Lecture 1 Genetics BIOL3401
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to Genetics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Genetics
The study of genes, genetic variation and heredity
Traits
Are observable characteristics of an organism
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, double helix of two polynucleotide chains that carry genetic information
Gene
unit of heredity/ a sequence of DNA that encode a functional product
Chromosome
structure found inside the nucleus made of DNA packaged around proteins
Genome
all the DNA found within all our chromosomes
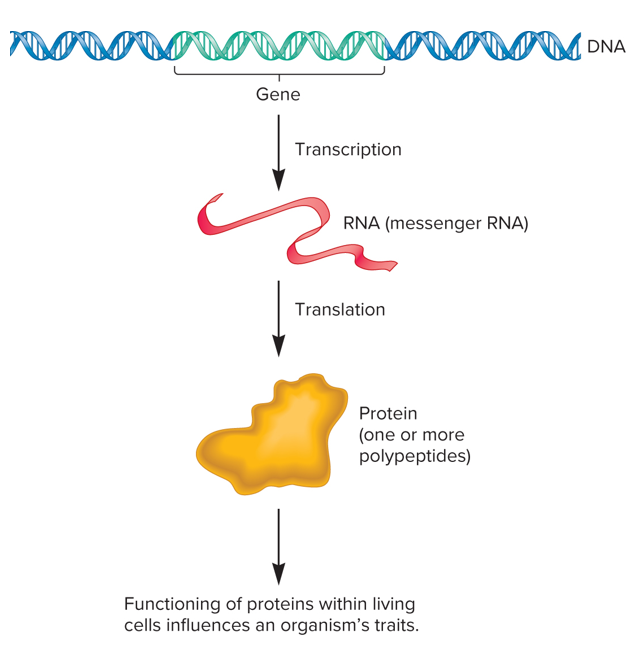
The central dogma
Genetic information flows only in one direction, from DNA, to RNA, to protein, or RNA directly to protein.
DNA replication
the two strands separate and each serve as template to make two identical copy
DNA is what into RNA and then what into protein?
DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated into protein based on genetic code.
What directs the order of each amino acid base code?
genetic code
A protein coding gene always starts with what?
start codon (ATG - Met)
A protein coding gene always ends with what?
stop codon (TAA, TGA, TAG)
Gene expression
the process by which information stored in DNA is accessed through transcription and translation
Gene expression dictates what
Cell differentiation
Proteome
All of the proteins that a cell makes at a given time
Biological function of proteins
Structural proteins
Transport proteins
Membrane proteins
Enzymes
Four main types of large molecules
Nucleic acids
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Lipids
What type of trait: The color of a flower
Morphological Trait
What type of trait: Ability to metabolize a sugar
Physiological trait
What type of trait: Mating calls of birds species
Behavioral trait
Molecular level
Different alleles of a gene produce different proteins
Allele – one variant (version) of a gene
Cellular Level
Changes of cellular function
Organismal Level
Changes in appearance, behavior and other trait
Population Level
Survival, fitness and evolution
Traits are the result of what?
The interaction between genes and the environment
Sexually reproducing species are commonly what?
Diploid
Homologs contain….
The same genes, not necessarily the same alleles
Biological Evolution
The genetic makeup of a population can change over many generations
Natural Selection
the process in which individuals with greater reproductive success are more likely to pass their genes to future generations
Model organisms
Non-human species that are extensively studied to reveal the mechanisms of biological phenomena
Knockout (KO)
complete loss of function
Necessity
Loss of function analysis
Sufficiency
Rescue or gain of function anaysis
Transmission Genetics
Question: Inheritance patterns of traits as they are passed from parents to offspring
Approach: Genetic cross
Molecular Genetics
Question: Biochemical understanding of the hereditary material
Approach: Detailed analysis of DNA, RNA and proteins
Population Genetics
Question: Genetic variation and its role in evolution
Approach: Mathematical theories to explain the prevalence of certain alleles within populations
“Kingsley 3” rules – If you want to prove that factor A causes phenomena B, you need to show:
A is there at the right place and right time when B happens
Necessity: Loss of function analysis – Loss of A causes change of B
Sufficiency: Rescue or gain of function analysis – restoring A fixes B, more of A causes more of B