Unit 3
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
226 Terms
What is the origin of the Splenius Capitis?
• Lower ½ Ligamentum Nuchae
• Spinous Processes C7-T4
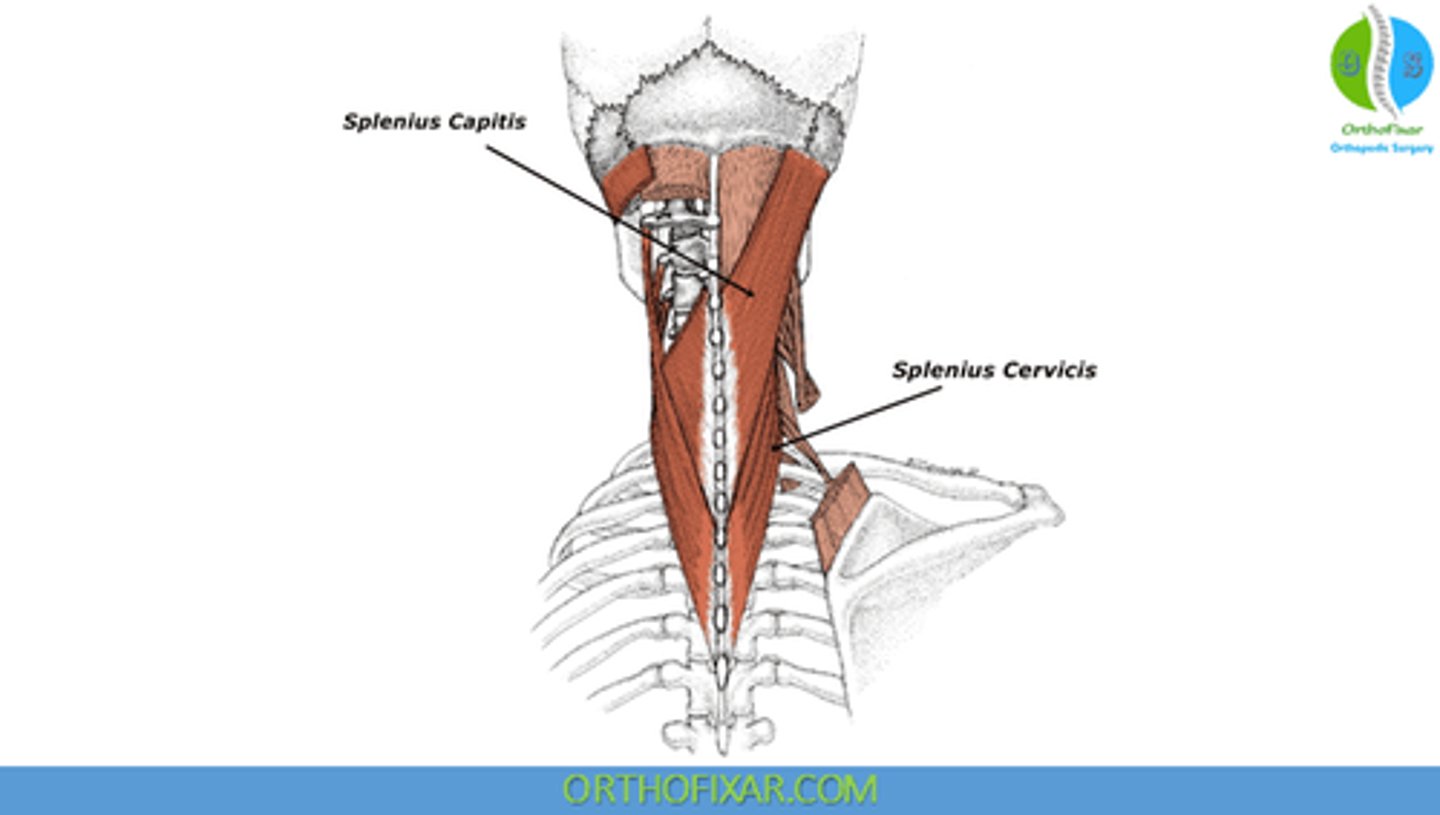
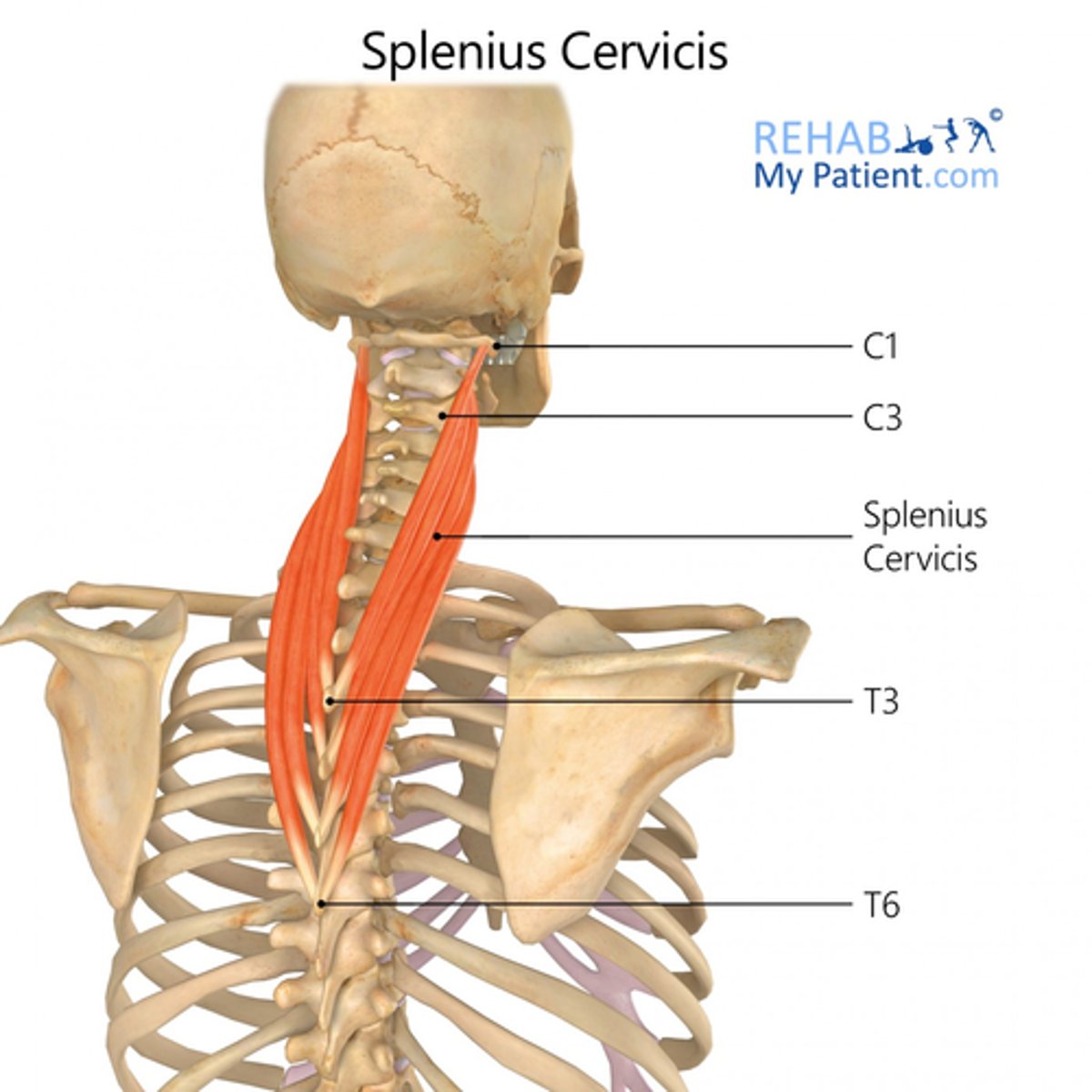
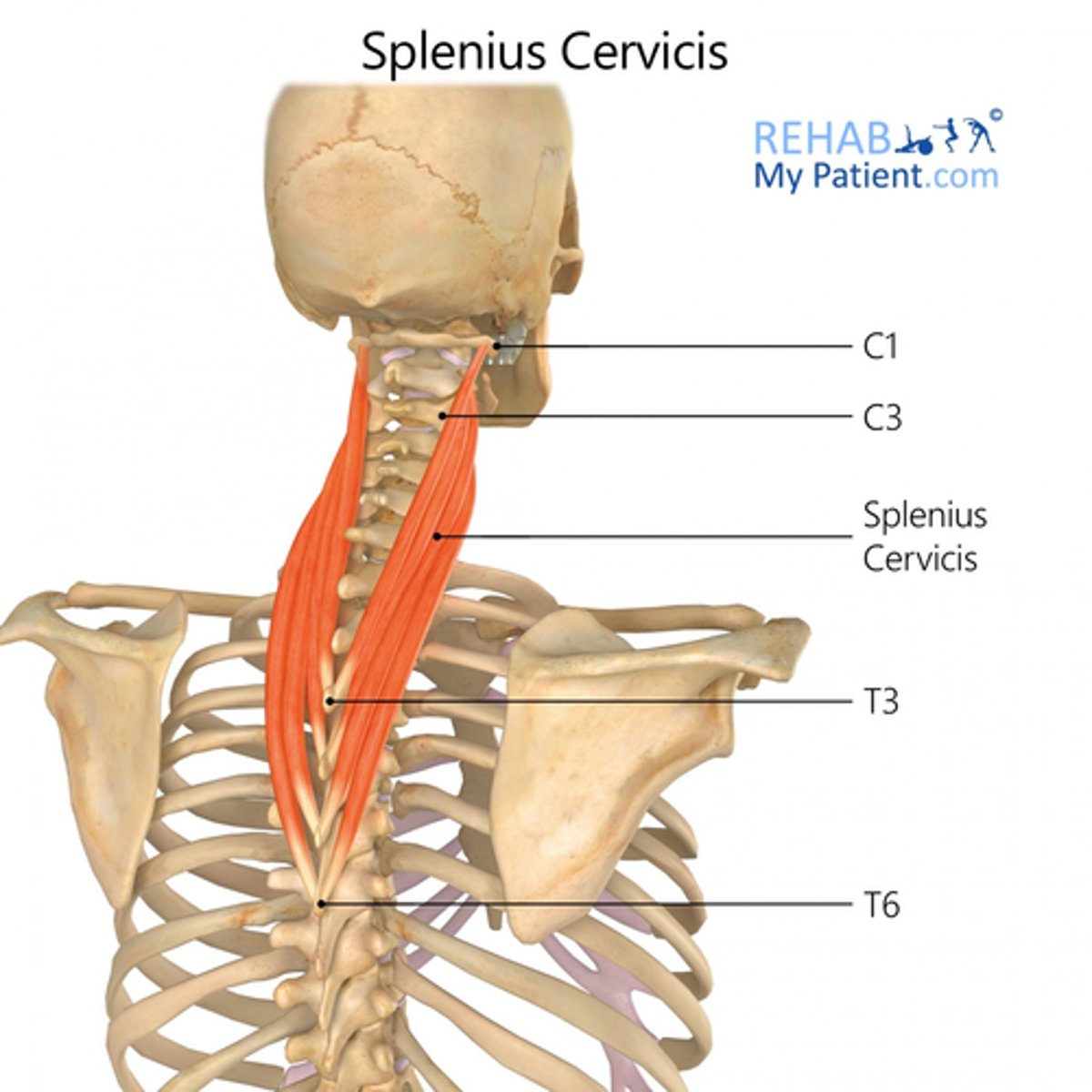
What is the origin of the Splenius Cervicis?
• Spinous processes T3 - T6
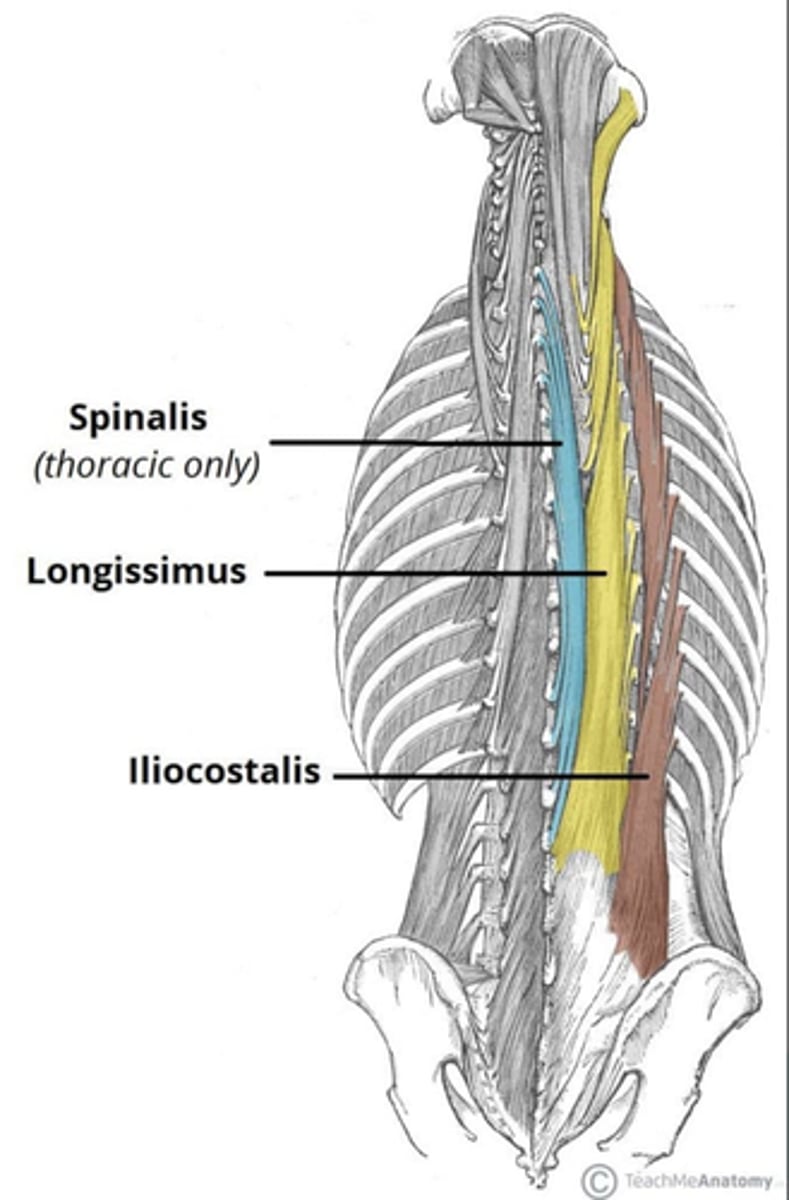
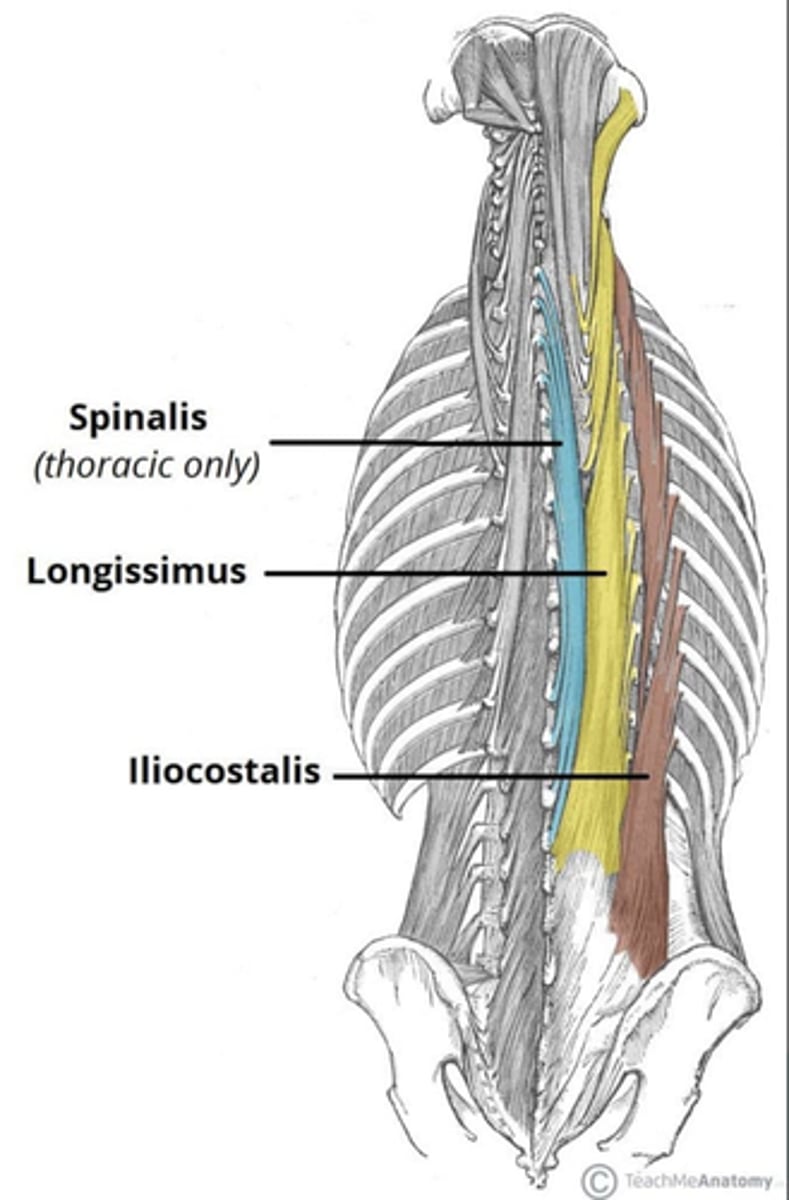
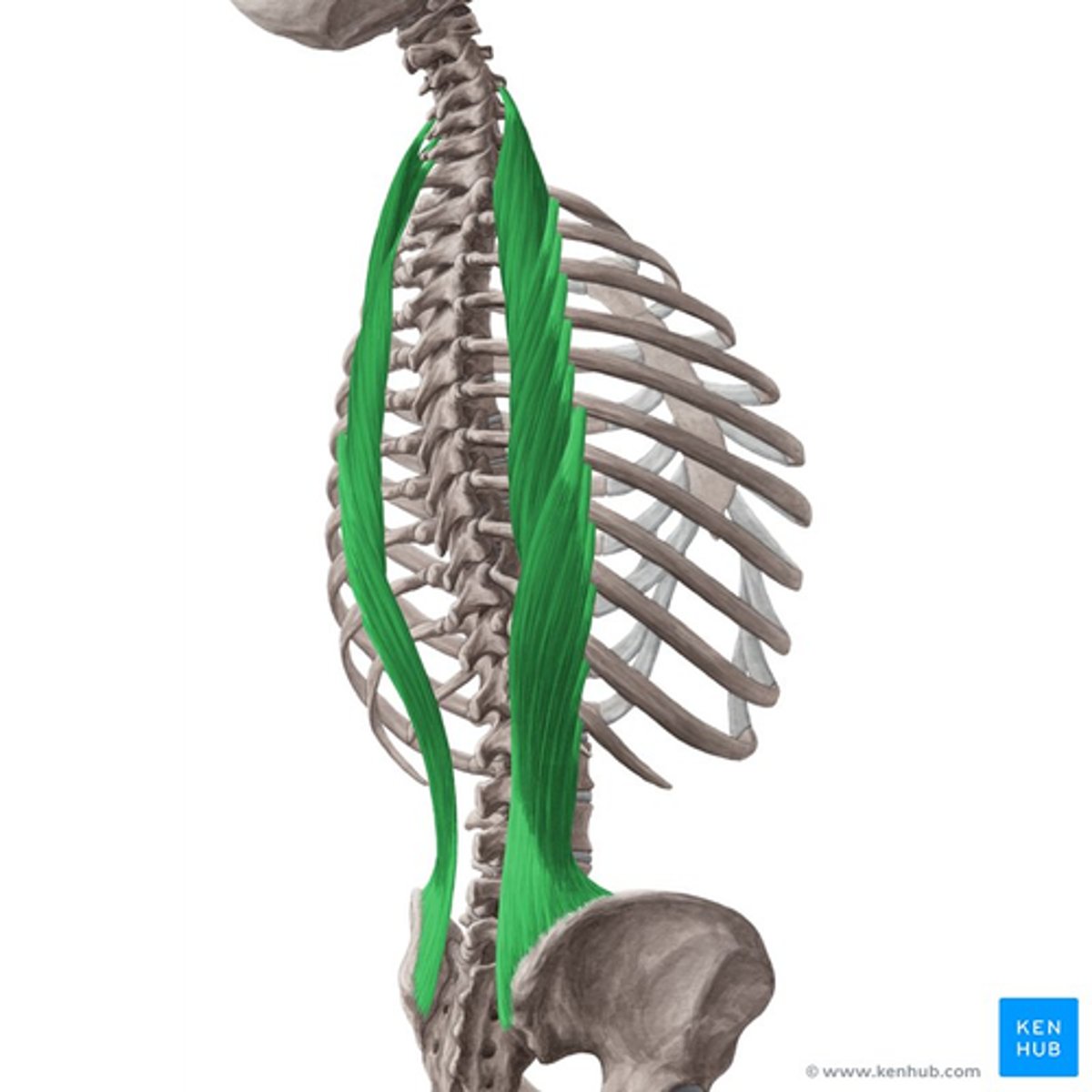
What is the origin of the Iliocostalis?
• Spinous processes
• Ribs
• Ilium
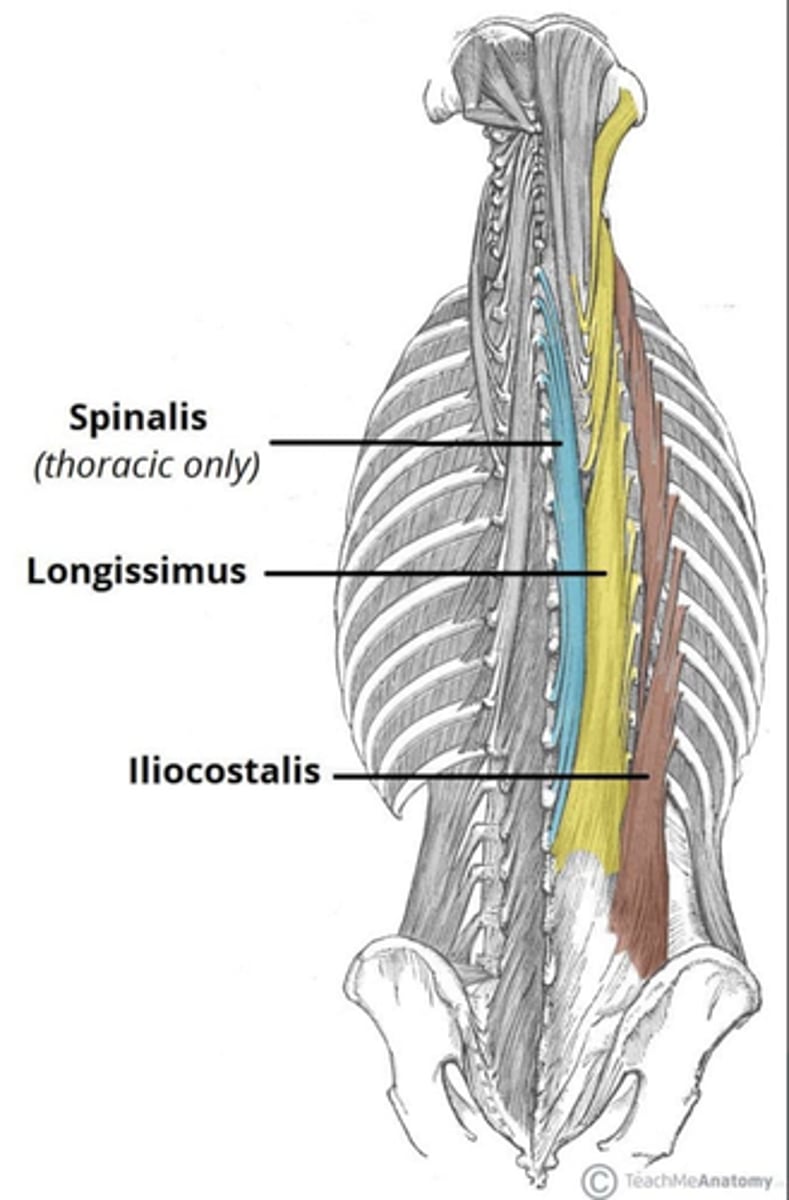
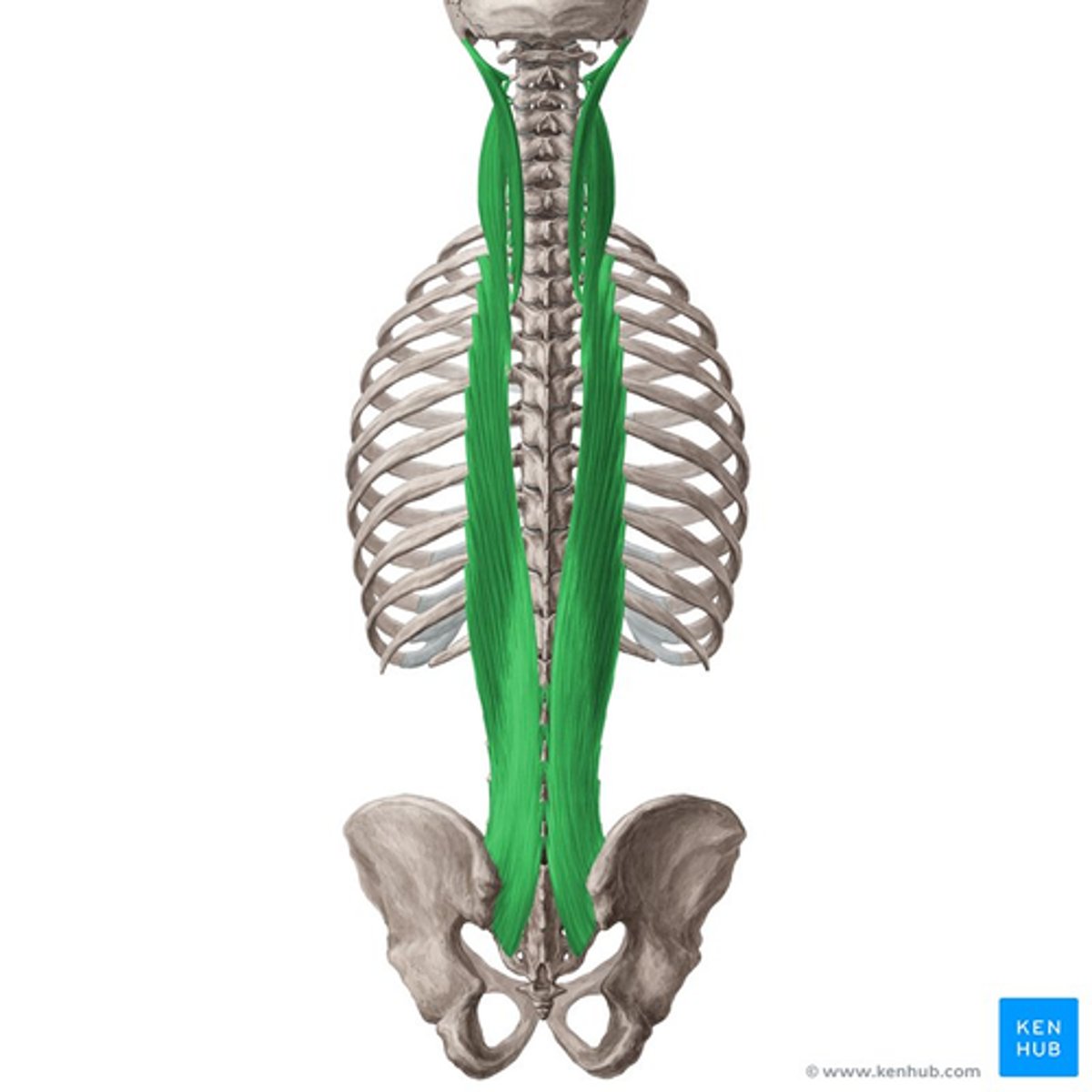
What is the origin of the Longissimus?
• Transverse processes
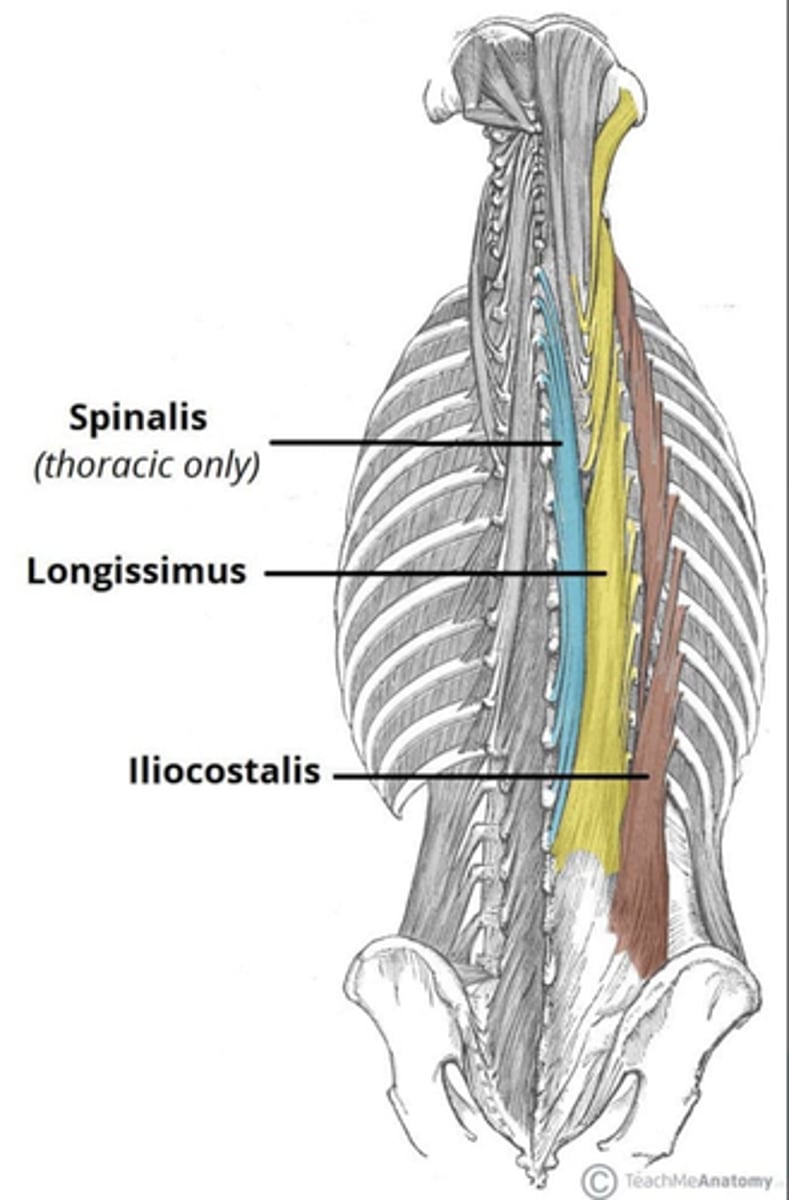
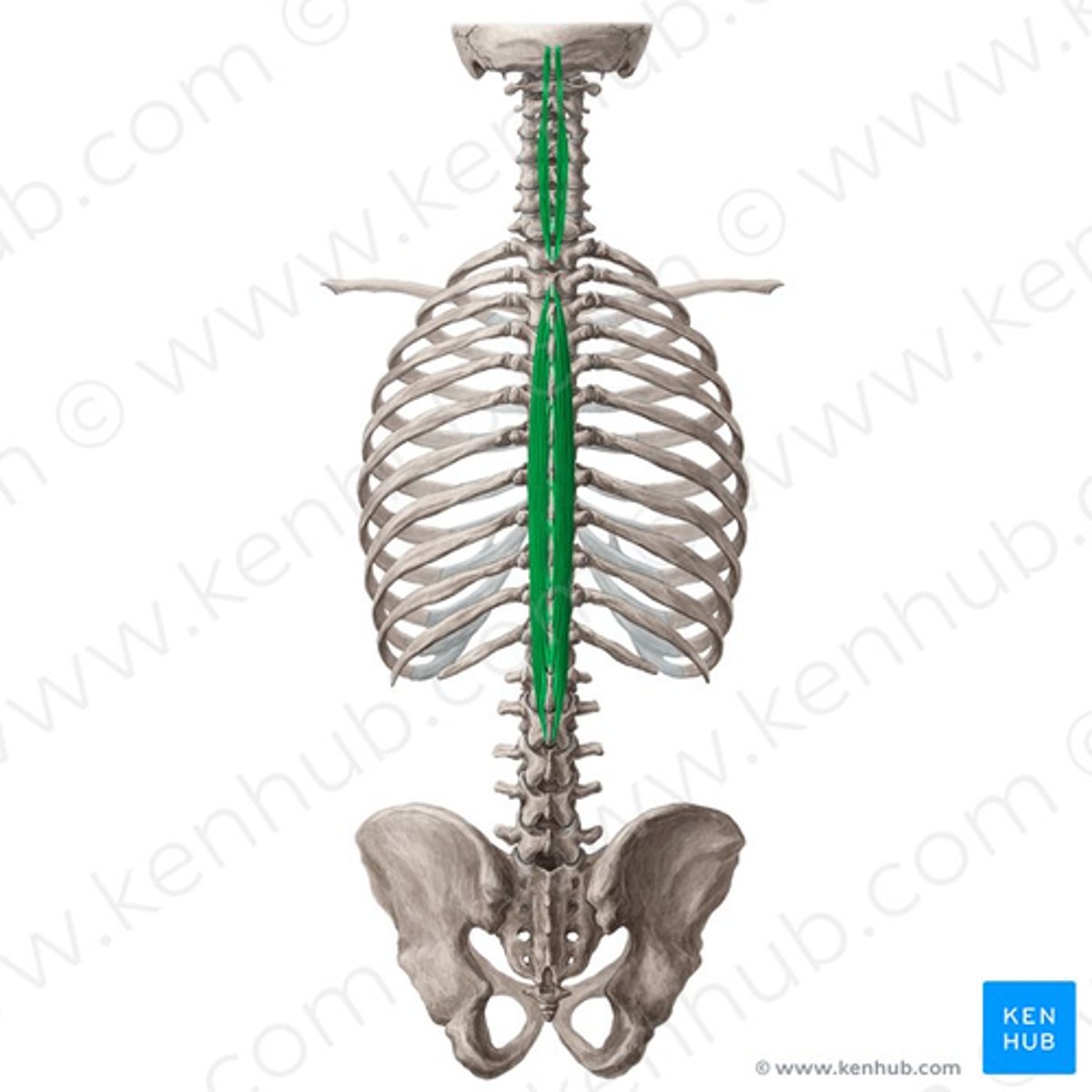
What is the origin of the Spinalis?
• Spinous processes
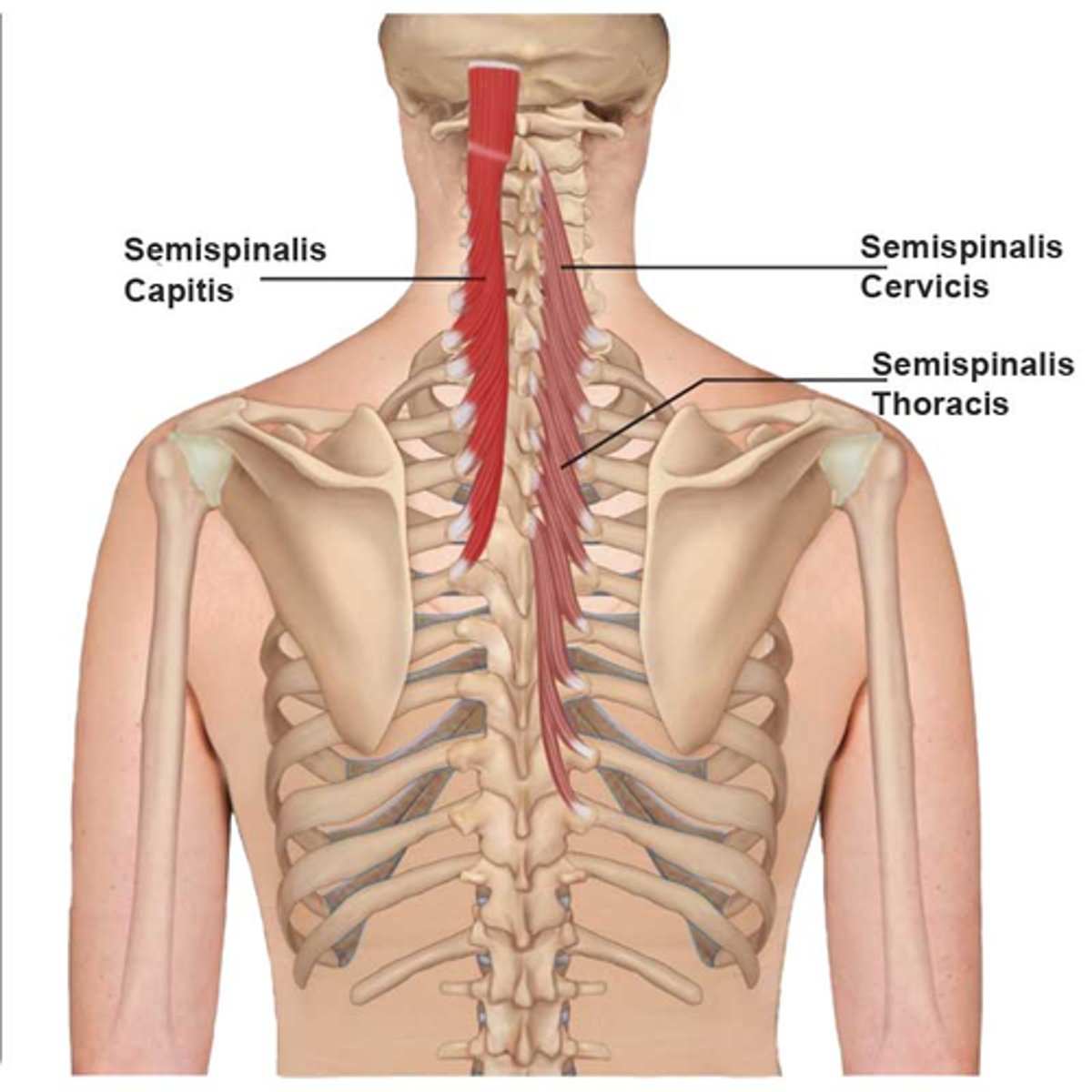
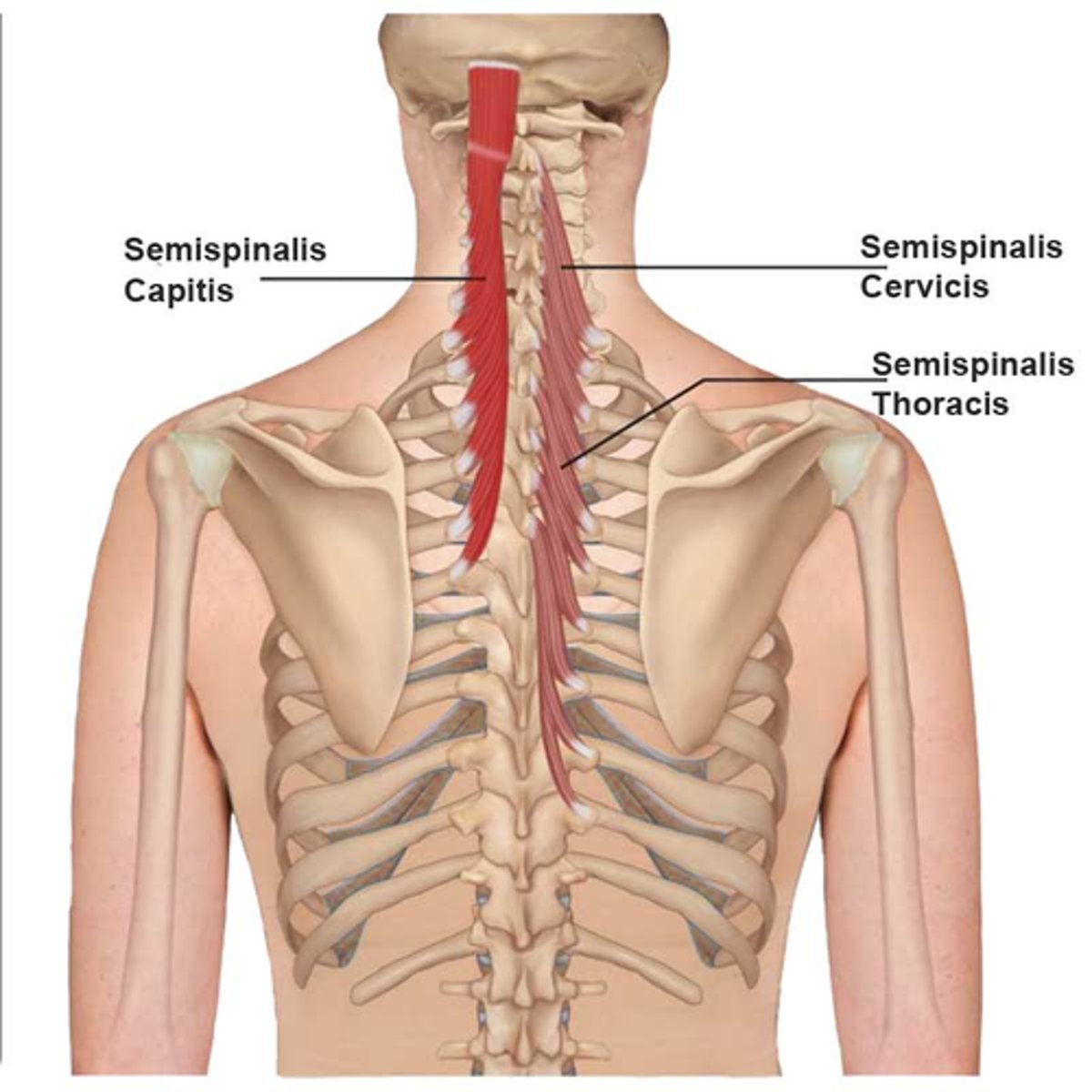
What is the origin of the Semispinalis (Thoracis,Cervicis and Capitus)?
