AEE111: Basic Aircraft Structures Principles & Pneumatic System
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AIRSYS M1 L1-L2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Powerplant
Wing
Landing Gear
Fuselage
Empennage
What are the 5 Major Aircraft Components?
Fuselage
It forms the main body of the aircraft, to which the wings, tailplane, canards, vertical fin, and engine are attached. It takes the form of a tube, housing the flight deck, passenger cabin, freight holds, and the majority of the equipment required to operate the aircraft.
Truss Type or Framework Type
Monocoque Type
Semi-Monocoque Type
What are the 3 Types of Fuselage?
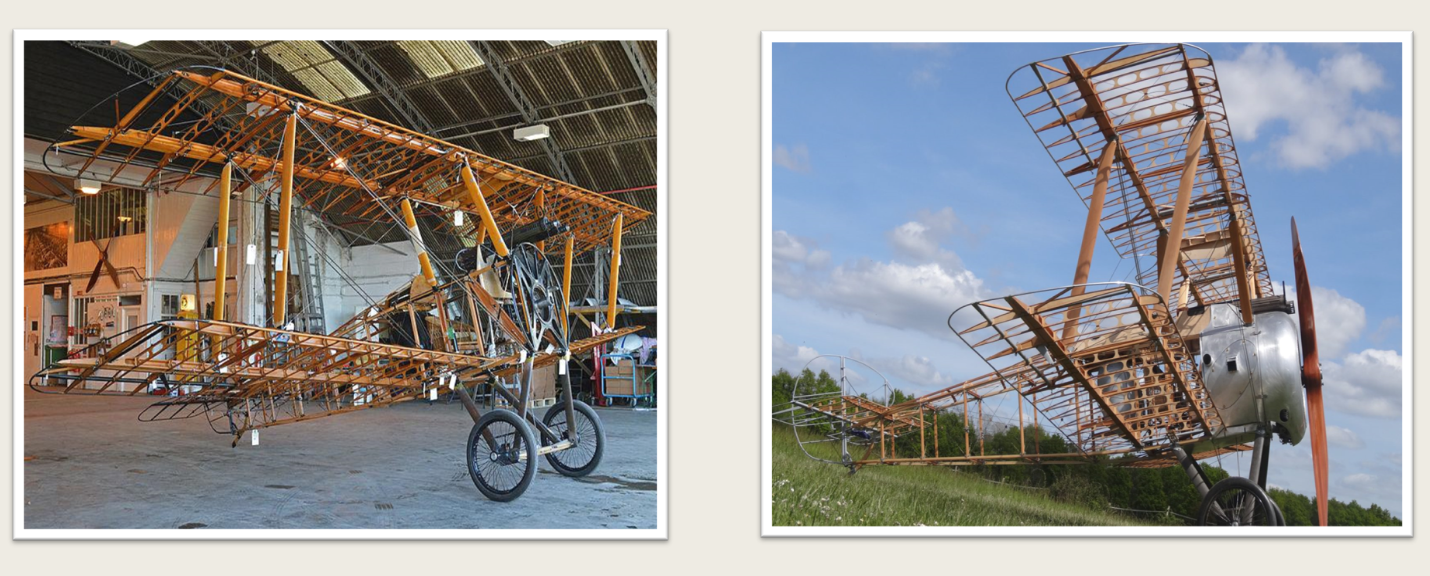
Truss Type
A rigid framework made up of members, such as beams, struts, and bars, designed to resist deformation from applied loads. It is generally covered with fabric.
Truss Type
What type of fuselage?

Monocoque Type
A type of fuselage where the skin bears all the loads placed on the structure, and the shape of the structure provides its strength and rigidity. The skin may be attached to formers to give its basic shape, but it carries all the flight and ground loads.
Monocoque Type
What type of fuselage?
