Ecosystem and Community Ecology: Carbon Cycle, Biodiversity, and Food Webs
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
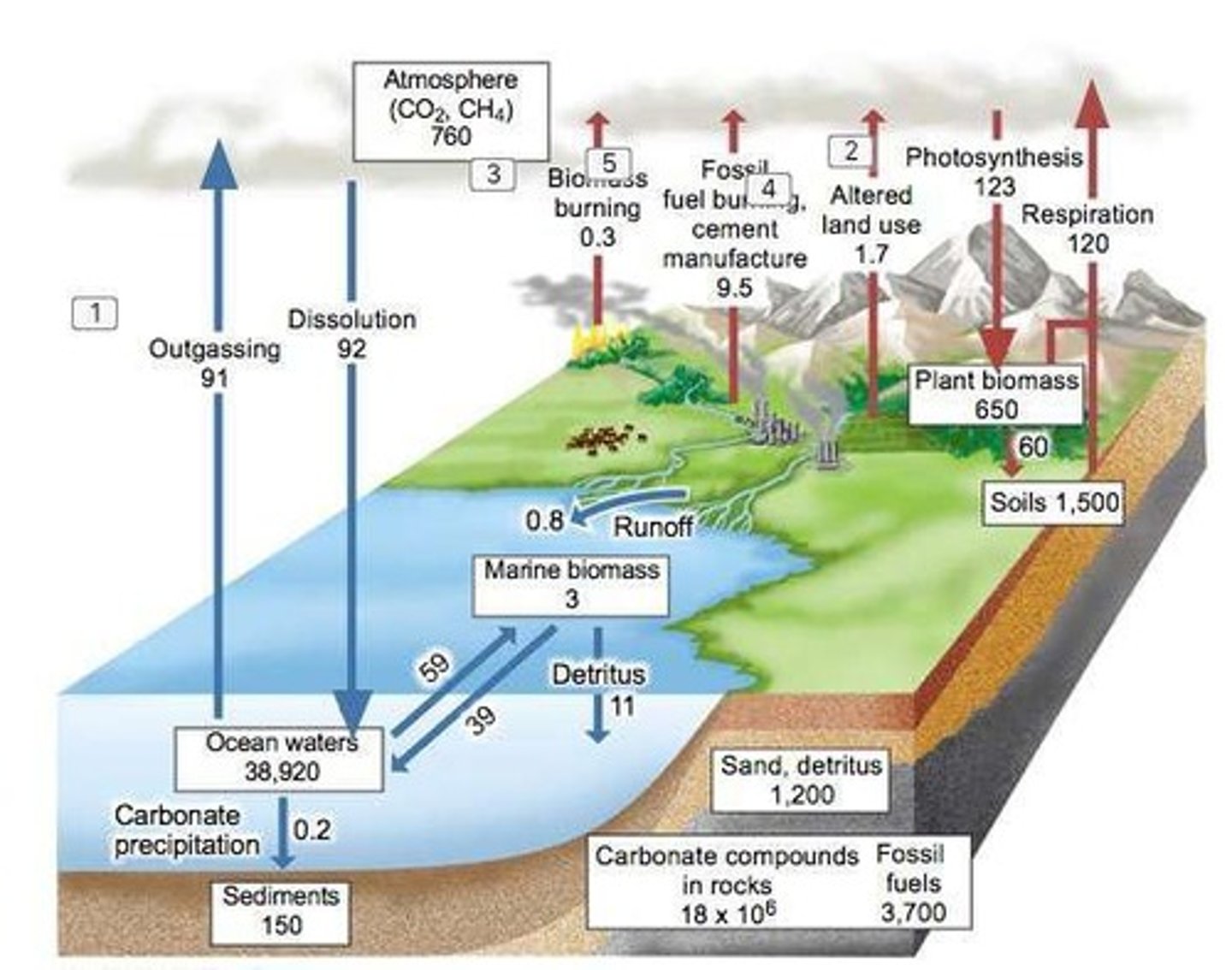
What is the Global Carbon Cycle?
the movement of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms, driven by biological, chemical, and physical processes.