• Lower Thoracic Transverse Processes
* Crosses 4-6 vertebral levels to insertion *
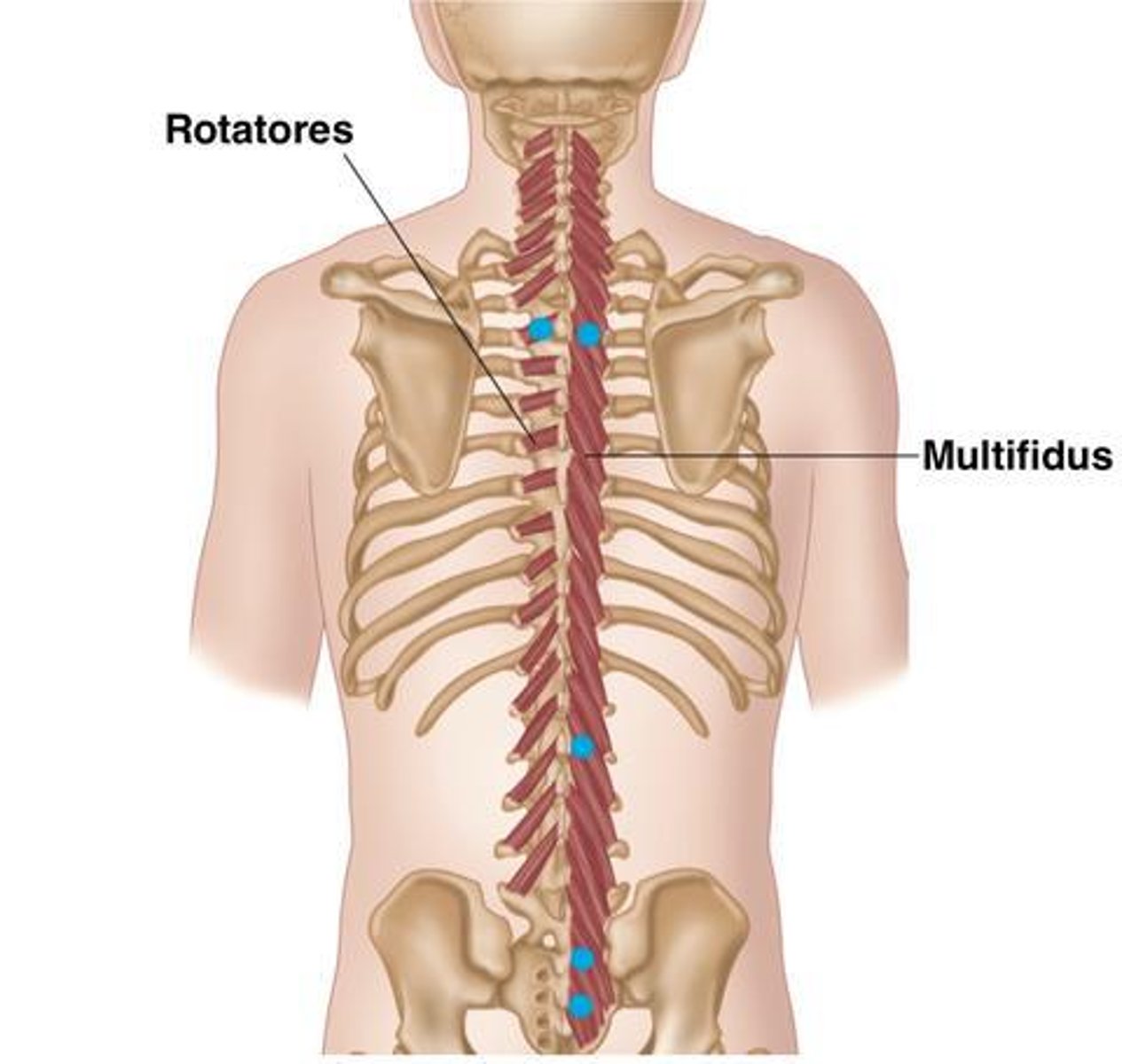
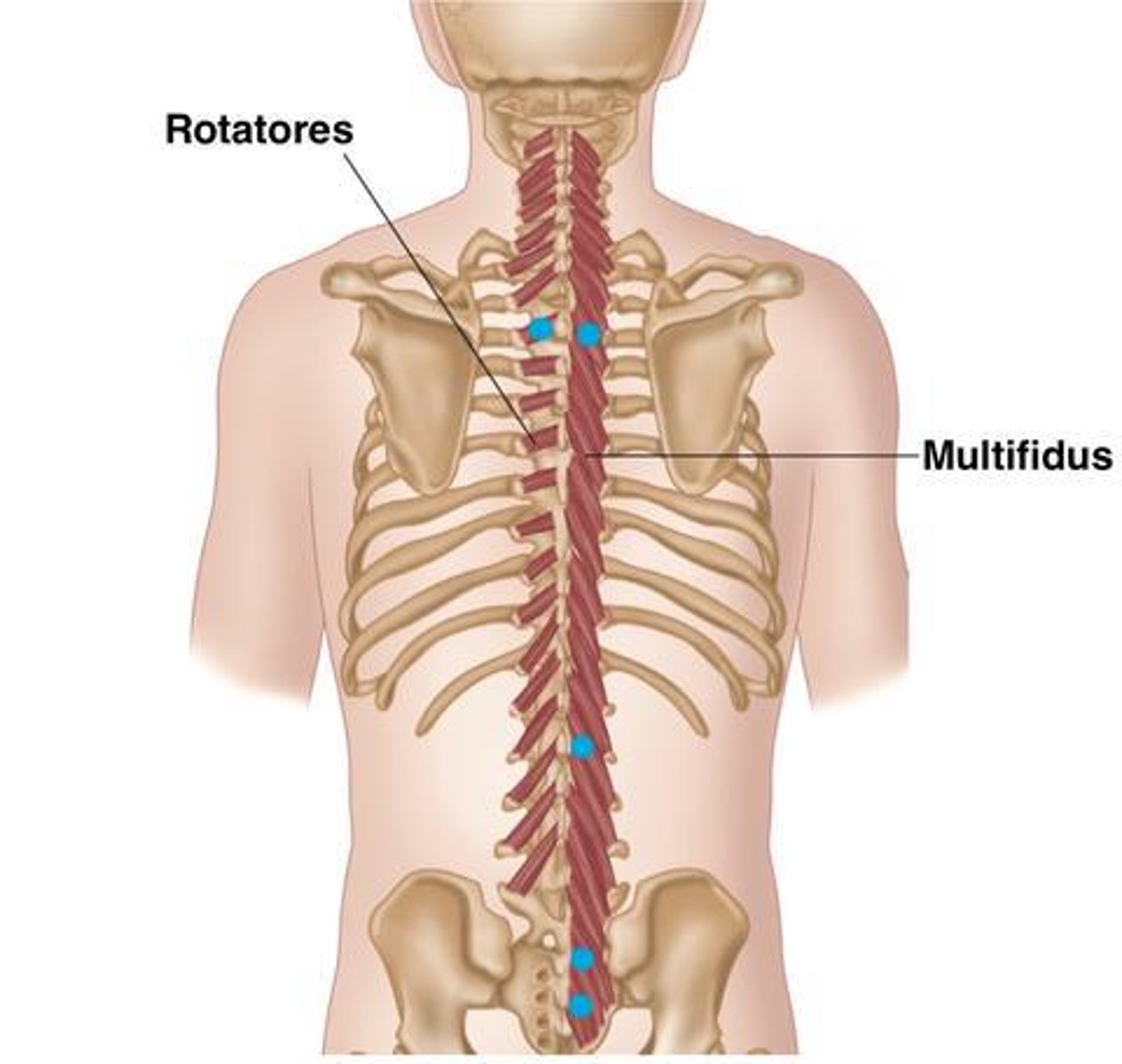
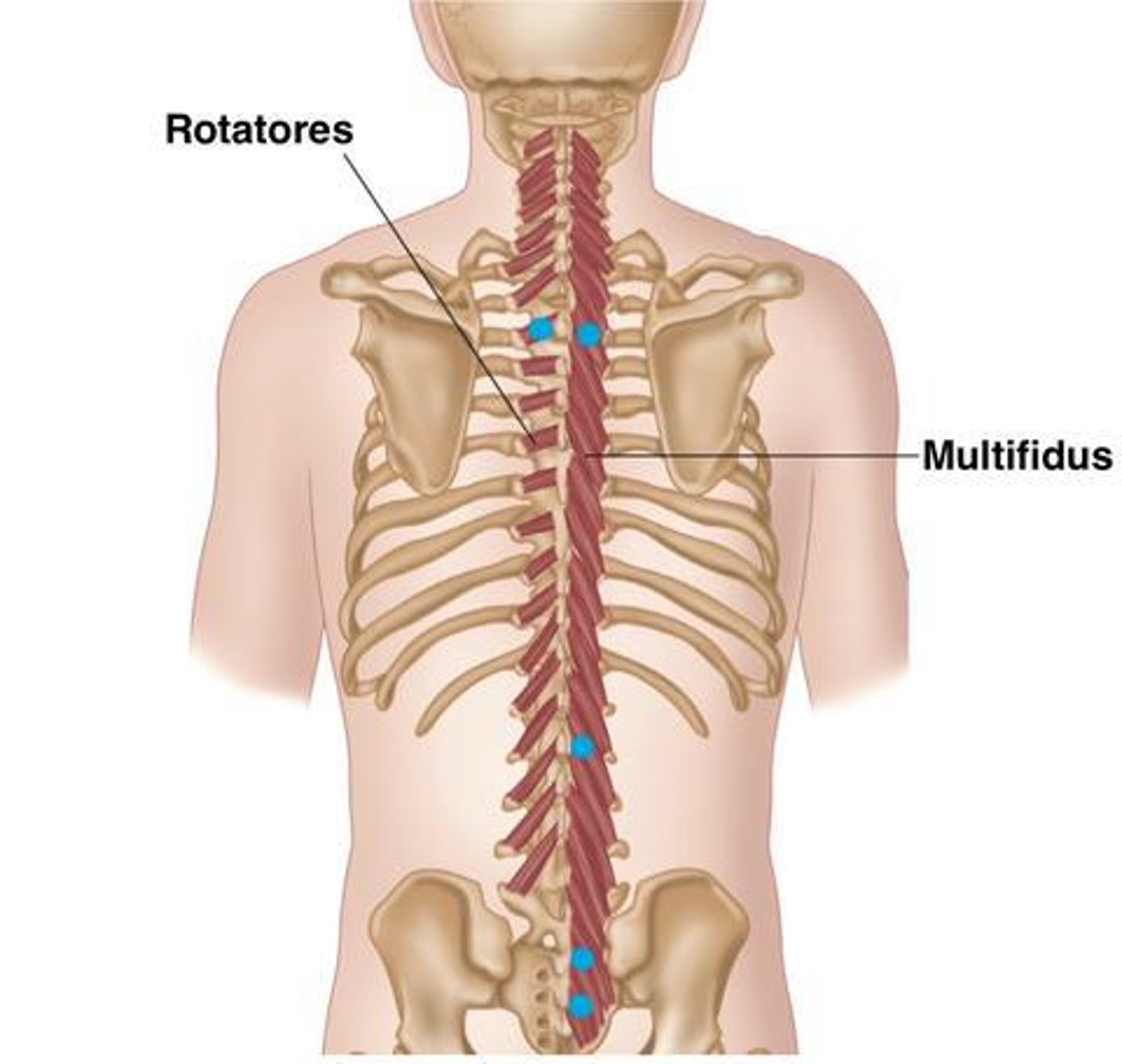
What is the origin of the Multifidus?
Crosses 2-4 vertebral levels to insertion
• Erector Spinae muscles
• Mamillary Processes of Lumbar Vertebrae
• Transverse Processes Thoracic Vertebrae
• Articular Processes Cervical Vertebrae
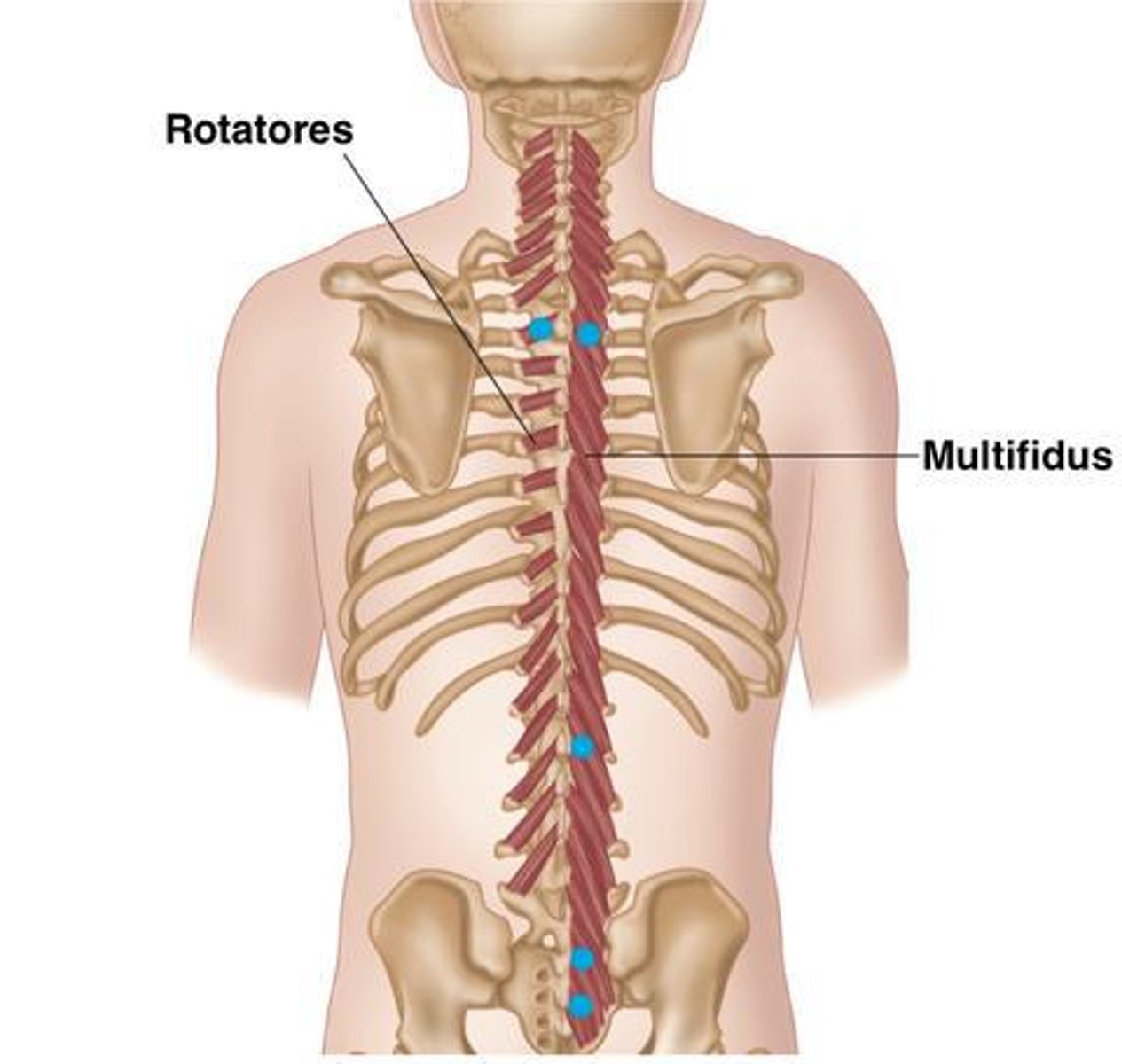
What is the origin of the Rotatores?
• Mammillary processes (L)
• Transverse processes (T)
• Articular processes (C)
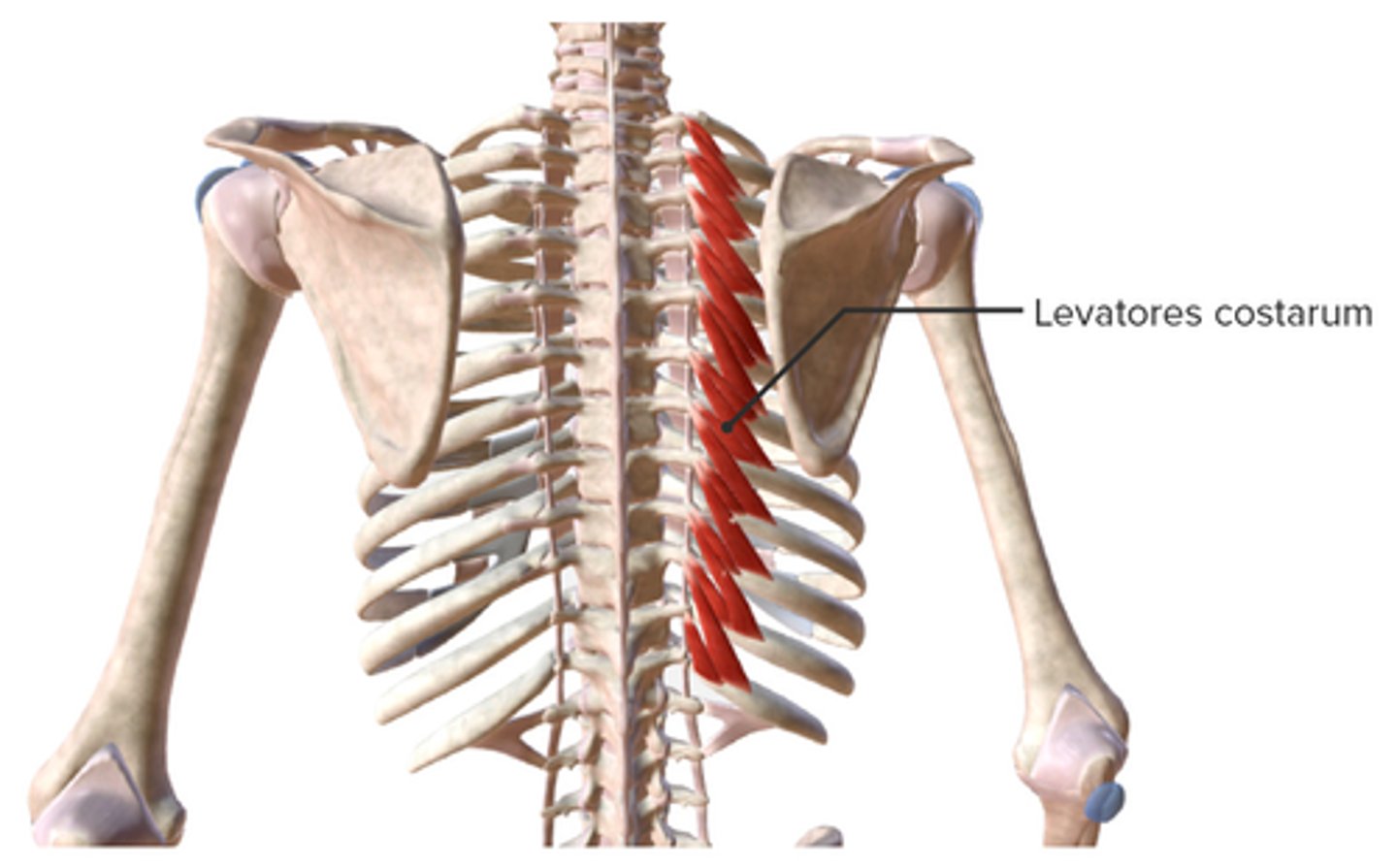
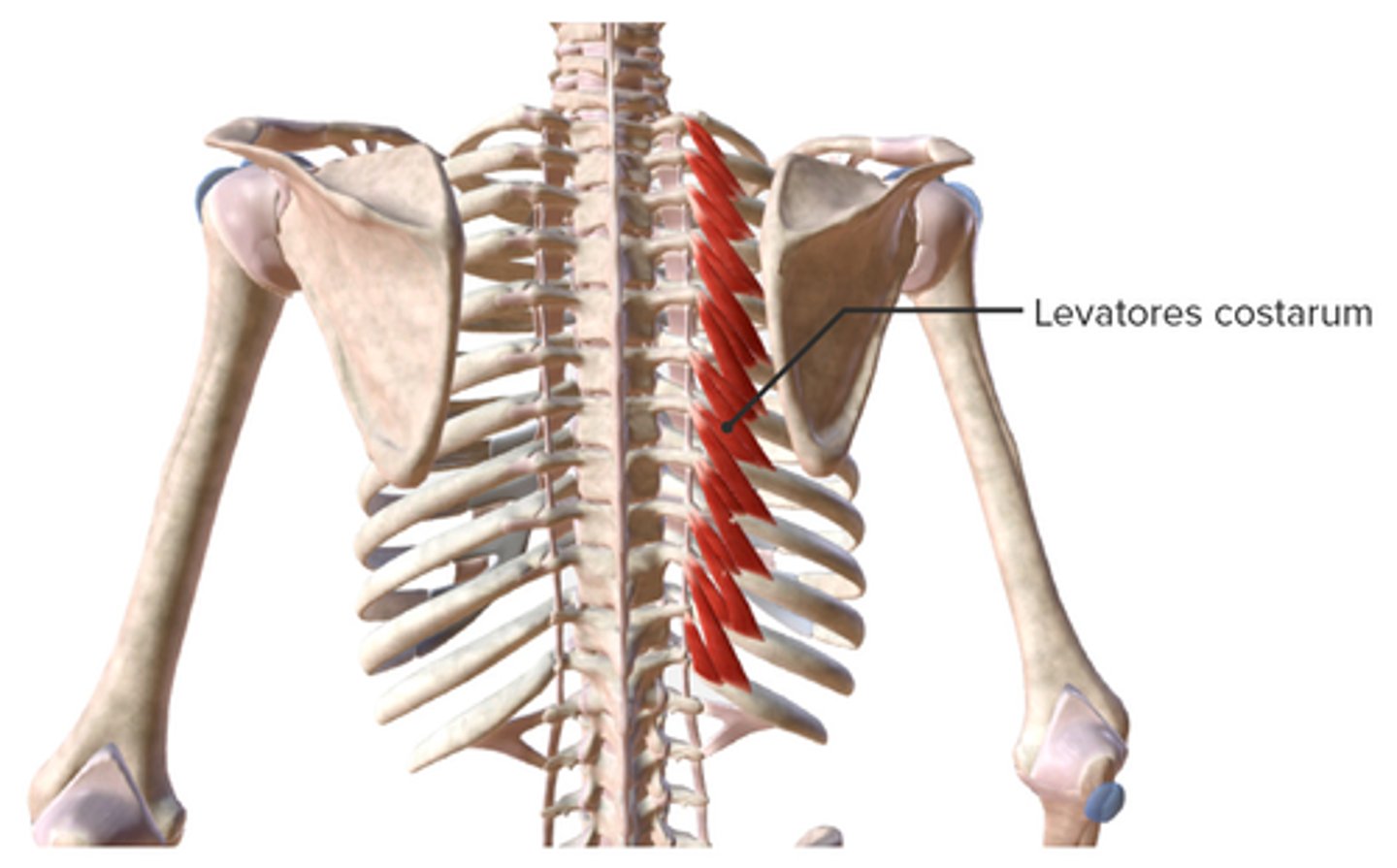
What is the origin of the Levator Costorum?
• Transverse Processes C7-T11
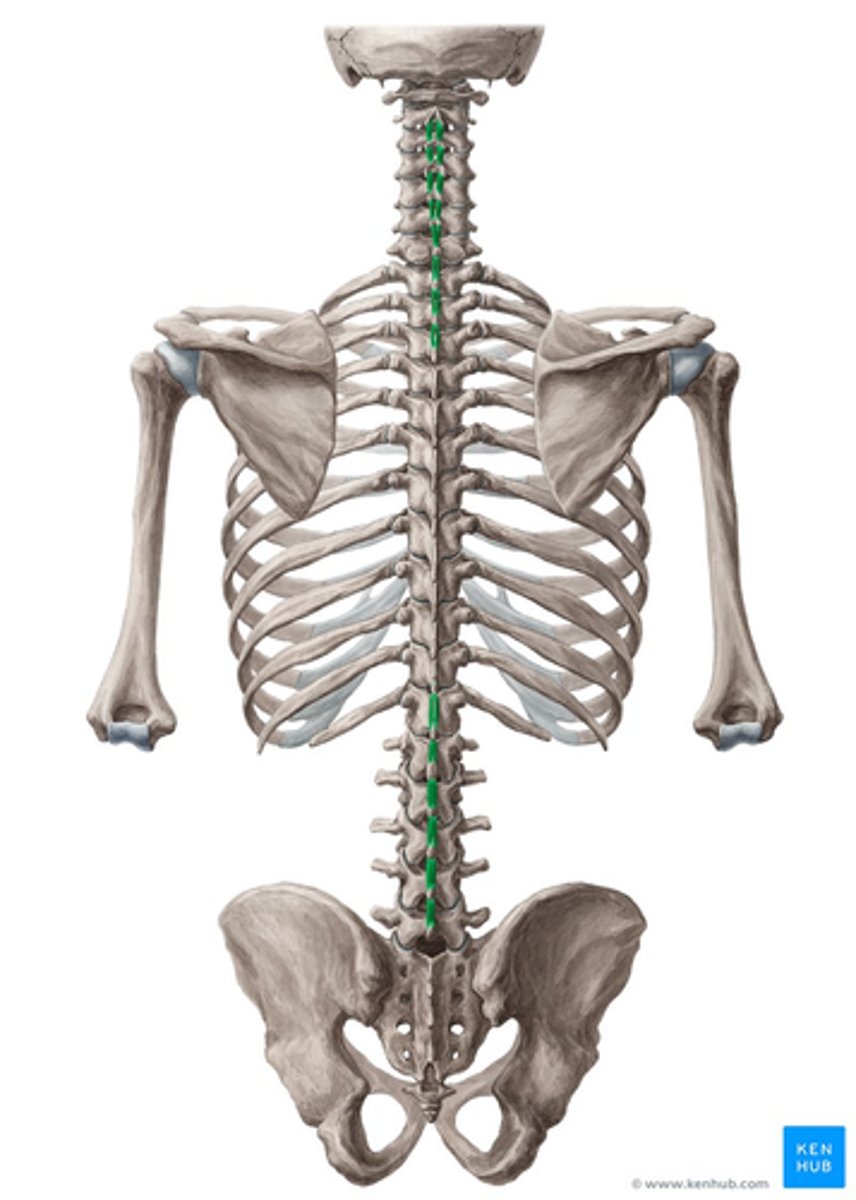
What is the origin of the Interspinales?
• Spinous Processes
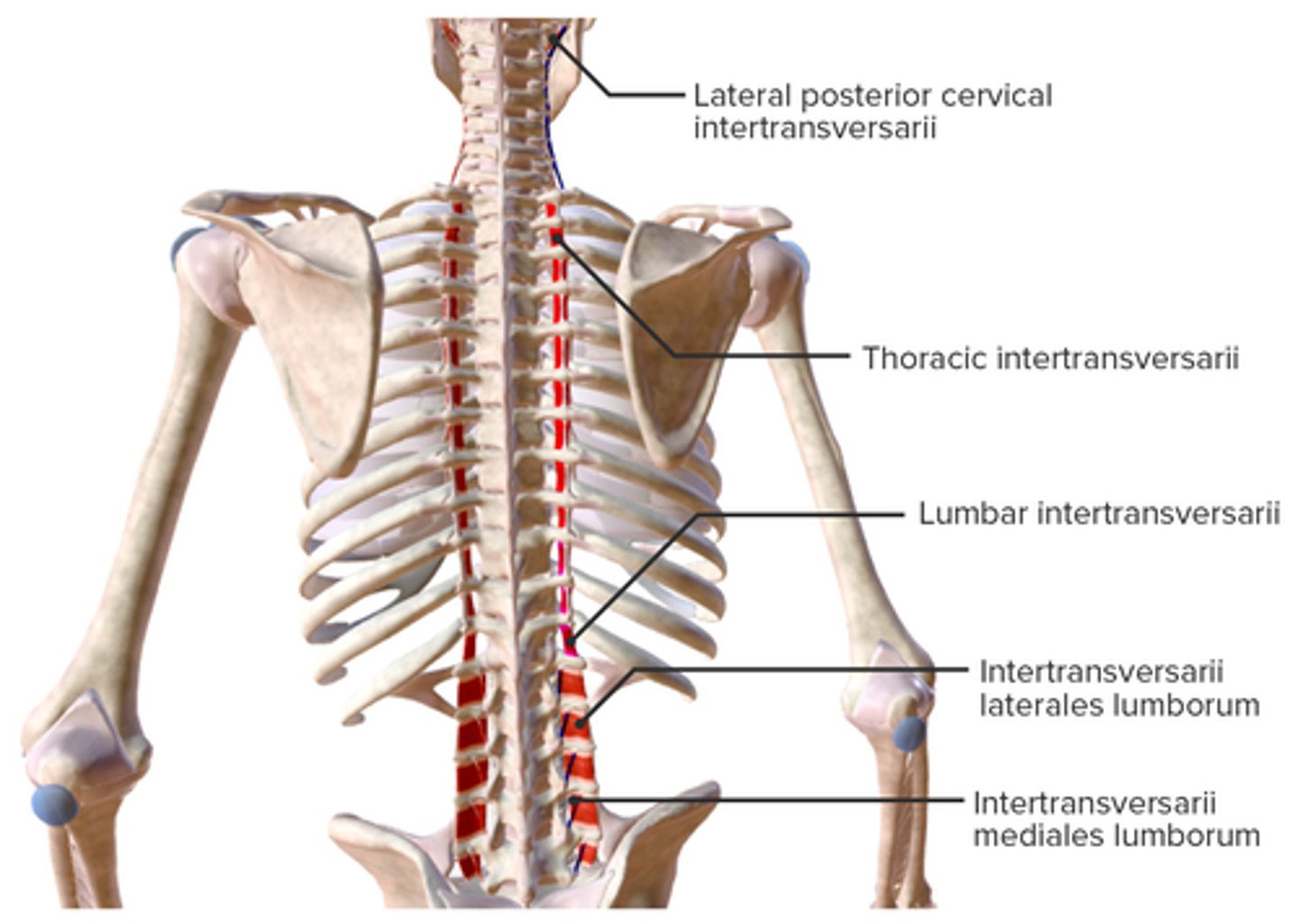
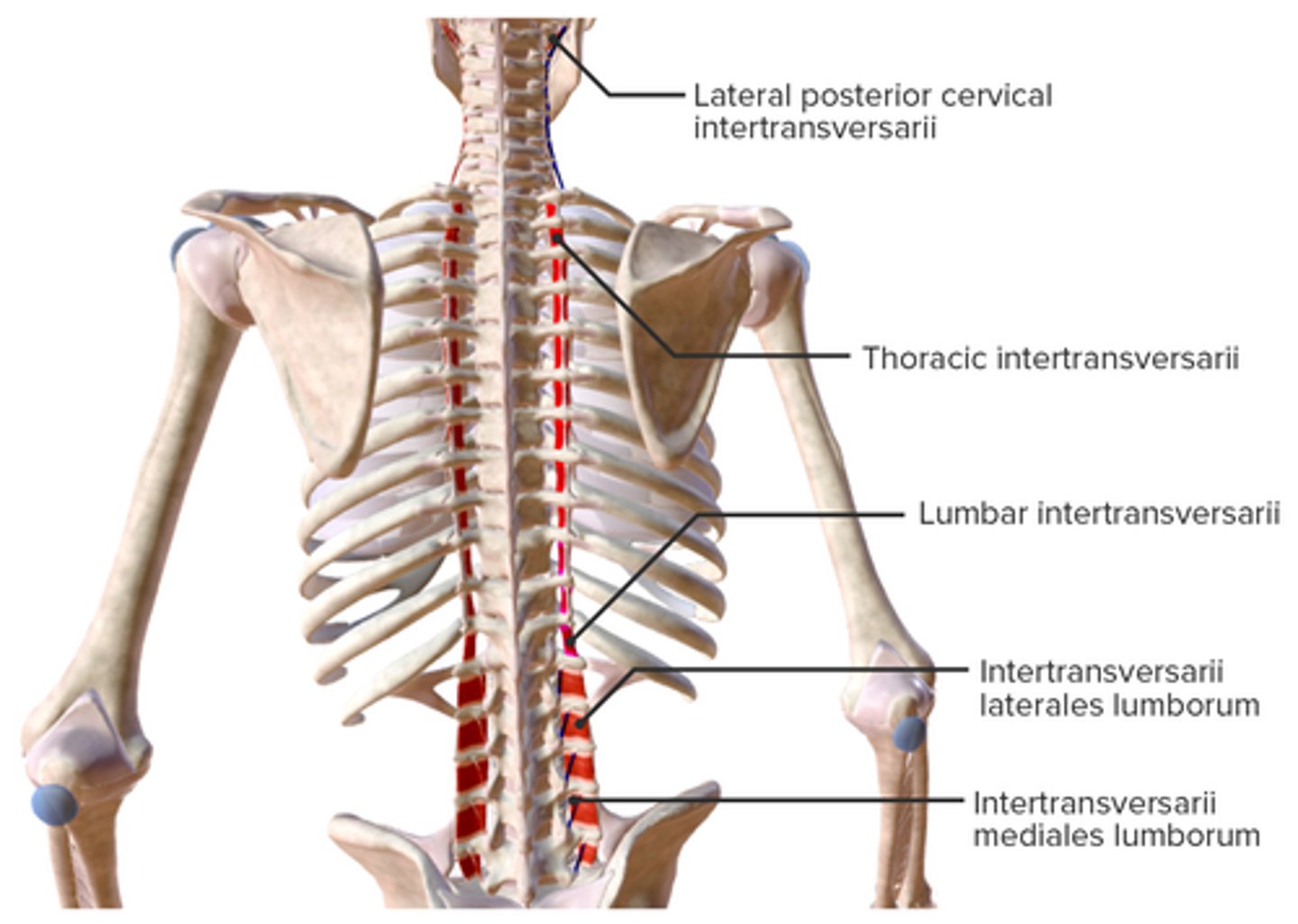
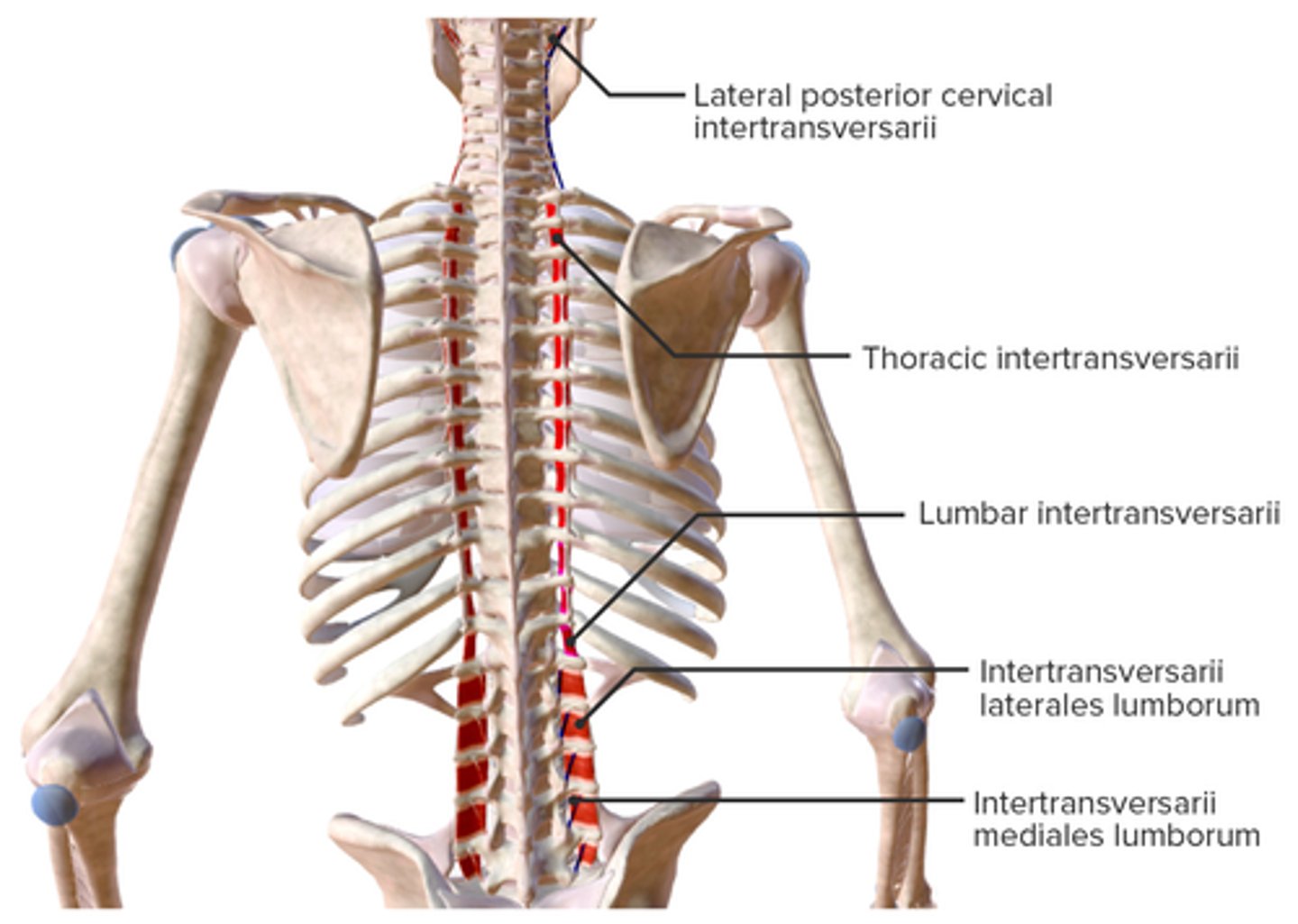
What is the origin of the Intertransversarii?
• Transverse Processes
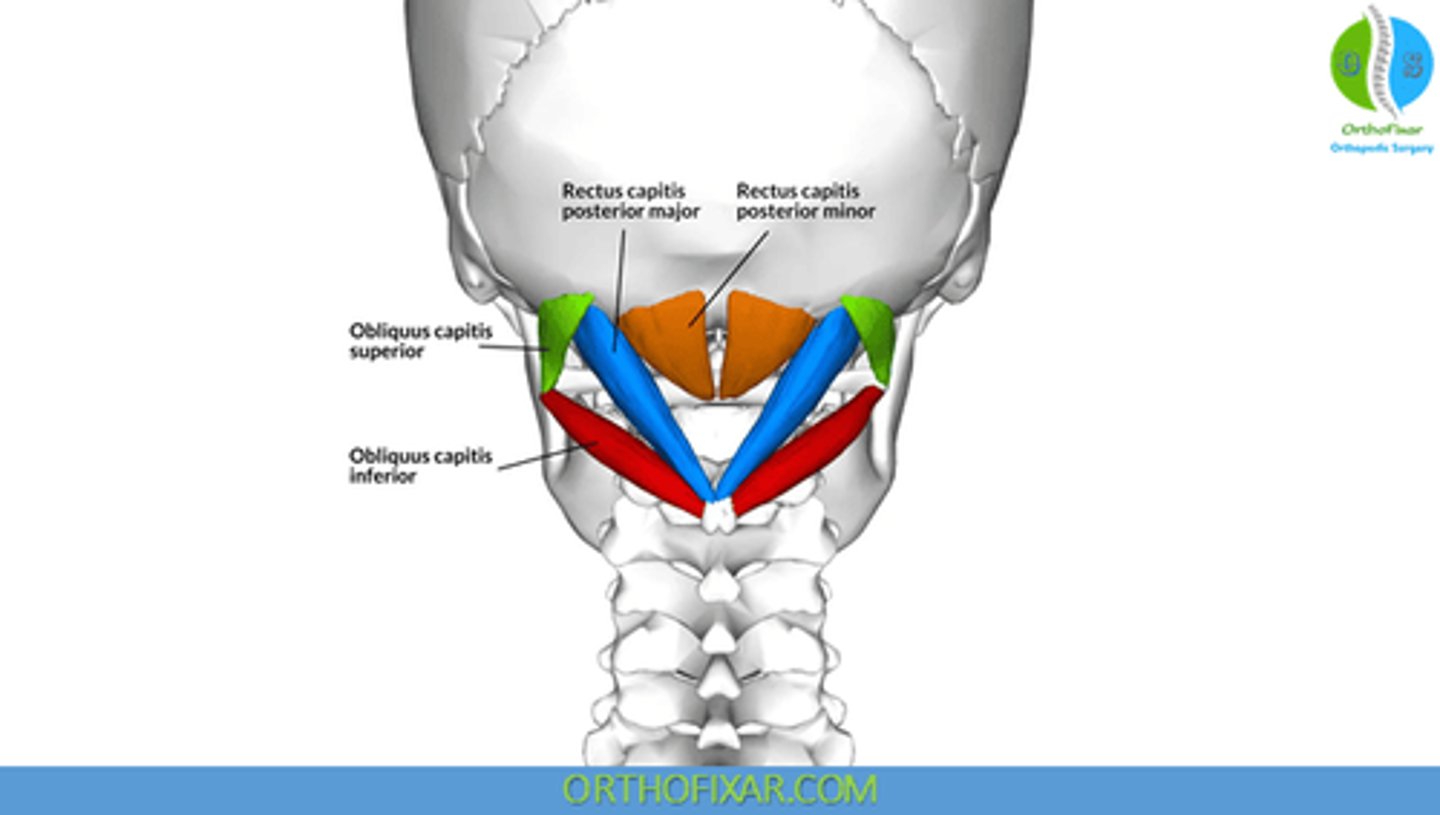
What is the origin of the Rectus Capitis Posterior Major?
• Spinous Process C2 (Axis)
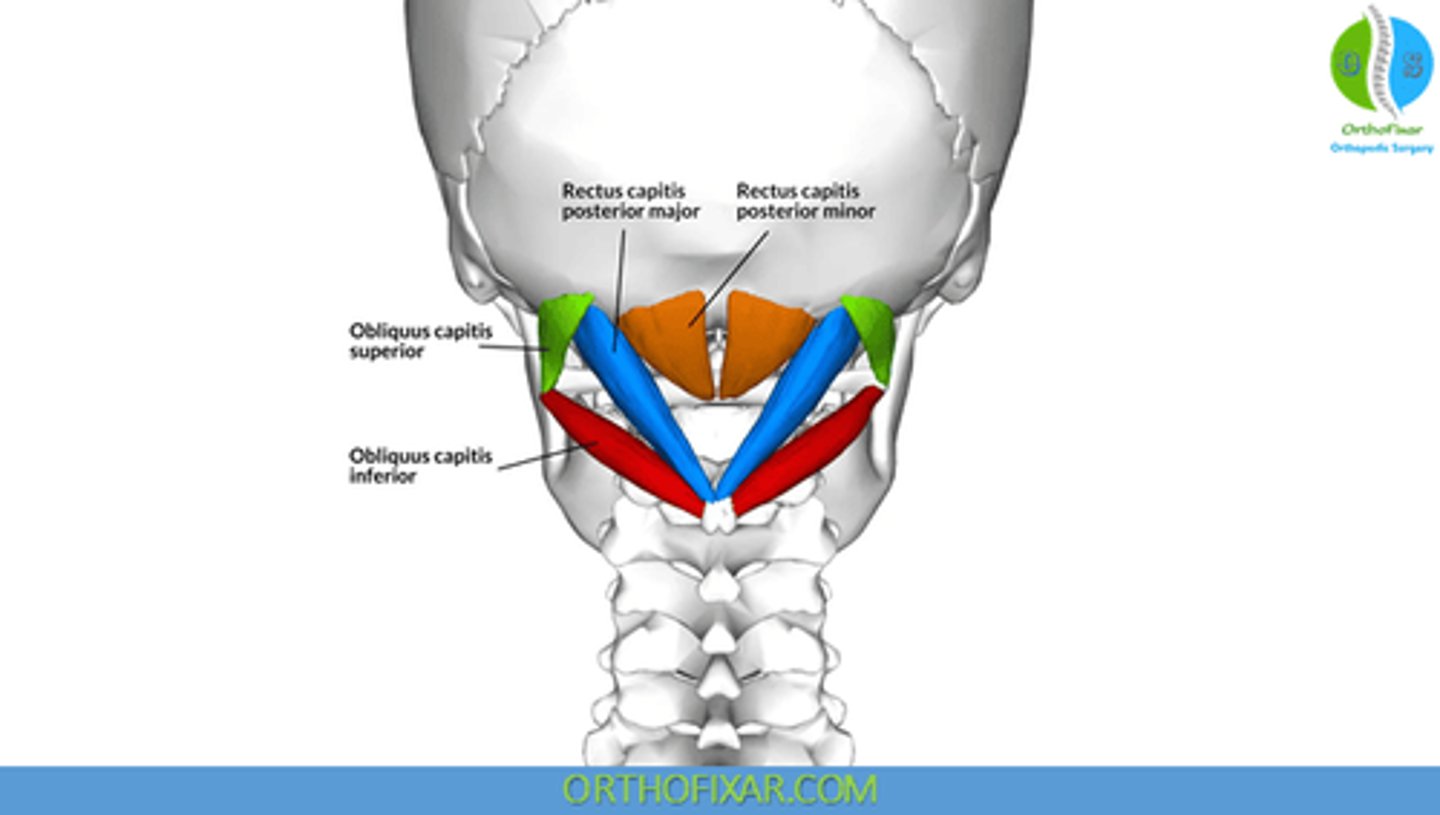
What is the origin of the Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor?
• Posterior Tubercle C1 (Atlas)
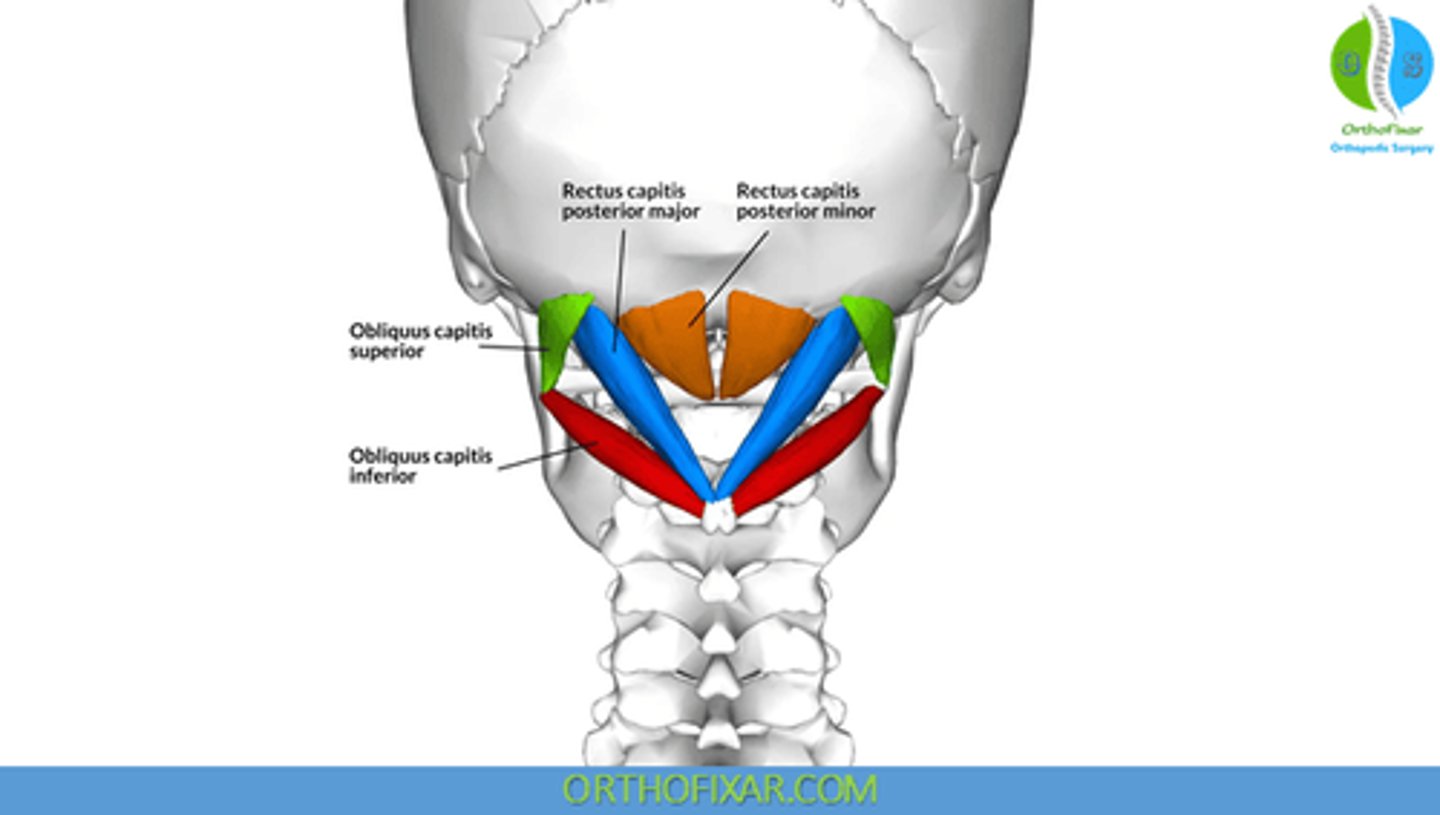
What is the origin of the Obliquus Capitis Superior?
