3. Repeated Measures ANOVAs
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the purpose of a Repeated Measures ANOVA?
Compare means when the same subjects are measured under multiple conditions or over time.
Data points are not independent
What are the two benefits of repeated measures?
Sensitivity
unsystematic variance is reduced
more sensitive to experimental effects
Economy
fewer participants are needed
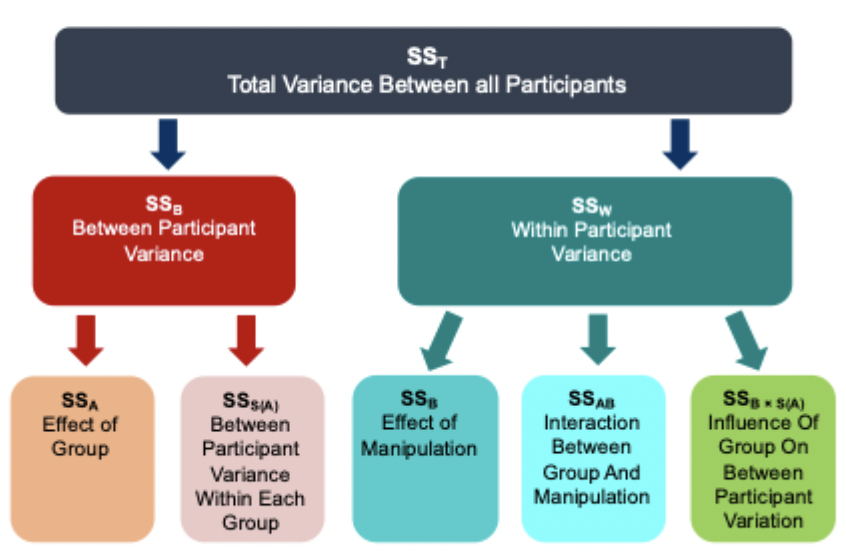
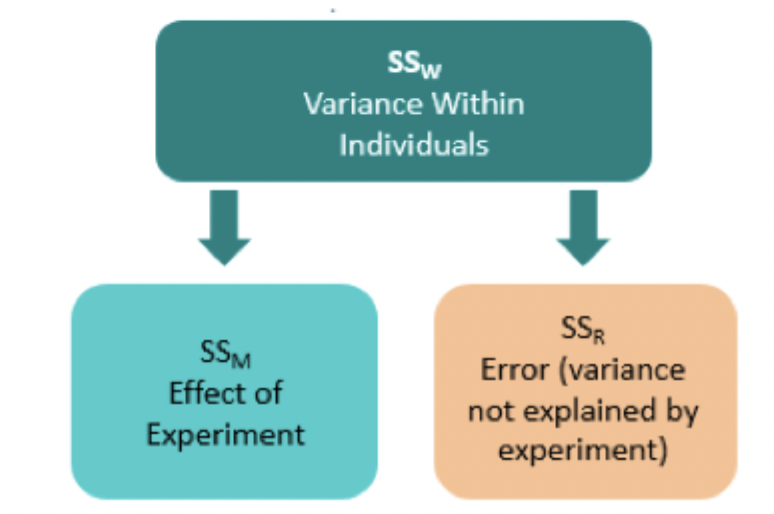
In repeated measure ANOVAs how can the variance be divided?
Variance within individuals divided into effect of experiment and error (variance not explained by experiment)
(variance between individuals becomes error variances)

What are the components of the F statistic?
F = MSM/MSR
MSM - variance explained by model (‘systematic variance’)
MSR - variance left over (noise)
What are the problems with repeated measures?
same participants in all conditions, so scores across conditions correlate
this violates the assumption of independence
Regarding sphericity, what does a standard ANOVA assume?
Standard ANOVA assumes that correlation between conditions is the same
or ‘variances in the differences between conditions are equal"‘
How is sphericity measured and what do we hope to find?
Measured using Mauchly’s test
We want no significant difference in correlations
p<.05, sphericity is violated
p>.05, sphericity is met
What is sphericity?
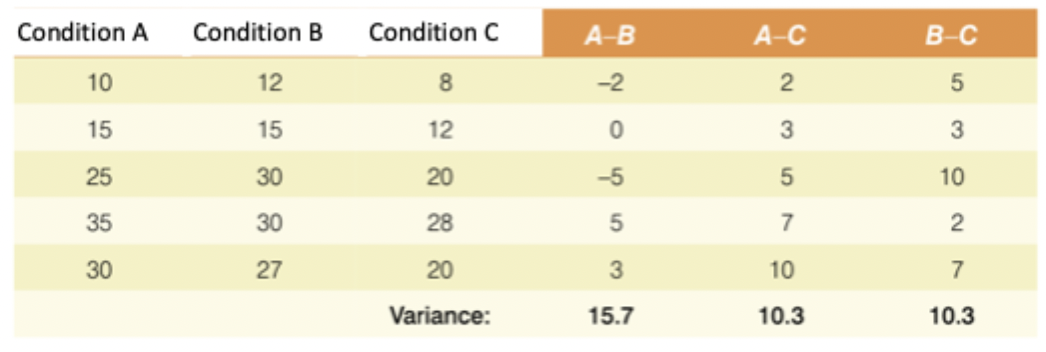
It means that the variances of the differences between all pairs of conditions are equal.
we are taking multiple measurements from the same subjects
results across conditions correlate (low scorers vs high scorers)
variance needs to be close across conditions