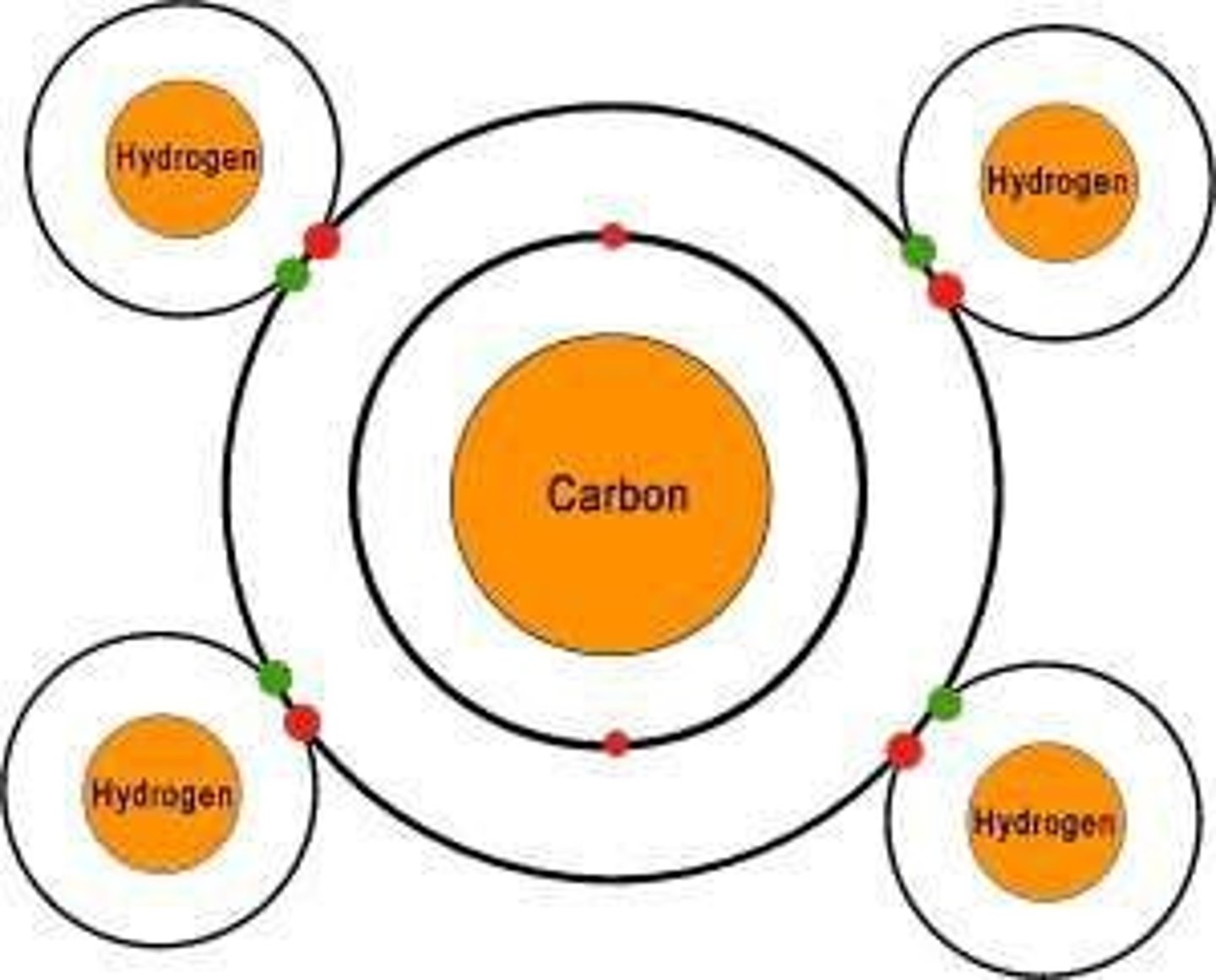
What percentage of the human body is made up of carbon?
About 18-19%.
How do primary producers contribute to the carbon cycle?
Primary producers fix carbon from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, converting inorganic carbon into organic forms.