• Transverse Process C1 (Atlas)
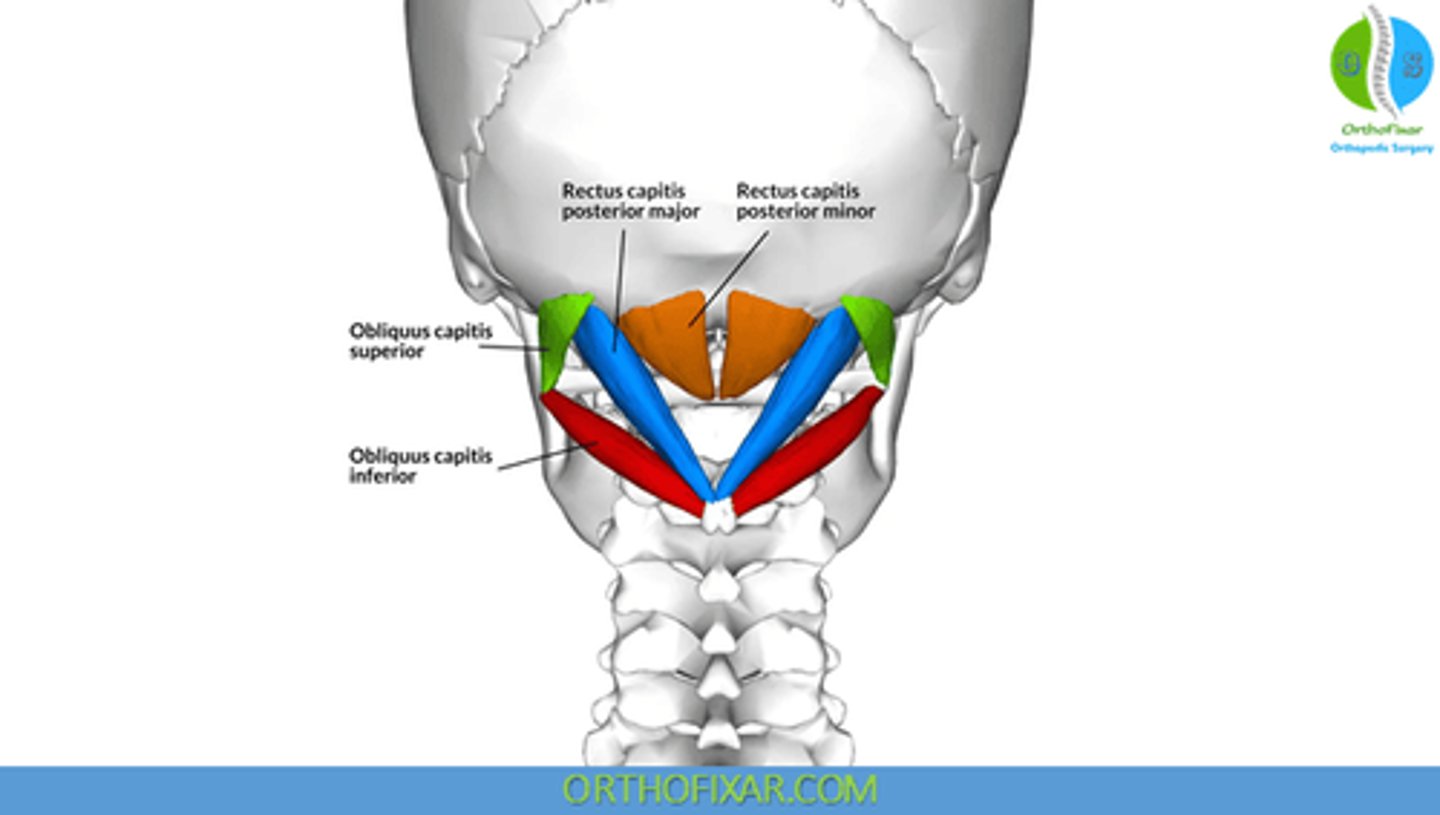
What is the origin of the Obliquus Capitis Inferior?
• Spinous Process C2 (Axis)
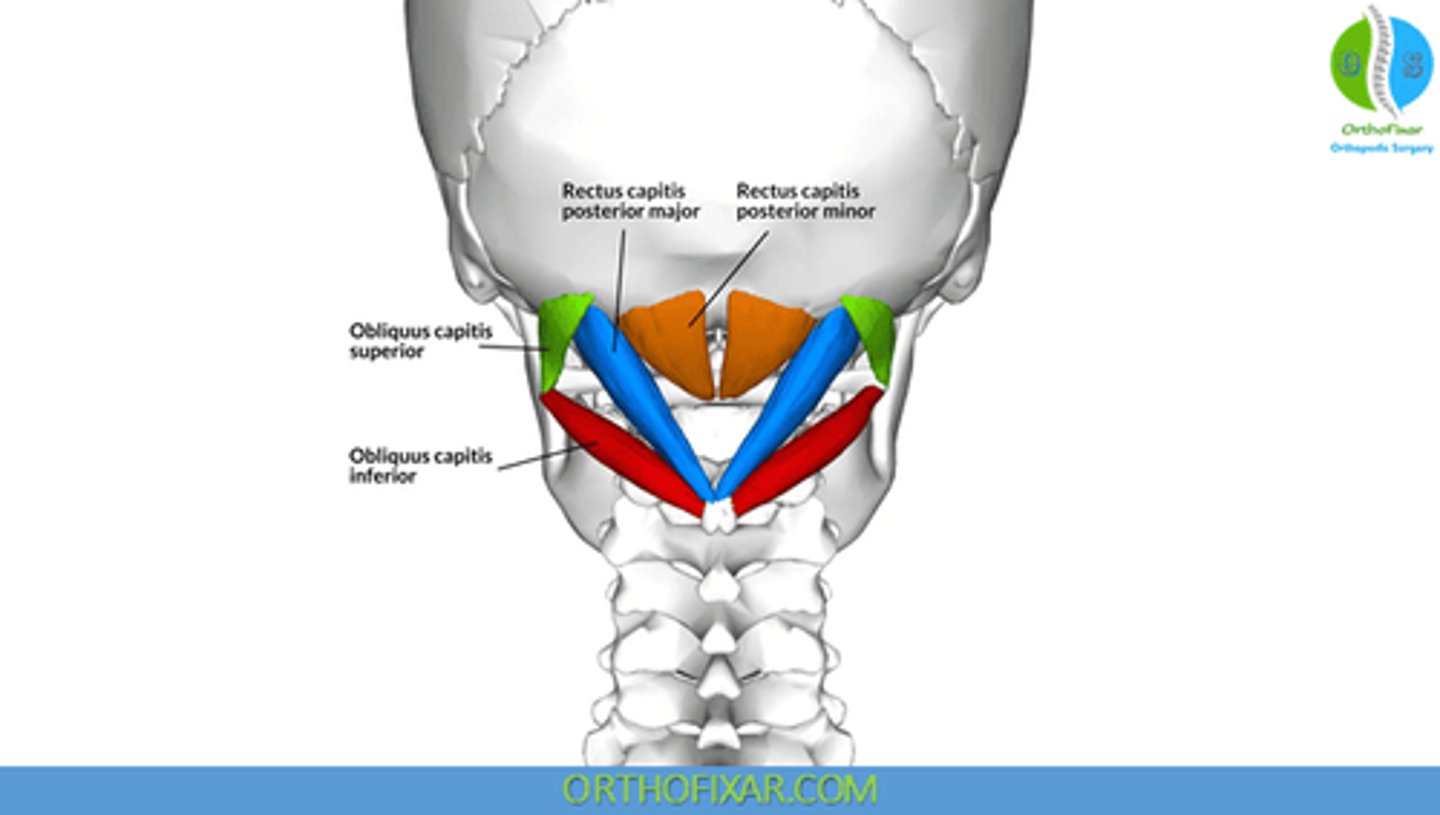
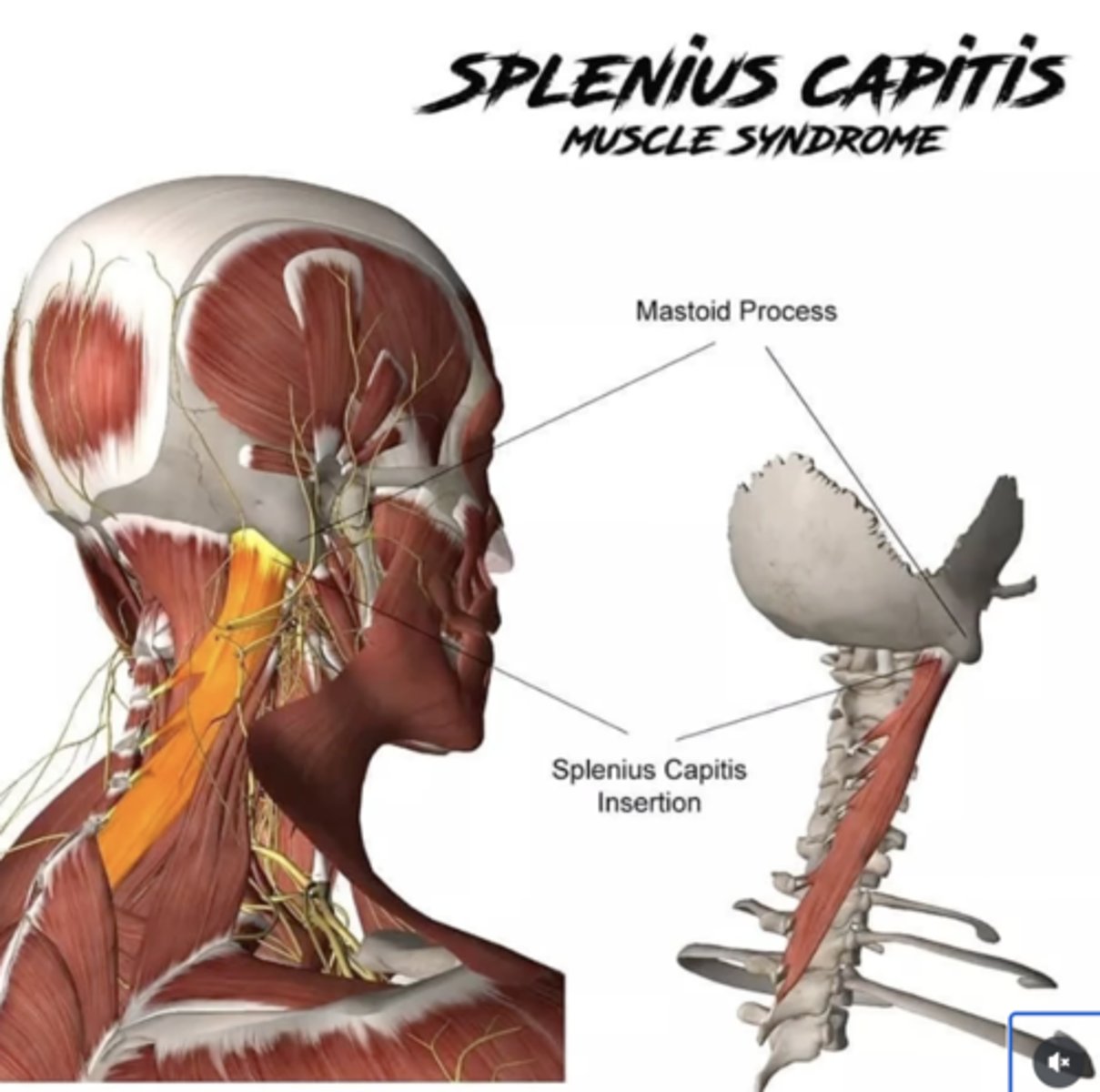
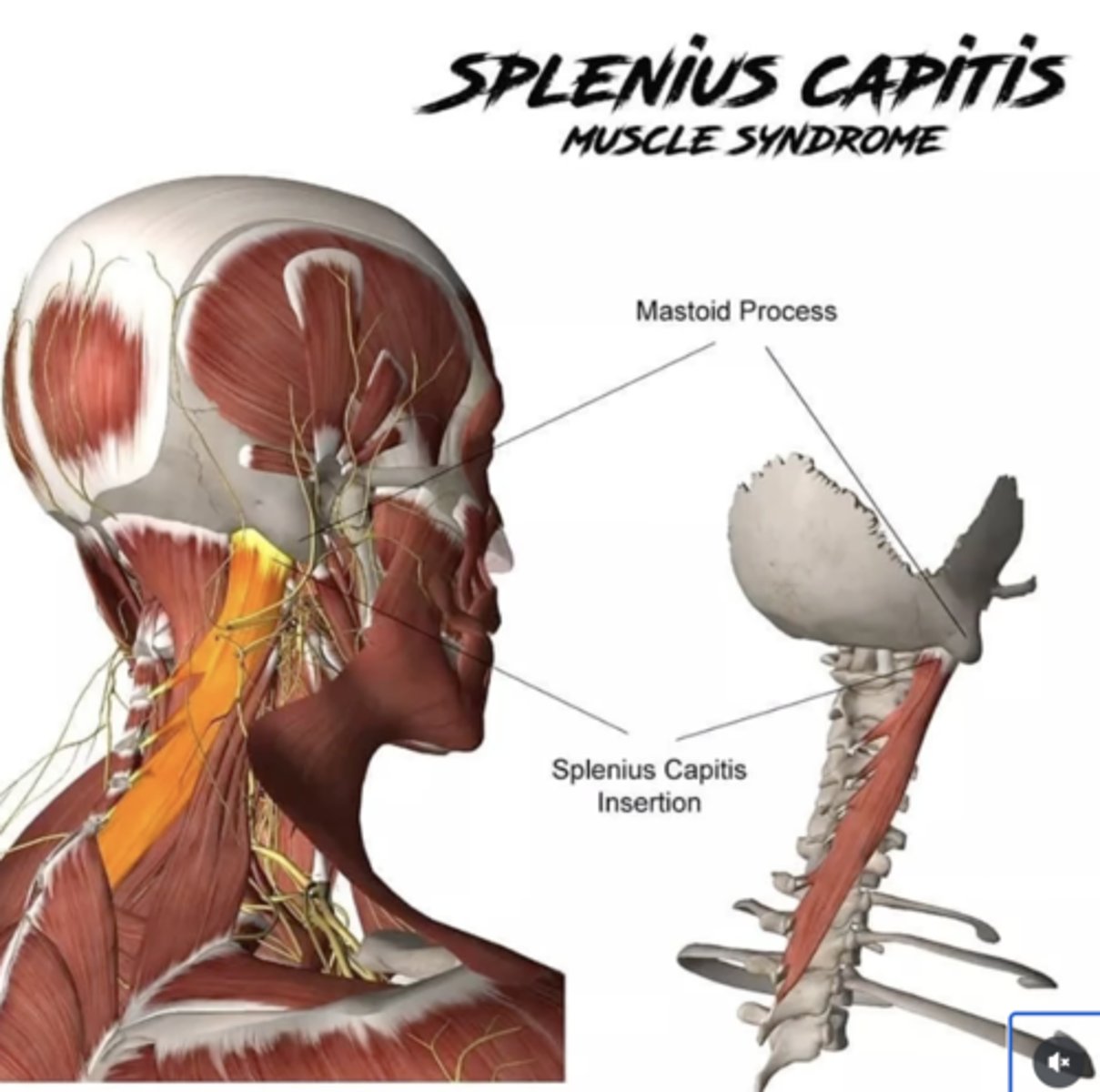
What is the insertion of the Splenius Capitis?
• Mastoid Process
• Lateral 1/3 Superior Nuchal Line
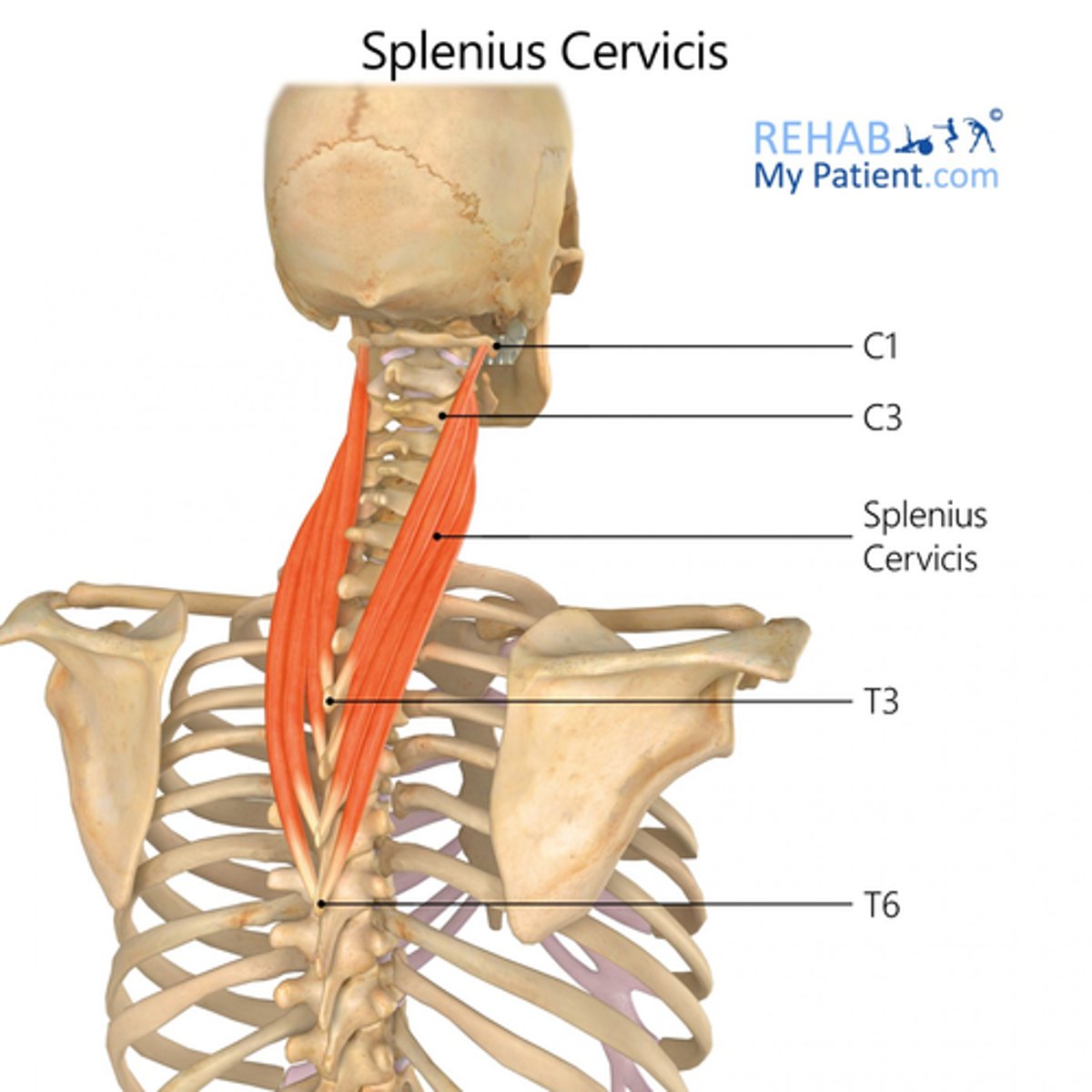
What is the insertion of the Splenius Cervicis?
• Transverse Processes C1-C3
What is the insertion of the Iliocostalis?
• Ribs (Thoracic and Lumbar)
• Transverse Processes (Cervical)
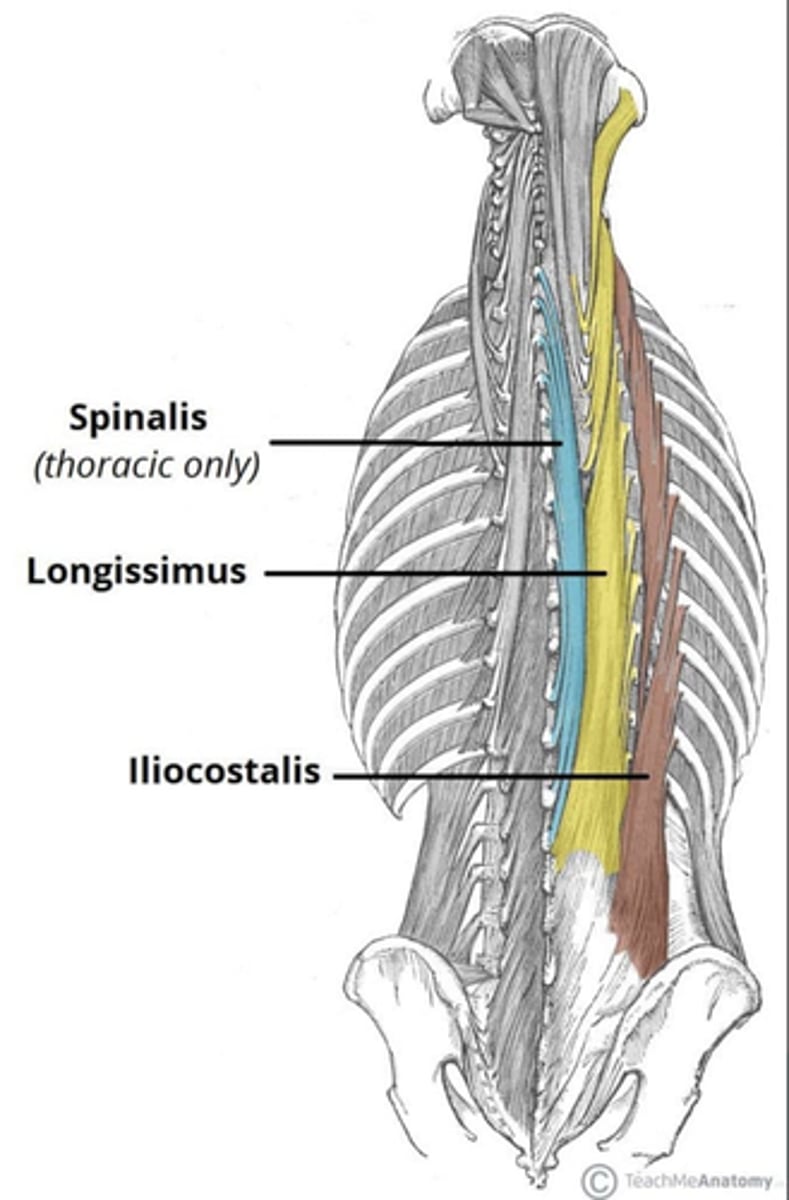
What is the insertion of the Longissimus?
• Transverse Processes
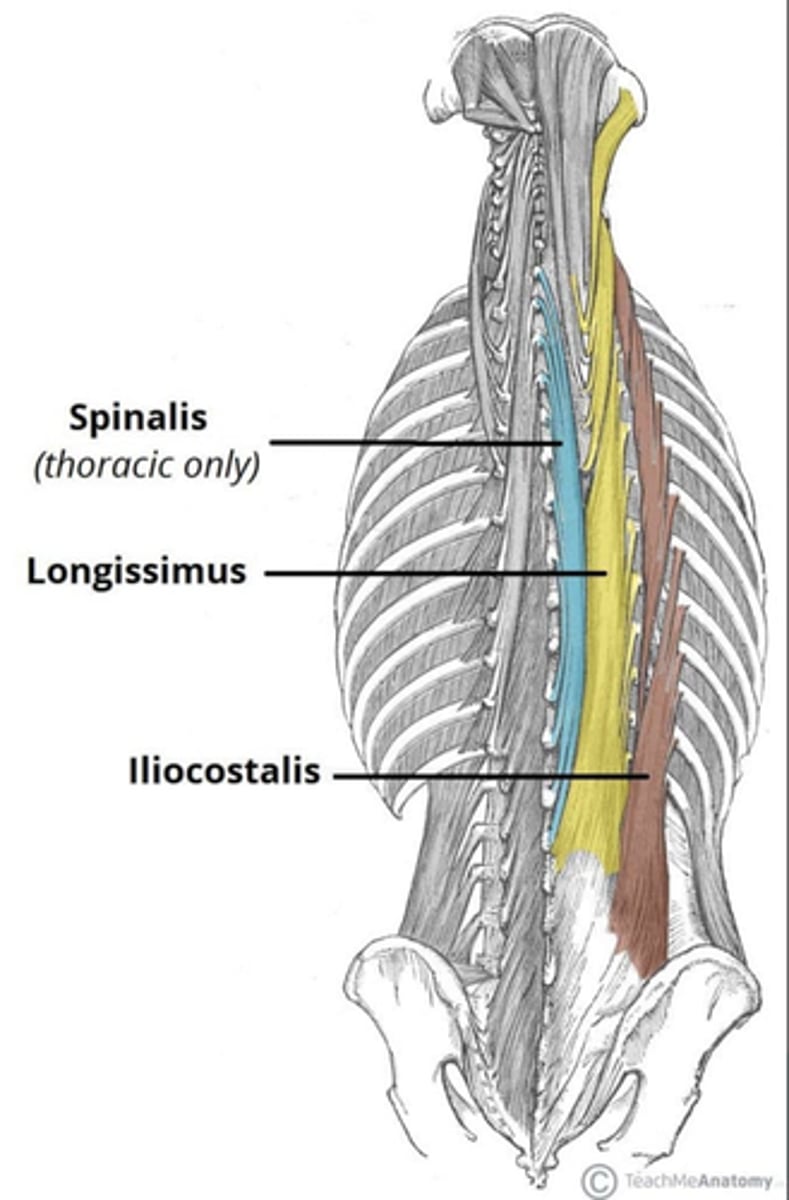
What is the insertion of the Spinalis?
• Spinous Processes
What is the insertion of the Semispinalis (Thoracis, Cervicis and Capitus)?
• Spinous Processes
• Occiput (Capitis)
What is the insertion of the Multifidus?
• Base of Spinous Processes
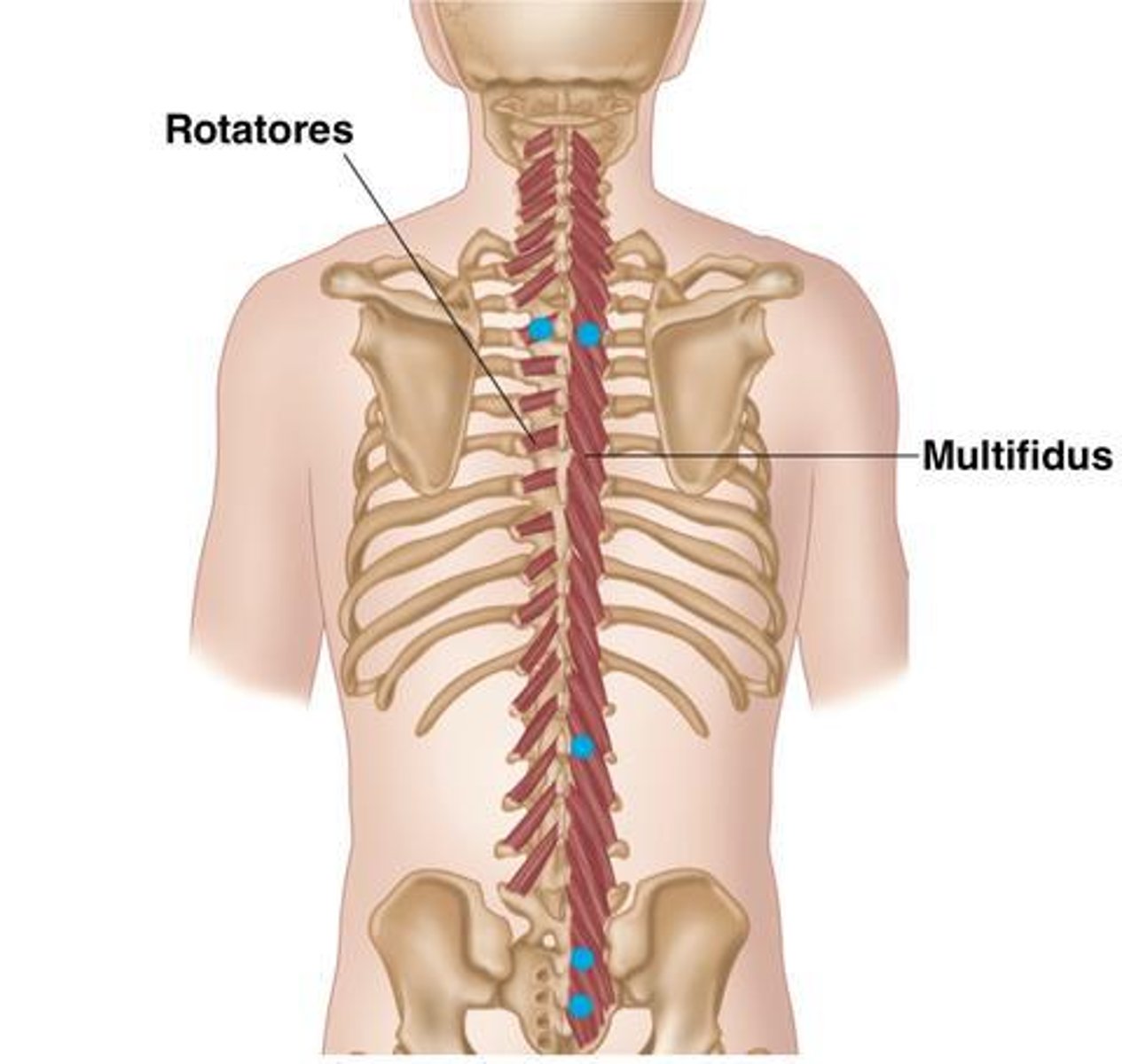
What is the insertion of the Rotatores?
• Spinous Processes
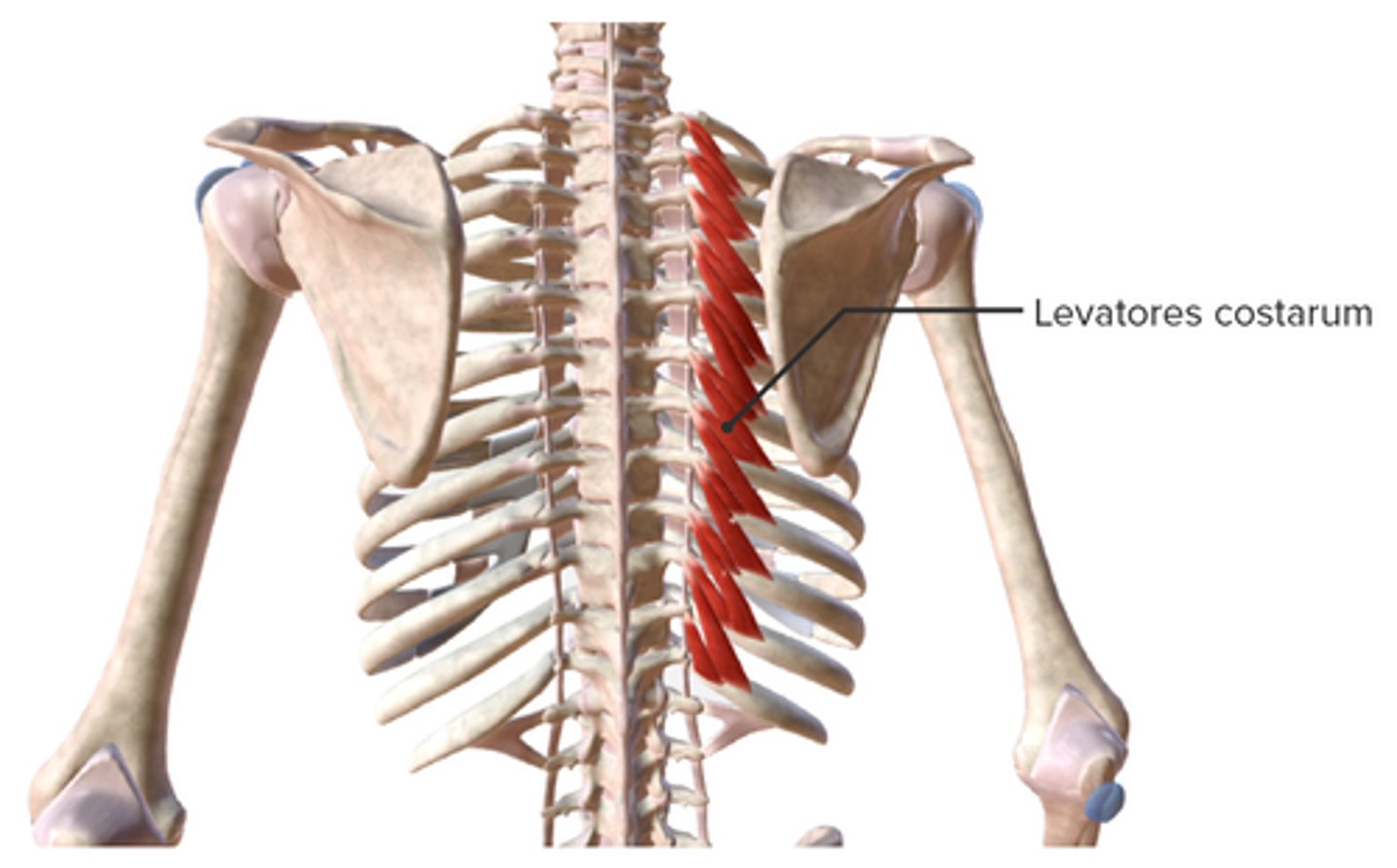
What is the insertion of the Levator Costorum?
• Rib below origin near Tubercle
What is the insertion of the Interspinales?
• Spinous Process Above
What is the insertion of the Intertransversarii?
• Transverse Process
What is the insertion of the Rectus Capitis Posterior Major?
• Lateral portion of Occipital Bone, below Inferior Nuchal Line
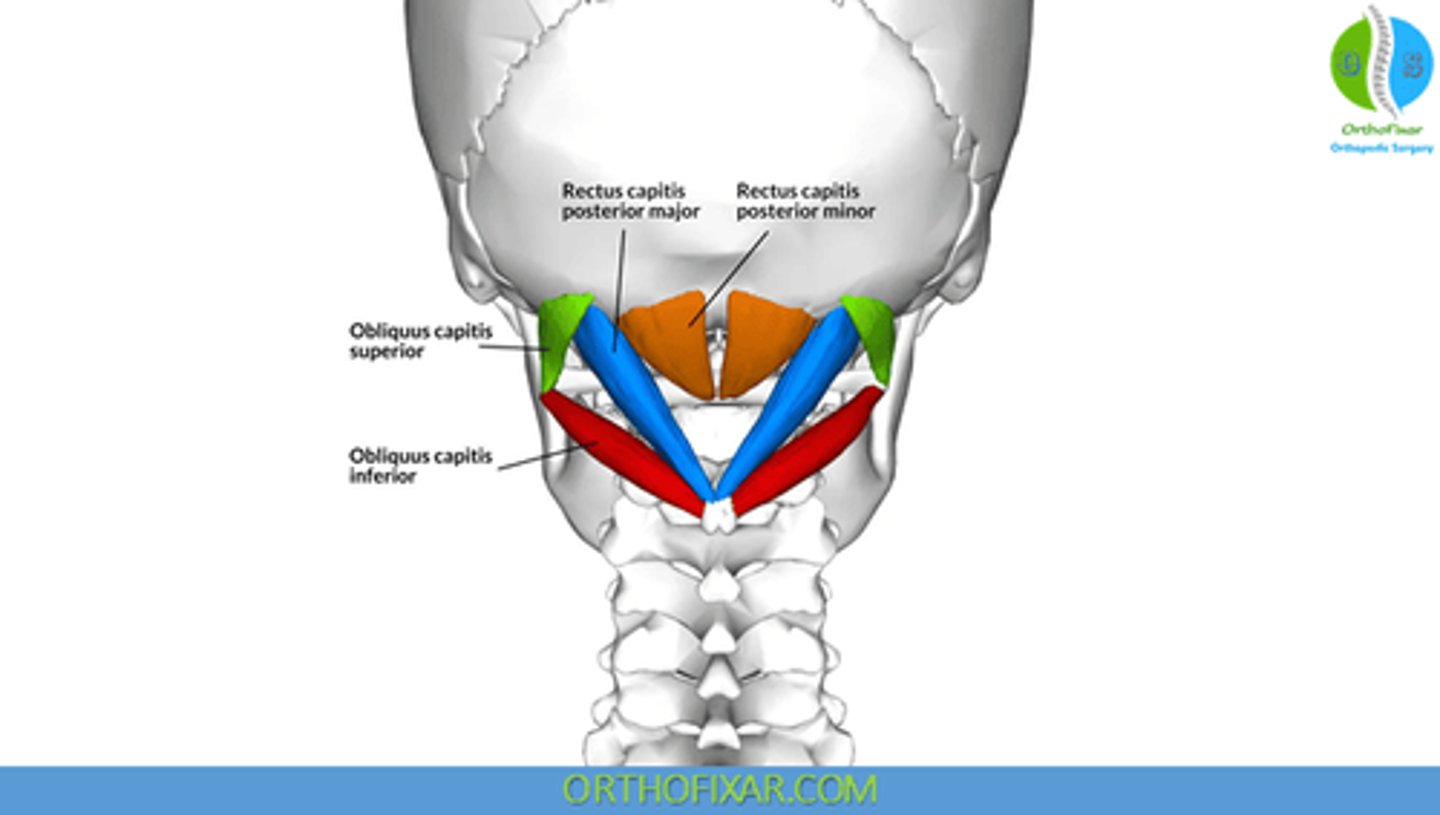
What is the insertion of the Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor?
• Medial Portion of Occipital Bone, below Inferior Nuchal Line
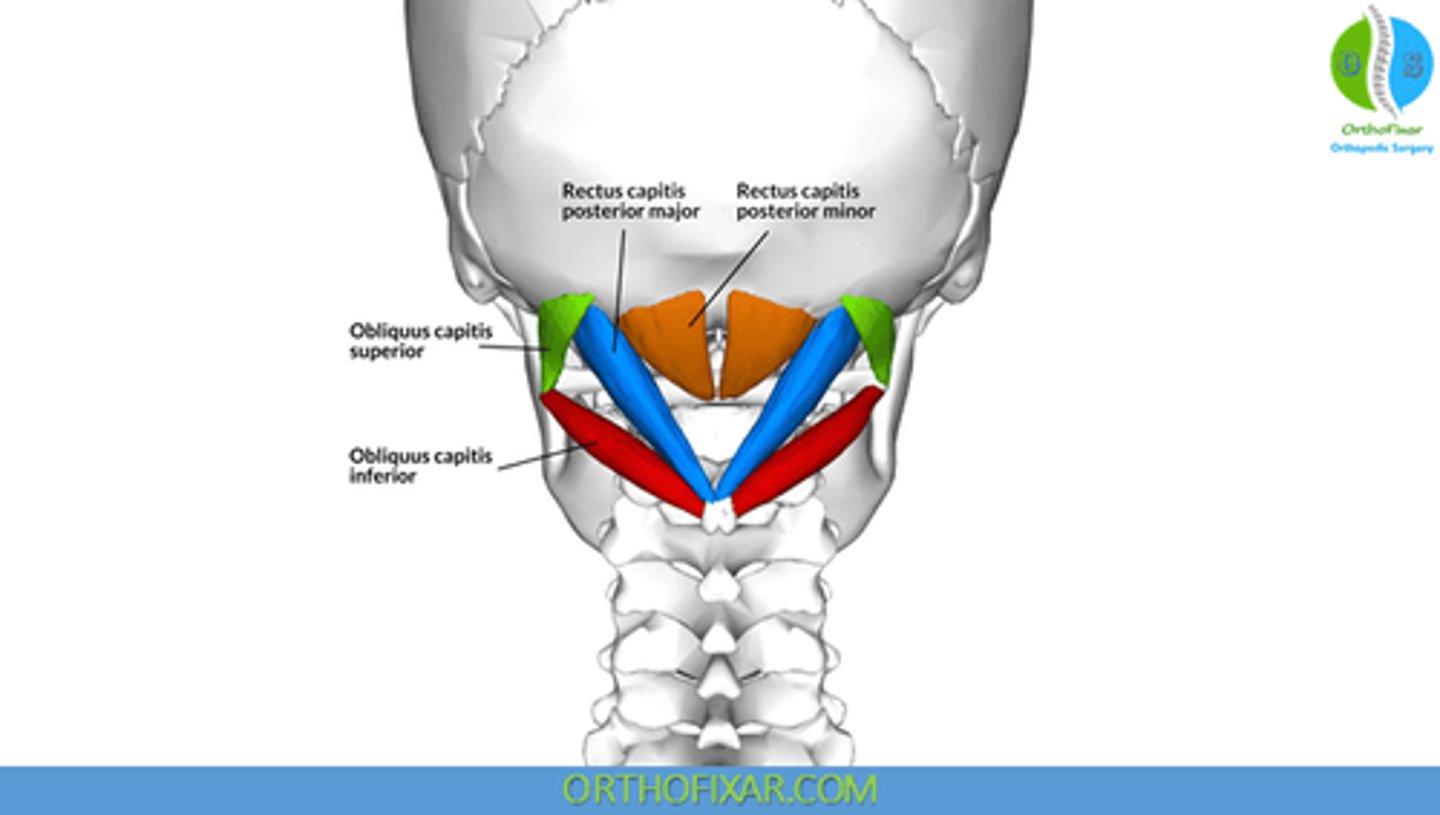
What is the insertion of the Obliquus Capitis Superior?
• Occiput, between Superior and Inferior Nuchal Lines
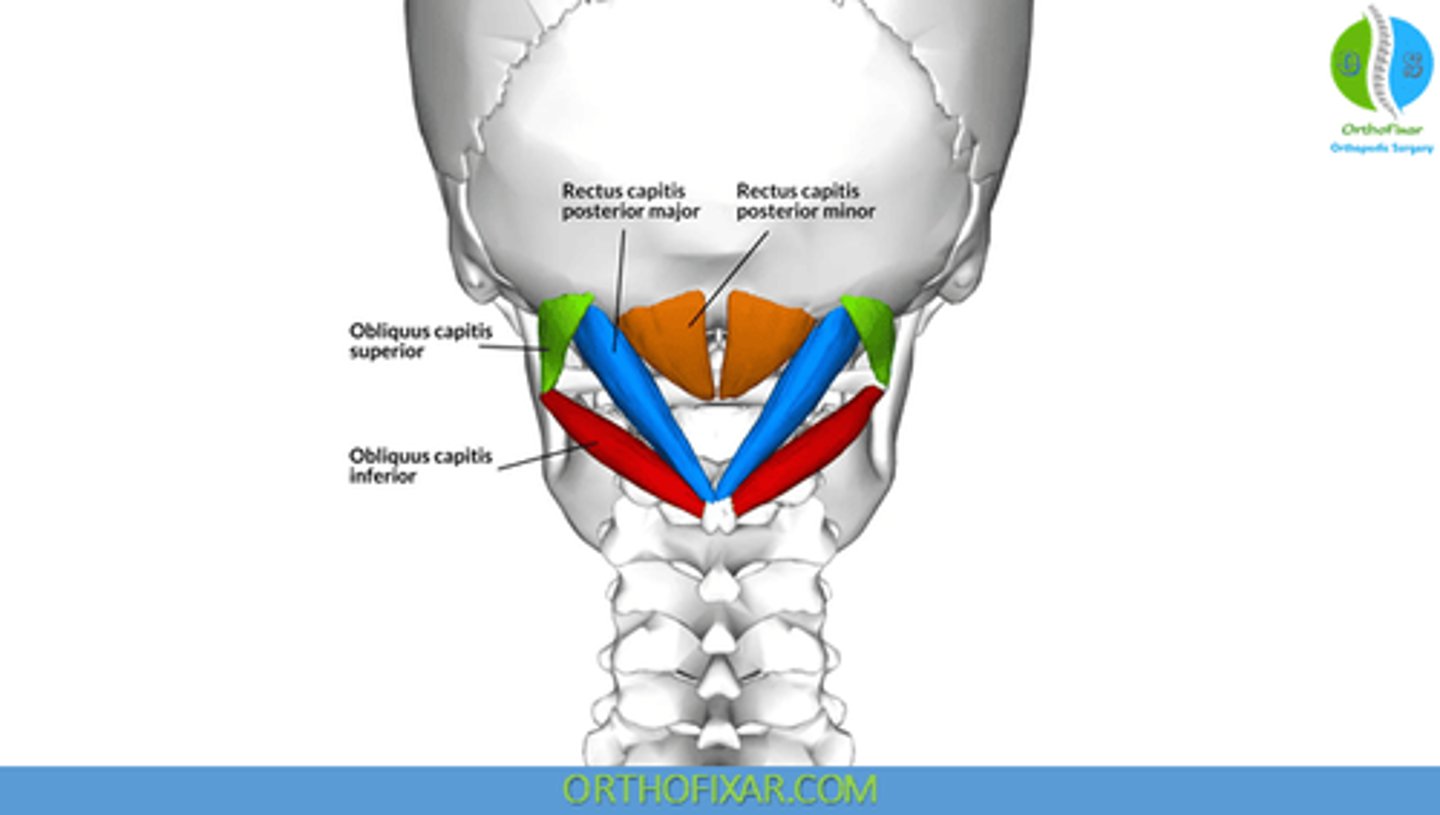
What is the insertion of the Obliquus Capitis Inferior?