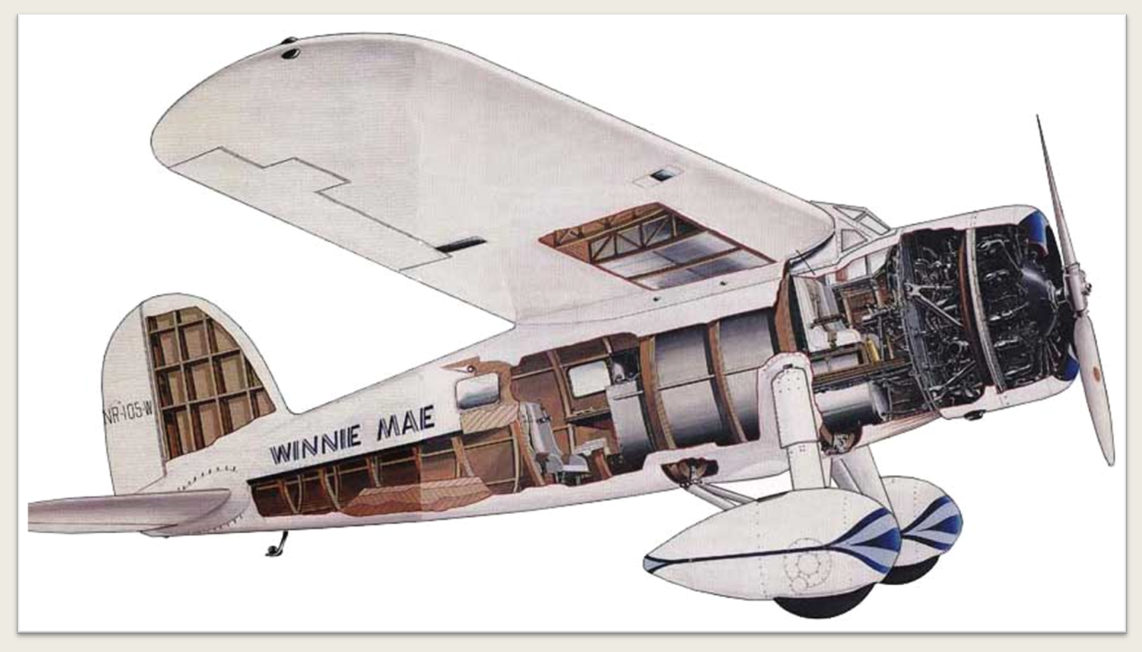
Semi-Monocoque Type
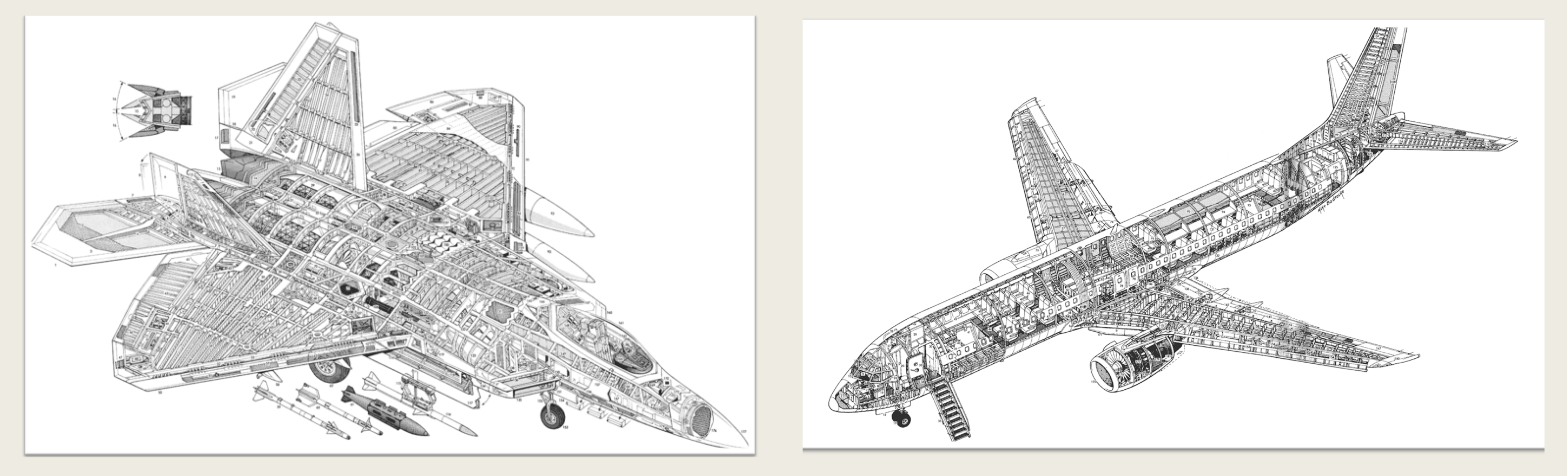
In this type, the loads imposed on the skin are shared by a series of frames, stringers, and formers that are attached to it. Frames strengthen the fuselage and help distribute the load. Stringers are lighter longitudinal members that reinforce the skin, and formers are used to maintain the skin’s profile between frames.