What are the two main forms of carbon found in the atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4).
What is the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Decomposers link primary producers and consumers by converting organic matter into inorganic forms that can be reused by primary producers.
What is the significance of phosphorus in ecosystems?
Phosphorus is a key element in constructing lipid membranes and fueling cells.
What are ecosystem functions?
Ecosystem functions are ecological processes that control the fluxes of energy, nutrients, and organic matter through an environment.
How does biodiversity affect ecosystem function?
Biodiversity loss reduces the efficiency of resource use and biomass production, while diverse communities tend to be more productive due to the presence of highly productive species.
What is the difference between gross and net primary production?
Gross primary production is the total amount of energy captured by photosynthesis, while net primary production is the energy remaining after accounting for the energy used in respiration by primary producers.
What is trophic efficiency?
Trophic efficiency refers to the percentage of energy transferred from one trophic level to the next in a food chain.
What is the role of mineral dust in ecosystems?
Mineral dust can affect nutrient cycling and ecosystem productivity by providing essential minerals to the soil.
What are the potential relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem function?
Relationships can be saturating, linear, or accelerating, depending on how biodiversity influences ecosystem processes.
What is the sampling effect in biodiversity?
The sampling effect suggests that diverse systems are more likely to include highly productive species, enhancing overall ecosystem productivity.
What is complementarity in the context of biodiversity?
Complementarity refers to niche partitioning or positive interactions among species that enhance resource use and ecosystem function.
What is the insurance hypothesis in biodiversity?
The insurance hypothesis posits that some species maintain ecosystem function when others fail, providing stability to the ecosystem.
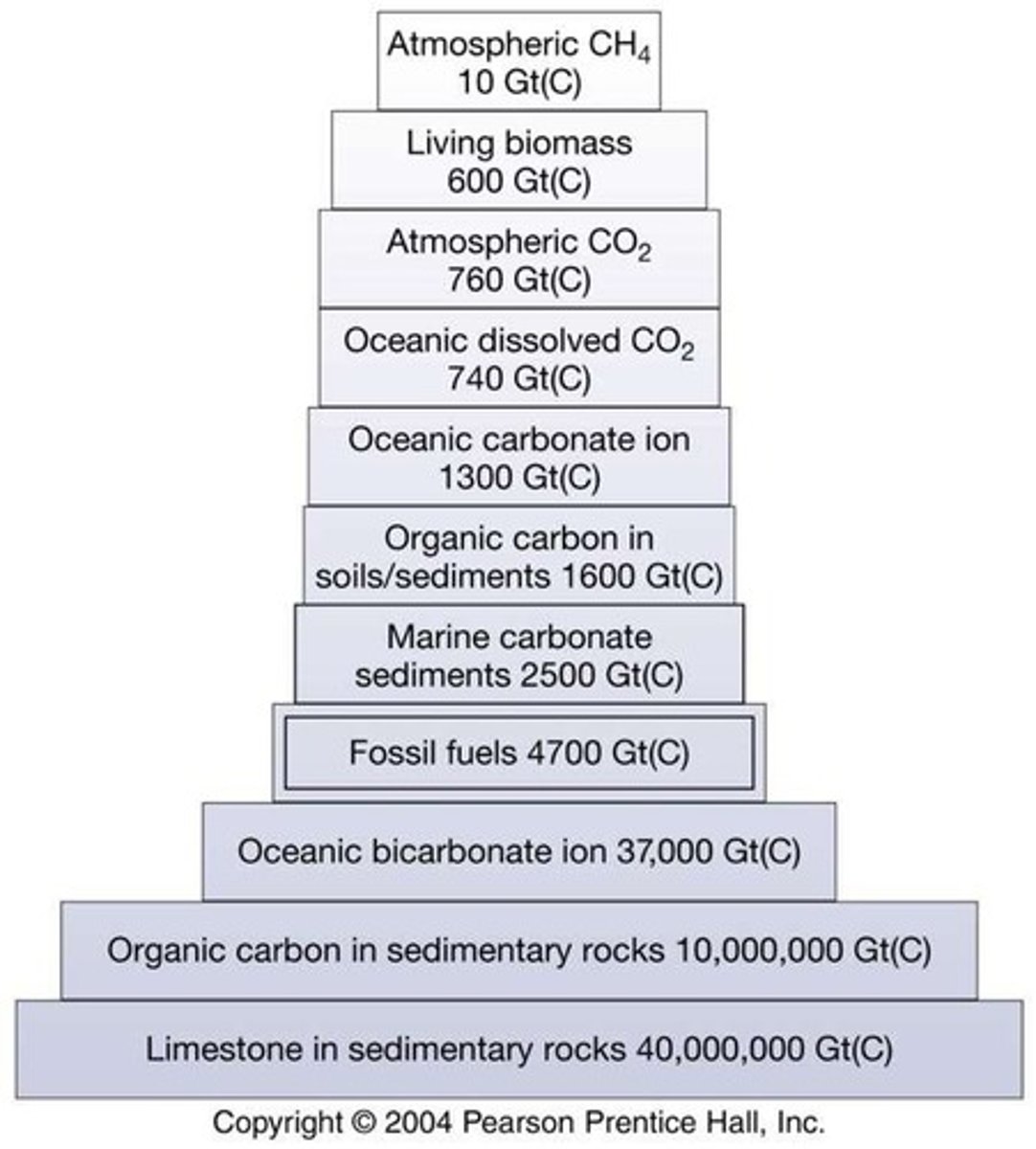
What is the significance of carbon flux in ecosystems?
Carbon flux refers to the movement of carbon in various forms (e.g., CO2, CH4) between different reservoirs such as the atmosphere, biomass, and soils.
What are the main components of the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle includes processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, and ammonification.
How does nitrogen pollution affect ecosystems?
Nitrogen pollution can lead to nutrient imbalances, harmful algal blooms, and degradation of water quality.
What is the role of aquatic systems in the carbon cycle?
Aquatic systems store carbon in dissolved forms and contribute to carbon flux through processes like outgassing and dissolution.
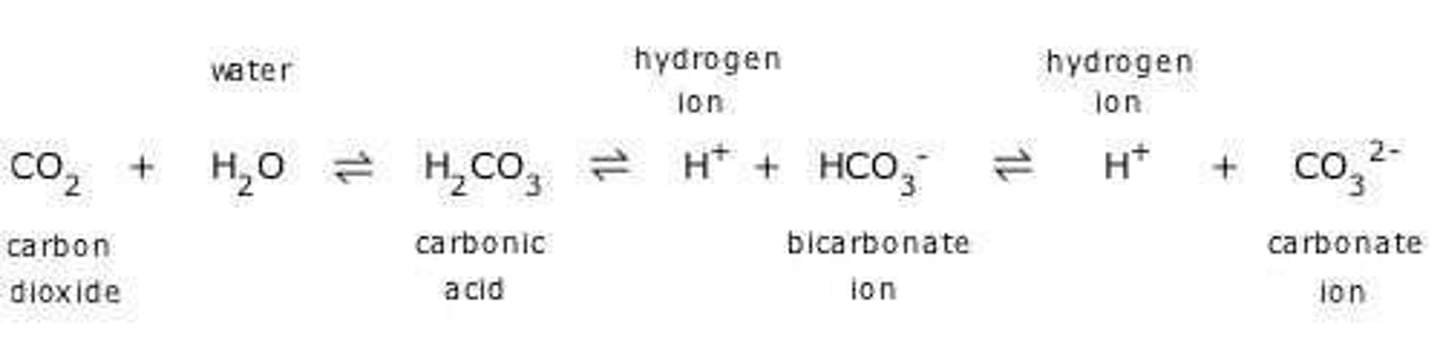
What is the significance of the 'Brown Food Web'?
The 'Brown Food Web' refers to the network of decomposers and detritivores that recycle organic matter back into the ecosystem.
What is the 'Green Food Web'?
The 'Green Food Web' consists of primary producers (plants) that capture energy through photosynthesis and serve as the base of the food chain.
What is the importance of carbonates in aquatic systems?