• Transverse Process C1
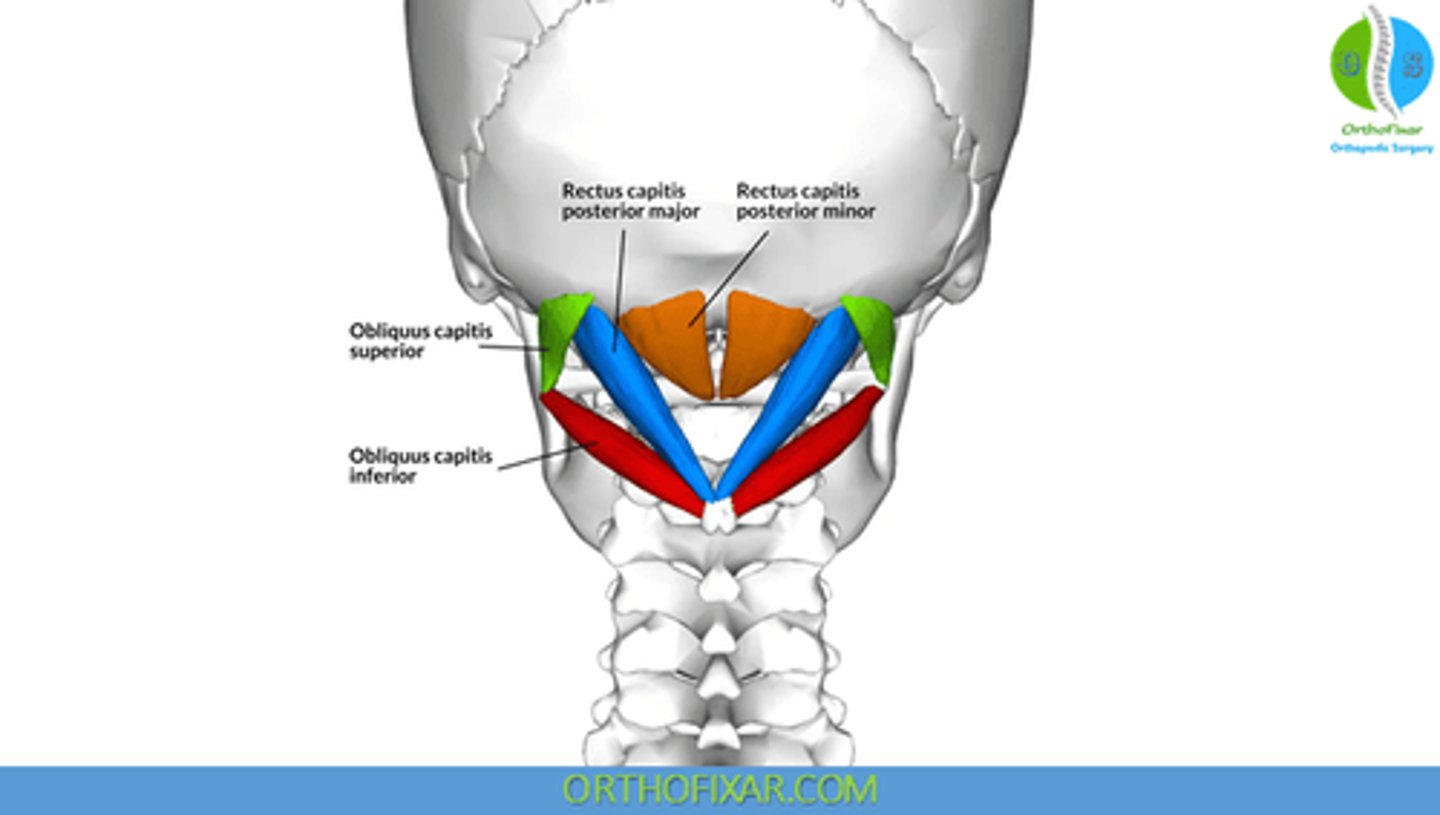
What is the action of the Splenius Capitis?
• Bilateral: extend head and neck
• Unilateral: rotate head ipsilaterally
What is the action of the Splenius Cervicis?
• Bilateral: extend neck
• Unilateral: lateral flexion, rotate neck ipsilaterally
What is the action of the Iliocostalis?
Primary extensors of vertebral column and head
• Bilateral: extend vertebral column, control flexion of vertebral column
• Unilateral: laterally flex vertebral column, ipsilateral rotation of head
What is the action of the Longissimus?
Primary extensors of vertebral column and head
• Bilateral: extend vertebral column, control flexion of vertebral column
• Unilateral: laterally flex vertebral column, ipsilateral rotation of head
What is the action of the Spinalis?
Primary extensors of vertebral column and head
• Bilateral: extend vertebral column, control flexion of vertebral column
• Unilateral: laterally flex vertebral column, ipsilateral rotation of head
What is the action of the Semispinalis (Thoracis, Cervicis and Capitus)?
• Bilateral: extension of the vertebral column
• Unilateral: rotate the vertebral column to opposite side
• Semispinalis Capitis:
• Extends head (Bi)
• Extends and upward rotates chin to ipsilateral side
(Uni)
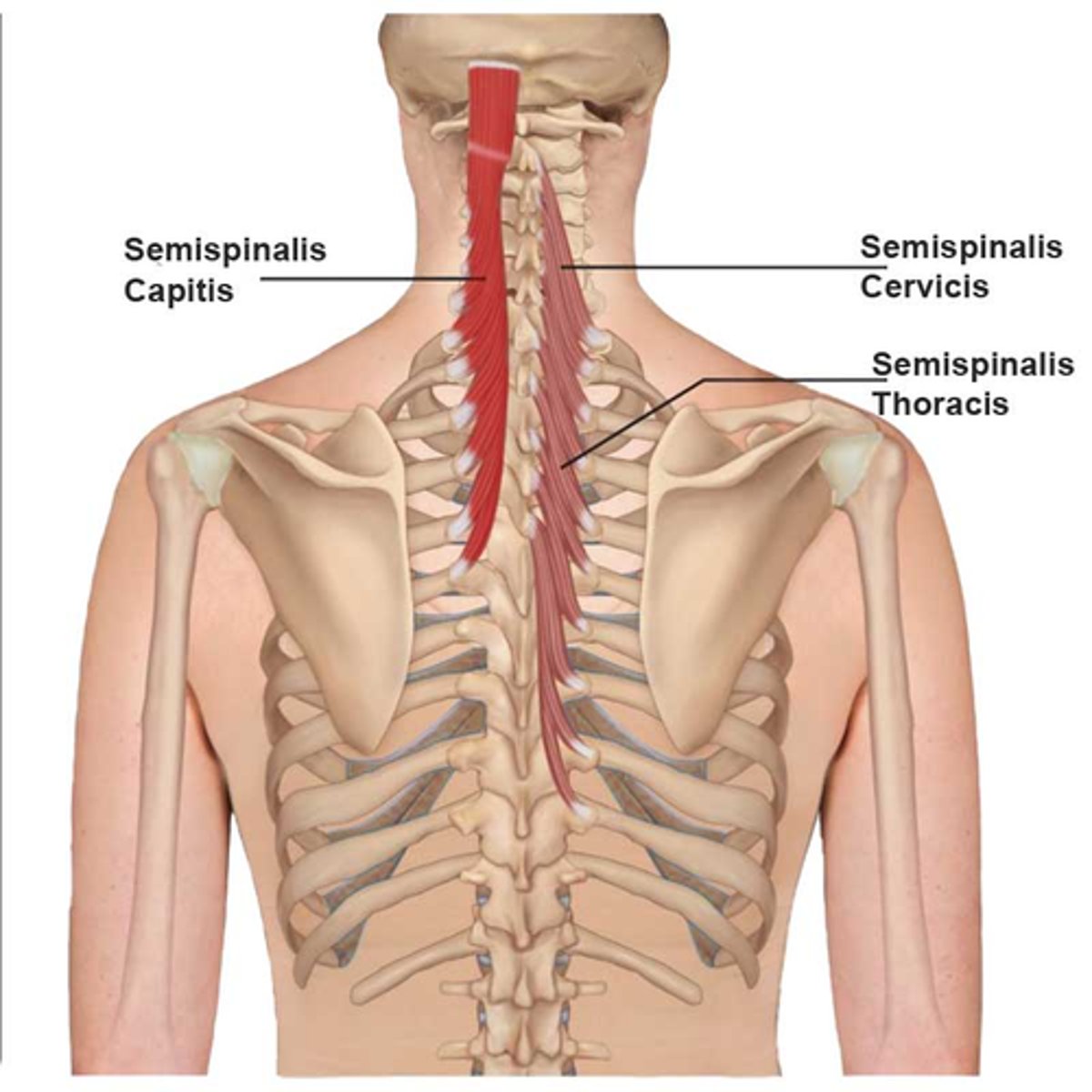
What is the action of the Multifidus?
• Bilateral: extension of the vertebral column
• Unilateral: rotate the vertebral column to opposite side
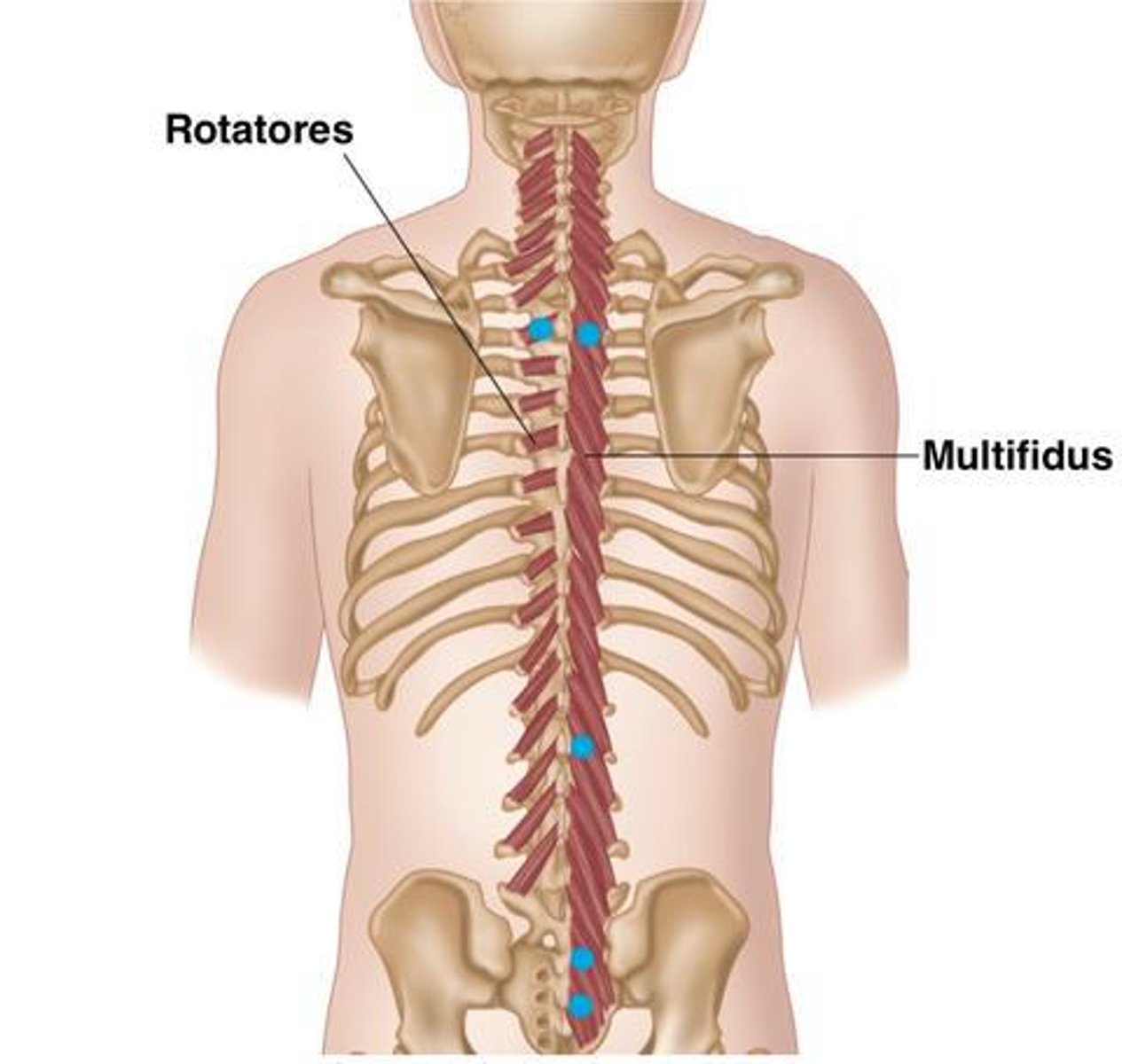
What is the action of the Rotatores?
• Unilateral: rotate the vertebral column to opposite side
What is the action of the Levator Costorum?
• Elevates Ribs
What is the action of the Interspinales?
• Stabilize adjoining vertebrae during movement
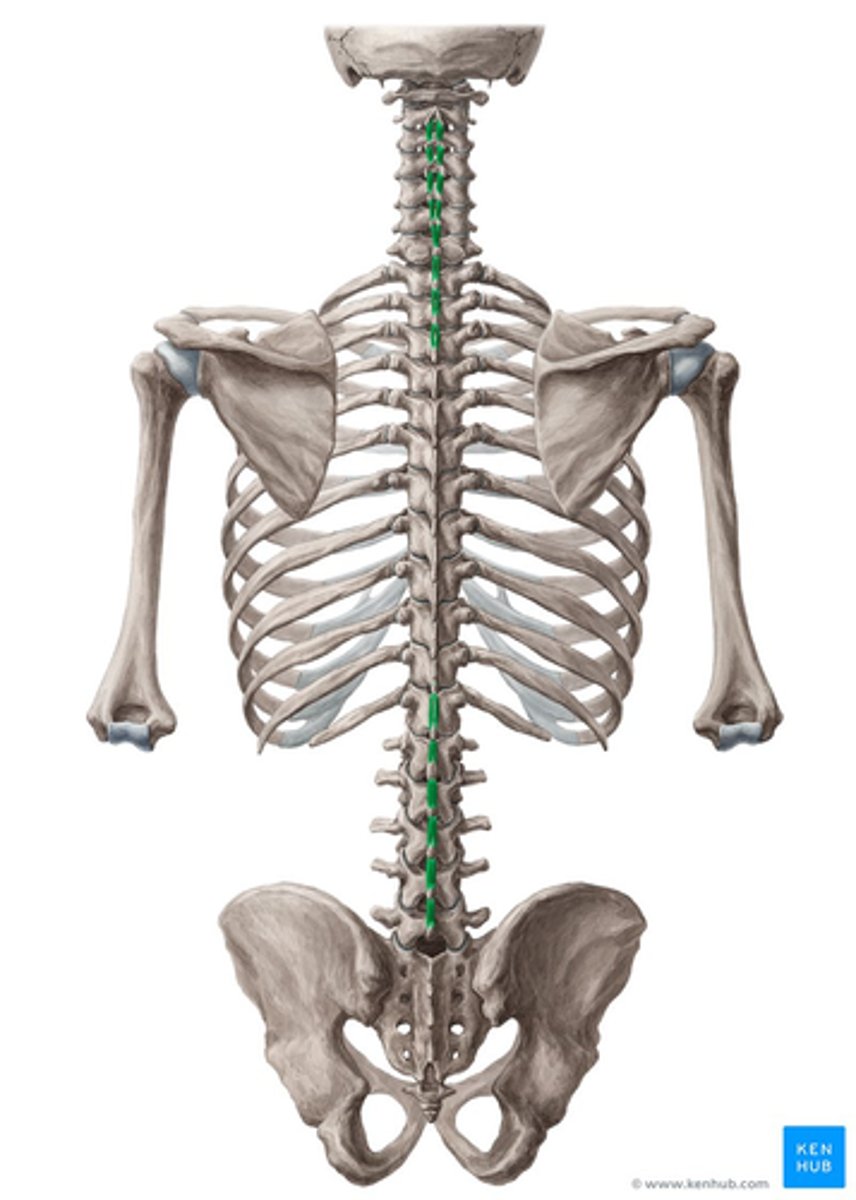
What is the action of the Intertransversarii?
• Stabilize adjoining vertebrae during movement
What is the action of the Rectus Capitis Posterior Major?
• Bilateral: Extension of head
• Unilateral: Ipsilateral rotation of head
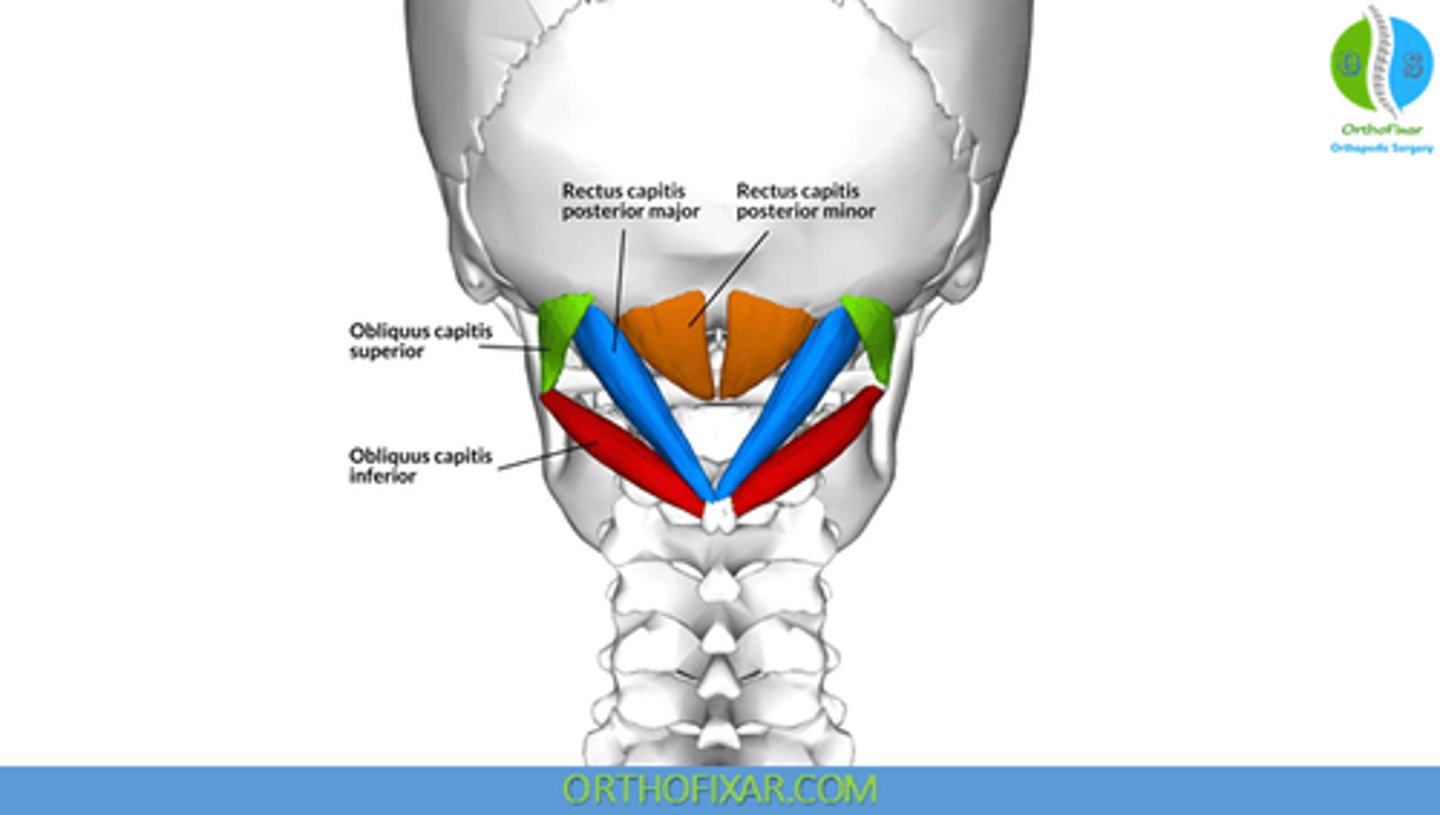
What is the action of the Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor?
• Extension of head
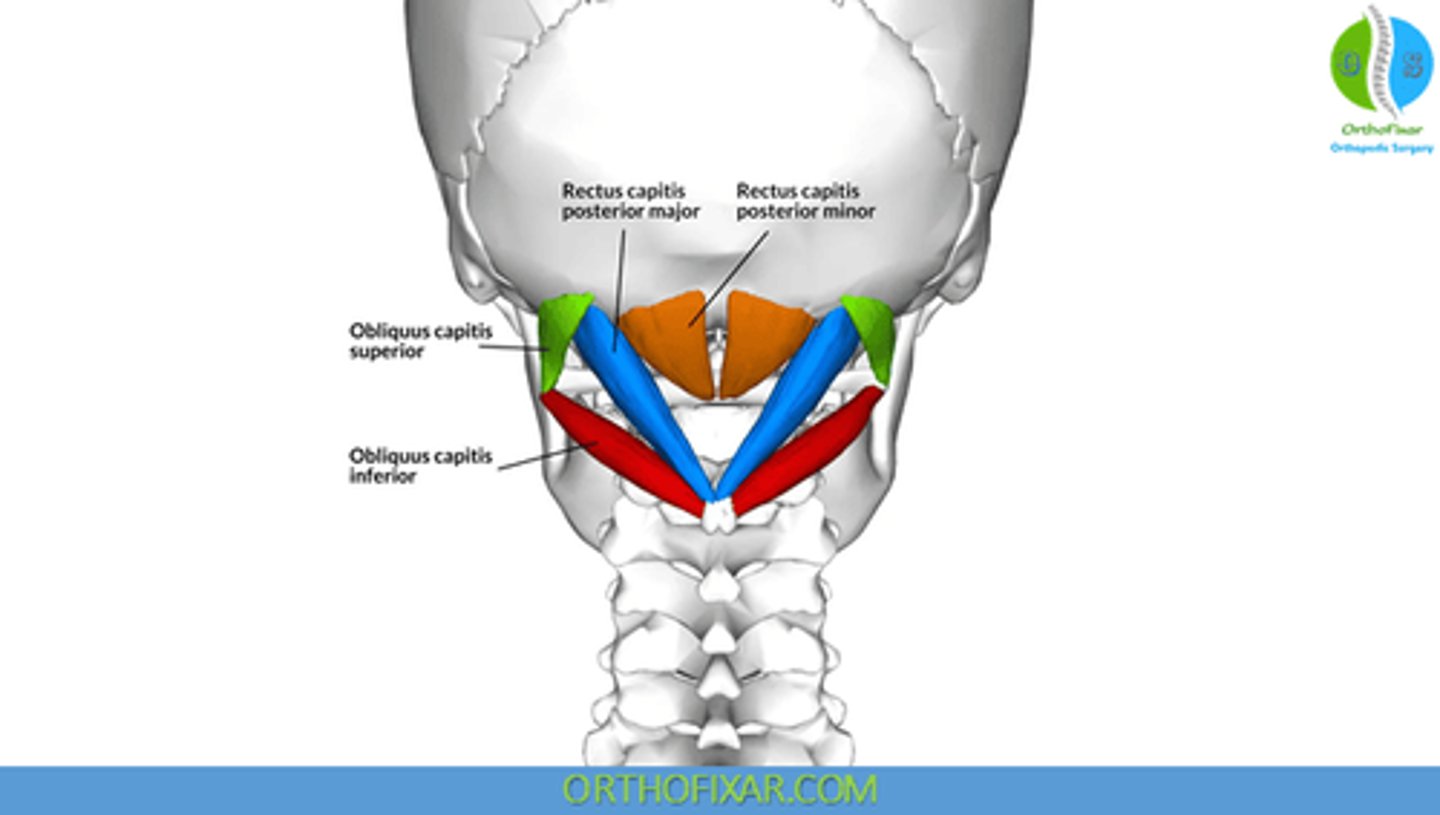
What is the action of the Obliquus Capitis Superior?
• Bilateral: Extension of head
• Unilateral: lateral flexion of the head
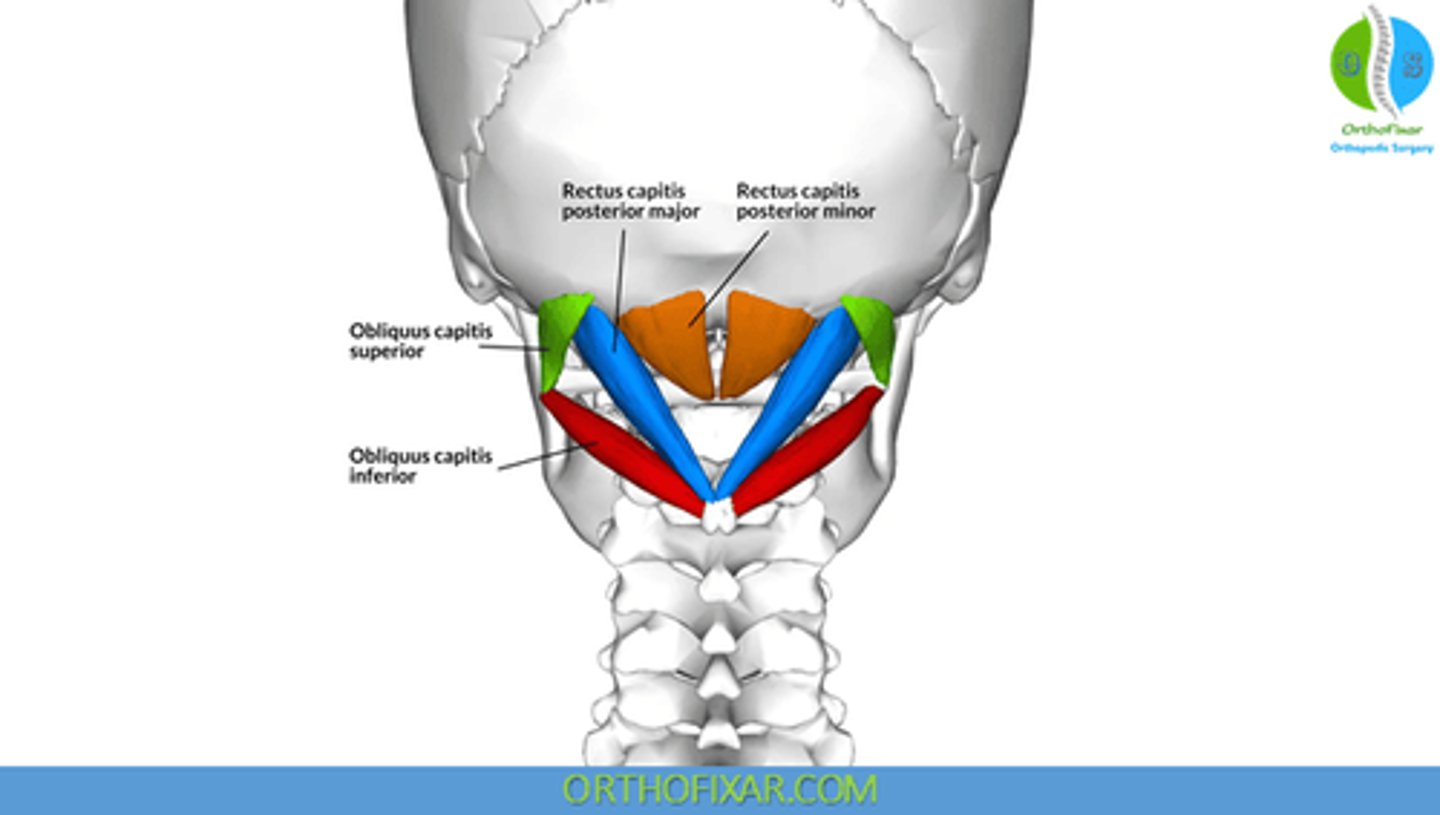
What is the action of the Obliquus Capitis Inferior?
• Ipsilateral head rotation
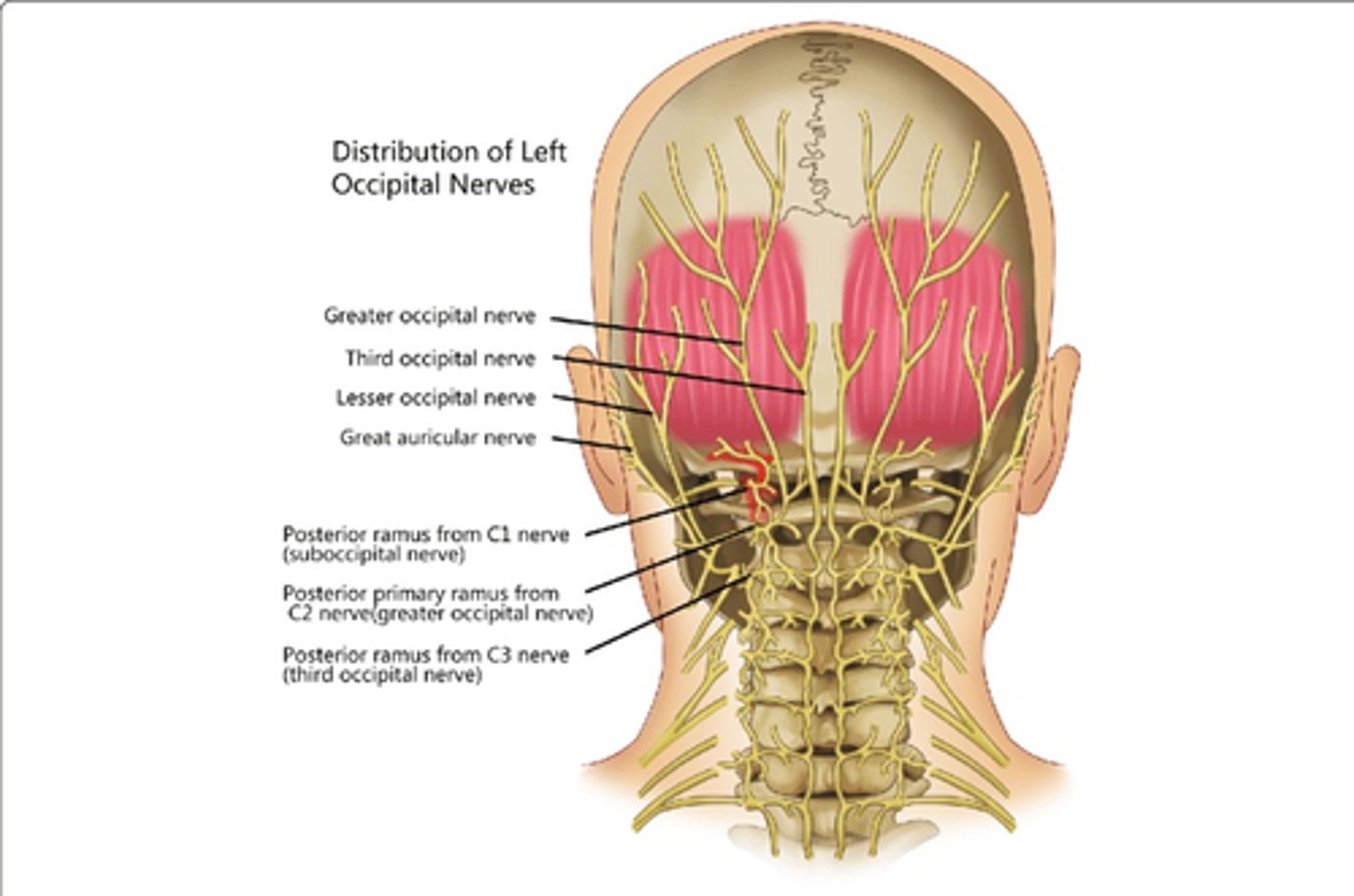
Which nerve(s) innervate Splenius Capitis?
• Posterior Rami of Middle Cervical Nerves
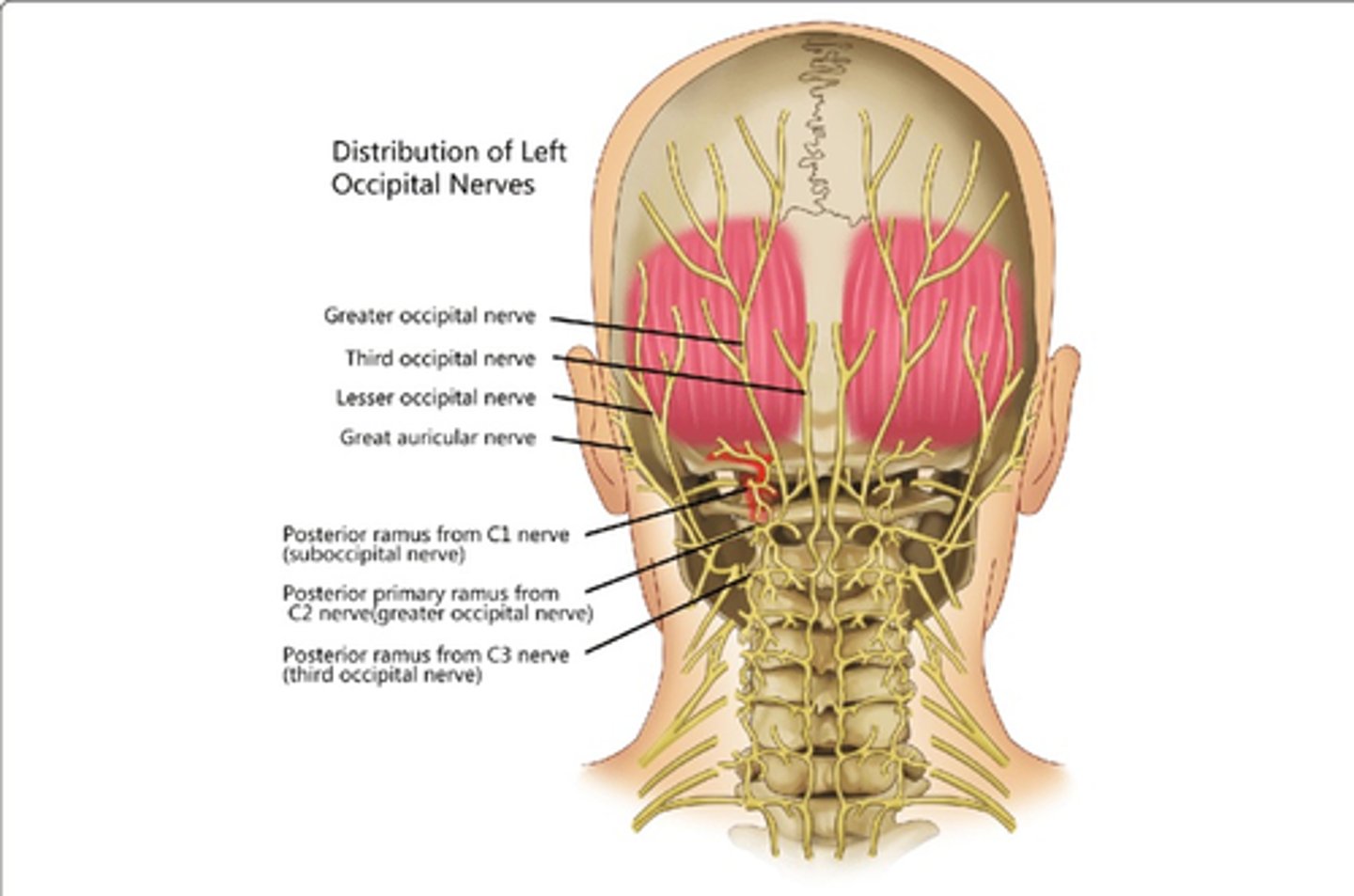
Which nerve(s) innervate Splenius Cervicis?
• Posterior Rami of Lower Cervical Nerves
Which nerve(s) innervate Iliocostalis?
• Posterior Rami
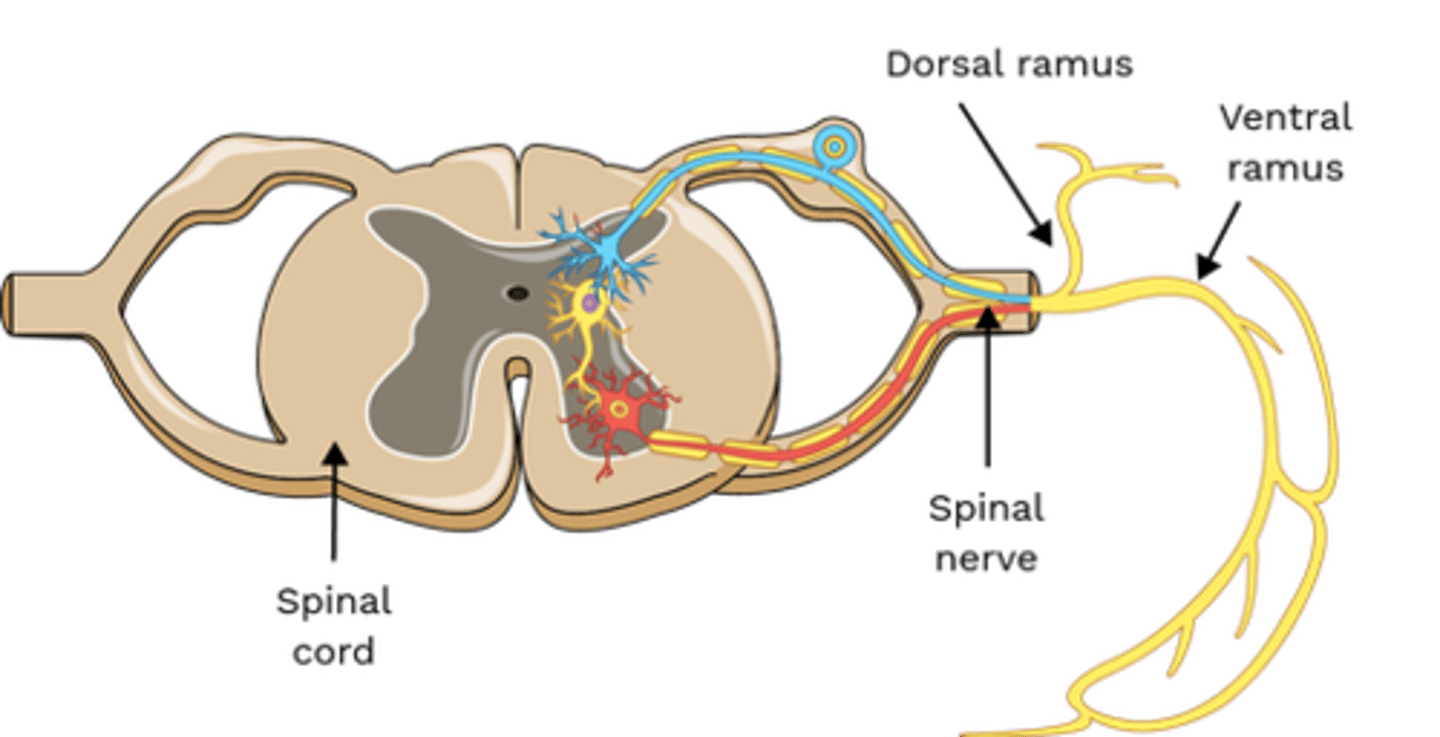
Which nerve(s) innervate Longissimus?
• Posterior Rami
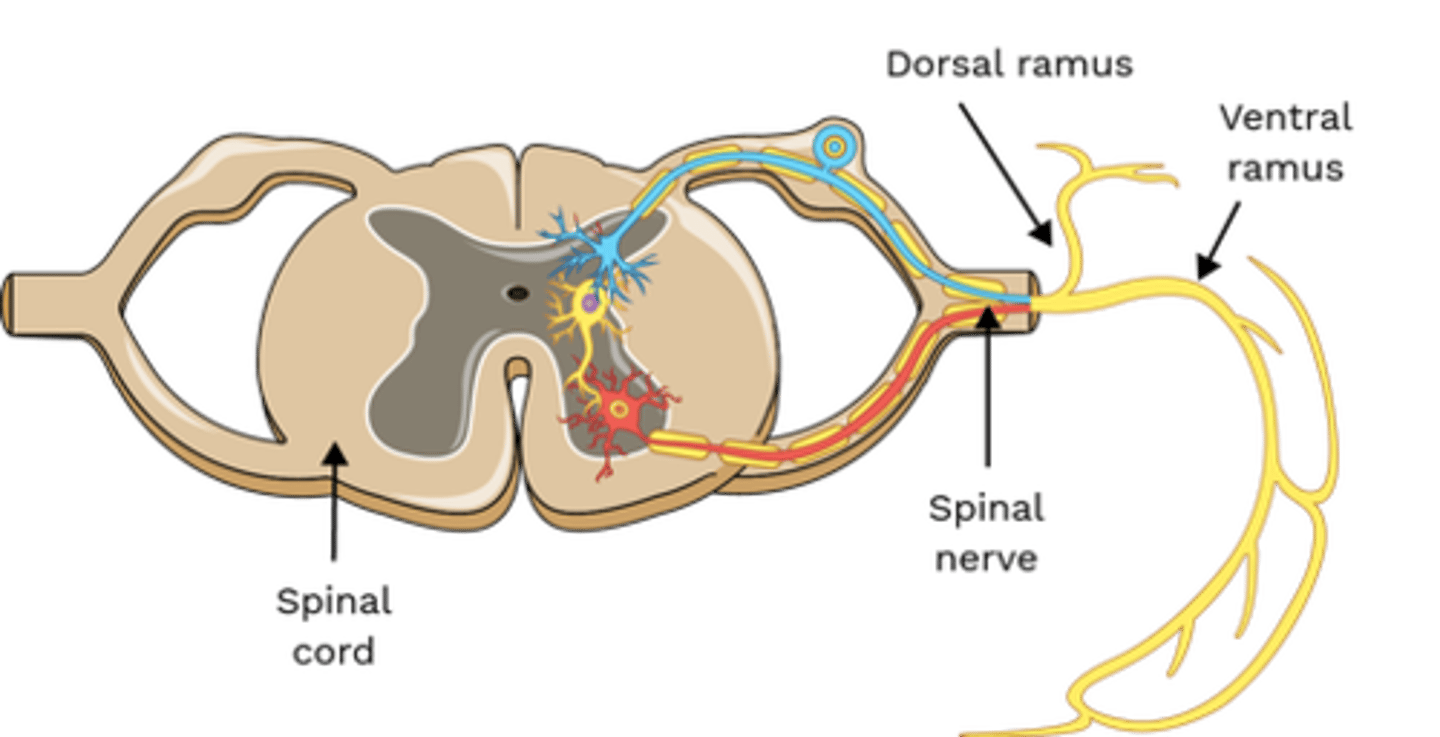
Which nerve(s) innervate Spinalis?
• Posterior Rami
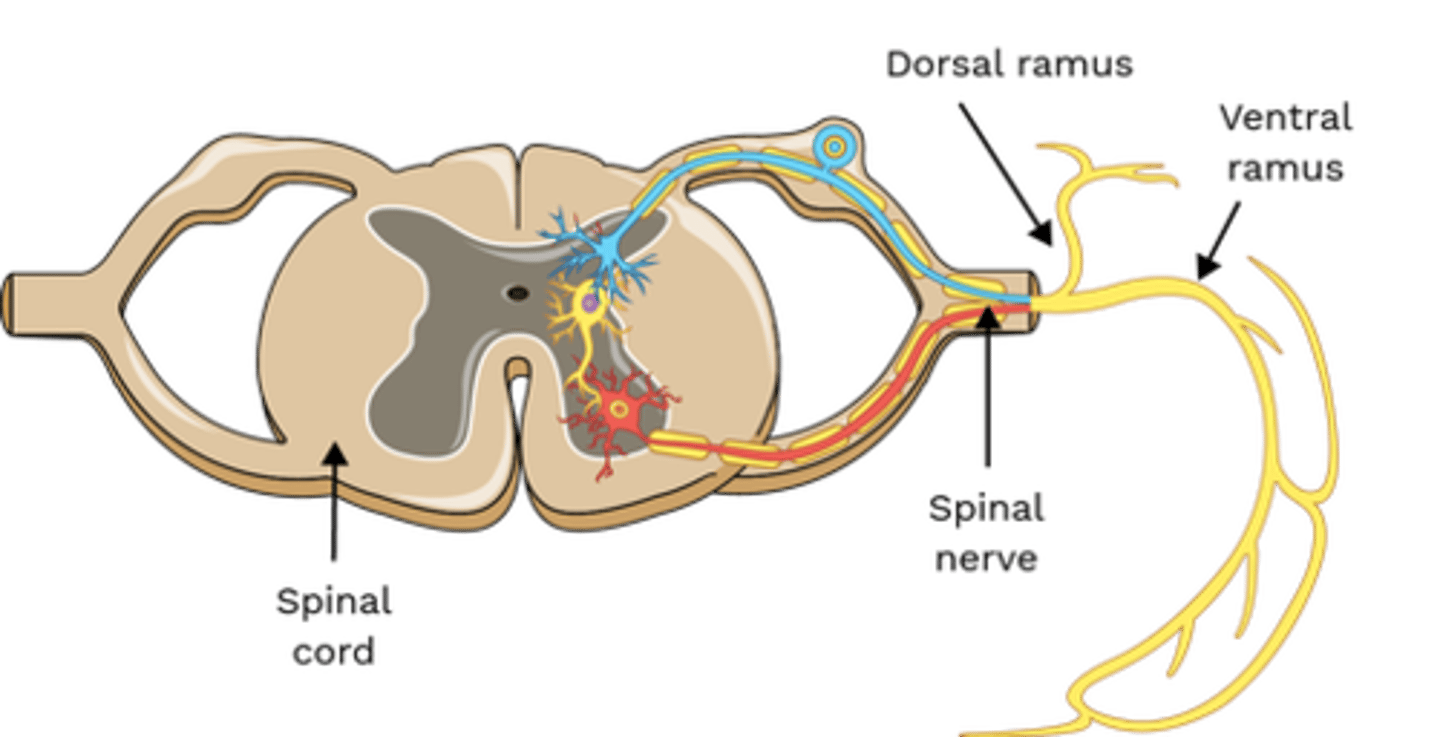
Which nerve(s) innervate Semispinalis (Thoracis, Cervicis and Capitus)?