Semi-Monocoque Type
What type of fuselage?

Wings
Previously referred to as main planes, they produce the lift that supports the weight of the aircraft in flight. They must have sufficient strength and stiffness to perform this function effectively.
Truss Type
Semi-Monocoque Type
Wing Structures
Wing Spar
Truss Type (Wing)
Are constructed so that they will absorb the downwards bending stresses when on the ground and the upwards, rearwards, and twisting stresses when in flight.
Drag Wire
Truss Type (Wing)
A wing support of an airplane for sustaining the backward reaction due to the drag of the wing.
Anti-Drag Wire
Truss Type (Wing)
It opposes the drag wire.
Compression Strut
Truss Type (Wing)
It opposes the compressive loads between the spars arising from the tensile loads produced by the drag and anti-drag wires.
Skin
Semi-Monocoque Type (Wing)
It takes the loads due to differences in air pressures and the mass and inertia of the fuel (if any) in the wing tanks. It generates direct stresses in a spanwise direction as a response to bending moments and also reacts against twisting (torsion).
Stringers
Semi-Monocoque Type (Wing)
These are spanwise members that give the wing rigidity by stiffening the skin in compression.
Ribs
Semi-Monocoque Type (Wing)
These maintain the airfoil shape of the wings, support the spars, stringers, and skin against buckling, and pass concentrated loads from engines, landing gear, and control surfaces into the skin and spars.
Ailerons
Semi-Monocoque Type (Wing)
Extend from about the midpoint of each wing outward to the tip and move in opposite directions to create aerodynamic forces that cause the airplane to roll.
Flaps
Semi-Monocoque Type (Wing)
When extended, they move simultaneously downward to increase the lifting force of the wing for takeoff and landings.
Biplane
Braced Monoplane
Cantilever Monoplane
Wing Categories
Biplane
Consists of two main wings stacked one above the other. The wing spars, interplane struts, and bracing wires form a lattice girder of great rigidity, which is highly resistant to bending and twisting.
Braced Monoplane
???
Cantilever Monoplane
In this design, the wing is self-supporting and attached to the fuselage at one end. The designer must ensure that the wing’s structure is capable of withstanding the torsional loads, the loads created along its length in flight, and its mass on the ground.
Low Wing
Wing location wherein the landing gear legs are shorter than those of a high-wing aircraft. If an engine-propeller combination is to be mounted on the wings, the propeller size is limited by the ground clearance unless the legs are extended.
Mid-wing
Wing location where aircraft have the advantage of improved aerodynamics for high-speed flight, but the disadvantage is having spars passing through the middle of the fuselage.
High-wing
Wing location where aircraft have the advantages of providing good downward visibility and making cargo loading and unloading easier.
Dihedral Angle
It is the angle between the wing and the horizontal plane when the wing is positioned above the horizontal plane.
Anhedral Angle
It is the angle between the wing and the horizontal plane when the wing is mounted below the horizontal plane.
Empennage
On conventional aircraft, the _______ or tailplane normally takes the form of a single vertical fin and horizontal surface. These are fitted to provide the aircraft with directional and longitudinal static stability and are mounted at the tail (rear) of the aircraft.
Landing Gear
The __________ supports the aircraft during landing and while it is on the ground. It must not only withstand the shocks during landing but also be positioned to prevent the airplane from nosing over when landing.