Carbonates play a crucial role in buffering ocean acidity and are involved in the formation of carbonate ions.
What is the impact of human activity on carbon reservoirs?
Human activities, such as fossil fuel burning and land use changes, have significantly altered carbon reservoirs and increased atmospheric CO2 levels.
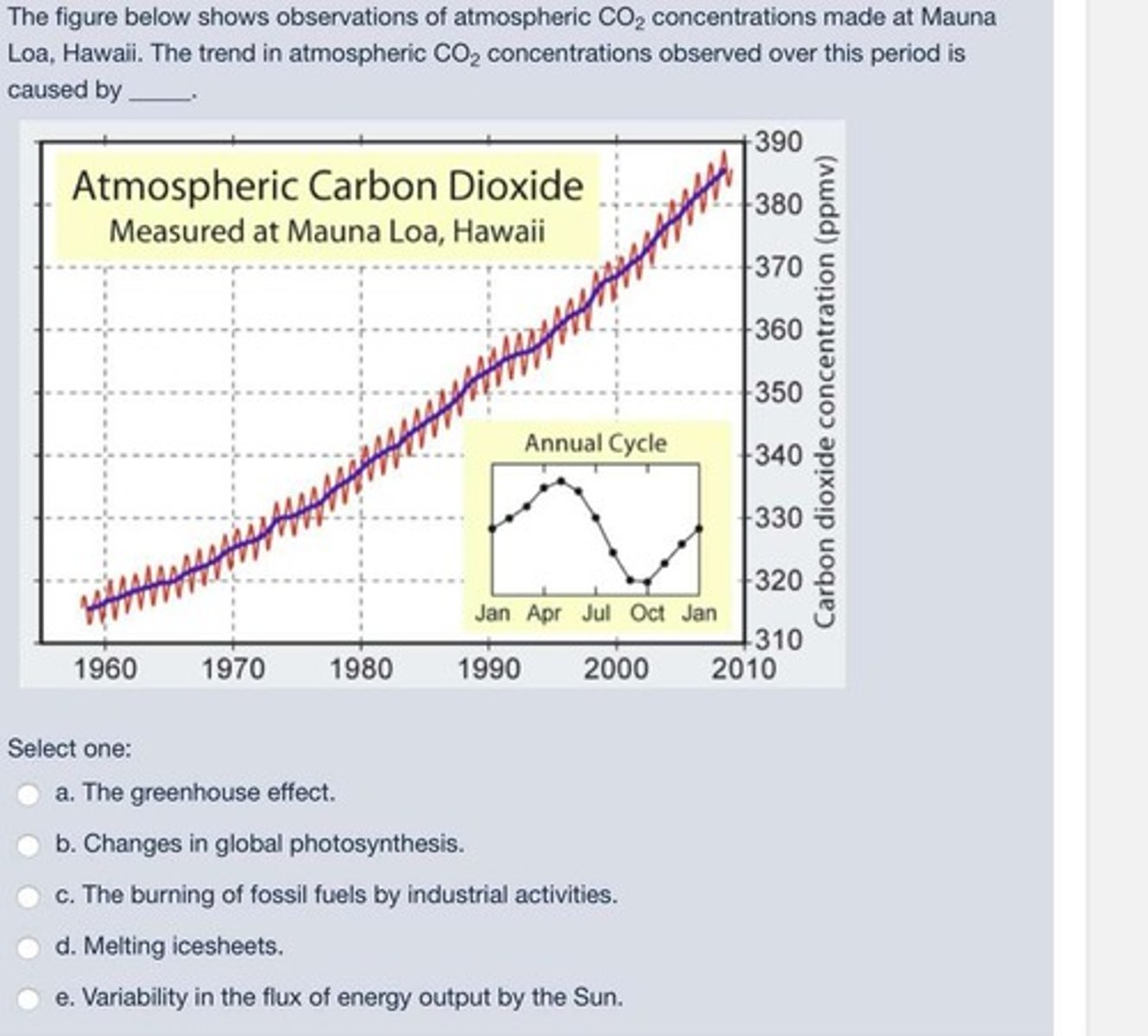
What is the definition of an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a collection of organisms and their physical environment, involving interactions between biota and the environment.