• Posterior Rami
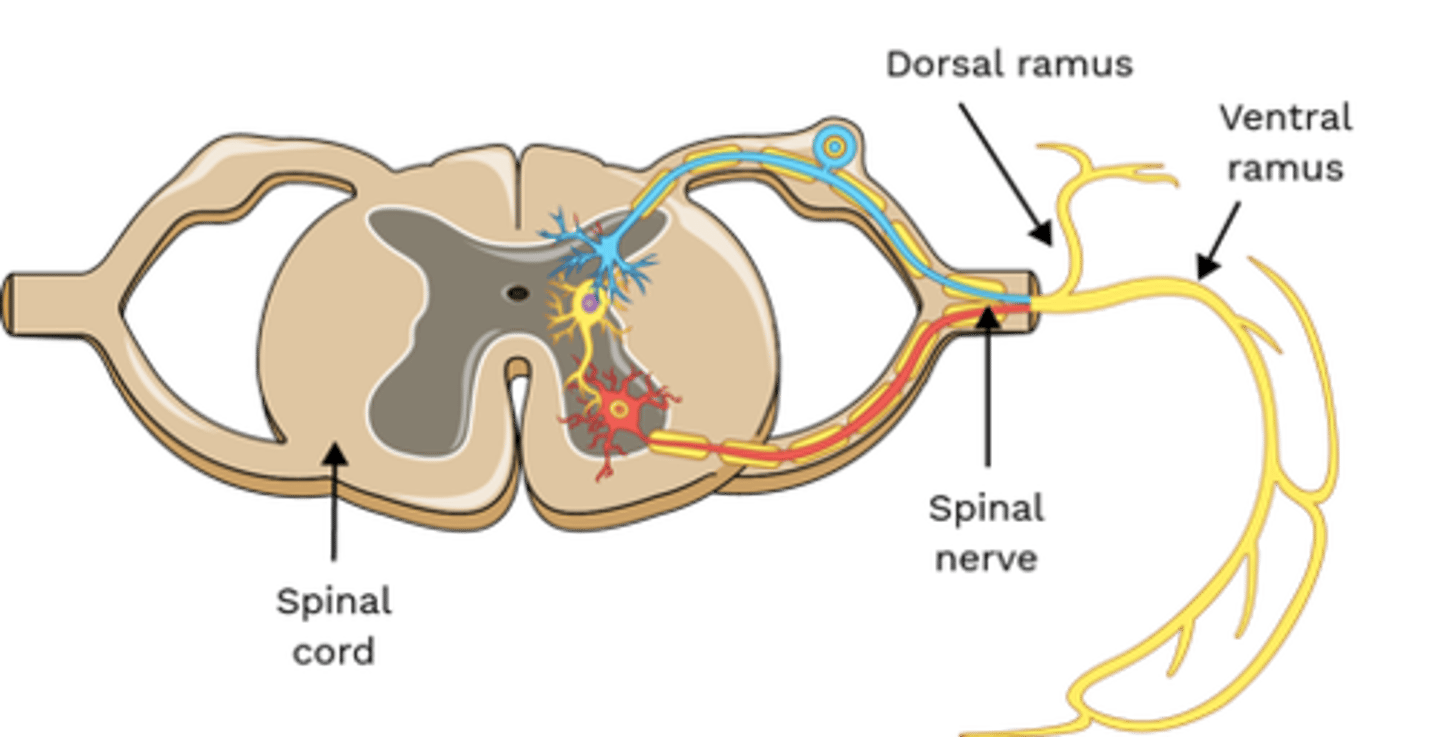
Which nerve(s) innervate Multifidus?
• Posterior Rami
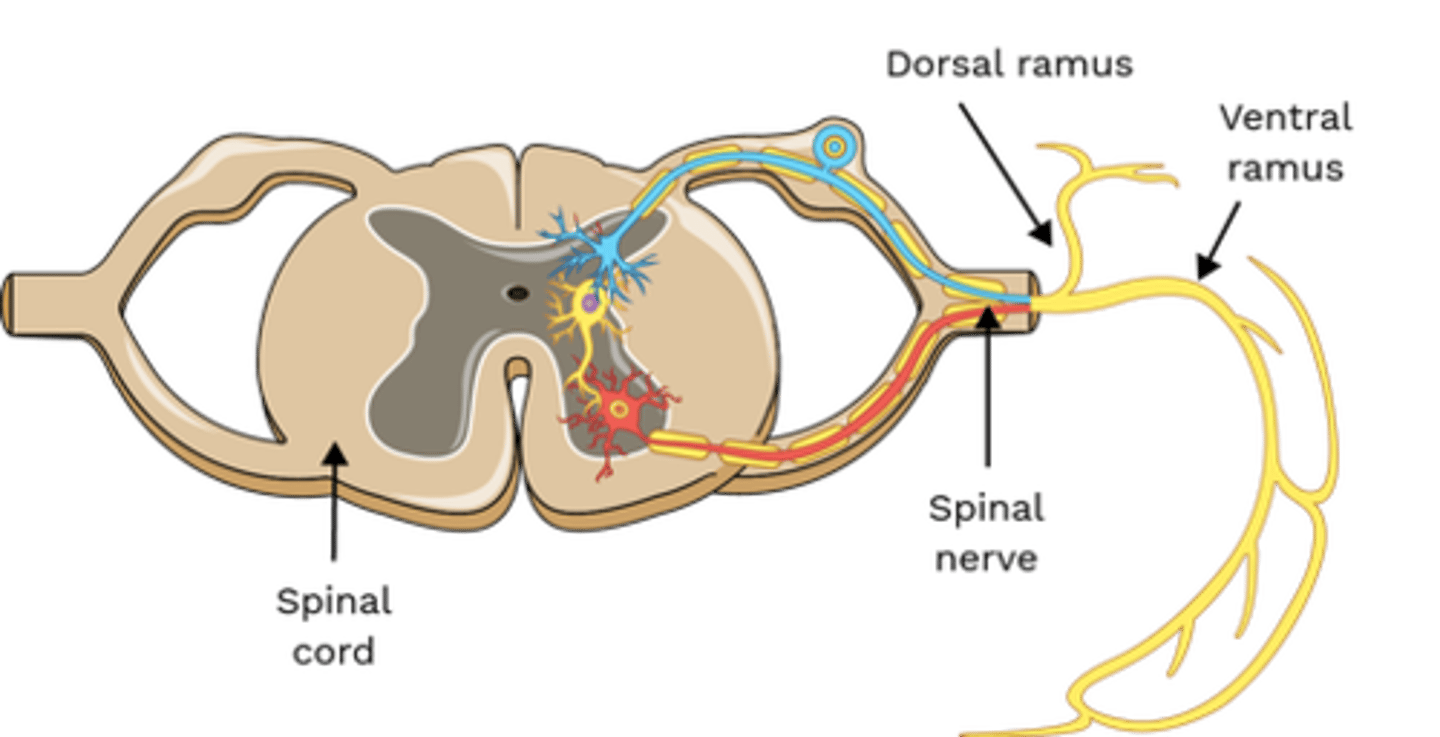
Which nerve(s) innervate Rotatores?
• Posterior Rami
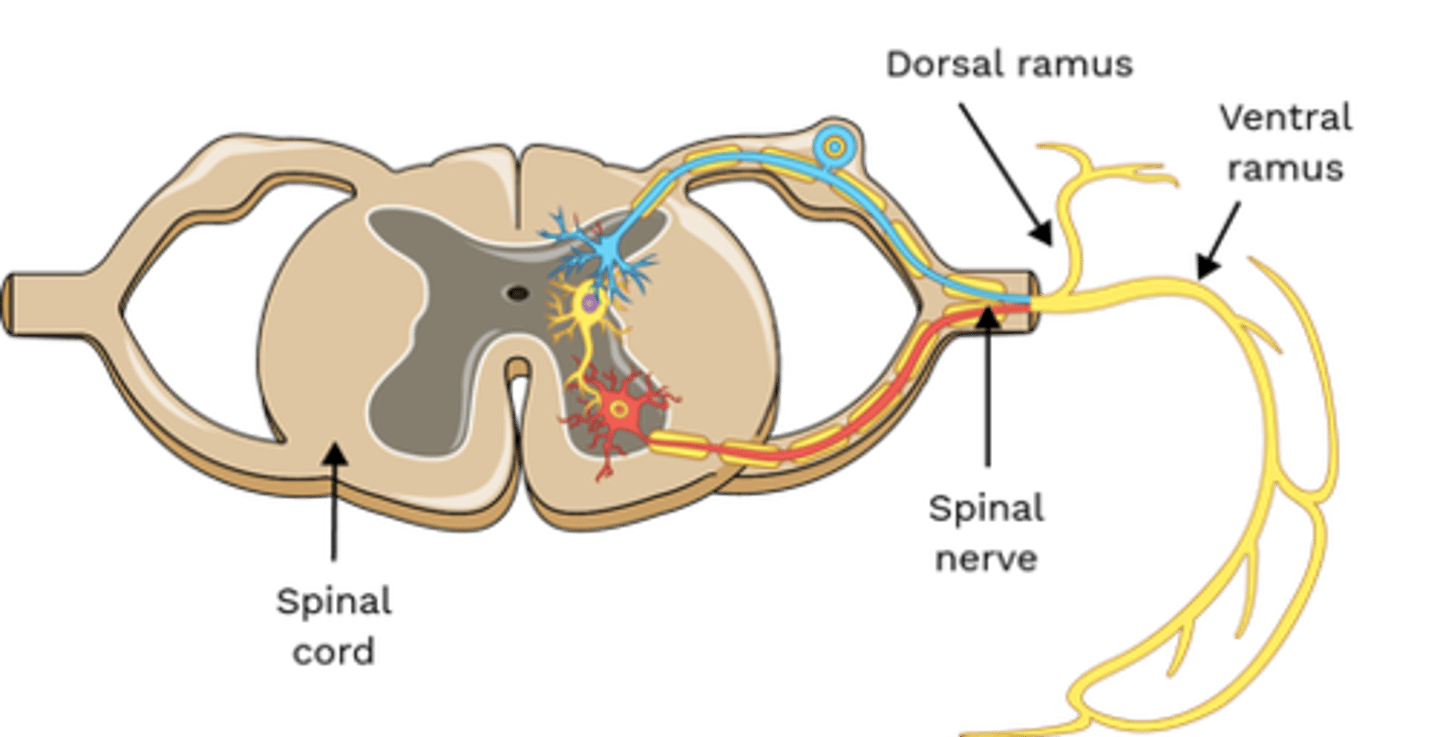
Which nerve(s) innervate Levator Costorum?
• Posterior Rami
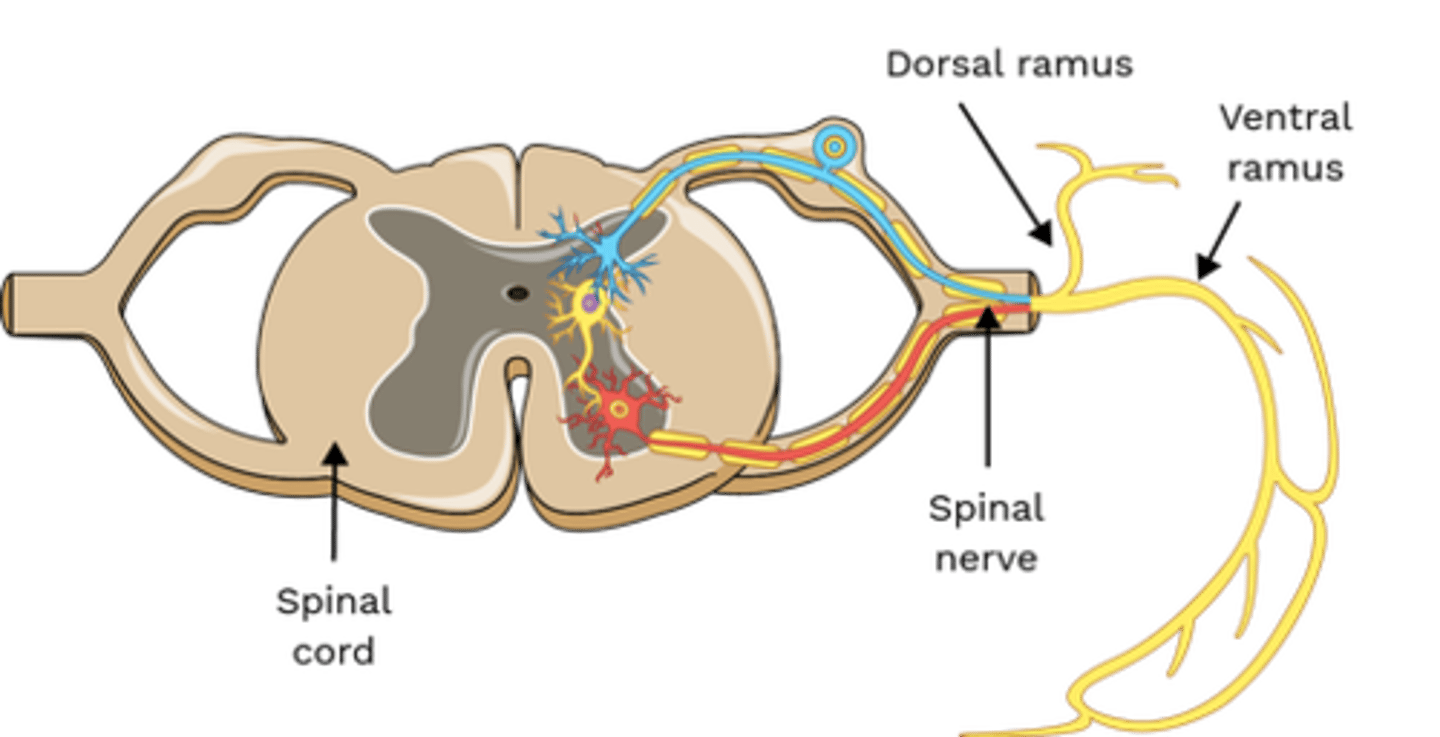
Which nerve(s) innervate Interspinales?
• Posterior Rami
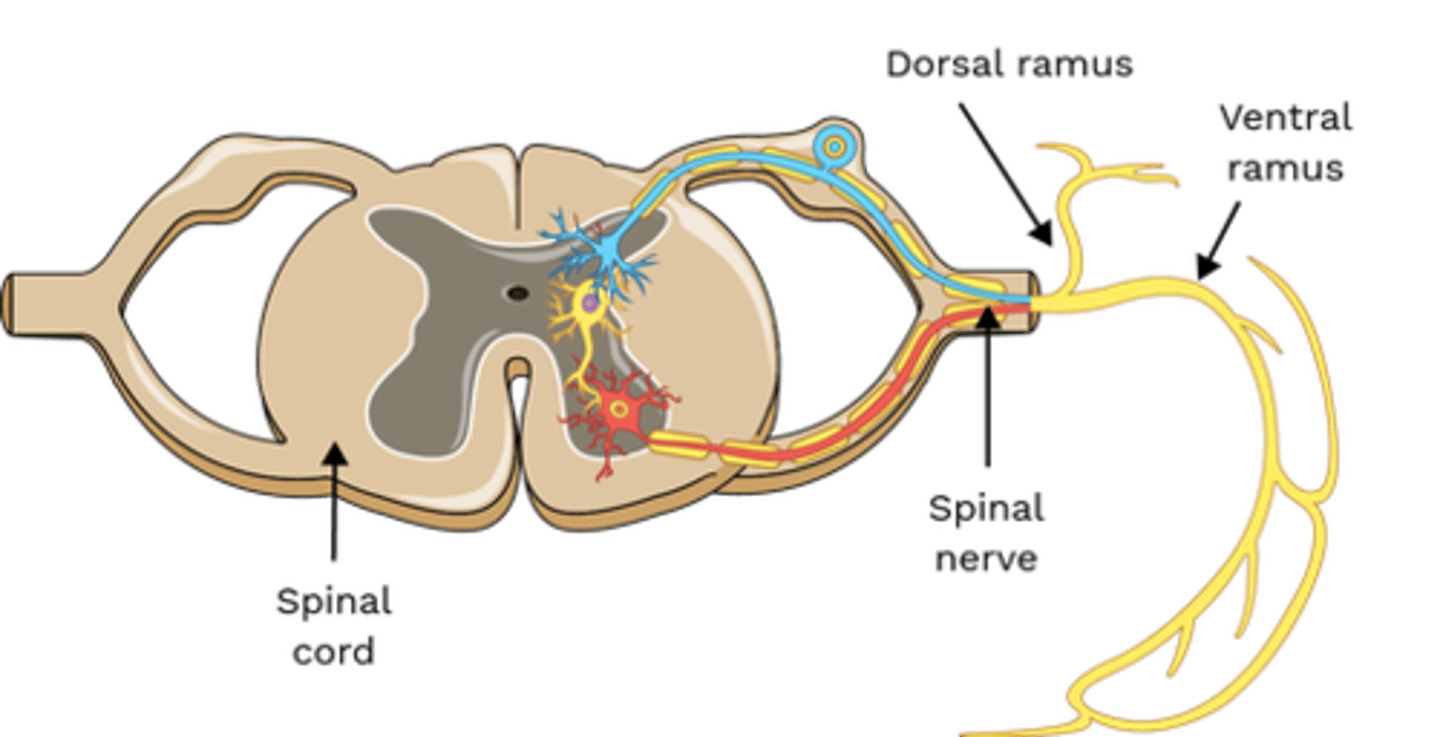
Which nerve(s) innervate Intertransversarii?
• Posterior Rami
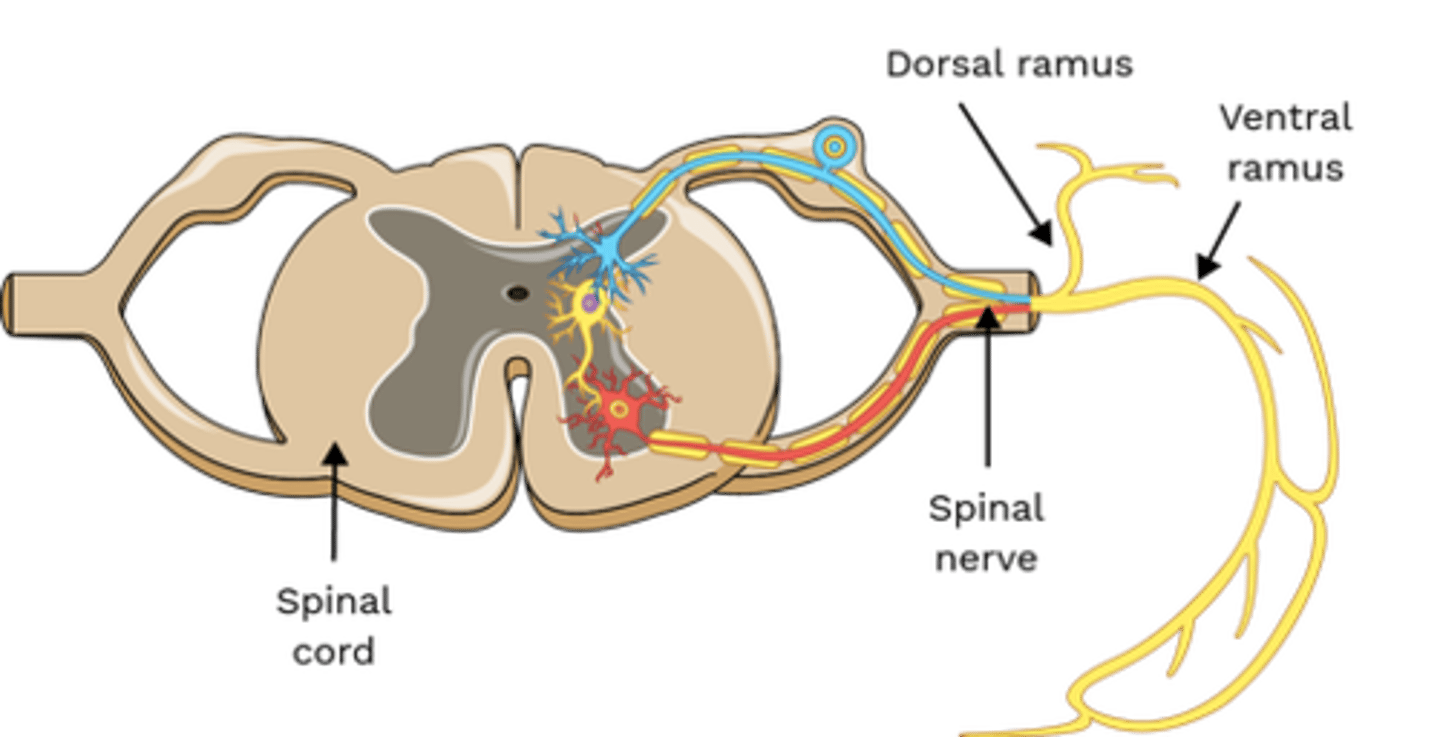
Which nerve(s) innervate Rectus Capitis Posterior Major?
• Posterior Rami, C1
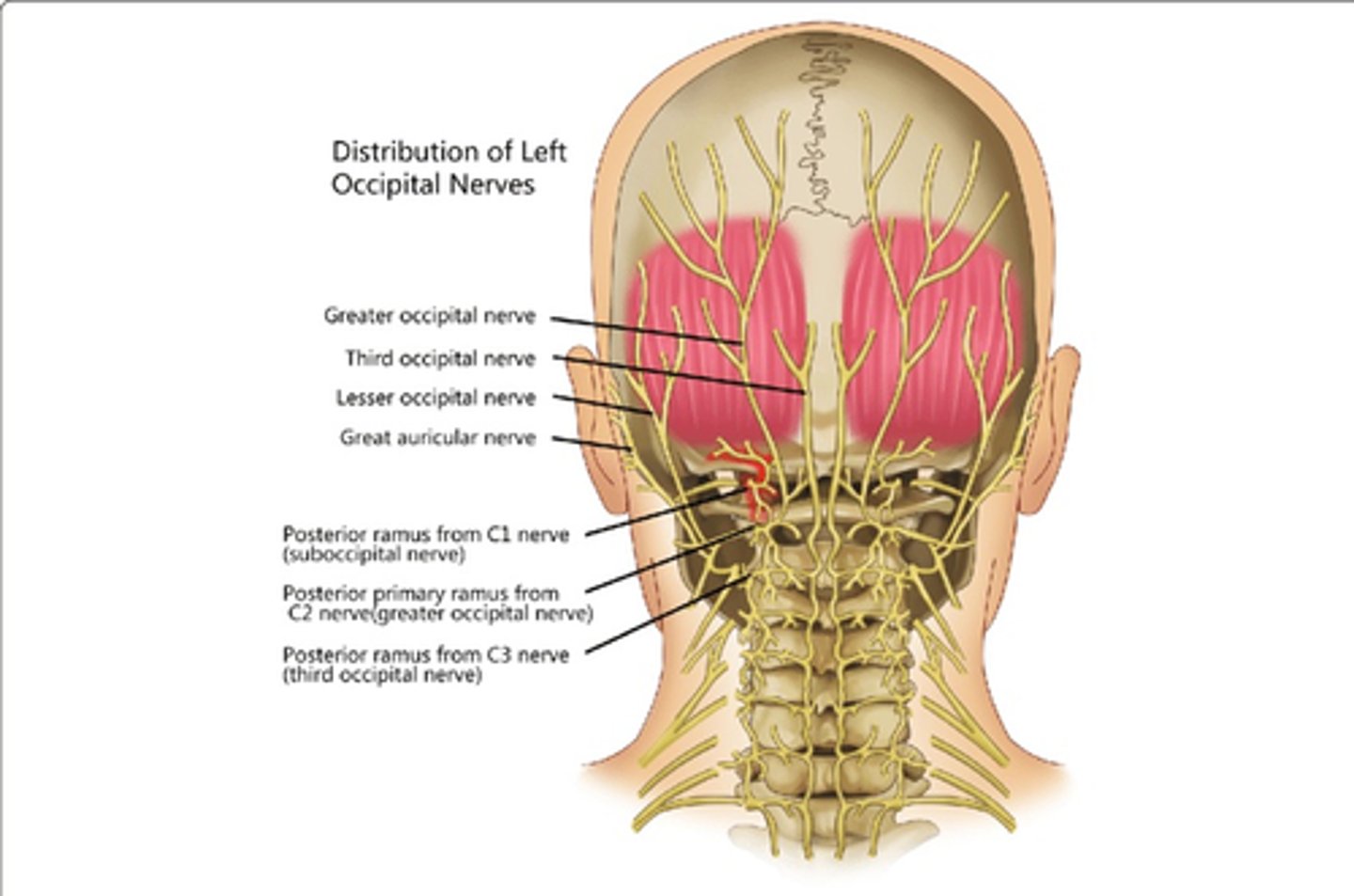
Which nerve(s) innervate Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor?
• Posterior Rami, C1
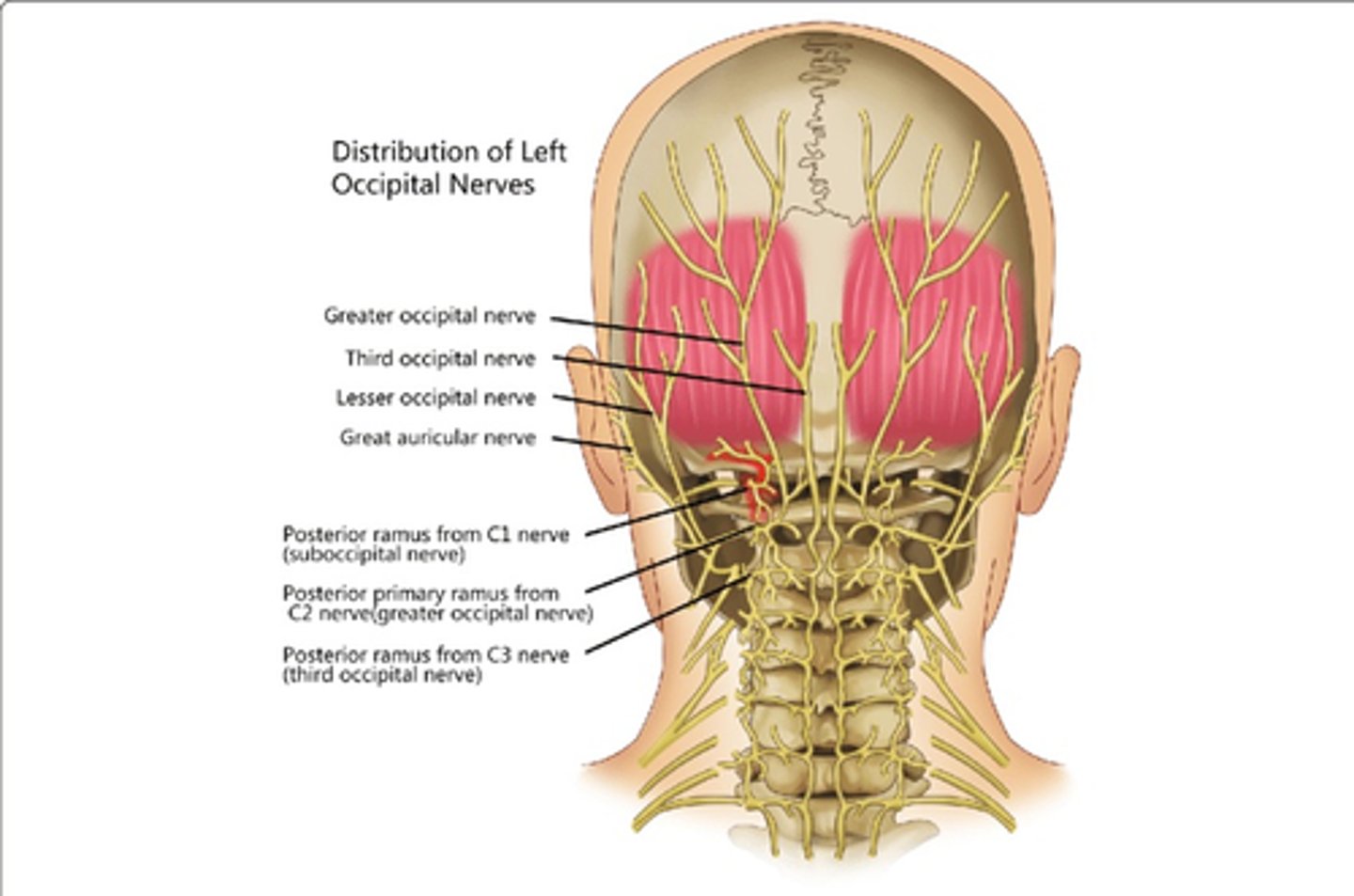
Which nerve(s) innervate Obliquus Capitis Superior?
• Posterior Rami, C1
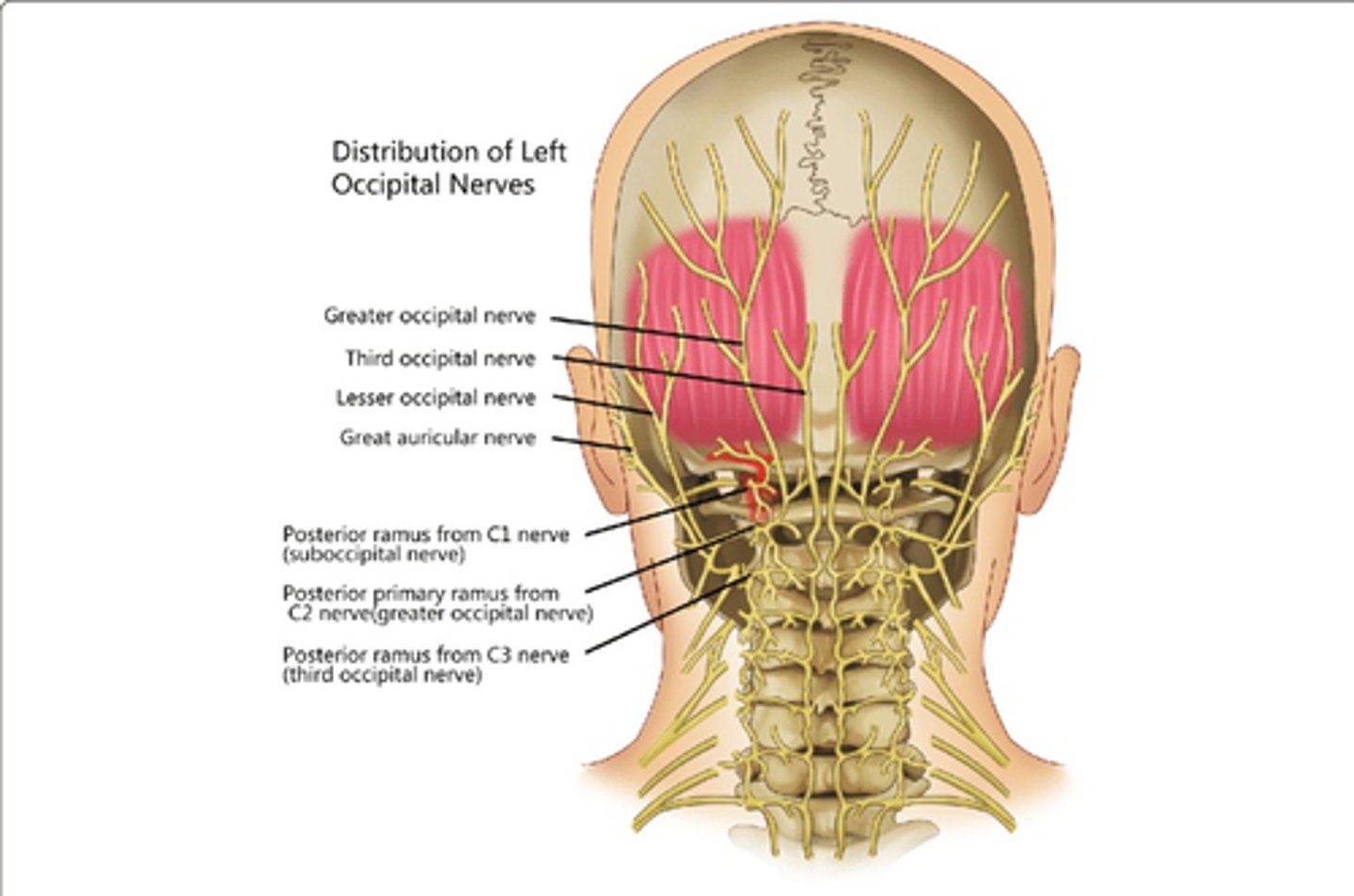
Which nerve(s) innervate Obliquus Capitis Inferior?
• Posterior Rami, C1
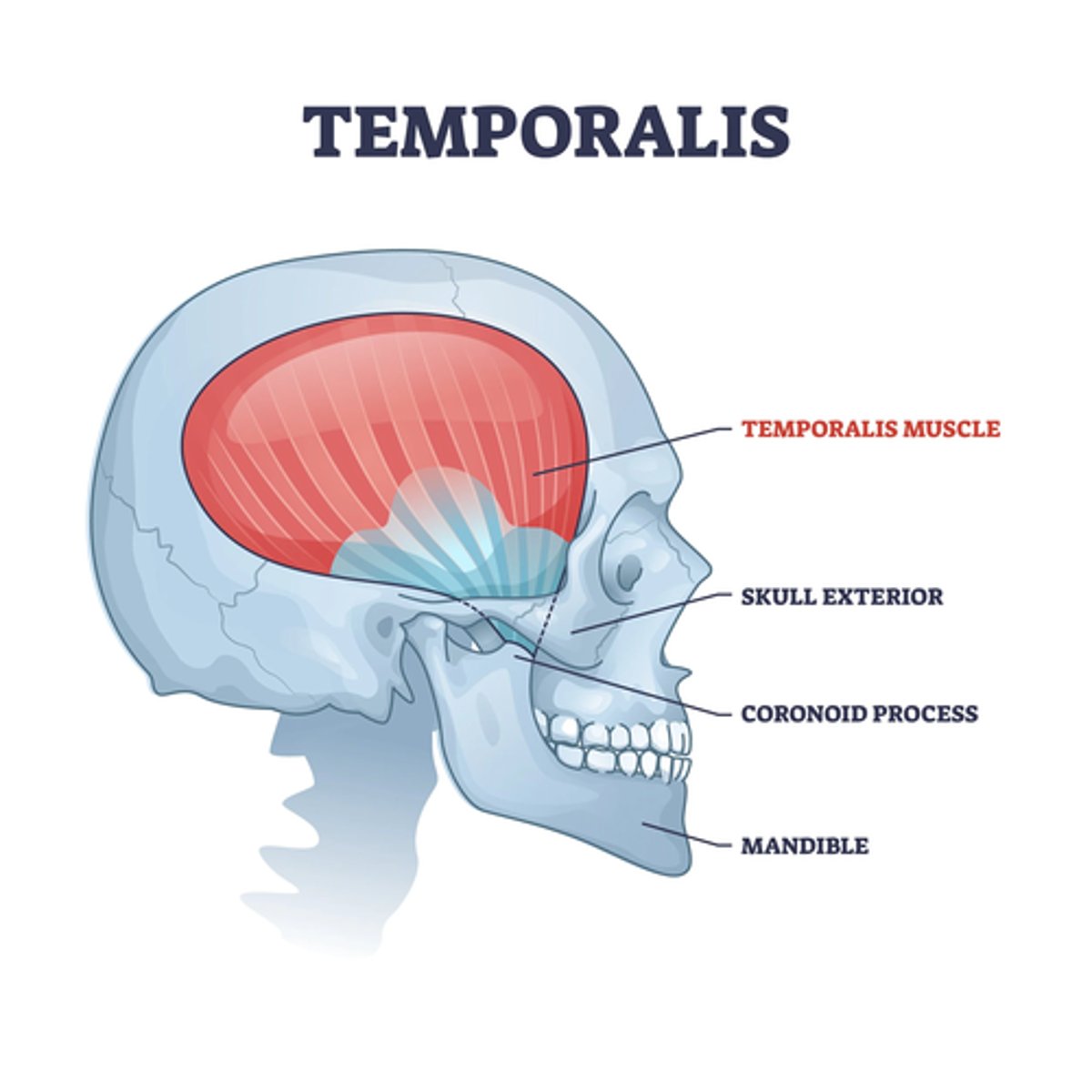
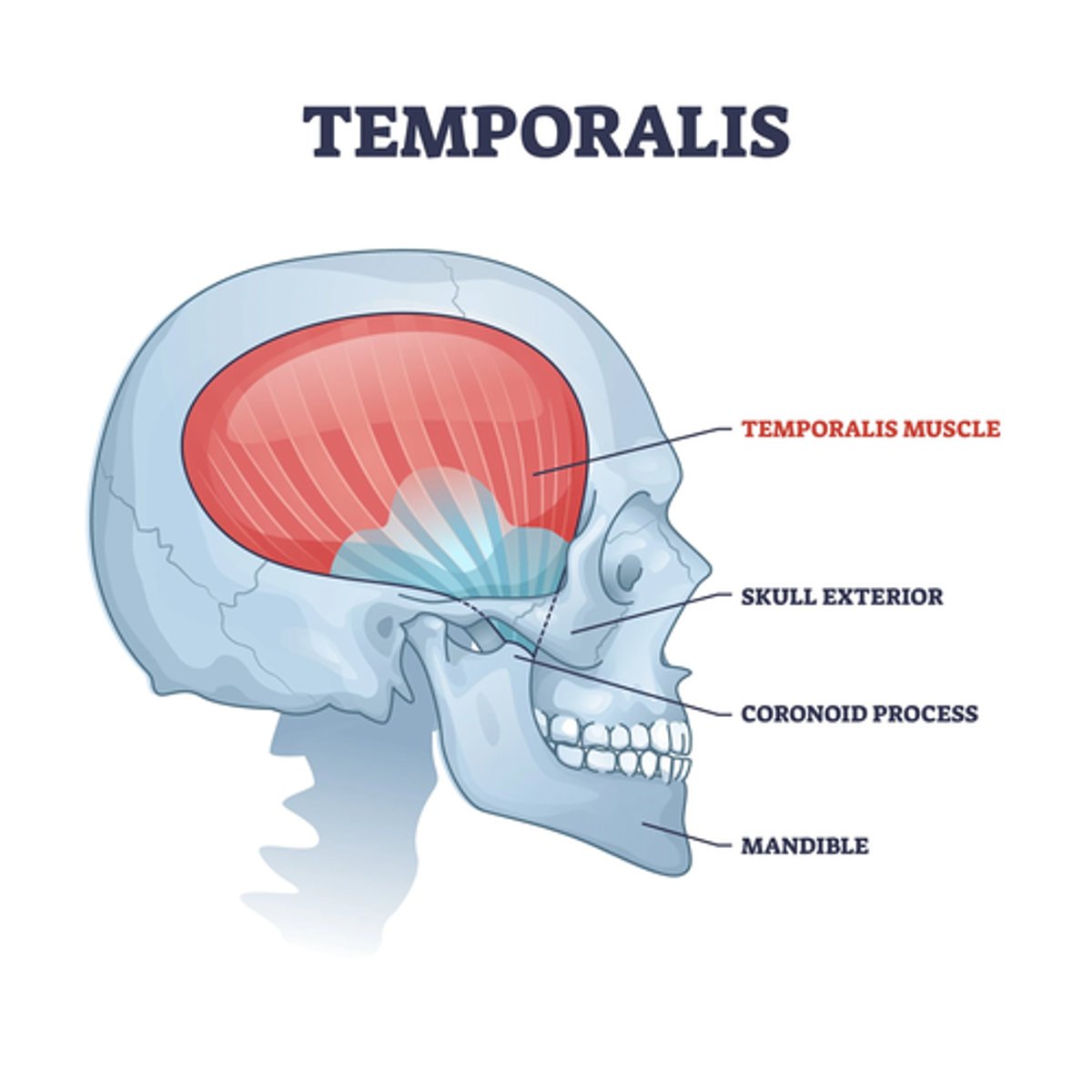
What is the origin of the Temporalis muscle?
• Temporal fossa
• Temporal fascia
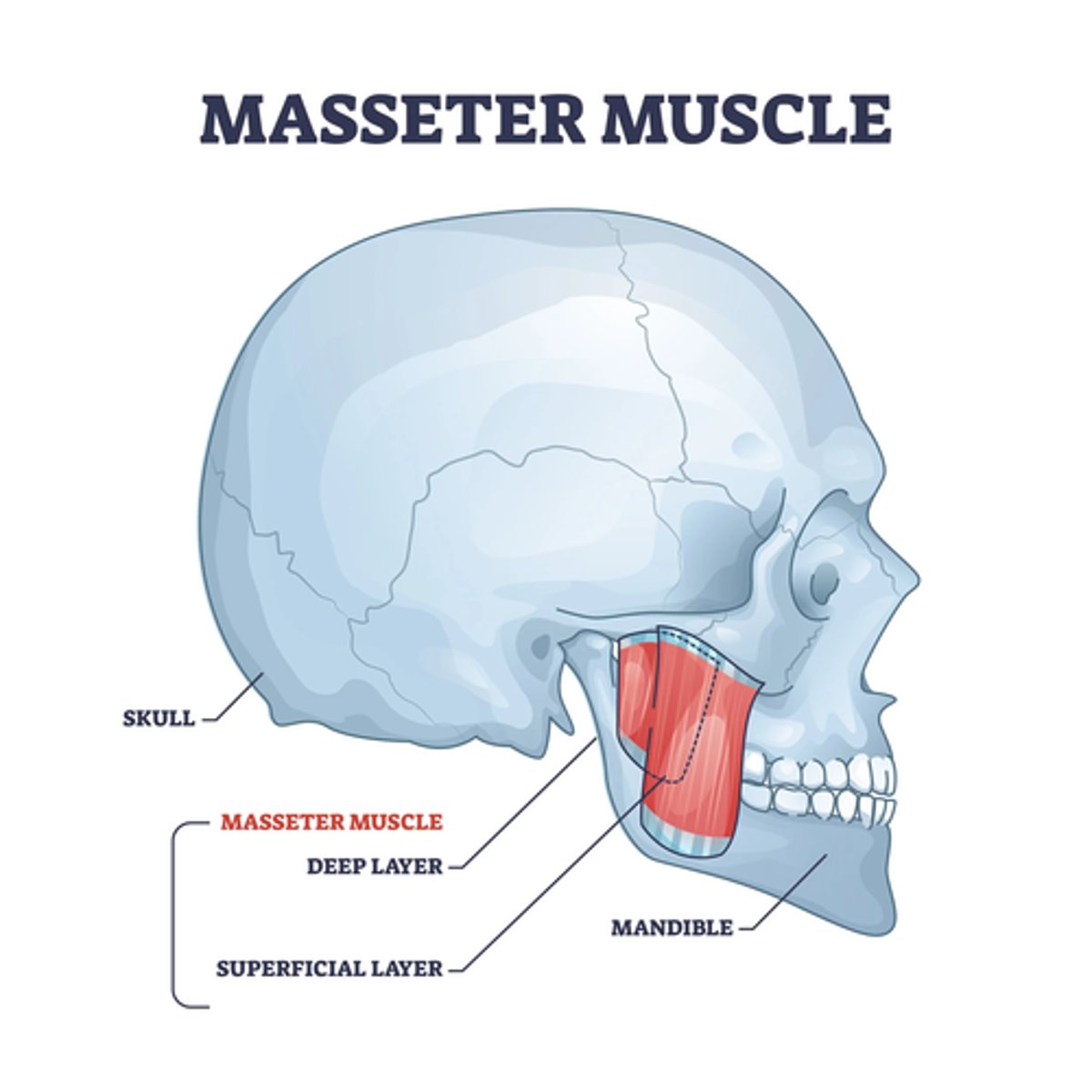
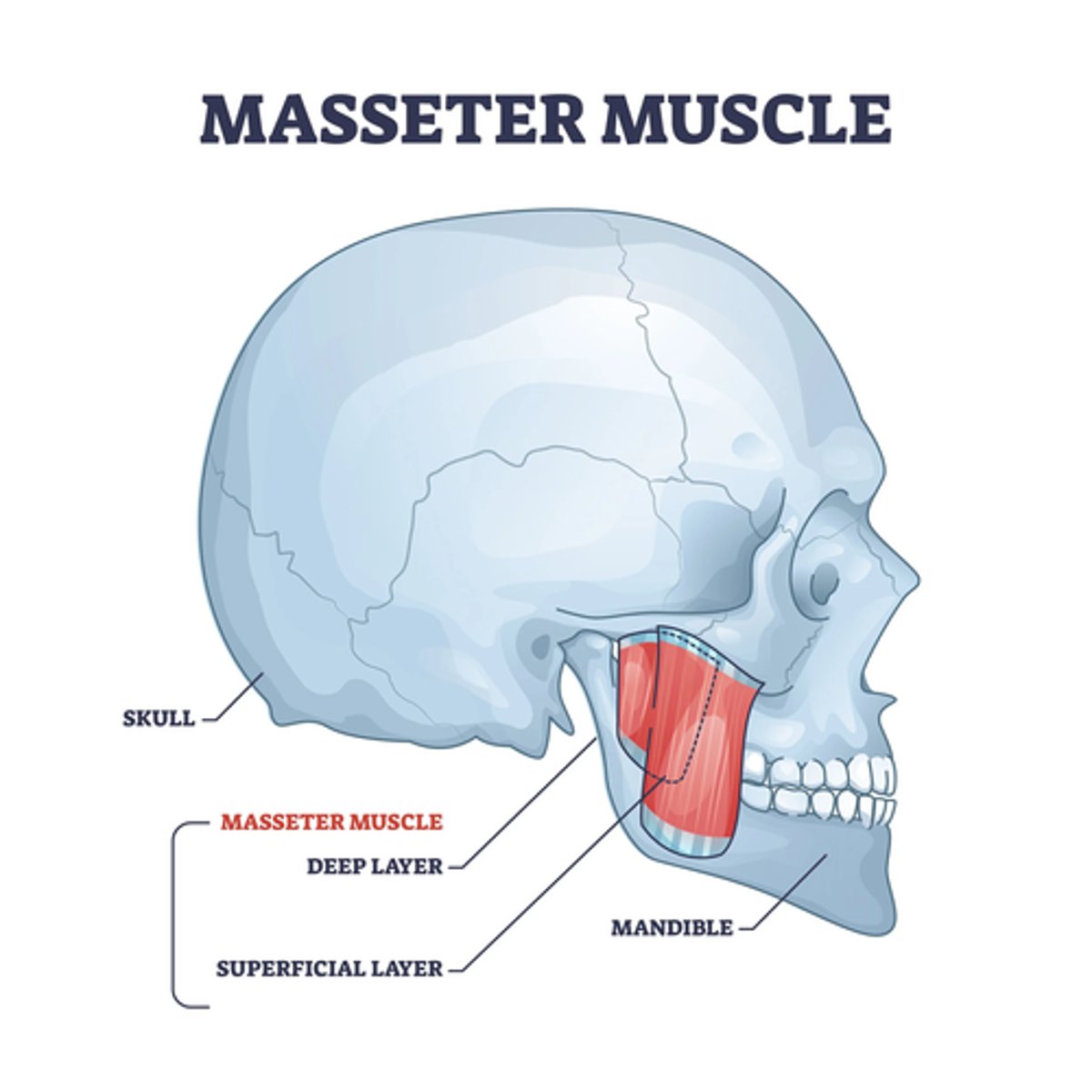
What is the origin of the Masseter muscle?