ATA 100-chapter numbers
_________________ were a common referencing standard for all commercial aircraft documentation. This commonality permits greater ease of learning and understanding for pilots, aircraft maintenance
technicians, and engineers alike.
Air Transport Association
The standard numbering system was published by the ________________ on June 1, 1956.
ATA 01 - ATA 04
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
Reserved for Airline Use
ATA 05
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
TIME LIMITS/MAINTENANCE CHECKS
ATA 06
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
DIMENSIONS AND AREAS
ATA 07
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
LIFTING AND SHORING
ATA 08
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
LEVELING AND WEIGHING
ATA 09
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
TOWING AND TAXI
ATA 10
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
PARKING, MOORING, STORAGE AND RETURN TO SERVICE
ATA 11
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
PLACARDS AND MARKINGS
ATA 12
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
SERVICING - ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
ATA 18
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
VIBRATION AND NOISE ANALYSIS (HELICOPTER ONLY)
ATA 89
ATA Chapter: Aircraft General
FLIGHT TEST INSTALLATION
ATA 20
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
STANDARD PRACTICES - AIRFRAME
ATA 21
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
AIR CONDITIONING AND PRESSURIZATION
ATA 22
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
AUTO FLIGHT
ATA 23
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
COMMUNICATIONS
ATA 24
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
ELECTRICAL POWER
ATA 25
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
EQUIPMENT/FURNISHINGS
ATA 26
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
FIRE PROTECTION
ATA 27
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
FLIGHT CONTROLS
ATA 28
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
FUEL
ATA 29
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
HYDRAULIC POWER
ATA 30
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
ICE AND RAIN PROTECTION
ATA 31
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
INDICATING / RECORDING SYSTEM
ATA 32
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
LANDING GEAR
ATA 33
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
LIGHTS
ATA 34
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
NAVIGATION
ATA 35
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
OXYGEN
ATA 36
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
PNEUMATIC
ATA 37
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
VACUUM
ATA 38
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
WATER/WASTE
ATA 39
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
ELECTRICAL - ELECTRONIC PANELS AND MULTIPURPOSE COMPONENTS
ATA 40
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
MULTISYSTEM
ATA 41
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
WATER BALLAST
ATA 42
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
INTEGRATED MODULAR AVIONICS
ATA 44
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
CABIN SYSTEMS
ATA 45
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
DIAGNOSTIC AND MAINTENANCE SYSTEM
ATA 46
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
ATA 47
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
NITROGEN GENERATION SYSTEM
ATA 48
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
IN FLIGHT FUEL DISPENSING
ATA 49
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
AIRBORNE AUXILIARY POWER
ATA 50
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
CARGO AND ACCESSORY COMPARTMENTS
ATA 51
ATA Chapter: Structure
STANDARD PRACTICES AND STRUCTURES - GENERAL
ATA 52
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
DOORS
ATA 53
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
FUSELAGE
ATA 54
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
NACELLES/PYLONS
ATA 55
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
STABILIZERS
ATA 56
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
WINDOWS
ATA 57
ATA Chapter: Airframe Systems
WINGS
ATA 61
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
PROPELLERS
ATA 70
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
STANDARD PRATICES ENGINE
ATA 71
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
POWER PLANT
ATA 72
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
ENGINE - RECIPROCATING
ATA 73
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
ENGINE - FUEL AND CONTROL
ATA 74
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
IGNITION
ATA 75
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
BLEED AIR
ATA 76
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
ENGINE CONTROLS
ATA 77
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
ENGINE INDICATING
ATA 78
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
EXHAUST
ATA 79
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
OIL
ATA 80
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
STARTING
ATA 81
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
TURBINES (RECIPROCATING ENGINES)
ATA 82
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
ENGINE WATER INJECTION
ATA 83
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
ACCESSORY GEARBOXES
ATA 84
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
PROPULSION AUGMENTATION
ATA 85
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
FUEL CELL SYSTEMS
ATA 91
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
CHARTS
ATA 92
ATA Chapter: Powerplant
Electrical System Installation