What is an ecosystem?
A collection of organisms and the environment in which they live, involving interactions between organisms and their environment.
What are the two main components of an ecosystem?
Biota (living organisms) and the physical environment.
What is the focus of ecosystem ecology?
The flux of energy and materials within ecosystems.
What is the difference between gross primary production (GPP) and net primary production (NPP)?
GPP is the total amount of light energy converted to chemical energy by photosynthesis, while NPP is the rate at which new plant biomass accrues.
What is the typical ratio of NPP to GPP in many ecosystems?
NPP is about 50% of GPP.
Which ecosystem has a higher NPP: tropical forest or Serengeti plains?
Tropical forest has a higher NPP (2000 kcal/m2/yr) compared to Serengeti plains (1900 kcal/m2/yr).
What is Lindeman's efficiency?
The proportion of production transferred from one trophic level to the next.
What are the two important laws of thermodynamics relevant to ecosystems?
1st law: Energy is neither created nor destroyed; 2nd law: During energy transformation, some energy becomes unusable.
What is production efficiency?
The increase in biomass due to growth divided by biomass consumed.
What are the production efficiencies for ectotherms and endotherms?
Ectotherms: 10-50%; Endotherms: 1-5%.
What is the nitrogen cycle's significance in ecosystems?
Nitrogen is essential for proteins and nucleic acids, and most nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as N2.
What is the Haber-Bosch process?
A method for synthesizing ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, crucial for increasing nitrogen availability in agriculture.
Why is water essential to ecosystems?
Water limitation slows productivity and decomposition, and access to clean water is critical for human health.
What is conservation biology?
The scientific study of phenomena that affect the maintenance, loss, and restoration of biological diversity.
What are the four major threats to biodiversity?
Habitat loss, climate change, pollution, and overexploitation.
What is demographic stochasticity?
The variation in population dynamics due to random events affecting birth and death rates.
What is a metapopulation?
A group of spatially separated populations of the same species that interact through immigration and emigration.
What percentage of mammal biomass on Earth do wild mammals comprise?
Wild mammals comprise a small percentage of the total mammal biomass, significantly altered by human activity.
What is the role of primary producers in an ecosystem?
Primary producers convert light energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food web.
What is the significance of nutrient cycles in ecosystems?
Nutrient cycles, or biogeochemical cycles, are essential for recycling elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus within ecosystems.
How does energy flow through an ecosystem?
Energy flows in one direction from primary producers to consumers and decomposers, while materials cycle within the ecosystem.
What is the impact of fossil water depletion?
Draining fossil water leads to significant environmental issues, including land subsidence and reduced water availability.
What is the average water usage per day for an American compared to an African family?
An American uses 100 to 176 gallons/day, while an African family uses about 5 gallons/day.
Why is biodiversity important for human well-being?
Biodiversity supports ecosystem services that are crucial for food security, clean water, and health.
How much biodiversity have we lost in the last 48 years?
Animal populations have declined by about 50%.
What are the major drivers of biodiversity decline?
Habitat loss, climate change, pollution, overexploitation, and invasive species.
What is a species-specific approach to conservation?
An approach focusing on individual species, often involving laws like ESA and CITES.
What is a system-level approach to conservation?
A more recent strategy that considers entire ecosystems, such as the Everglades or afro-montane forests.
What is the significance of cheetah habitat reduction?
Cheetahs have experienced a 90% reduction in habitat, impacting their survival.
What are key research objectives for cheetah conservation?
Understanding population sizes, genetic diversity, home range size, diet, diseases, and human attitudes.
Why is low genetic variation a problem in small populations?
It may lead to reduced reproductive success and increased extinction risks.
What is effective population size?
The number of individuals in a population that contribute genes equally to the next generation.
How is effective population size calculated?
Ne = (4NmNf) / (Nm + Nf), where Nm is the number of breeding males and Nf is the number of breeding females.
What are source and sink populations?
Source populations have reproduction exceeding mortality, while sink populations have mortality exceeding reproduction.