• Zygomatic arch
• Zygomatic process
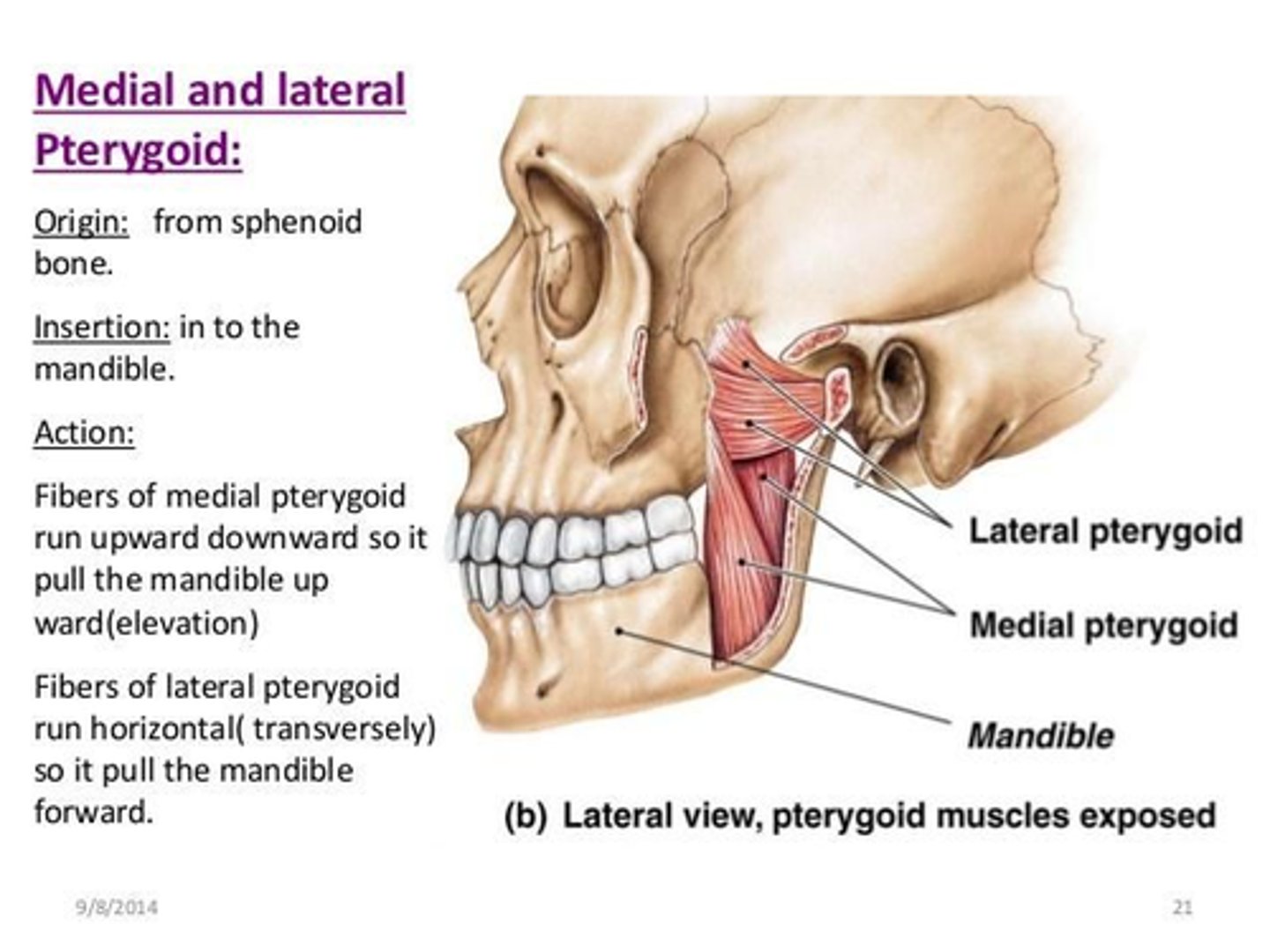
What is the origin of the Medial Pterygoid muscle?
• Deep head: medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate
• Superficial head: tuberosity of maxilla
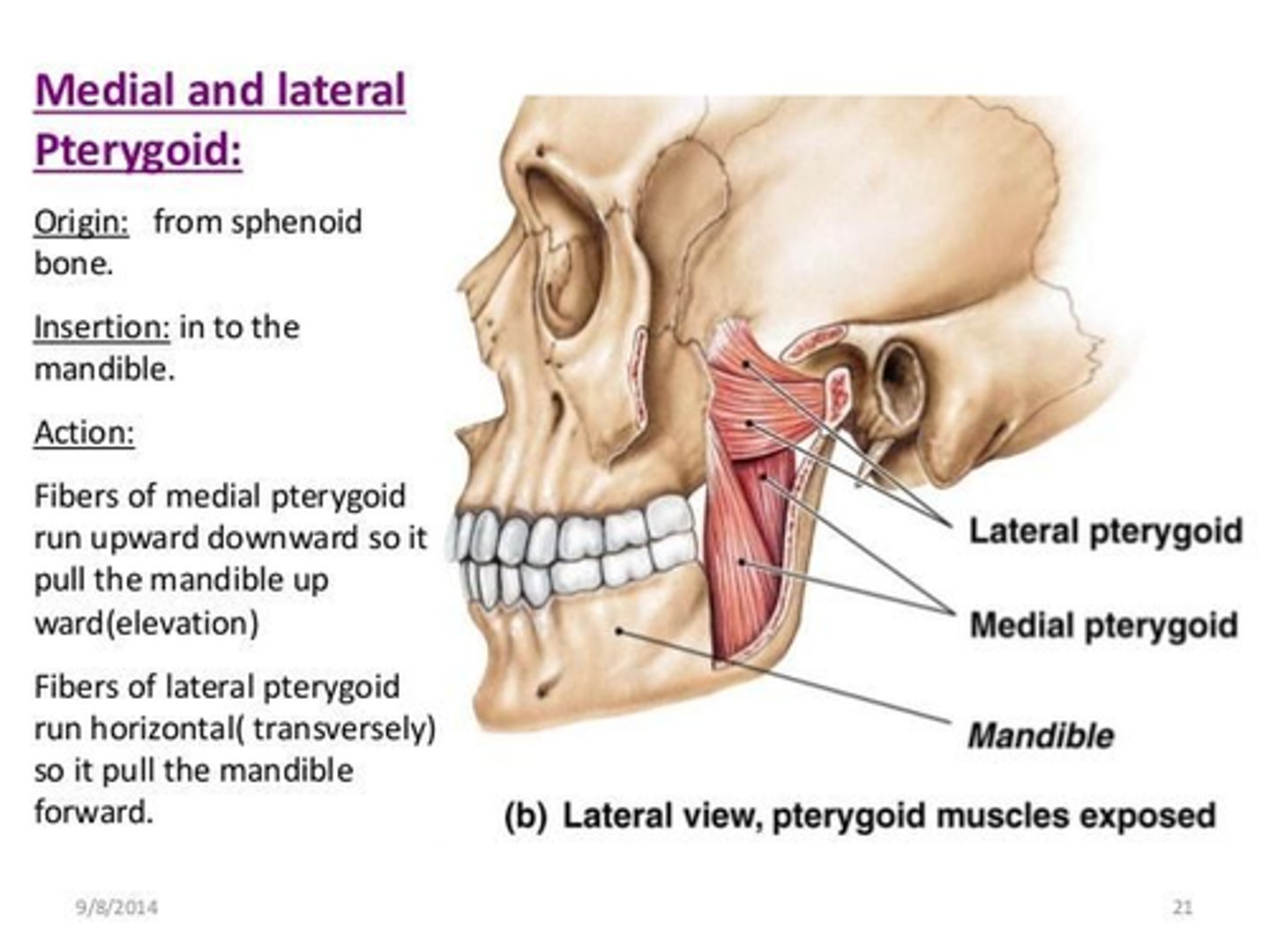
What is the origin of the Lateral Pterygoid muscle?
• Upper head: infratemporal surface (greater wing) of sphenoid
• Lower head: lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate
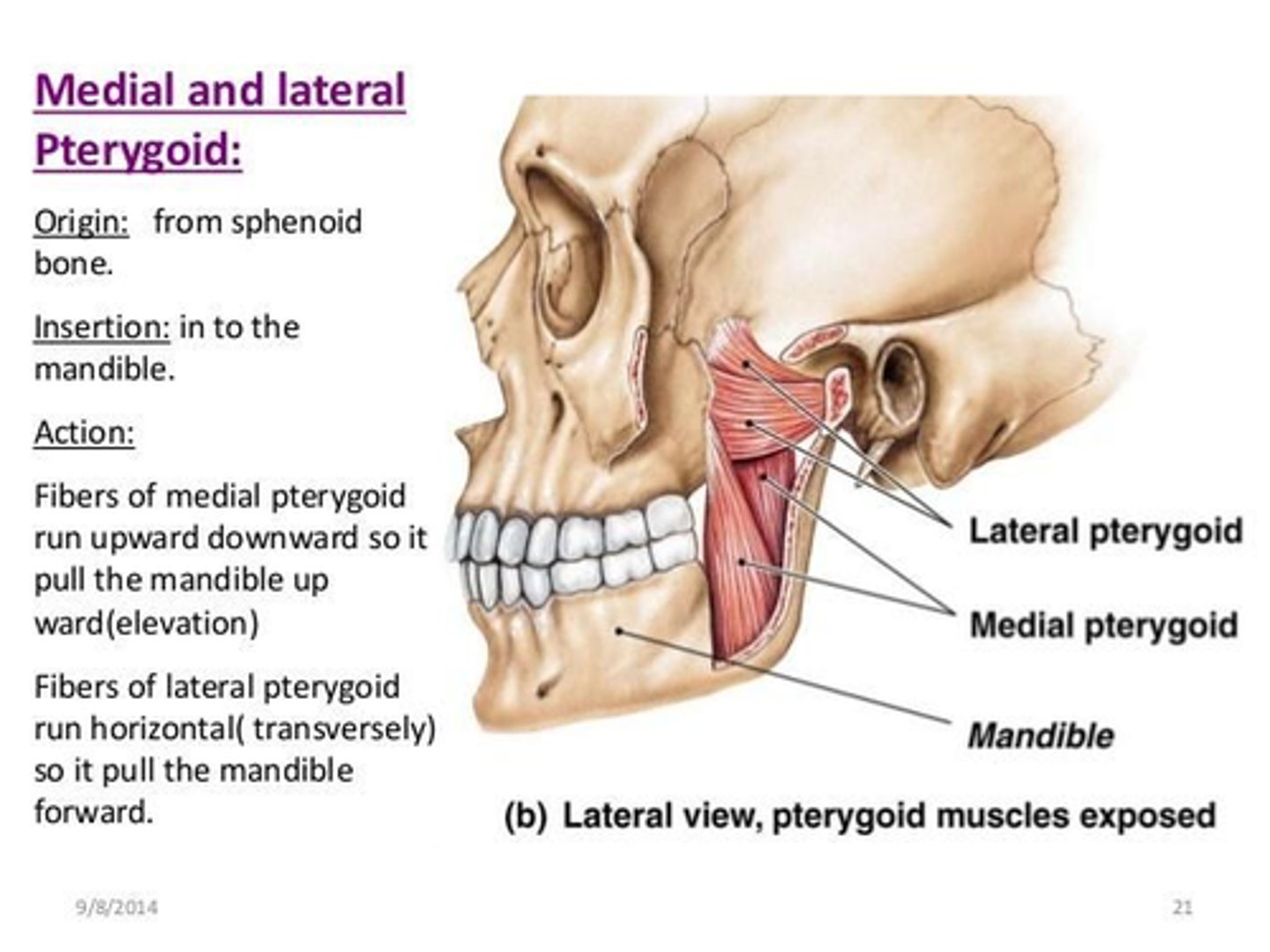
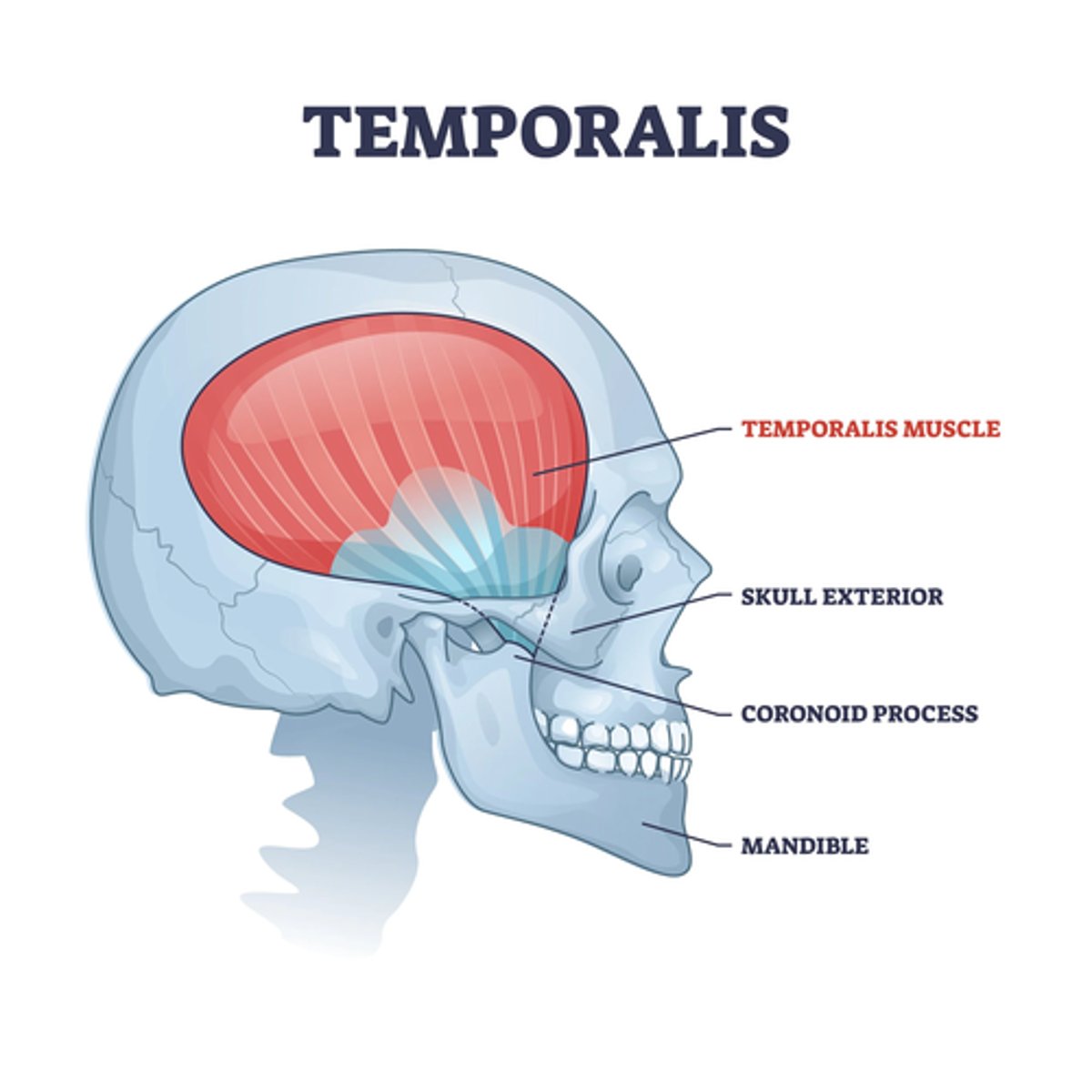
What is the insertion of the Temporalis muscle?
• Coronoid process and the anterior border ramus of mandible
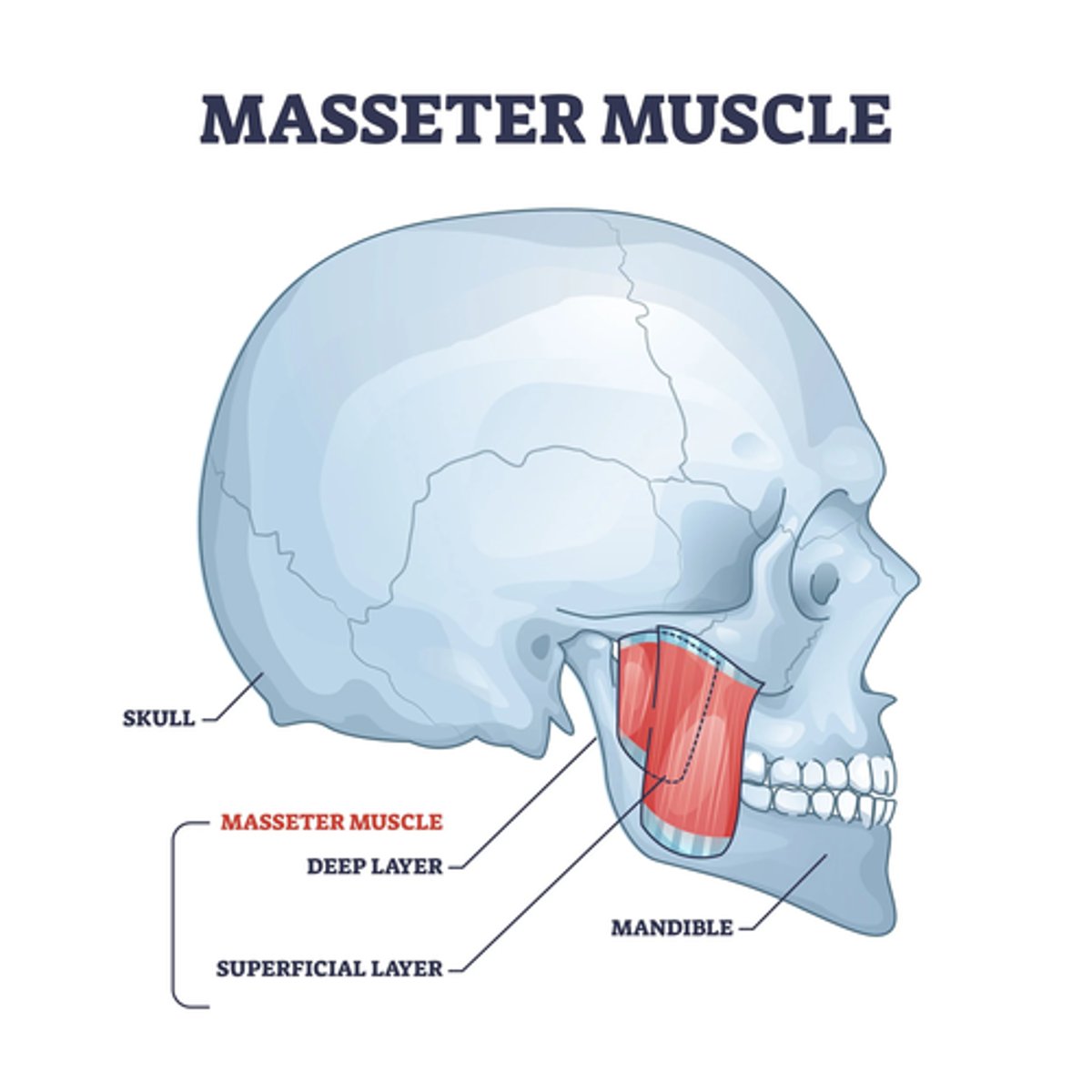
What is the insertion of the Masseter muscle?
• Ramus and the lateral surface of the mandible
What is the insertion of the Medial Pterygoid muscle?
• Internal surface of Ramus of the Mandible
• Angle of the Mandible
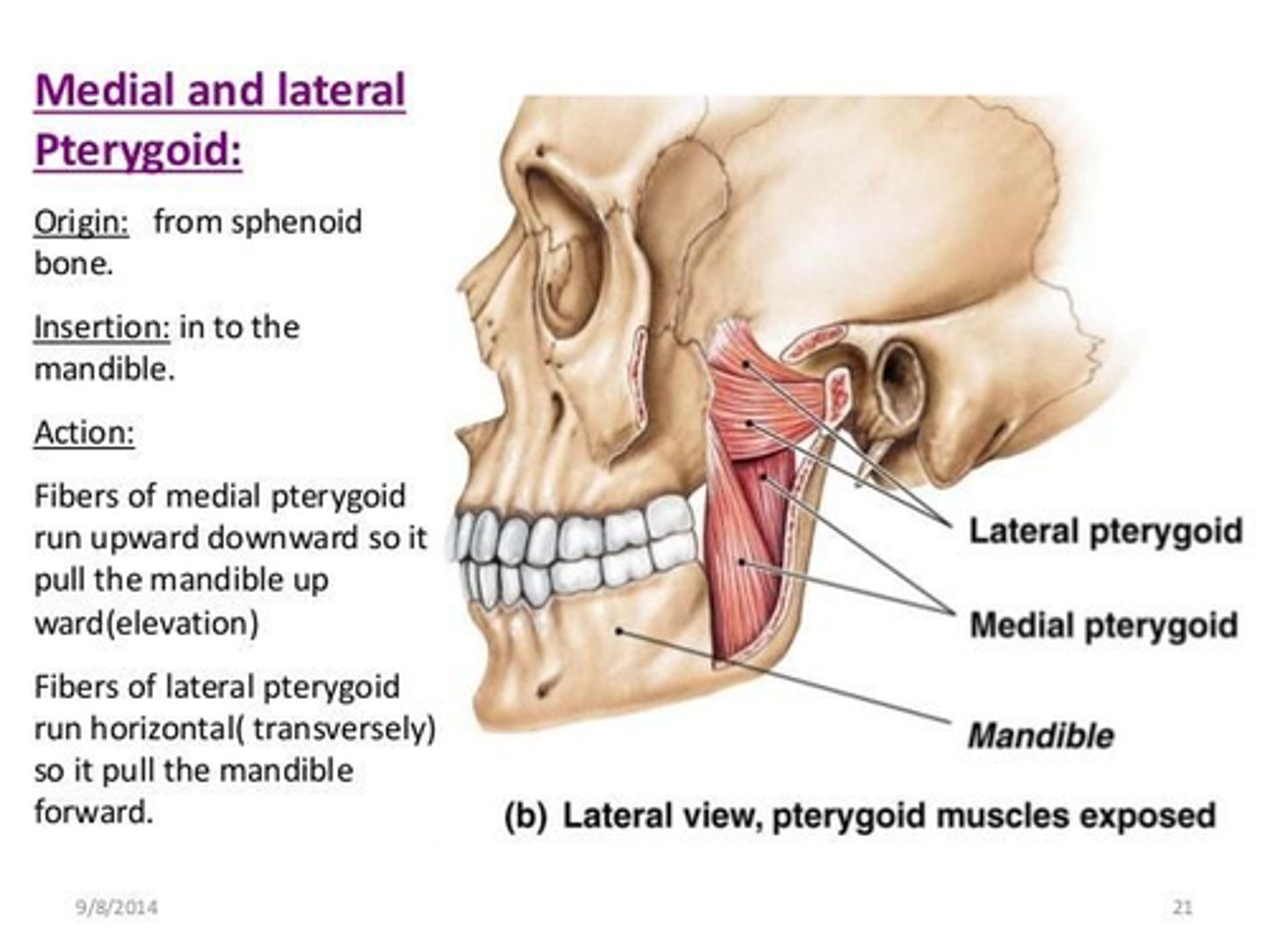
What is the insertion of the Lateral Pterygoid muscle?
• Articular disc, joint capsule
• Fovea of mandibular condyle
What is the action of the Temporalis muscle?
• Elevate and retract the mandible
What is the action of the Masseter muscle?
Elevate mandible
• Superficial fibers protrude the mandible
• Deep fibers retract the mandible
What is the action of the Medial Pterygoid muscle?
• Elevate mandible
• Assist with mandible protrusion
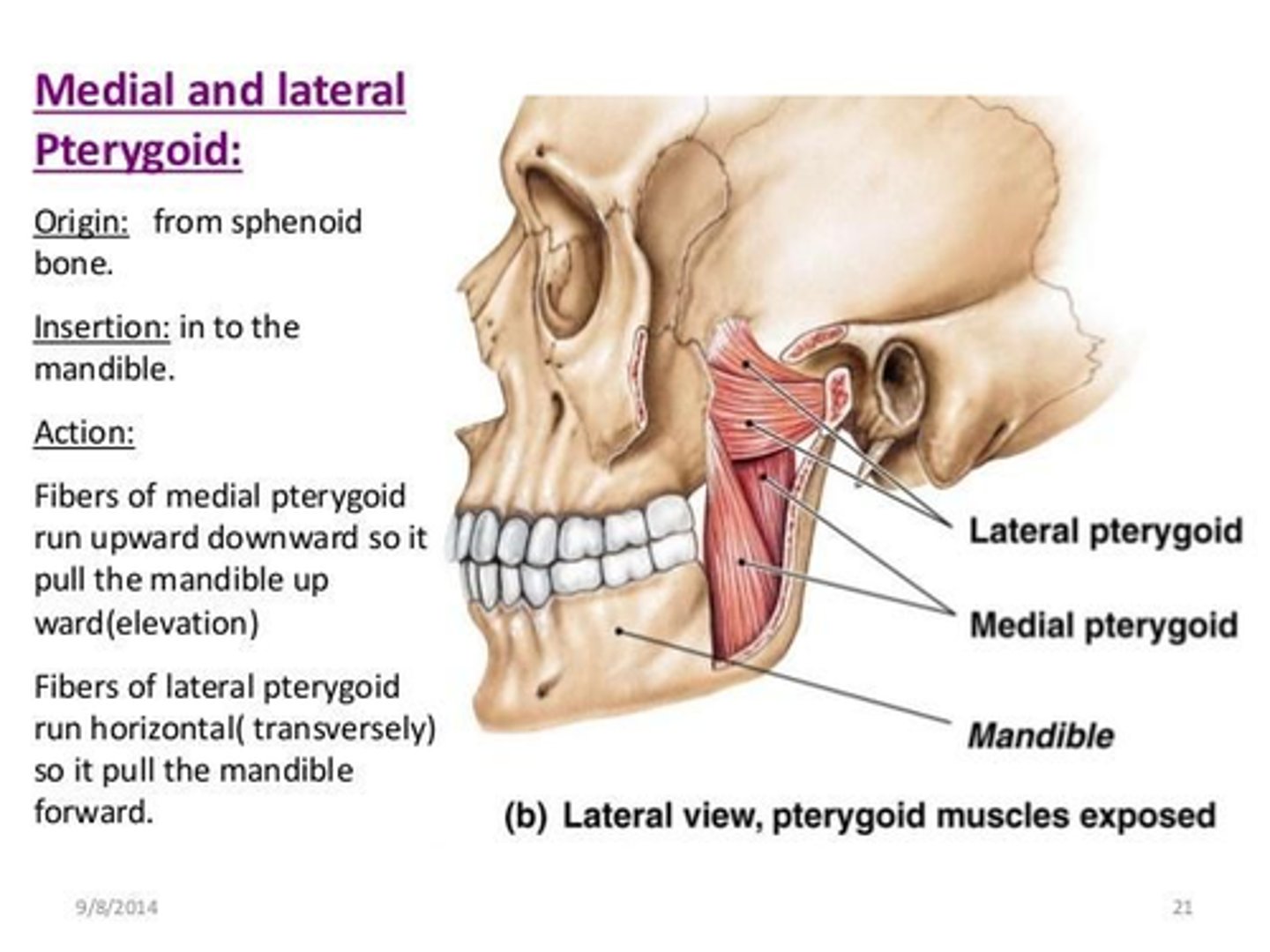
What is the action of the Lateral Pterygoid muscle?
• (Bilateral) Protrude mandible when opening mouth, depress the mandible
• (Unilateral) Deviate mandible contralaterally (grinding)

What is the nerve innervation of the Temporalis muscle?
• Trigeminal nerve V3, Mandibular Branch
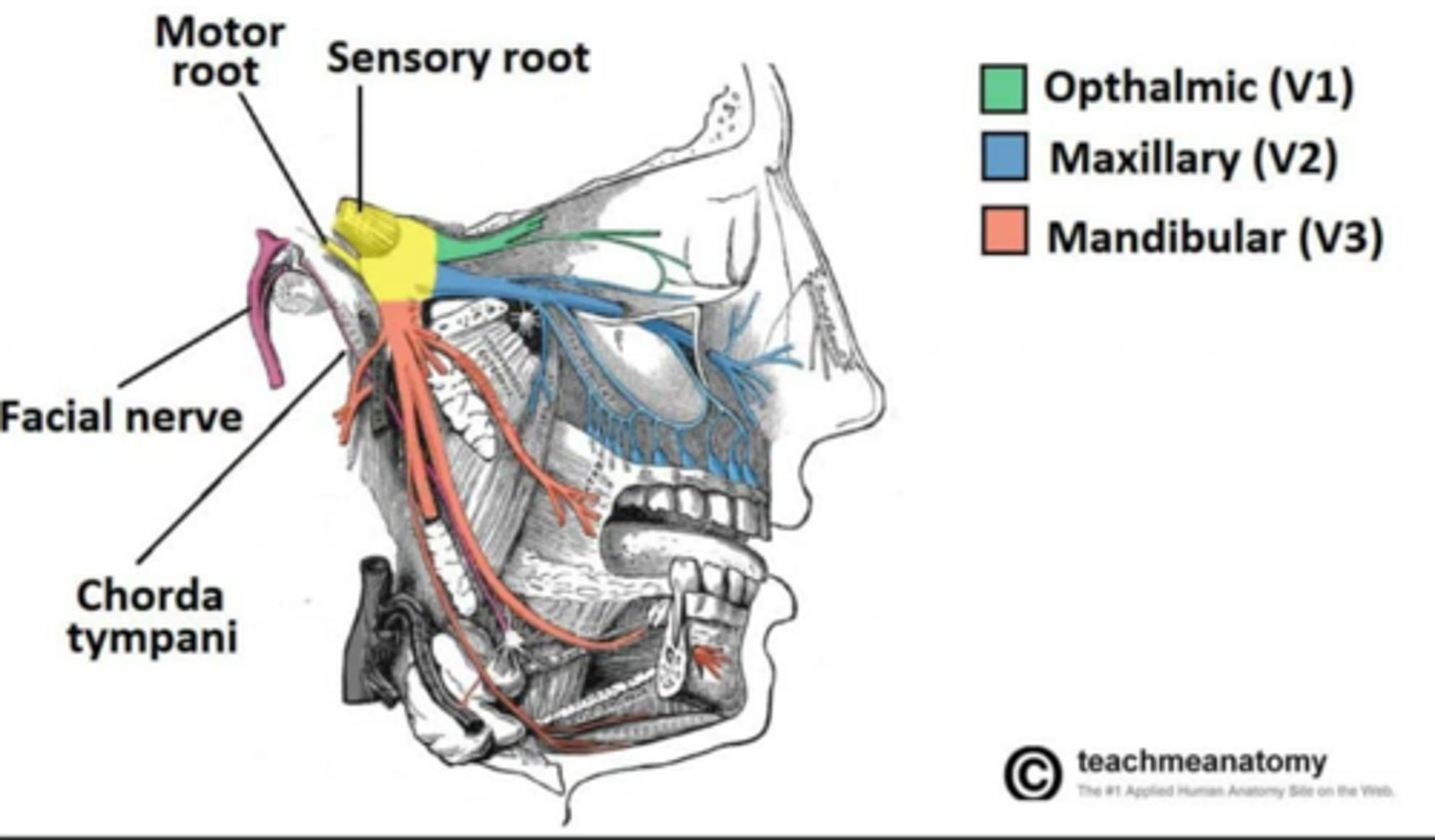
What is the nerve innervation of the Masseter muscle?
• Trigeminal nerve V3
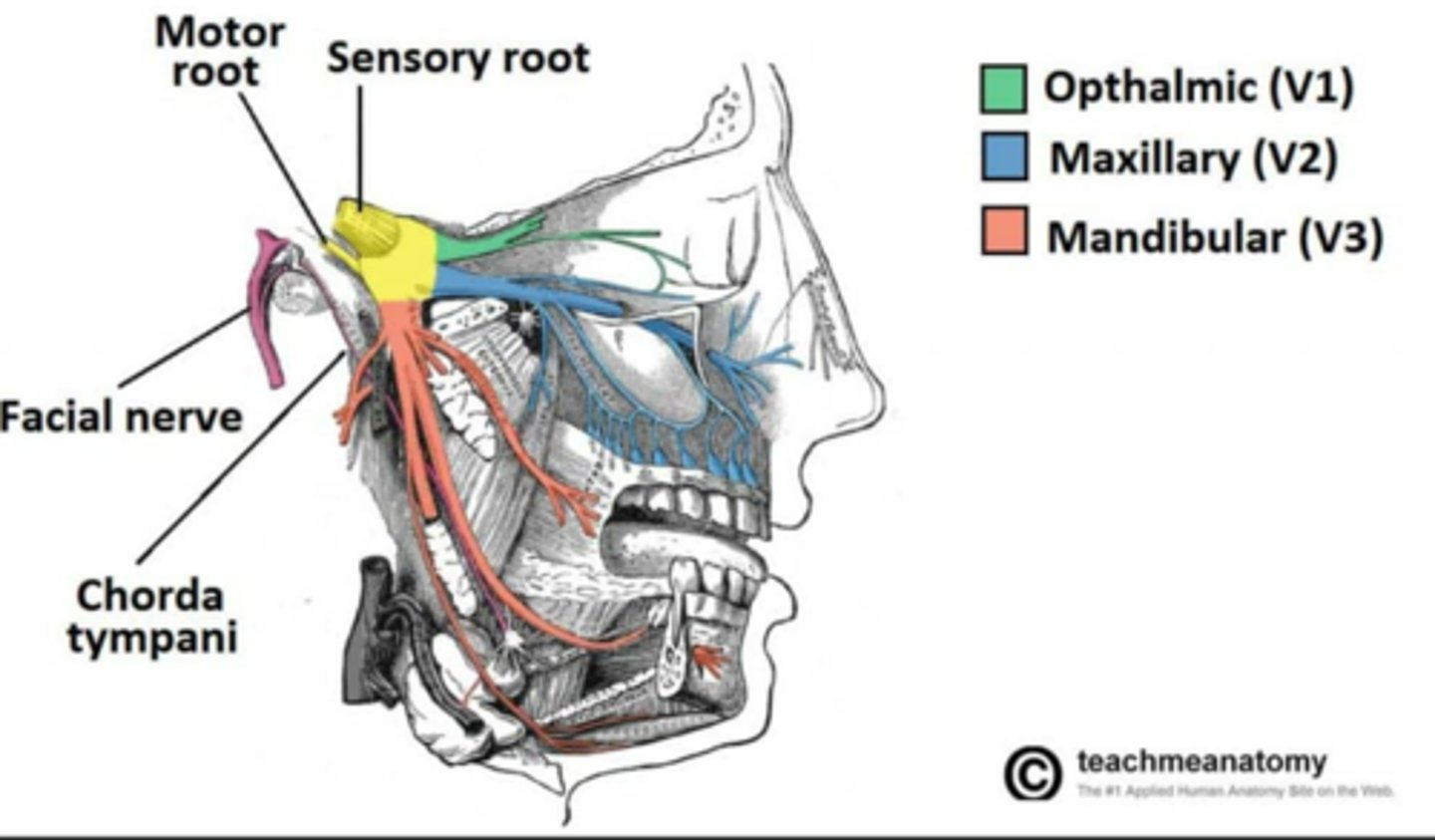
What is the nerve innervation of the Medial Pterygoid muscle?
• Trigeminal nerve V3
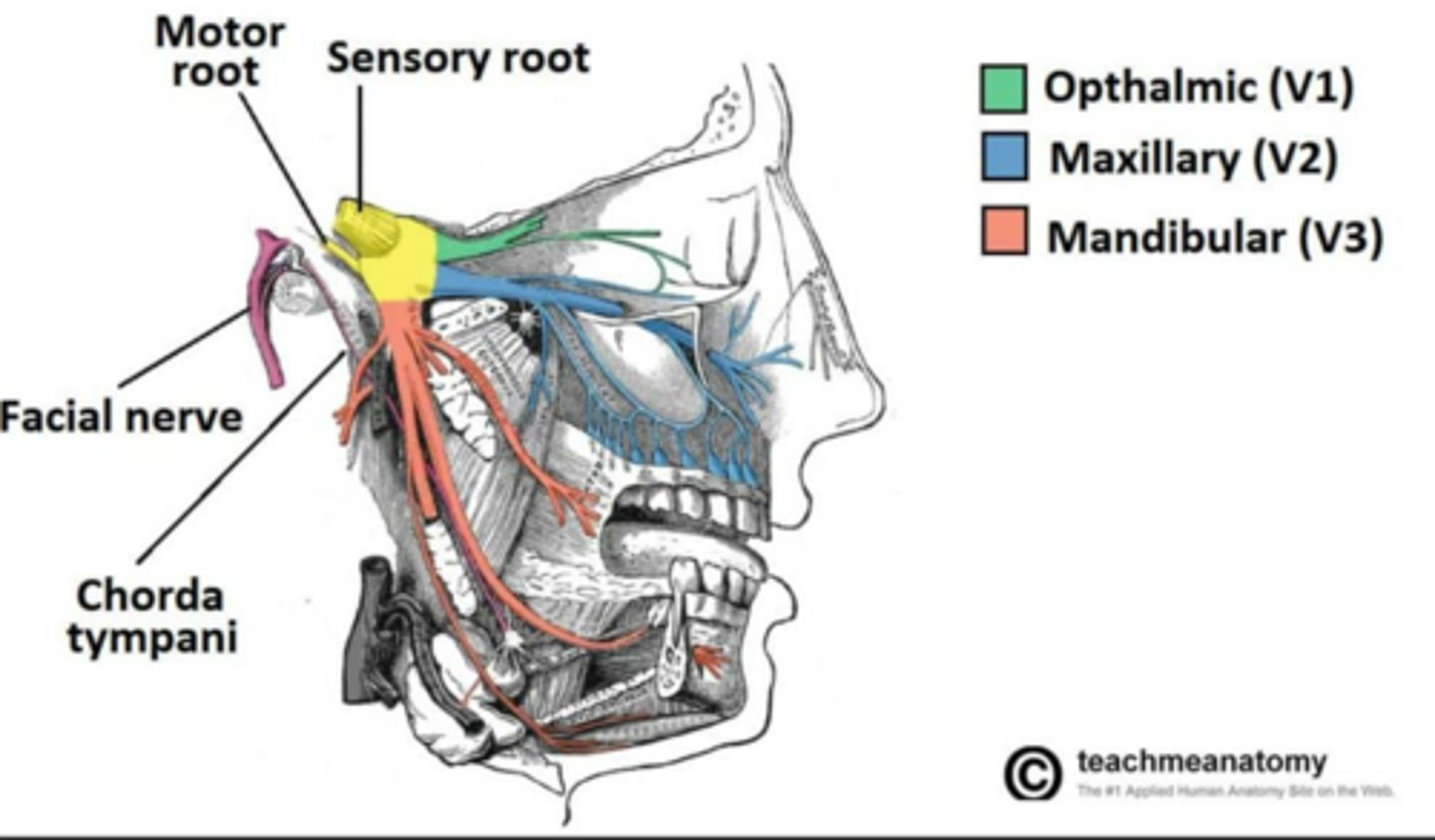
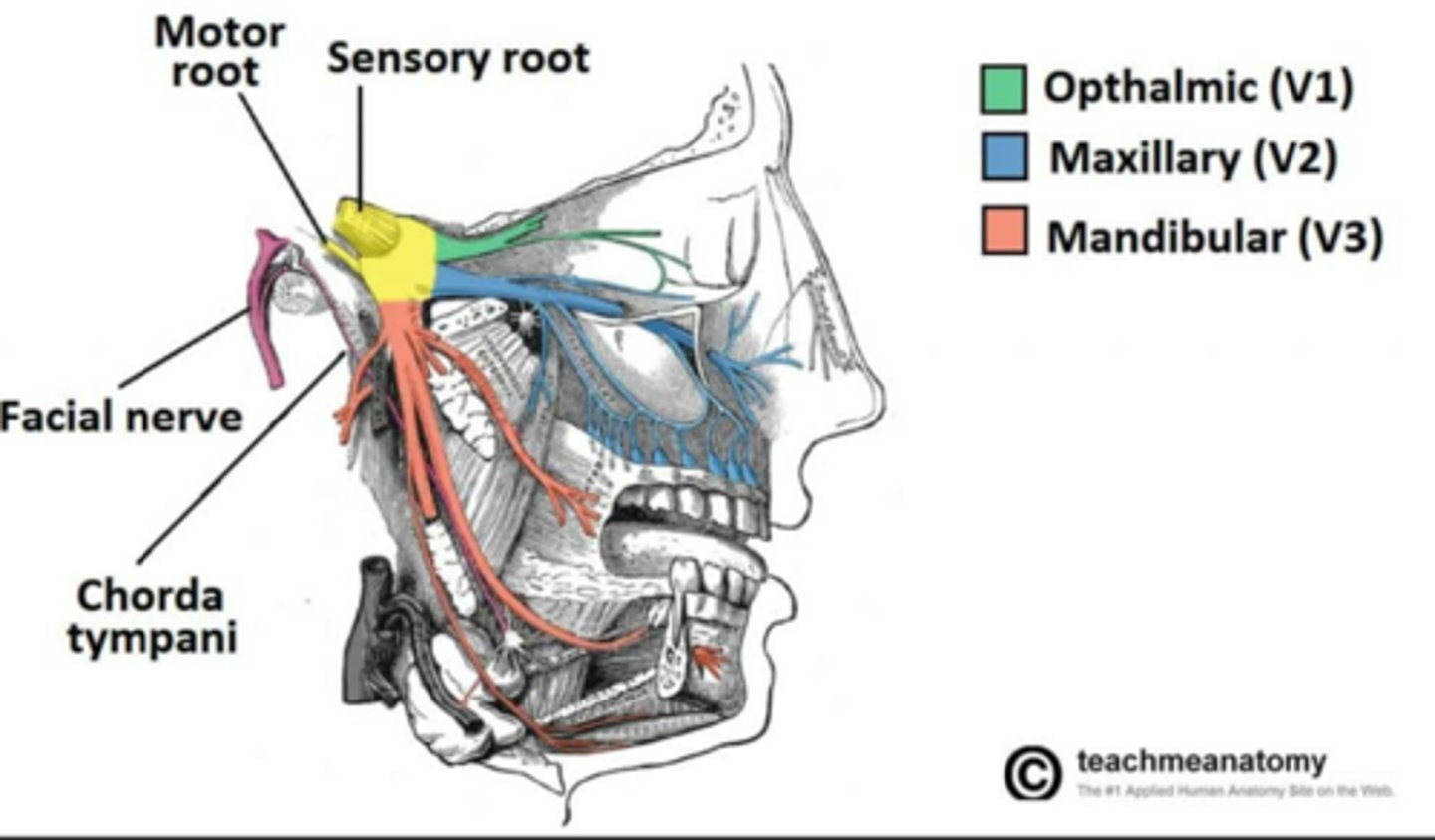
What is the nerve innervation of the Lateral Pterygoid muscle?
