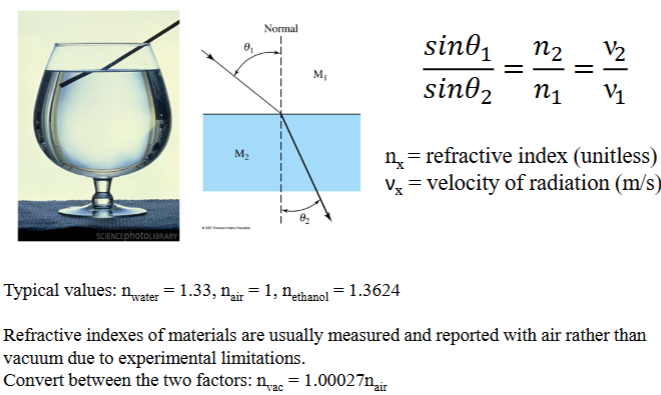
n_x
refractive index (unitless)
V_x
velocity of radiation (m/s)
Refractive indexes of materials
are usually measured and reported with air rather than vacuum due to experimental limitations.
Convert between the two factors: n_vac = 1.00027n_air
Methods of Propagation of Radiation: Scattering
Small fraction of radiation is transmitted at all angles from the original path and the intensity of this scattered radiation increases with particle size.
Rayleigh Scattering
scattering by molecules smaller than the wavelength of radiation; proportional to the inverse 4th power of wavelength (I ∝ 1/λ4 ); reason why sky is blue... greater scattering of the shorter wavelengths of the visible spectrum
Mie Scattering
scattering by large particles
Raman Scattering
scattering resulting in quantized frequency shifts; results in vibration energy transitions of the molecules. Discussed in Raman spectroscopy
Methods of Propagation of Radiation: Polarization
Bundles of EM waves in which the vibrations are equally distributed in the planes centered along the beam path.