What percentage of Earth's land surface has been degraded?
40-50% of Earth's land surface has been degraded.
What is the extinction risk for mammals, birds, fish, and amphibians?
25% of mammals, 12% of birds, 25% of fish, and 32% of amphibians are near extinction or endangered.
What is the latitudinal gradient in biodiversity?
Species richness generally increases towards the equator.
What are the main climatic factors associated with biodiversity?
Solar energy input and water availability.
What are the three hypotheses for the latitudinal gradient?
1. Rate of speciation, 2. Limits on how many species an environment can contain, 3. Resource availability.
How does habitat fragment size affect species loss?
Smaller fragments typically experience higher rates of species loss over time.
What role do wildlife corridors play in conservation?
They increase habitat connectivity, promoting species movement and genetic exchange.
What is the significance of the rosy periwinkle in conservation?
It has provided valuable compounds for cancer treatment, highlighting the economic value of biodiversity.
What are the consequences of extinction rates being 10-100 times higher than in the past?
This indicates a biodiversity crisis that could destabilize ecosystems and human livelihoods.
What hypothesis explains the high rate of speciation in the tropics?
The evolutionary rates hypothesis suggests high mutation rates and short generation times contribute to speciation.
What is the relationship between area and species richness?
The Species-Area Curve indicates that more area generally leads to more species.
What does MacArthur and Wilson's Island Equilibrium Model describe?
It describes the balance of species richness on islands between immigration and extinction rates.
What happens to immigration rates as the number of species on an island increases?
Immigration rates decline as the probability of new species arriving decreases.
What factors increase extinction rates on islands?
Increased interspecific competition and smaller average population sizes raise extinction rates.
What does the term 'equilibrium species richness' refer to?
It refers to the predicted number of species that an island can support at equilibrium.
What is the 'rescue effect' in island biogeography?
The rescue effect refers to the phenomenon where nearby species can help prevent extinction on islands.
What are the two models of population regulation in food webs?
Bottom-Up and Top-Down models describe how different factors control species populations.
What does the Bottom-Up model suggest?
It suggests that the availability of energy and nutrients for primary producers controls the abundance of higher trophic levels.
What does the Top-Down model imply?
It implies that populations of species are controlled by their predators.
What is a trophic cascade?
A trophic cascade is an ecological phenomenon where changes in one trophic level affect multiple levels below it.
What is the significance of apparent competition in ecology?
Apparent competition occurs when two species negatively affect each other indirectly through a shared predator.
How did the reintroduction of wolves in Yellowstone affect the ecosystem?
It stabilized stream banks, allowed bird and fish populations to recover, and decreased coyote numbers.
What role do wildlife corridors play in fragmented landscapes?
Wildlife corridors increase landscape connectivity, allowing species to move between habitats and enhancing biodiversity.
What is the main goal of restoration projects in ecology?
To recover ecological communities and their ecosystem functions and services.
What is the relationship between habitat size and species loss?
Larger habitat sizes generally predict lower rates of species loss.
What is the purpose of biomanipulation in environmental management?
To control species populations and improve ecosystem health by manipulating trophic interactions.
What is the role of heterotrophs in an ecosystem?
Heterotrophs are organisms that obtain their energy by consuming other organisms.
What is the difference between direct and indirect effects in food webs?
Direct effects involve immediate interactions between species, while indirect effects occur through a chain of interactions.
What is the significance of ecological networks?
Ecological networks depict various species interactions, not just trophic relationships, highlighting community dynamics.
What is the impact of species introductions on natural food webs?
Species introductions can alter food webs, leading to unexpected ecological consequences.
What is the ecological importance of large herbivores?
Large herbivores can affect plant and pollinator interactions, influencing ecosystem resilience.
What does the term 'species turnover' refer to?
Species turnover refers to the change in species composition over time while the total number of species remains constant.
What is the ecological significance of glaciation events?
Glaciation events can lead to major disturbances that affect species distribution and speciation rates.
What is the impact of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity?
Habitat fragmentation can lead to decreased biodiversity and increased extinction rates.