• Trigeminal nerve V3
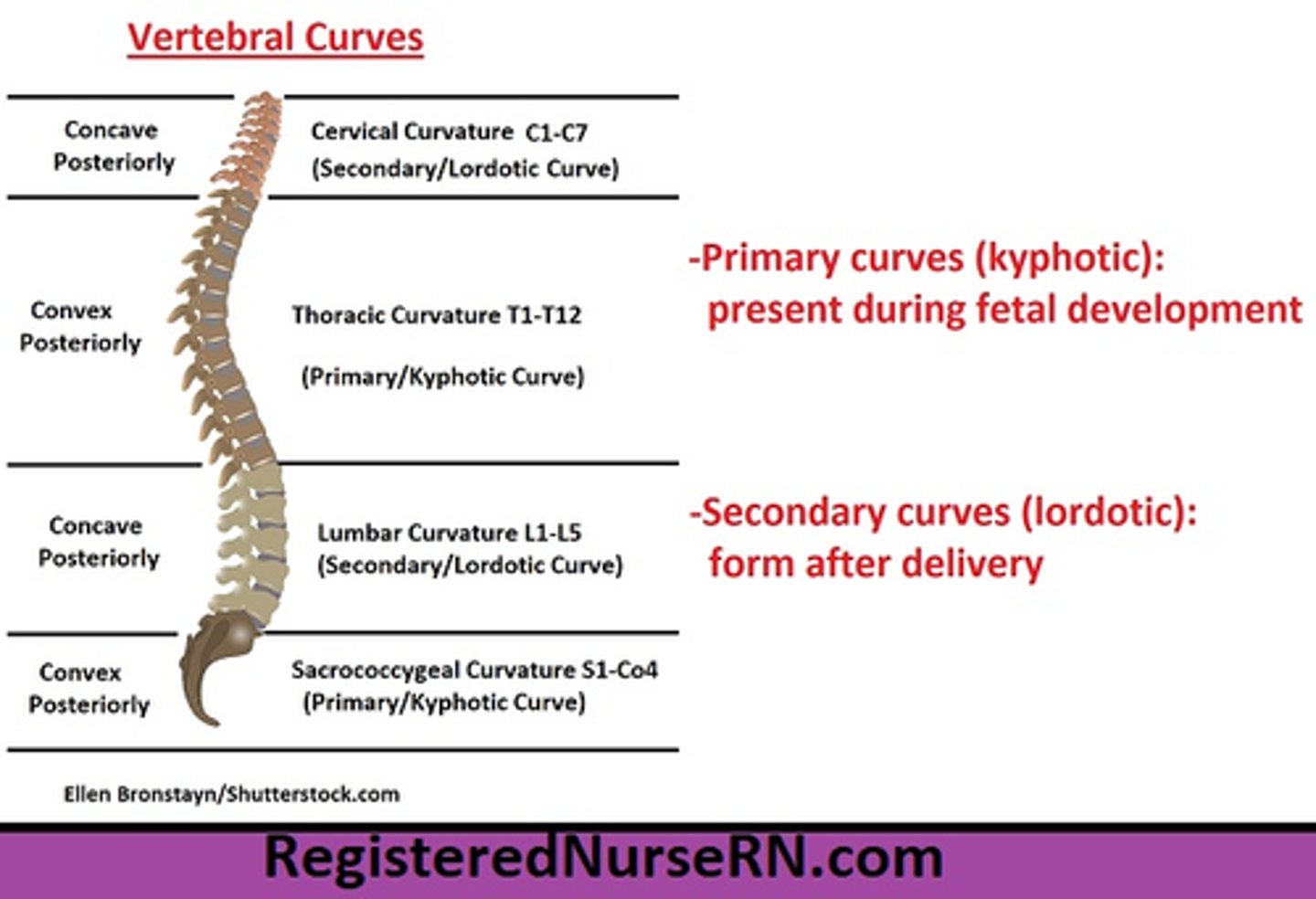
What are the Primary and Secondary curvature of the Spine?
• Primary is the anterior concave curvature.
* Kyphosis, Thoracic and Sacral portions of Spine
• Secondary is the anterior convex curvature
* Lordosis, Cervical and Lumbar portions of Spine
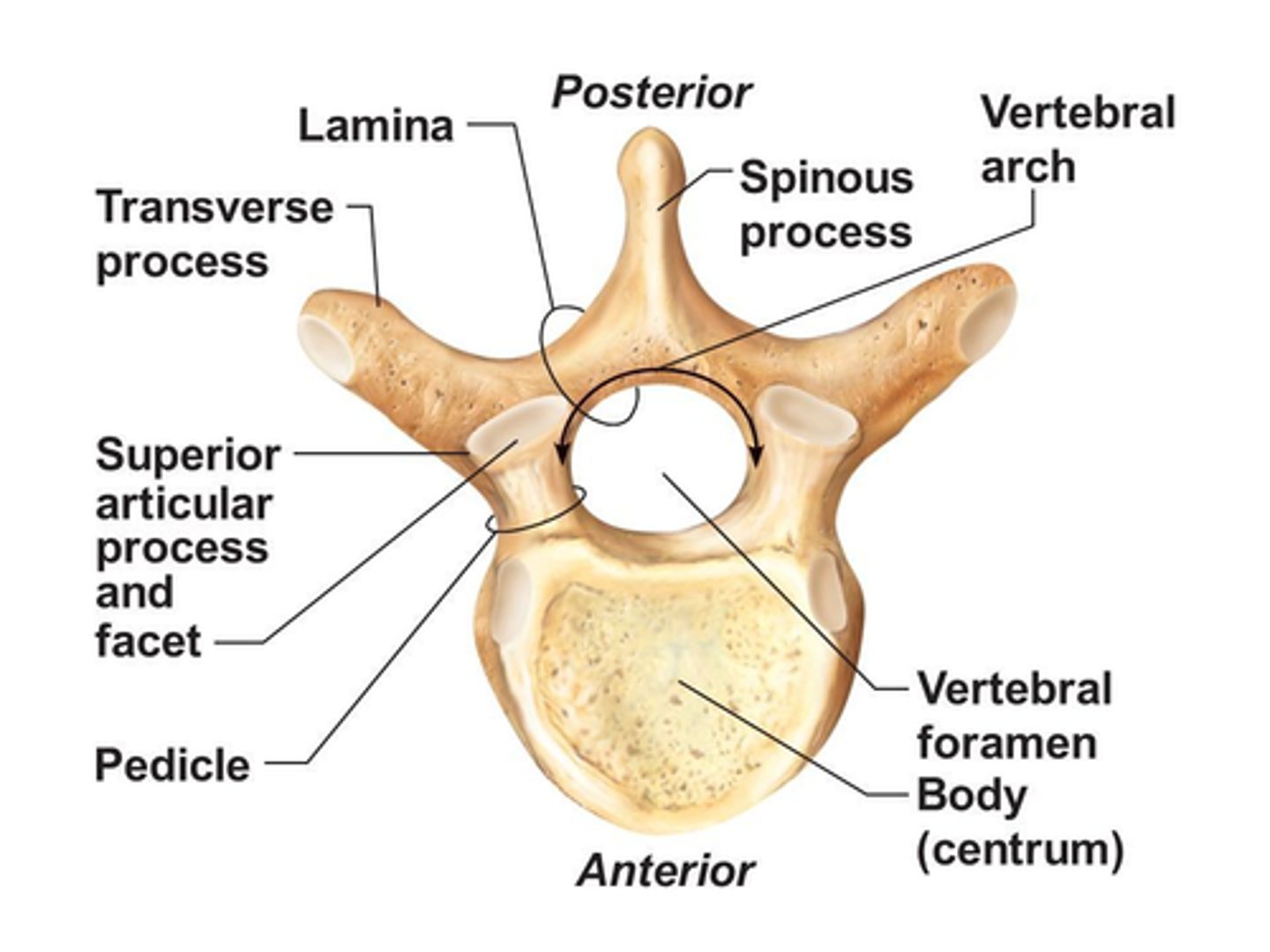
What is the Spinous Process of a typical vertebrae?
• Junction of the two Lamina
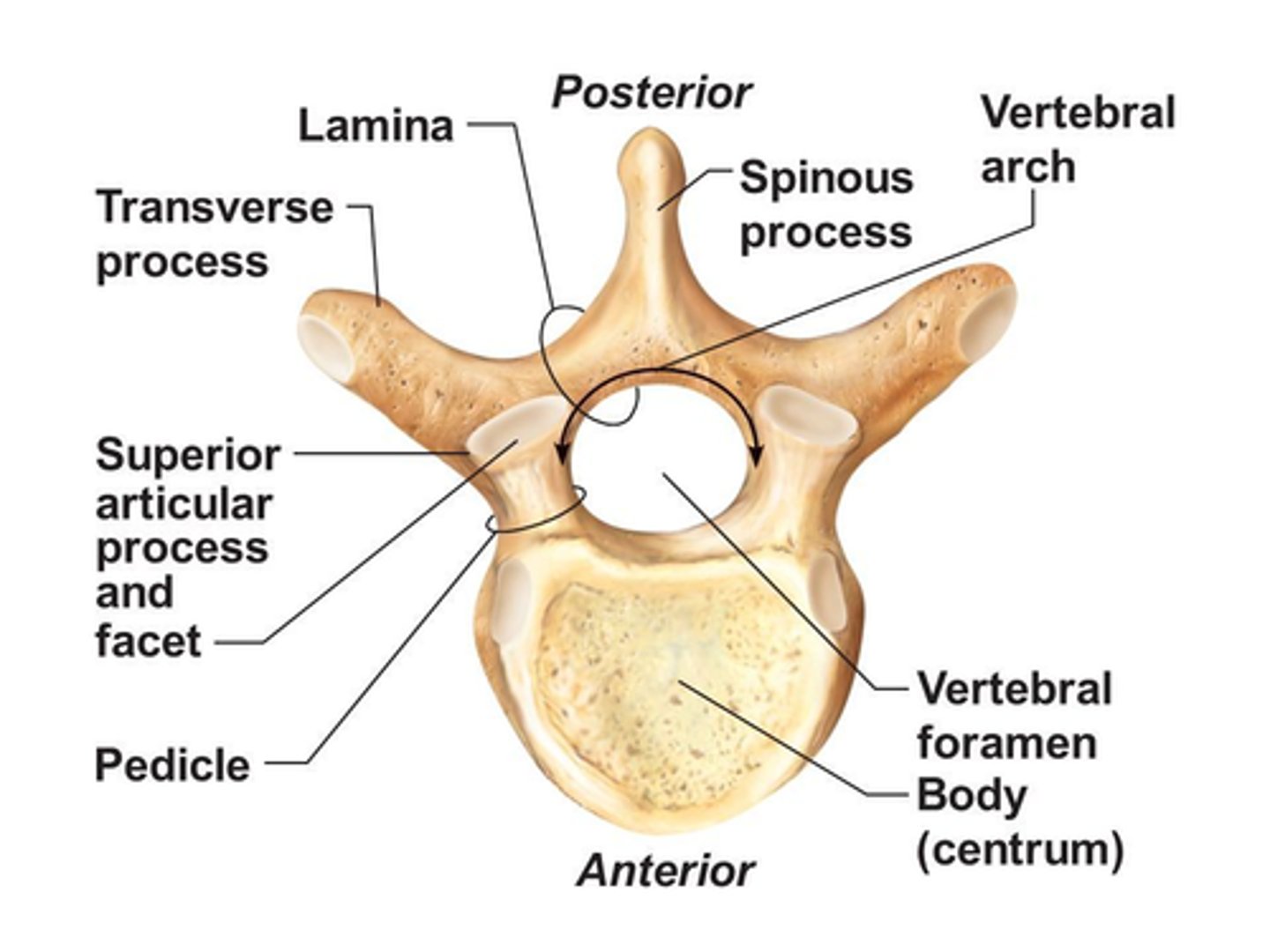
What is the Transverse Process of a typical vertebrae?
• Junction of Pedicle and Lamina on each side
• Articulation with ribs in Thoracic region
What is unique about the Atlas (C1)?
• No vertebral body or disc
• Has anterior arch
• Has Anterior Arch Facet for Dens
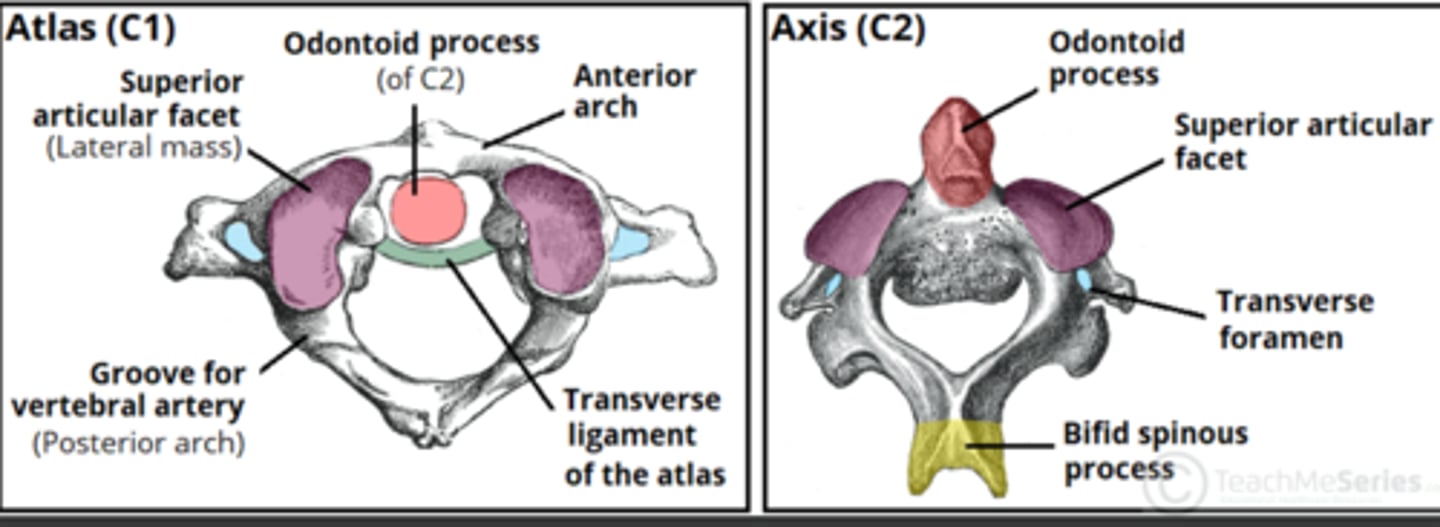
What are the unique features of Cervical Vertebrae?
• Laterally they have Foramen Transversarium for vessels to travel to skull
• Triangular Vertebral Canal
• C2 - C6 have Bipid Spinous Process
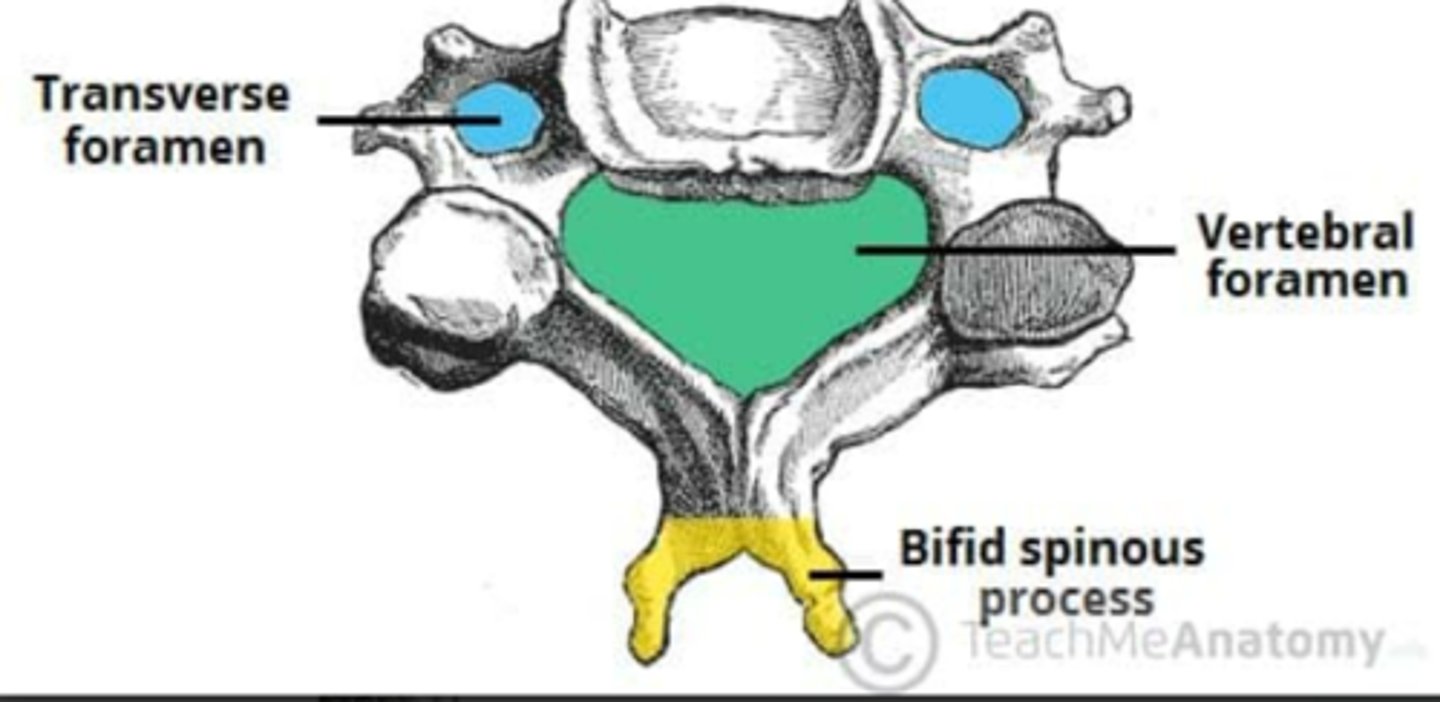
Describe the Ligaments of the Axis (C2)
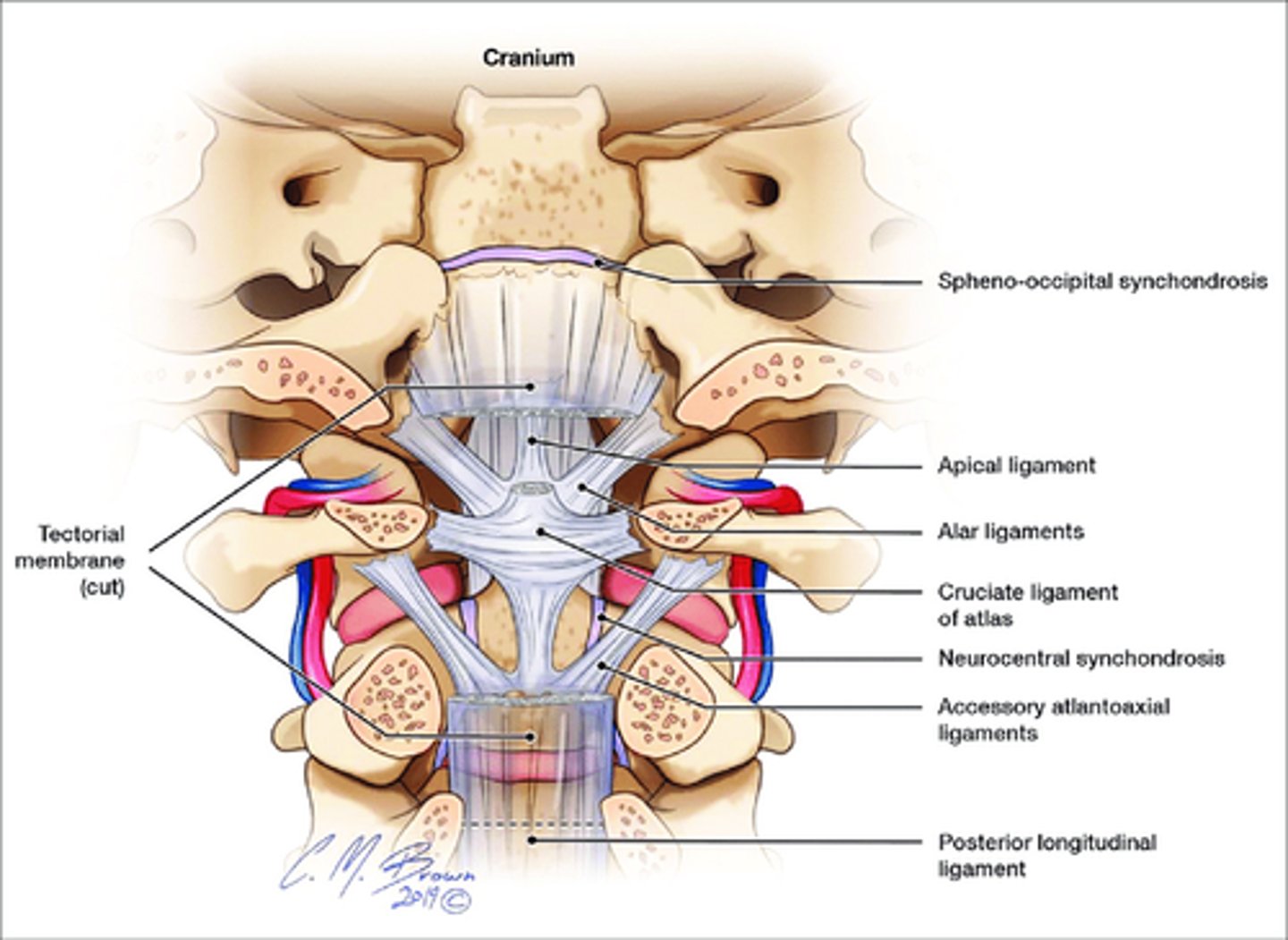
• Transverse Ligament that holds dens in contact with C1
• Posterior and Transverse Ligaments together for Cruciform Ligament, which is a key stabilizer of Atlantoaxial Joint
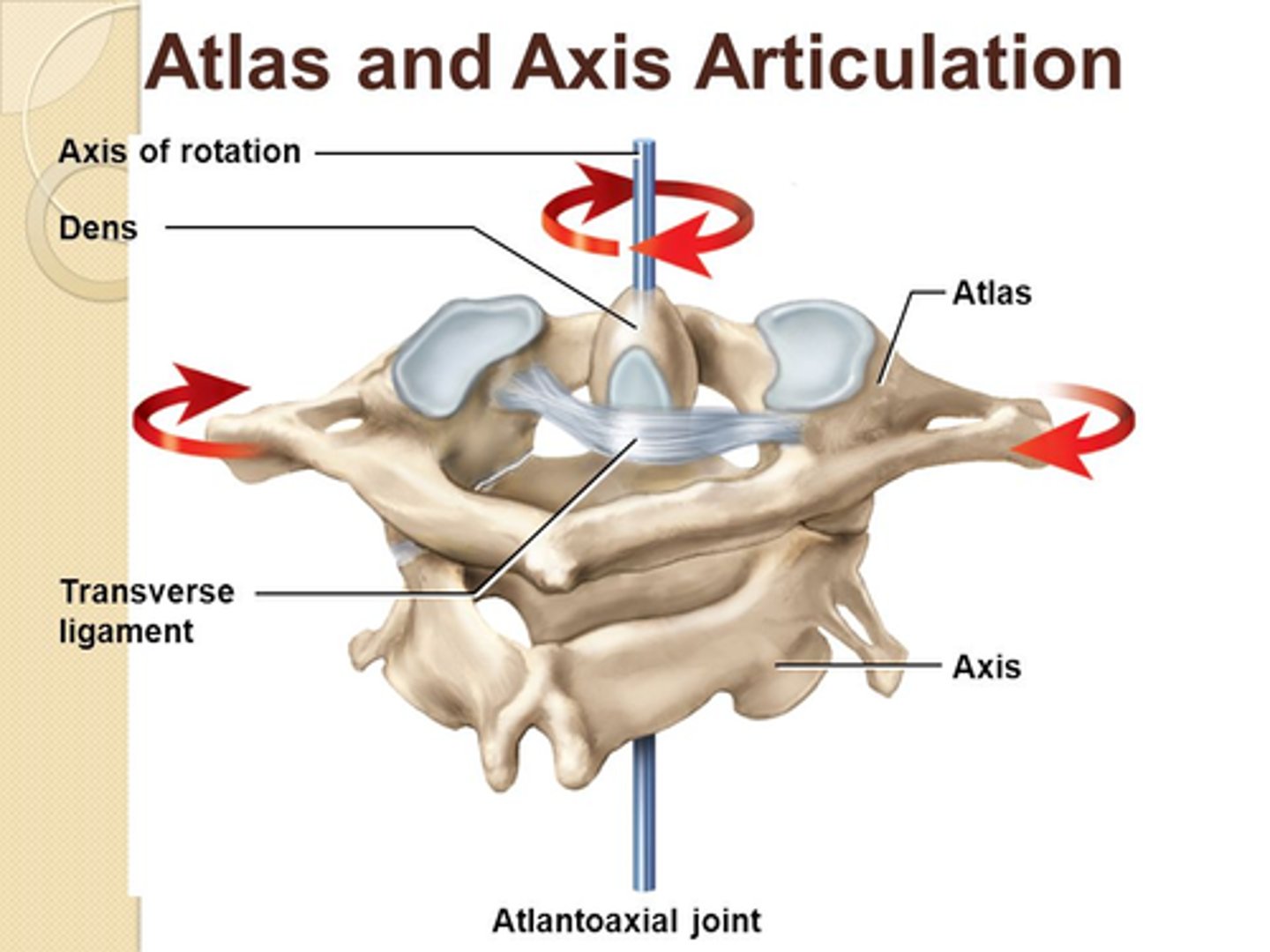
What is the Atlantoaxial joint responsible for?
• Articulation between Atlas (C1) and Dens of Axis (C2)
• Cervical Rotation
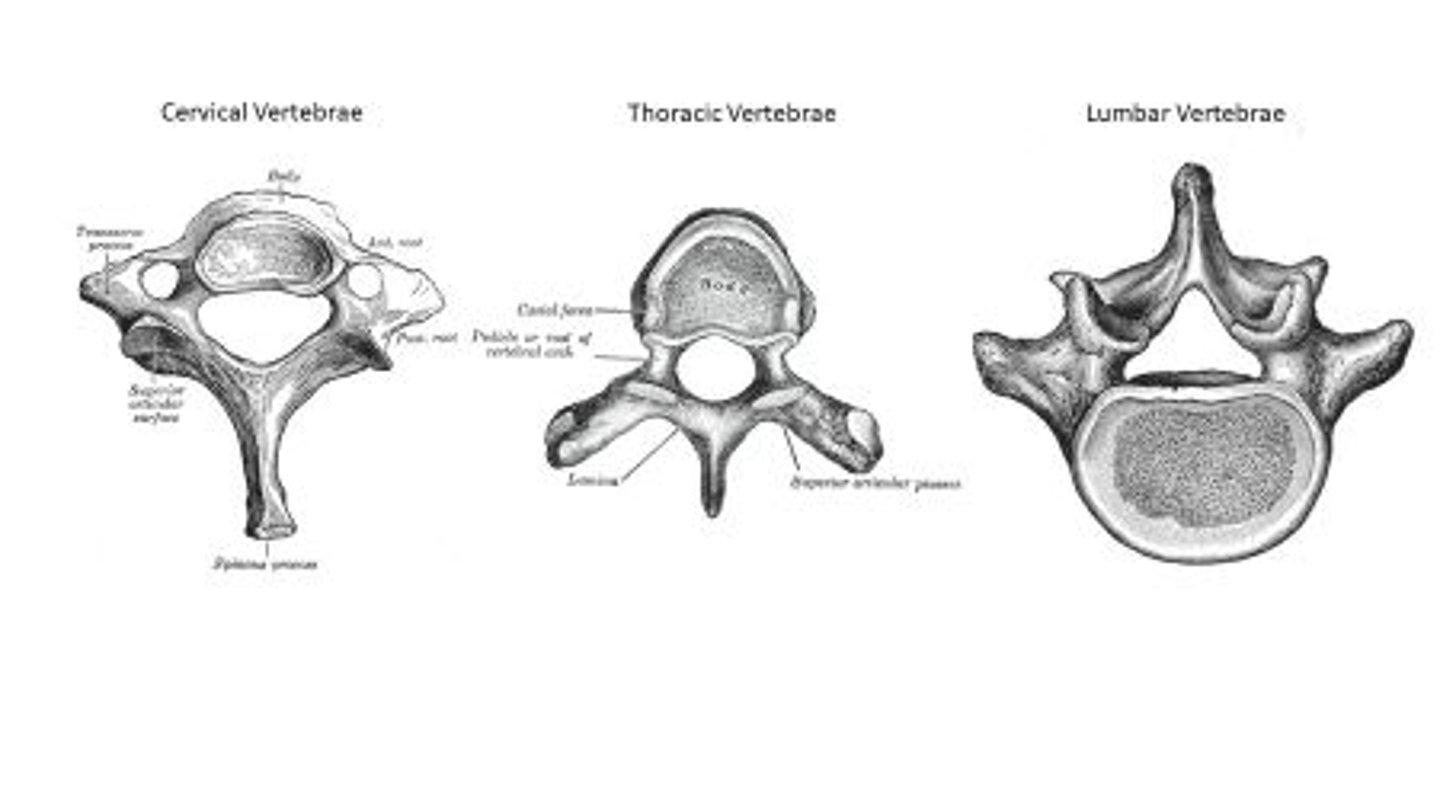
What shapes are the vertebral canals and bodies of the thoracic and Lumbar vertebrae?
Thoracic
• Heart shaped body
• Circular canal
Lumbar
• Cylindrical body
• Triangular Canal
What are the differences of the costal facets on the Thoracic Vertebrae?
• Superior (larger) articulates with rib at same level.
• Inferior (smaller) articulate with rib inferior.
• Transverse costal facet articulates with tubercle of rib at same level.
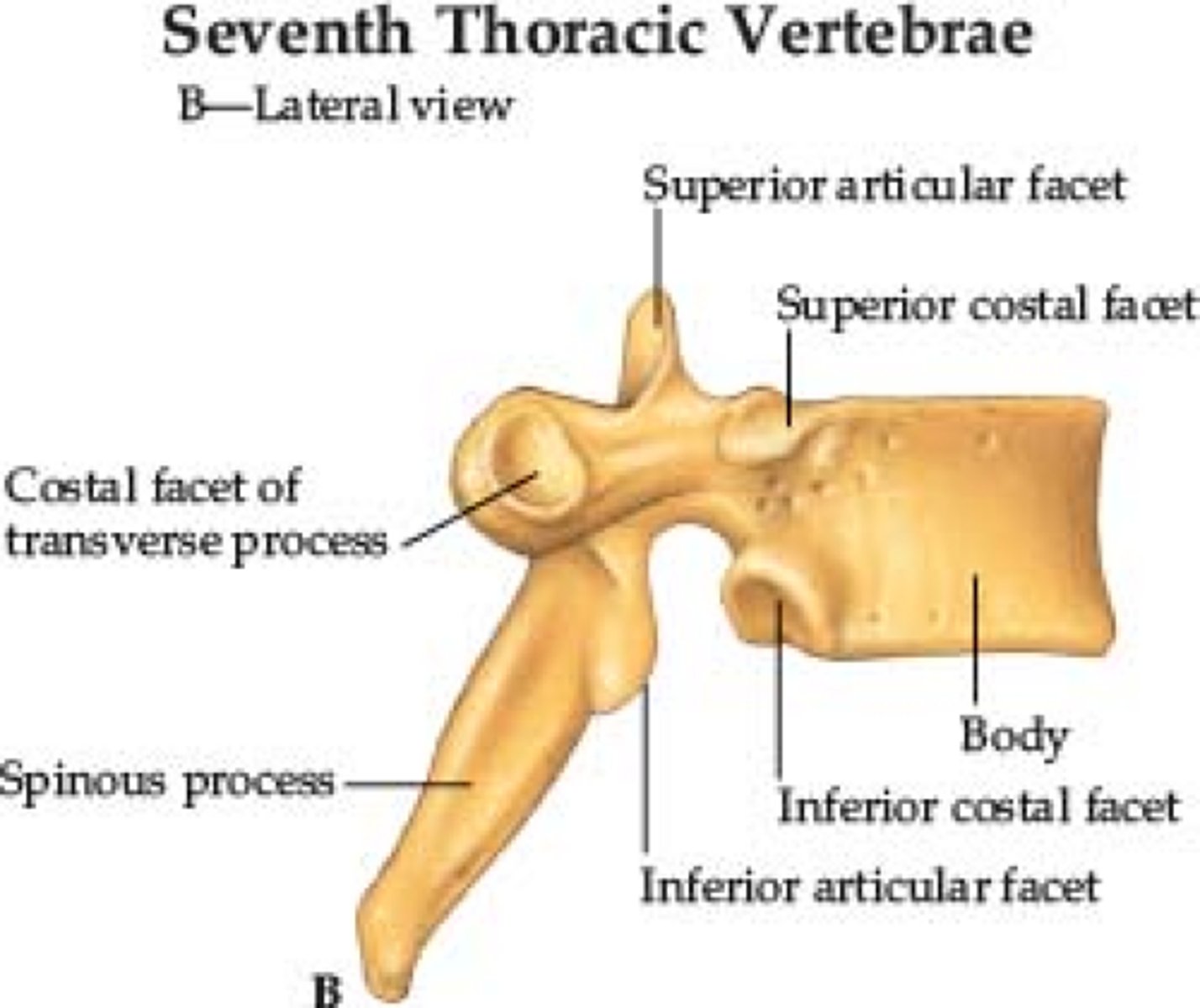
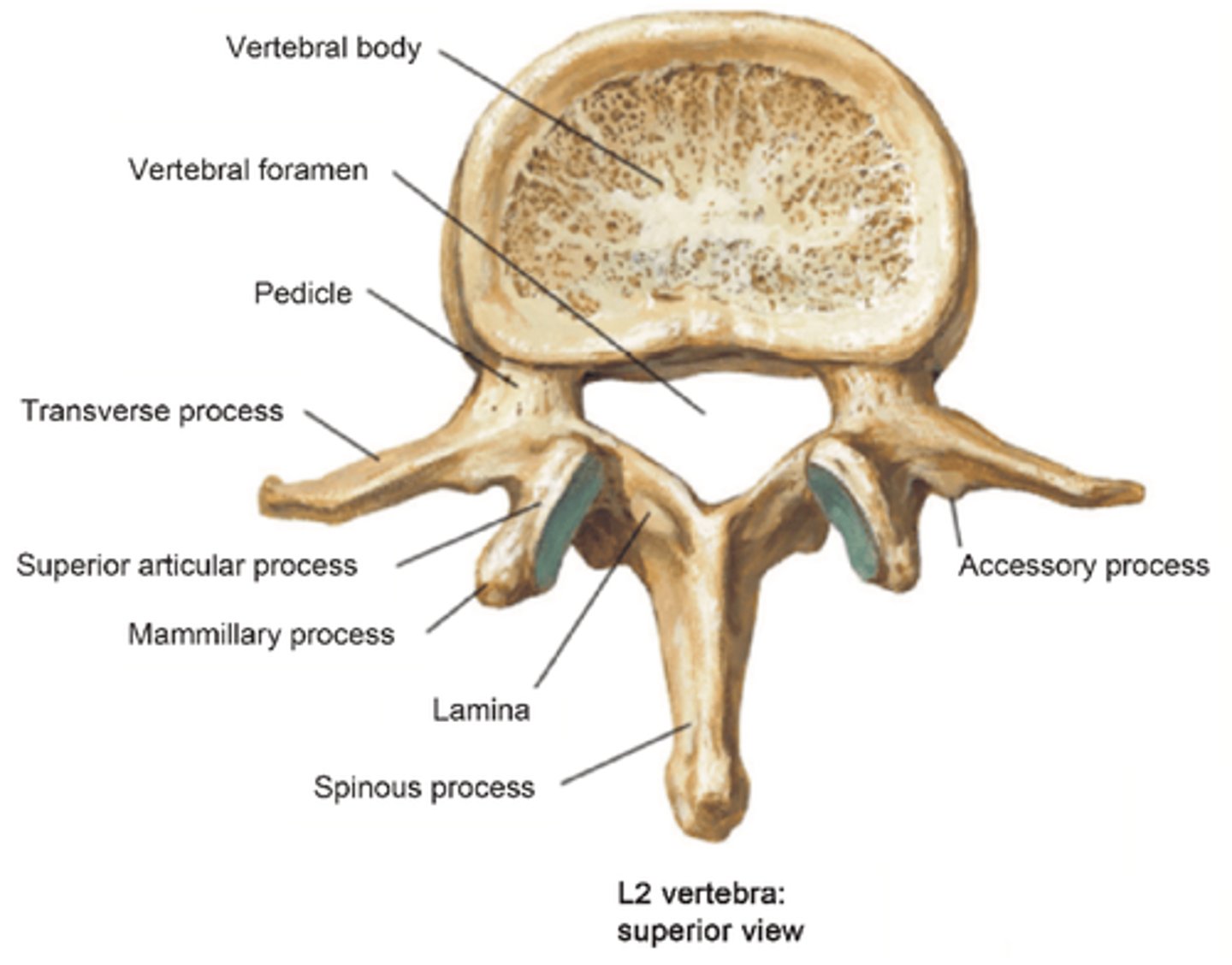
What are the unique features of the Transverse Process on the Lumbar Vertebrae?
• Thin and long (except L5)
• Very broad
• Accessory process on the posterior portion of the base
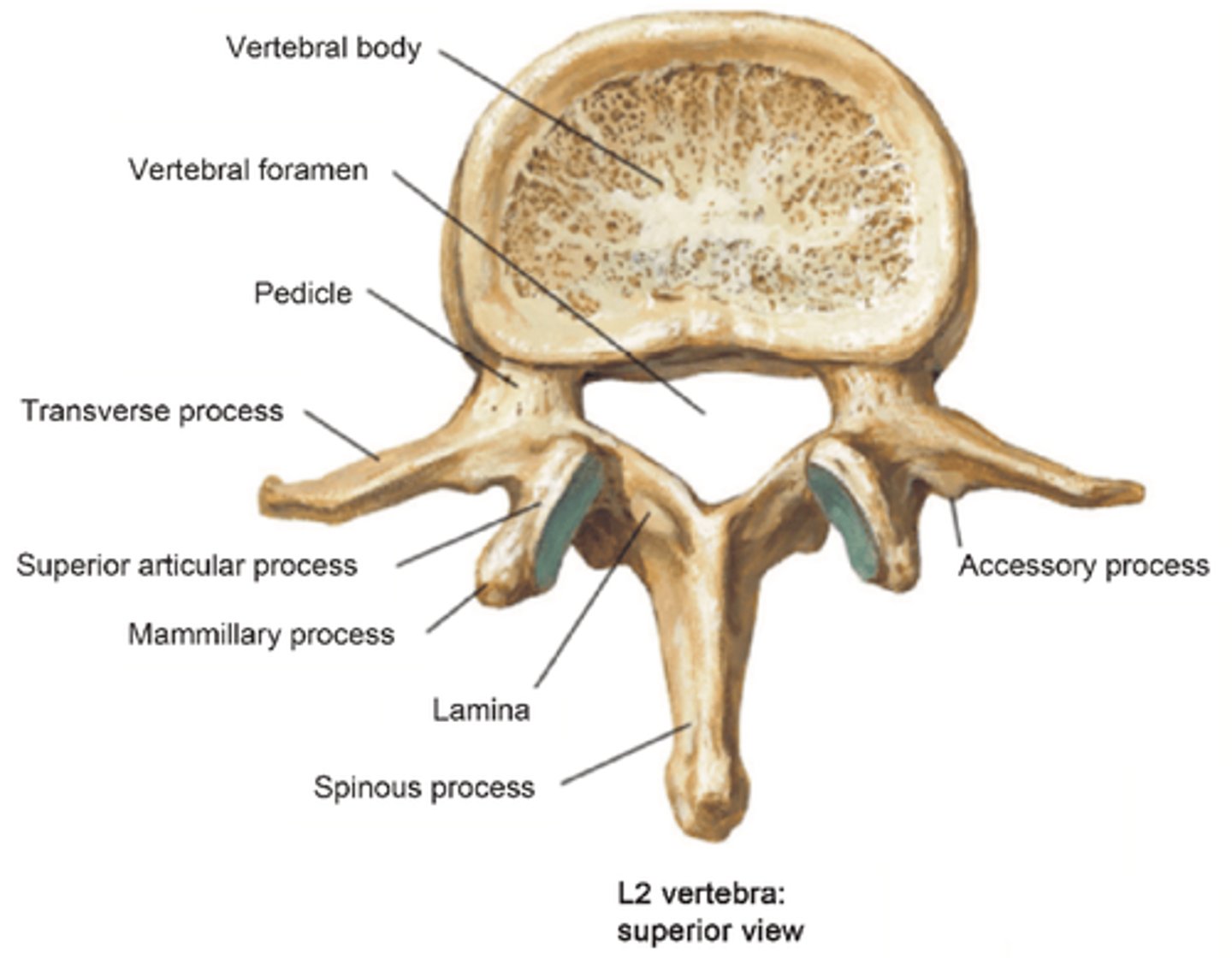
Where is the Mamillary Process?
• Superior facet of the Lumbar Vertebrae
• Multifidus and Intertransversarii attach here
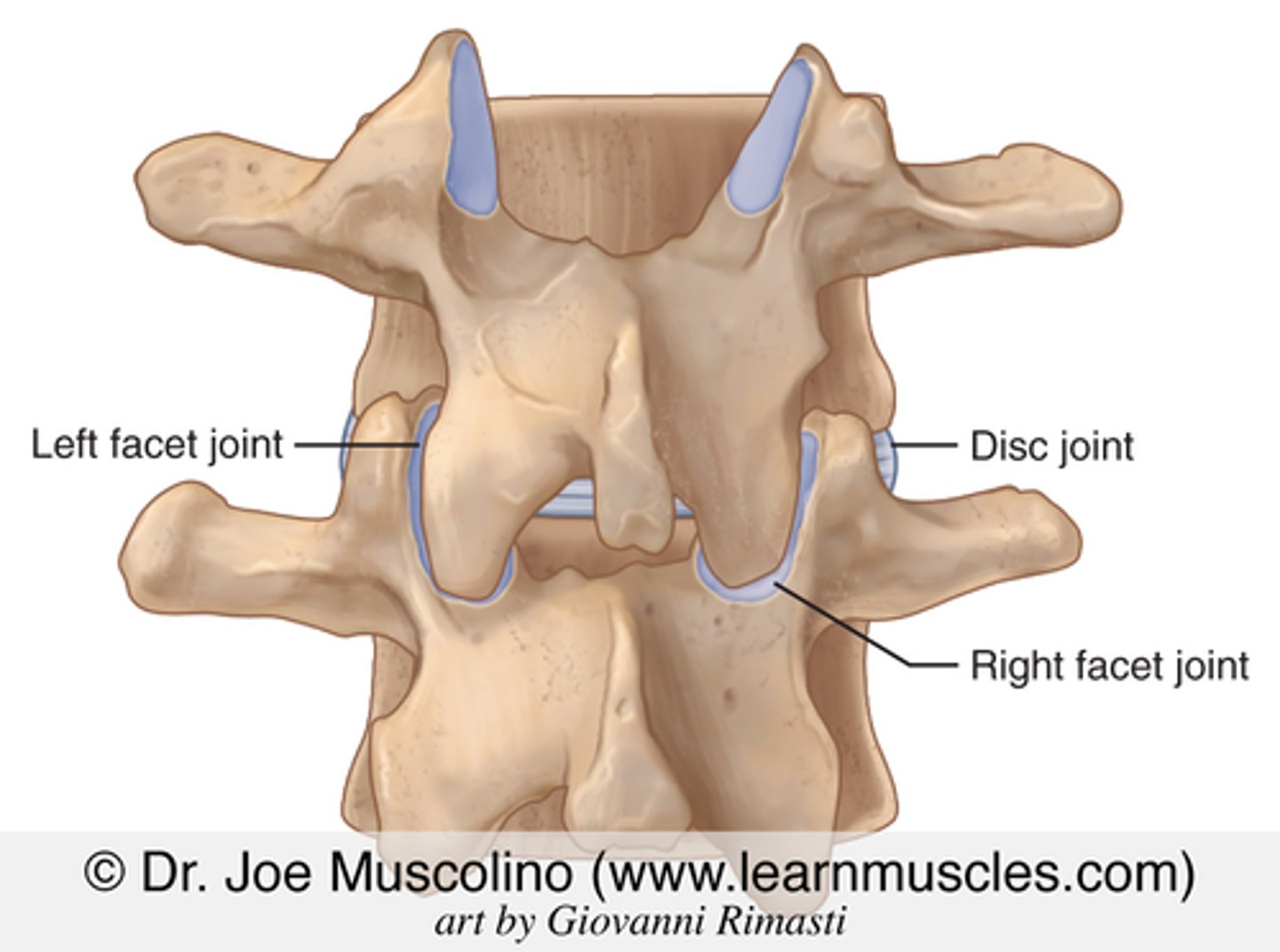
Describe the Superior and Inferior Facets of the Lumbar Vertebrae
• They project upward and downward
• Superior is concave and faces medially
• Inferior is convex and face laterally
* They fit together with vertebrae above and below
• Allow for stability and motion
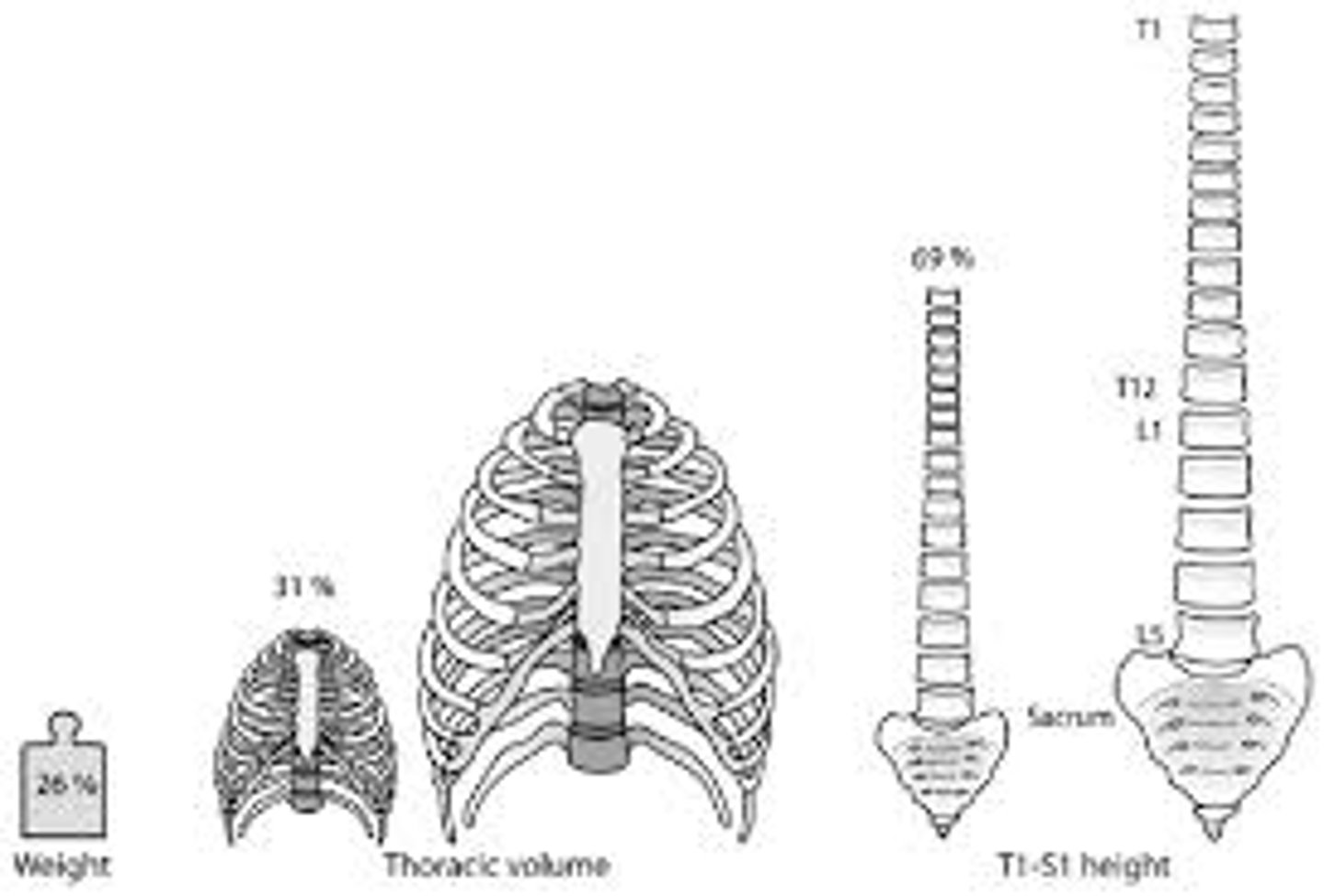
What is the pattern in the size of vertebrae?