When does sphericity apply?
When you have more than 2 levels of your IV
think of trying to make a sphere - you need three dimensions
If you run Mauchly’s test on a variable with only 2 levels you will get blanks in the output
What does sphericity affect?
the F-statistic calculation.
If the assumption holds, your F-ratios are valid.
If it’s violated, your F-statistics become inflated, which increases your risk of a Type I error (false positive).
What to do if sphericity is violated?
you adjust the degrees of freedom to make the test more conservative.
What are the 3 common corrections used if sphericity is violated?
Greenhouse–Geisser (most common, more conservative)
Huynh–Feldt (less conservative)
Lower-bound (most conservative, rarely used)
What calculation do we make to correct sphericity?
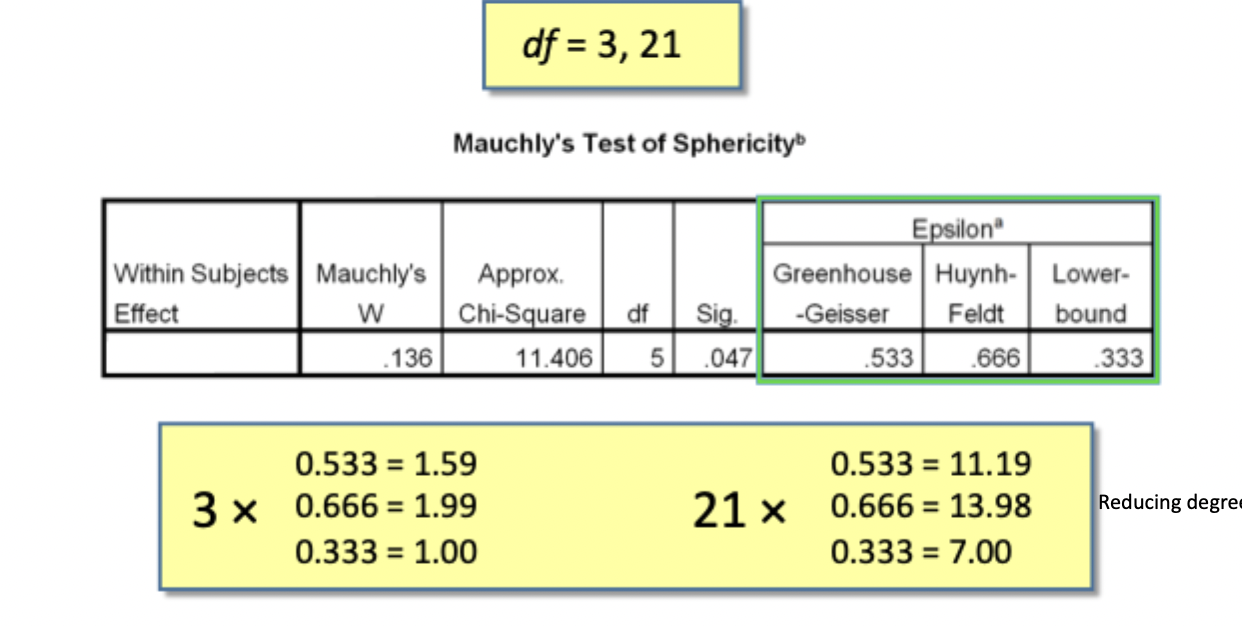
We multiply degrees of freedom by these estimates, thereby reducing degrees of freedom

How do we organise the data for SPSS in repeated measures ANOVA?
one row per participant
one column per condition
no need for coding variables
What is the Main ANOVA table called for repeated measures?
Tests of Within-subjects effects
In repeated measures where do you report from is mauchley’s test was non-significant
report from sphericity assumed row
In repeated measures where do you report from if sphericity is violates
report from the corrected rows e.g. greenhouse-geisser
How do you write up a repeated measures ANOVA
report F (df1,df2) and p for each main effect and any interactions
contrasts or post hoc tests can be reported in tables or in text
What is a mixed design ANOVA?
A mix of between-subjects and within-subjects factors.
Example: Different diet groups (between-subjects) measured at several time points (within-subjects).
Design: One factor varies between participants; the other within
produces 3 way interactions
How is the variance divided in mixed design ANOVA?