• They get larger from Cervical to Lumbar
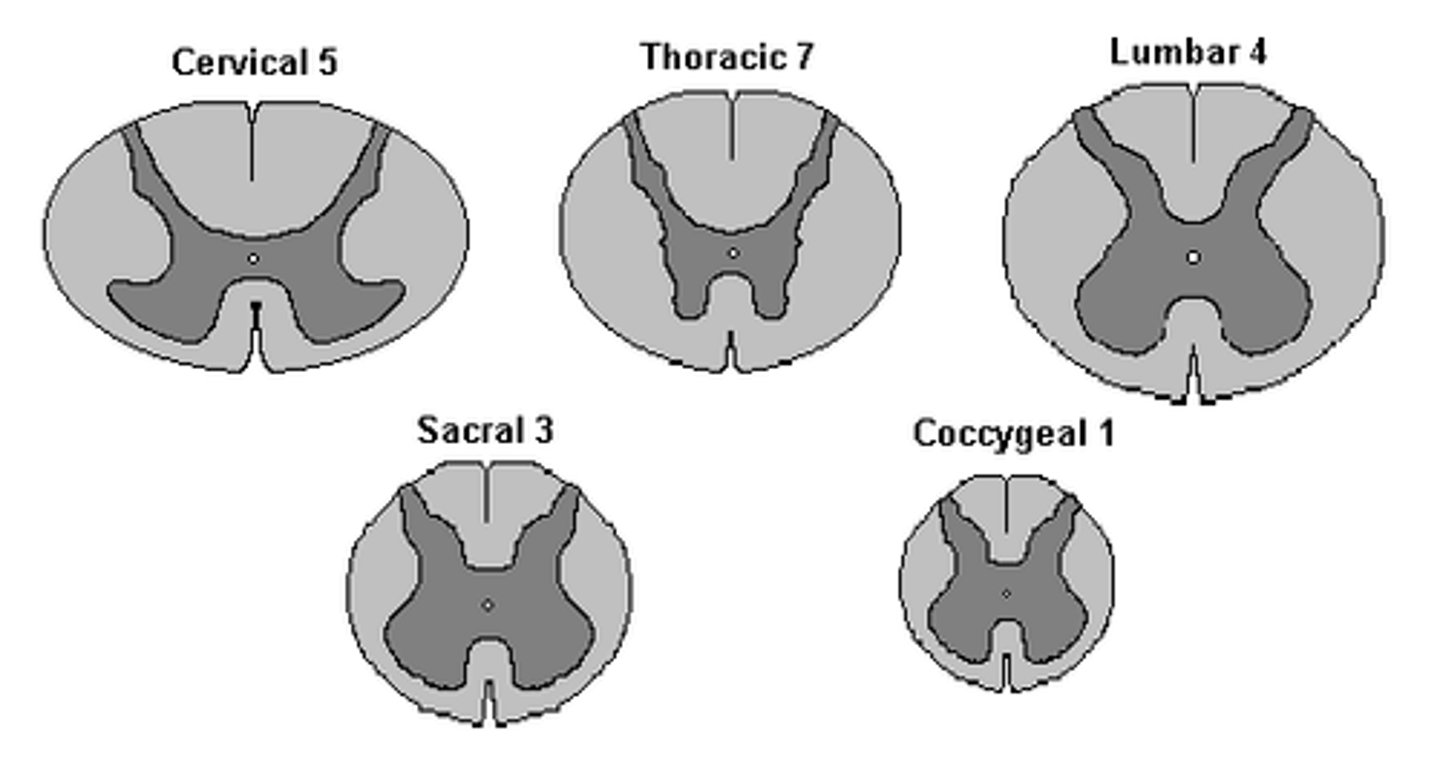
What is the pattern in the size of the foramen of the vertebrae?
• Largest in Cervical
→ Decreases in Thoracic
→ Then increases in Lumbar around L1/L2
• Due to enlargements of grey matter
• increased neural input/output of afferent(sensory) and efferent(motor) signals to/from limbs
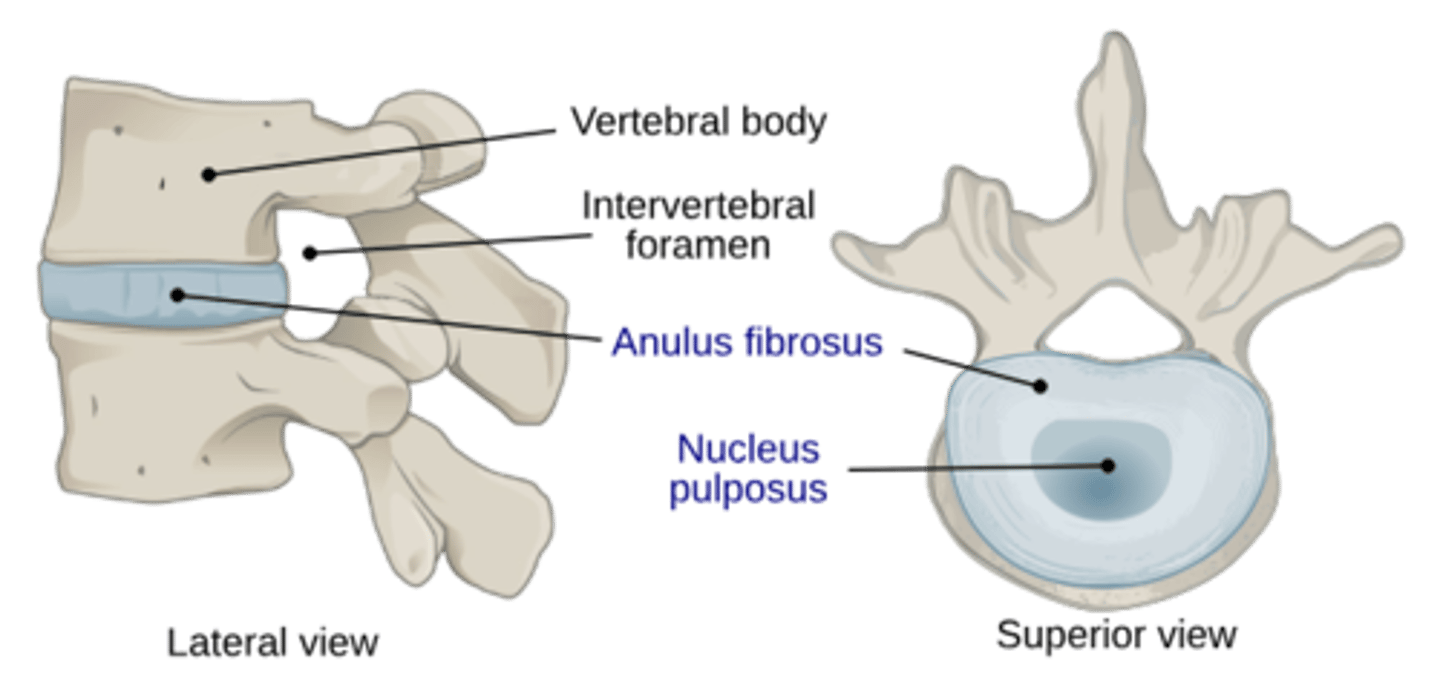
What is the make up of the Intervertebral Discs of the Vertebral Bodies?
• Outer ring is the Annulus Fibrosus that contain the Nucleus Pulposus
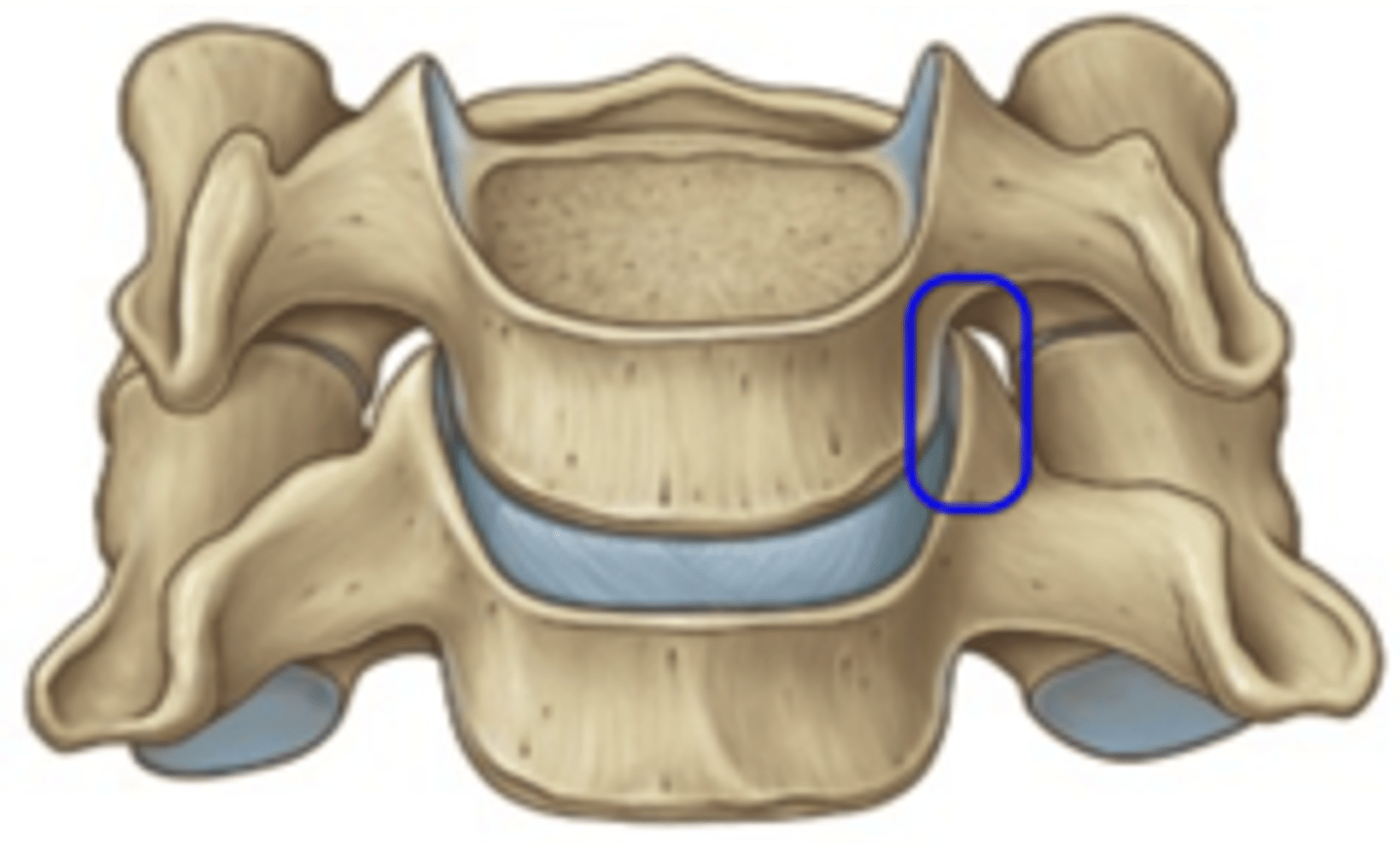
Where are the Uncovertebral Joints and what motions occur there?
• Synovial joints formed between the Uncinate Process inferior and Uncus superior on C3-C7
• Flexion, Extension
* Limits lateral flexion
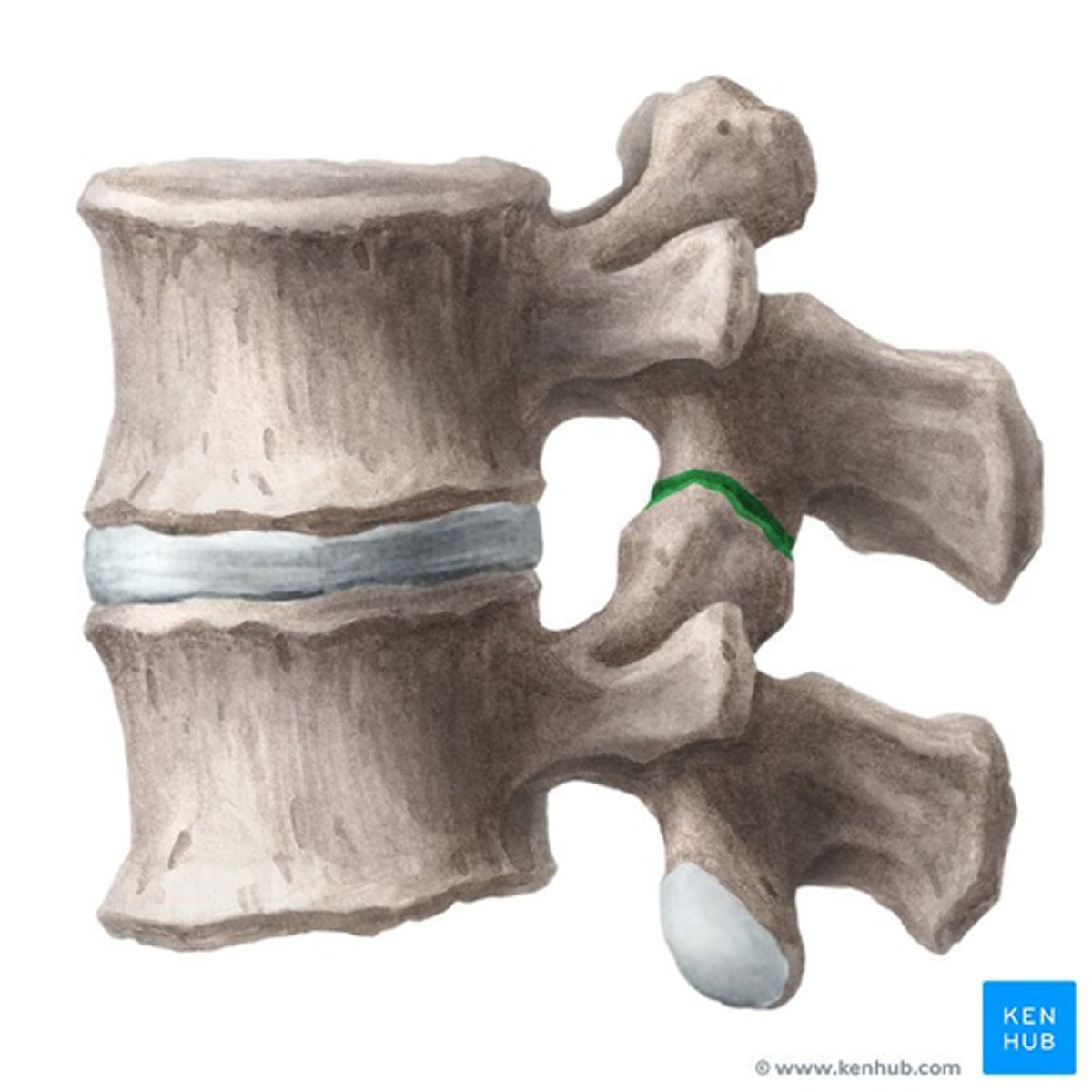
Where are the Apophyseal Joints?
• Where the superior and inferior facets articulate
• Thin articular capsule attached to margins of the articular facets surround joint
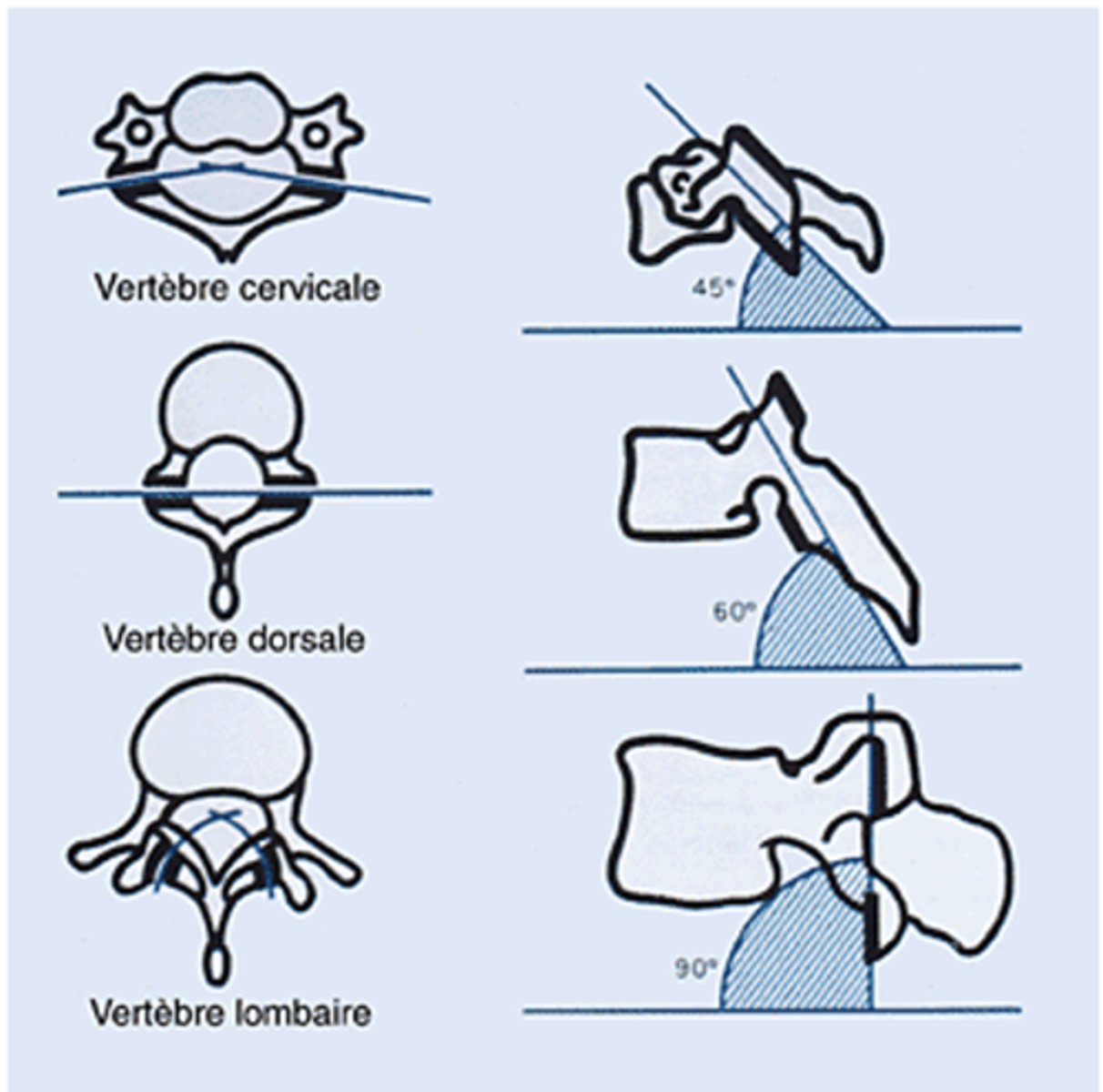
What are the facet joint angle orientations from the transverse plane for the different spinal regions?
Cervical
• 45 degrees. Allows Flex/Ext, Rot, and Lat Flex
Thoracic
• 60 degrees. Allows small amounts of Lat Flex, Rot, and Flex/Ext
Lumbar
• 90 degrees. Primarily Flex/Ext
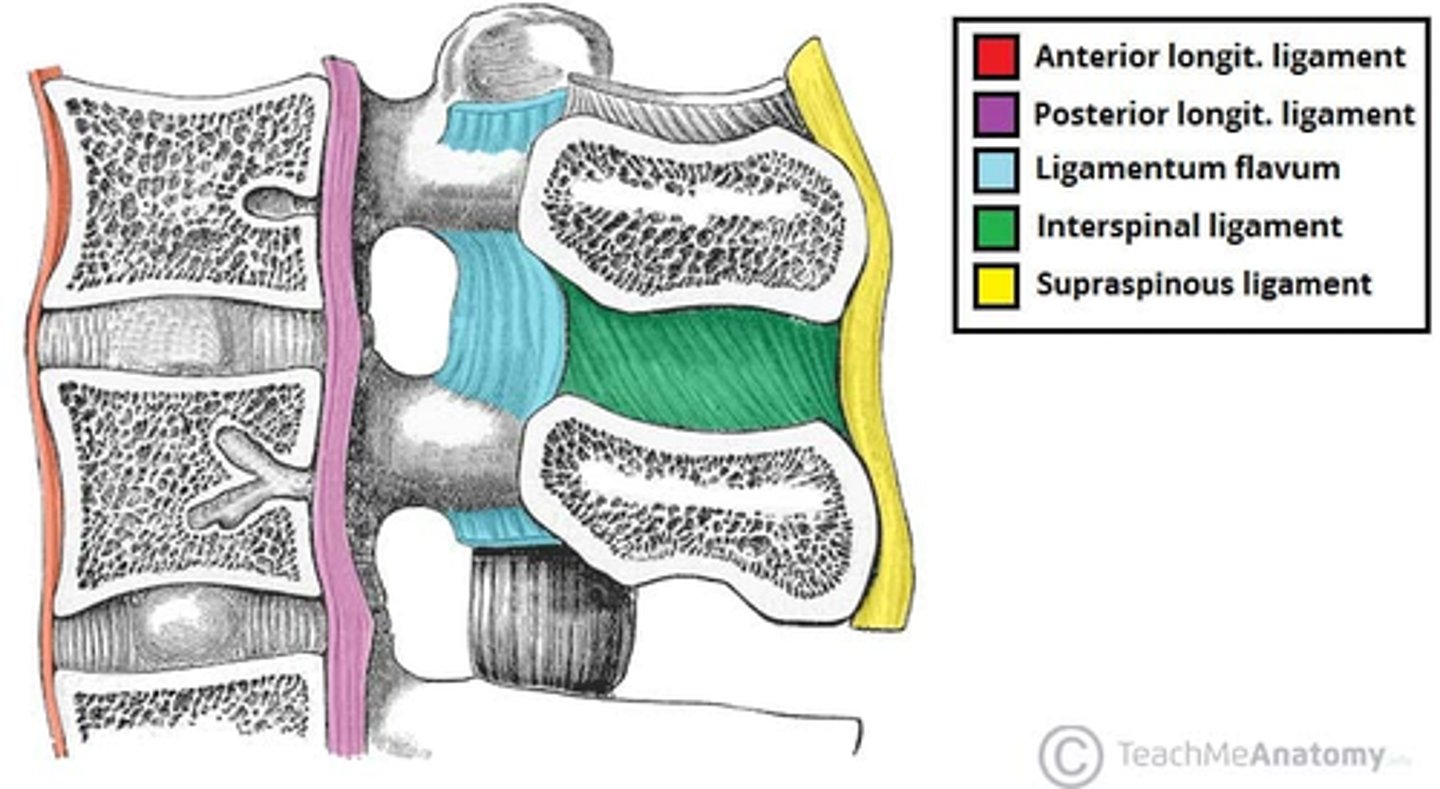
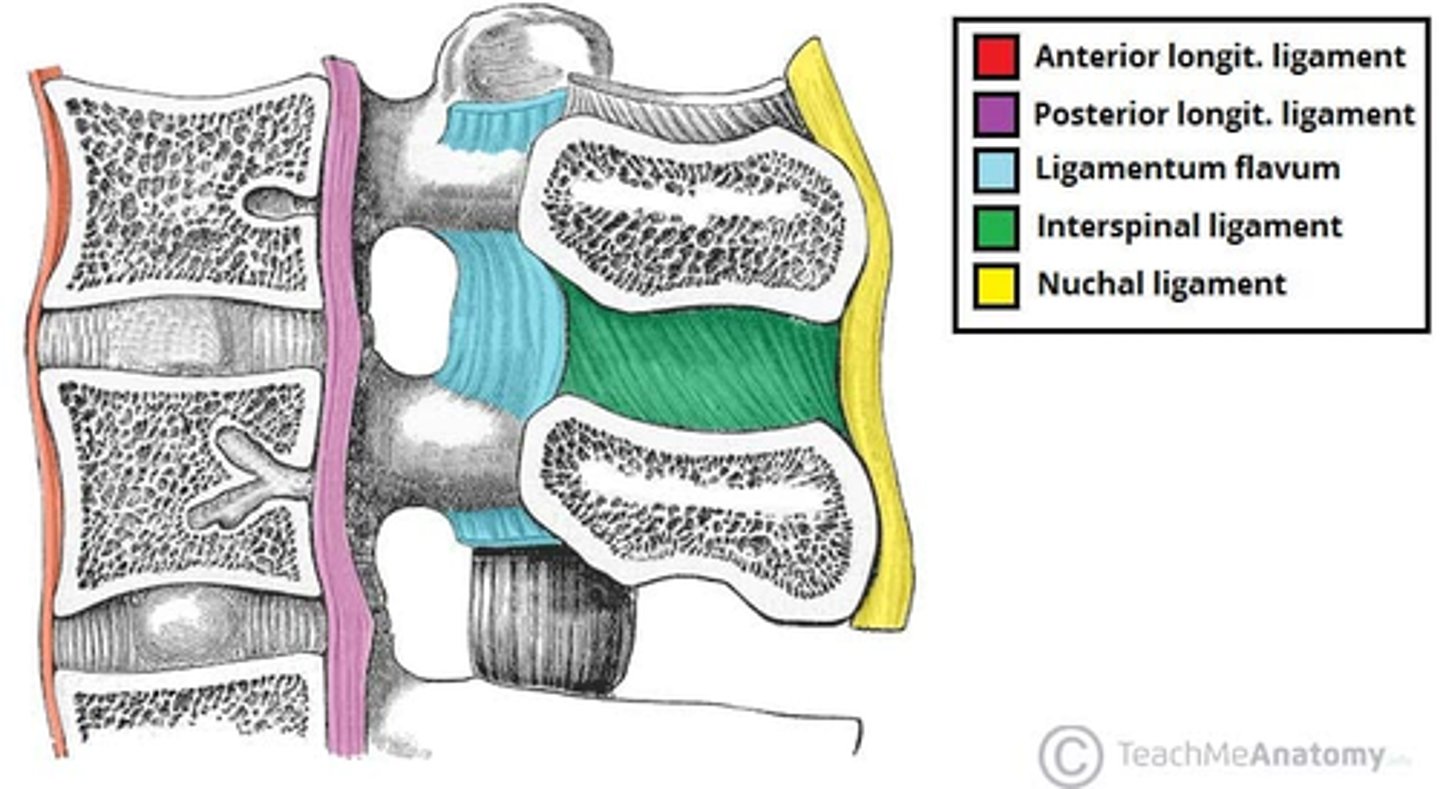
What are the major ligaments of the spine?
• Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
• Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
• Ligamentum Flava
• Ligamentum Nuchae and Supraspinous Ligament
• Interspinous Ligaments
• Intertransverse Ligaments
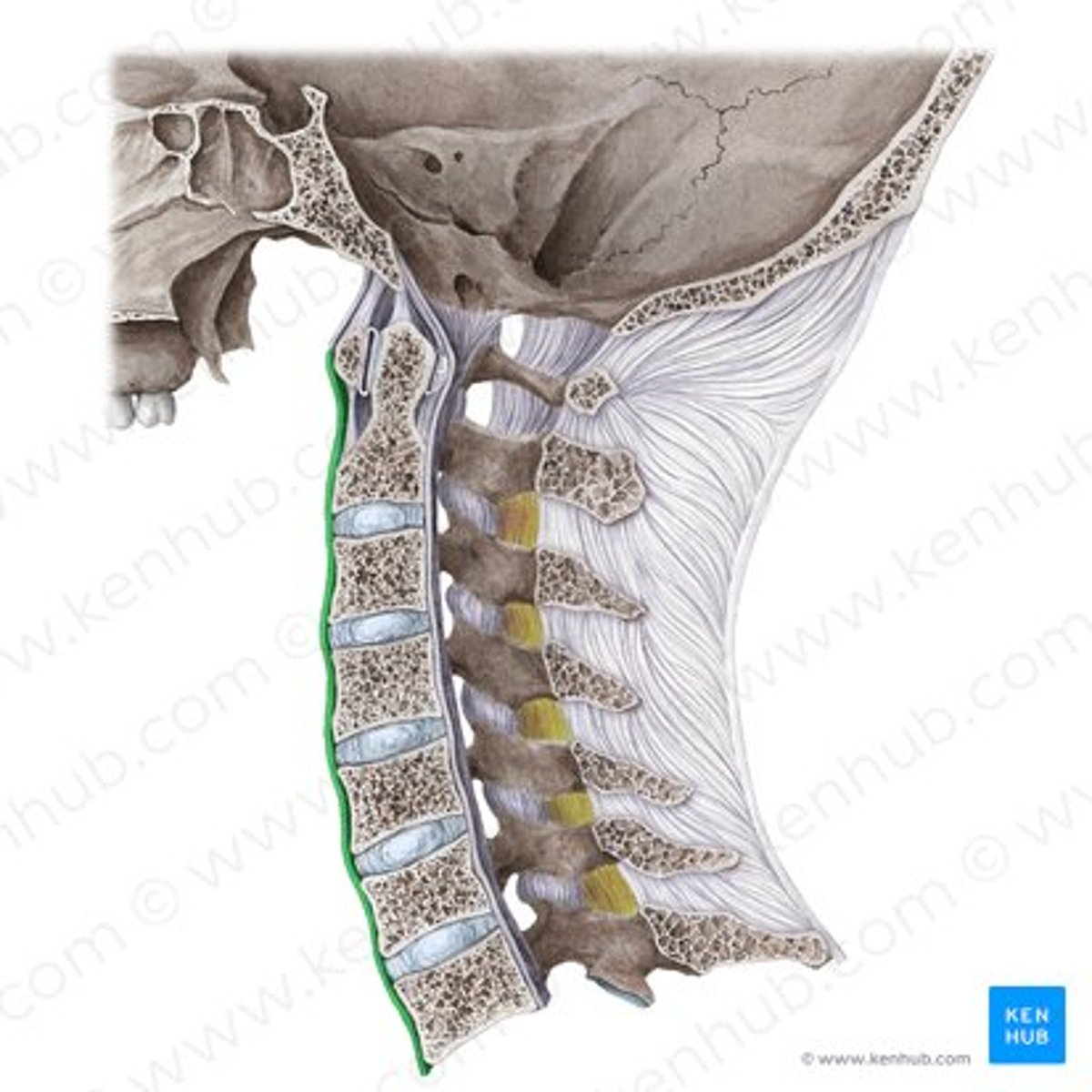
Where is the Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (A.L.L.), and what is it's primary responsibility?
Location
• It's superior attachment is on the base of the skull.
• It travels inferiorly on the anterior aspect of the spine, attaching to vertebral bodies and discs along the way.
• It's inferior attachment is on the anterior surface of the Sacrum
Responsibility
• Prevents hyperextension of the vertebral column
• Strong and broad fibrous band
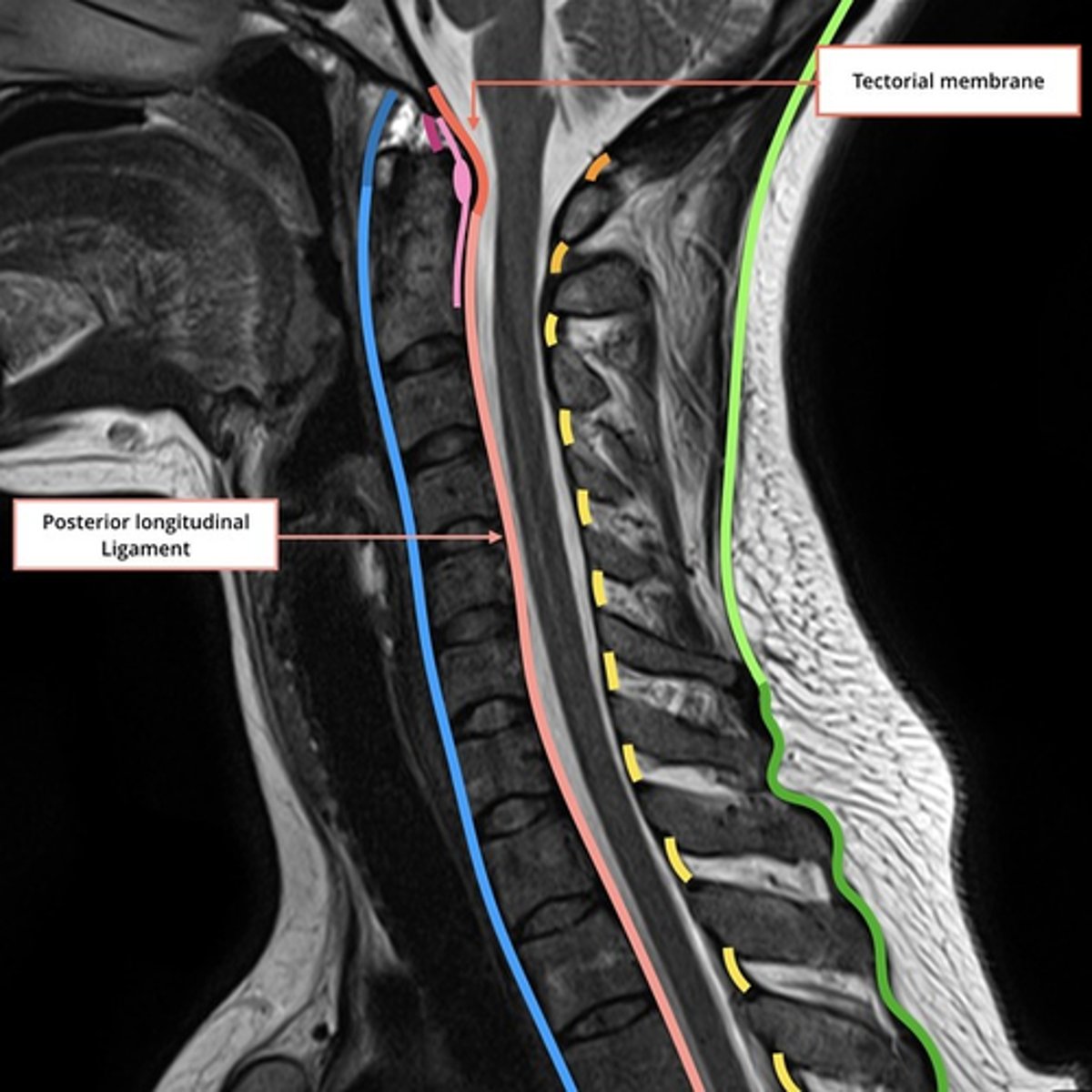
Where is the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (P.L.L.), and what is it's primary responsibility?
Location
• Superiorly, connects C2 to the intracranial aspect of the base of the skull (aka Tectorial Membrane)
• Travels inferiorly inside the vertebral canal, along the posterior surface of the vertebral bodies.
• Goes from Atlas to Sacrum.
• Like A.L.L., attaches to vertebral bodies and discs along its length.
Responsibility
• Prevents hyperflexion of the vertebral column
Where is the Ligamentum Flava, and what is it's primary responsibility?
Location
• Connects between the Lamina of adjacent vertebrae on the posterior surface of the Vertebral Canal.
• Posterior surface of Lamina below to anterior surface of Lamina above.
• Found from Axis (C1) to Sacrum
Responsibility
• Restores the spinal column to neutral position after flexion
• Resists separation of lamina
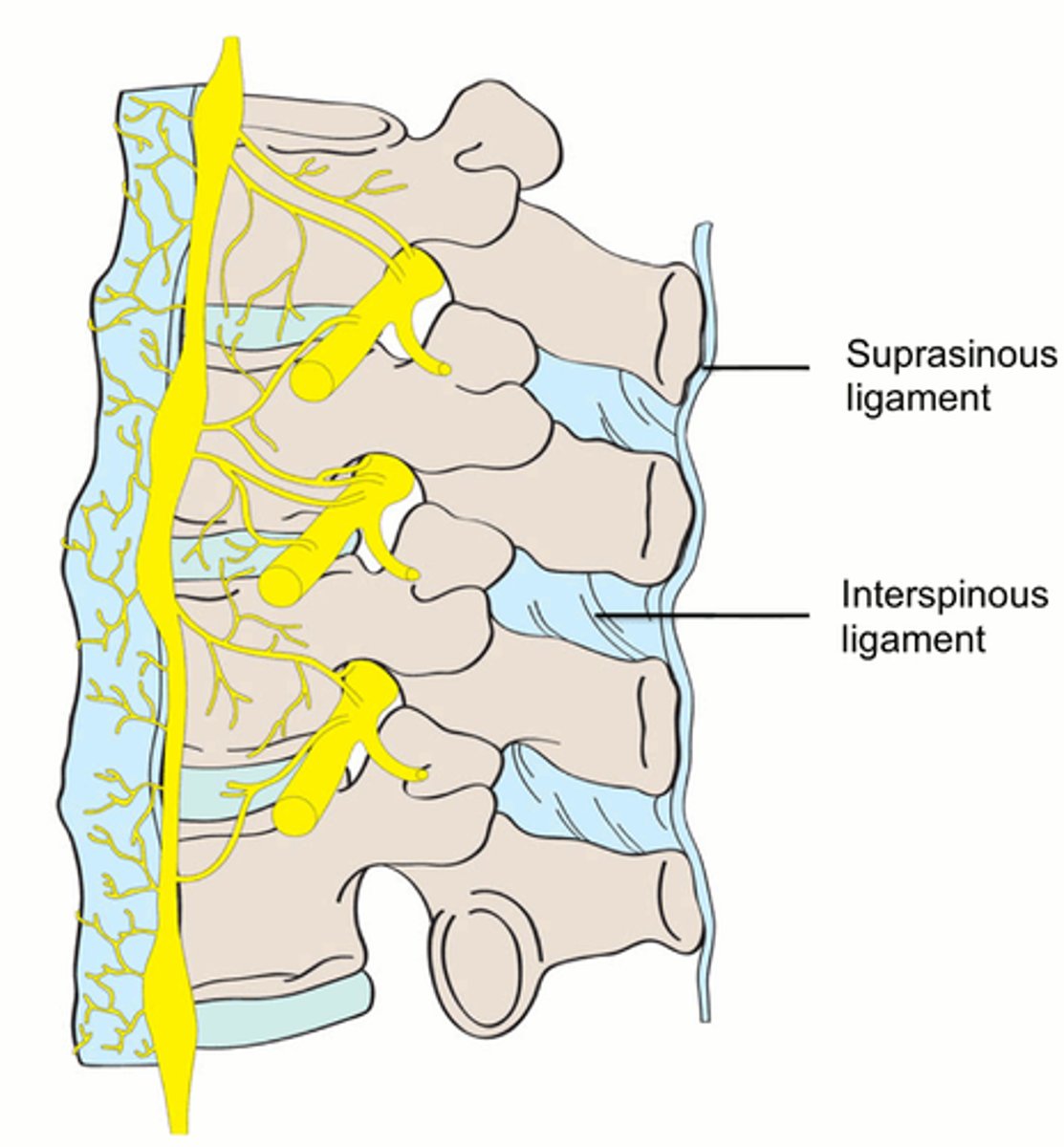
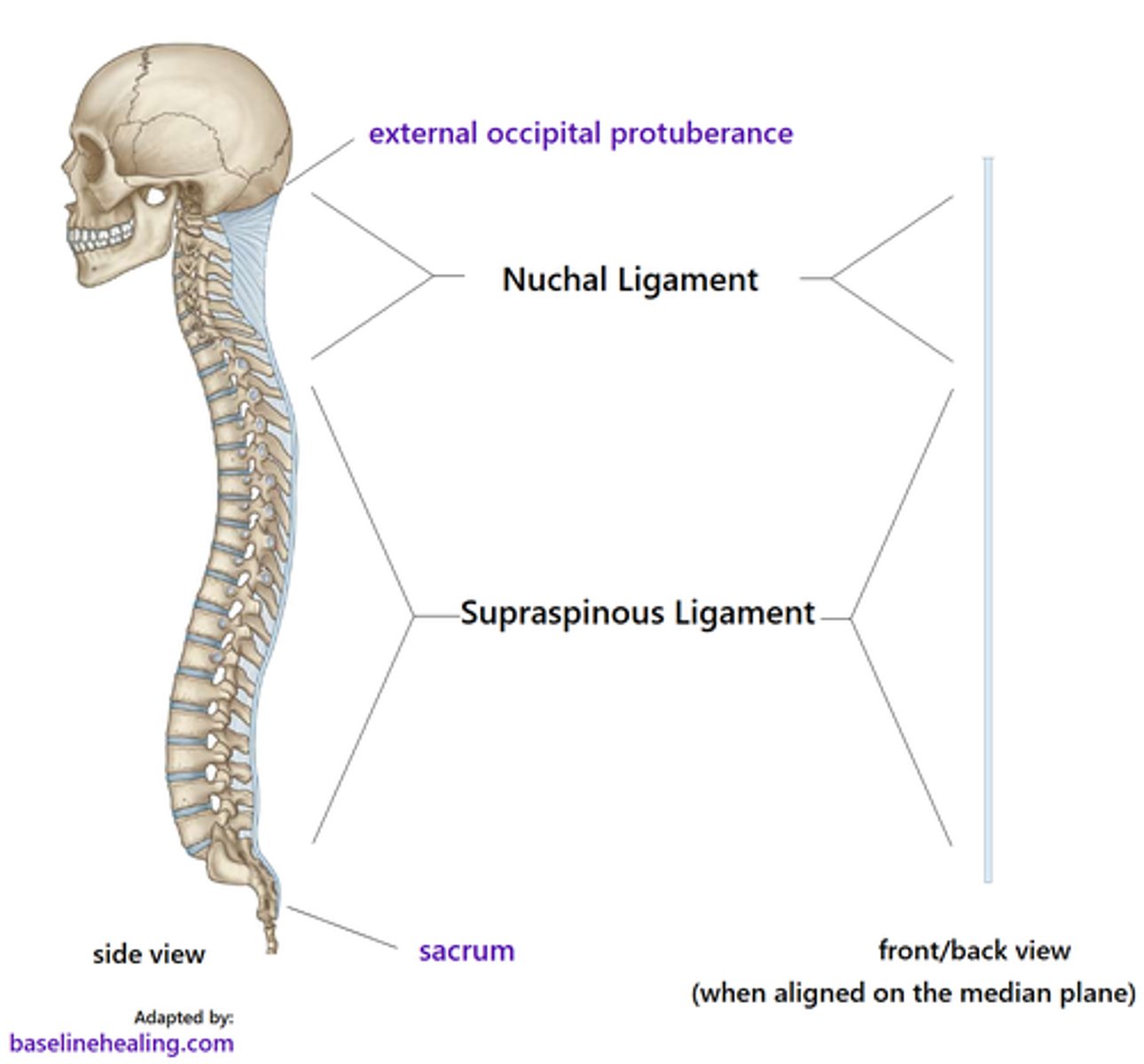
Where are the Ligamentum Nuchae and the Supraspinous Ligaments, and what are their primary responsibility?
Location
• Ligamentum Nuchae just goes from the Occipital Protuberance to the Spinous Process of C7. It's an expansion of the Supraspinous Ligament, but thicker.
• Supraspinous Ligament passes along the Spinous Processes of C7 to the Sacrum.
Responsibility
• Ligamentum Nuchae; provides attachment sites for muscles, resists flexion, and facilitates returning the head to anatomical position.
Where are the Interspinous Ligaments, and what are their primary responsibility?
Location
• Between the Spinous Processes.
• Blend with Supraspinous Ligament posteriorly and Ligamentum Flavum anteriorly.
Responsibility
• Prevent hyperflexion