Anat I - Bones, Joints, Muscle, Circulation
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Flat bones
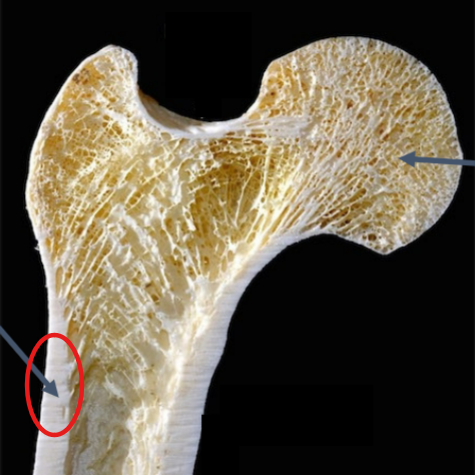
Compact Bone
Smooth bone found outside of long / flat / irregular bones
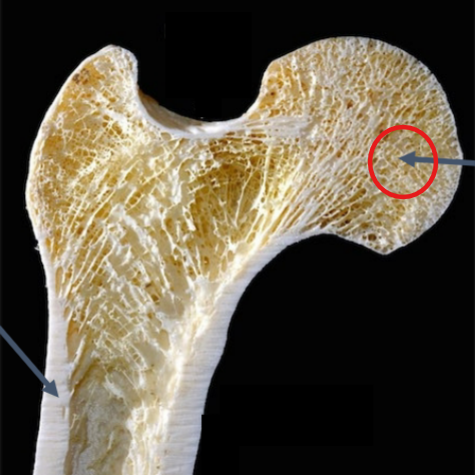
Trabecular Bone
“Spongy bone” found inside long / flat / irregular bones
Structure of flat bones
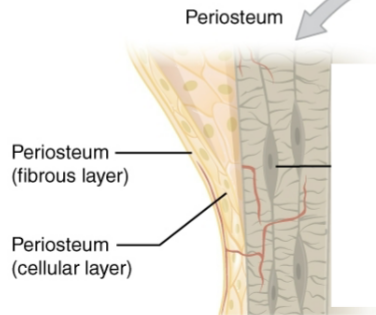
Periosteum
spongy bone
compact bone
Structure of long bones
Outside - epiphysis, metaphysis, diaphysis, articular cartilage, compact bone
Inside - epiphyseal line, spongy bone, medullary cavity, periosteum, nutrient foramen
Periosteum
Sheet of connective tissue that allows connection of tendons and ligaments
Outer fibrous layer
Contains fibroblasts and dense connective tissue (periosteum layer)
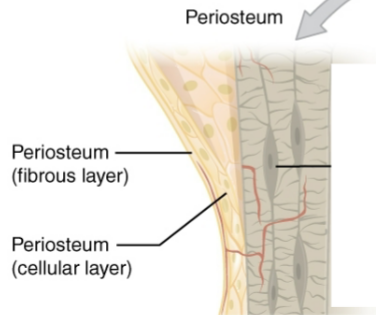
Inner cellular layer
Contains progenitor cells that become osteoblasts (periosteum layer)
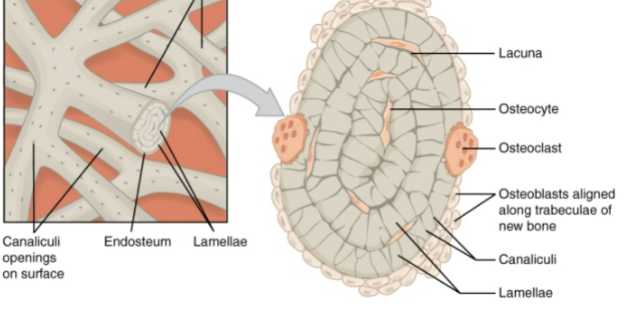
Endosteum
Similar structure to periosteum but found on inner surfaces of bone
Fibroblasts
Cells that secrete collagen and elastic fibers
Osteoblasts
Derived from mesenchymal stem cells and deposit bone matrix
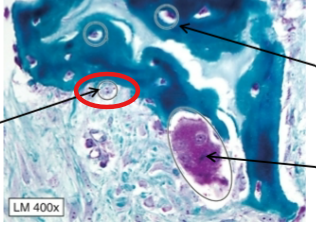
Osteoclasts
Derived from hematopoietic stem cells and resorb (eat) bone matrix
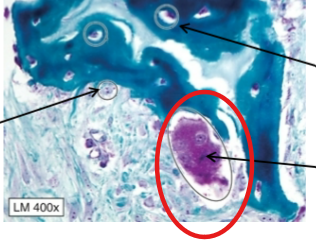
Osteocytes
Some osteoblasts that are trapped in bone and maintain matrix of bone tissue
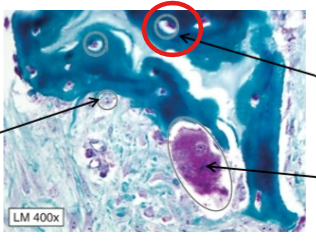
Surfaces, matrix
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts are found on bone __
while osteocytes are found within the bony __
Osteons
Structure that makes up compact bone, connected with nerves/vessels
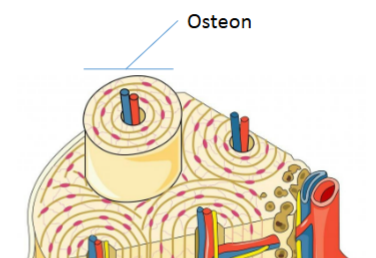
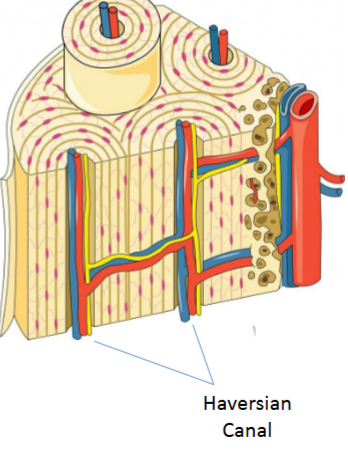
Harversian Canals
Pathways at center of each osteon that house nerves and blood vessels
Osteon structure for compact bone
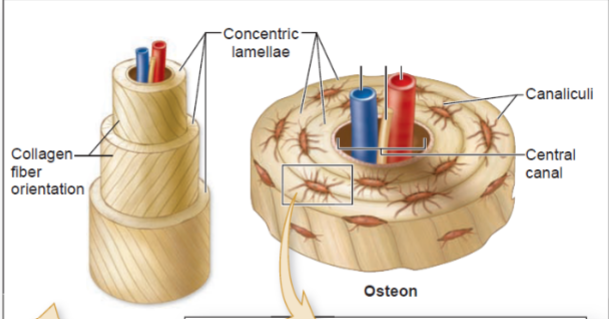
Osteon structure for spongy bone
Harversian canals
In contrast to compact bone, osteons of spongy bone have few to NO __ __
Trabecular
Osteoporosis more readily impacts the __ (compact/trabecular) bone which has a large surface area —> more metabolically active
Primary Osteoporosis
Age-related bone loss, commonly seen in post-menopausal women* and elderly
Secondary Osteoporosis
Bone loss due to changes in lifestyle, medication, and disease
Fibrous joints
Joints connected by ligaments
Sutures
Connect flat bones of the skull (fibrous type)

Syndesmosis
Connective tissue to shafts of adjacent long bones (i.e. radius/ulna, tibia/fibula) (fibrous type)

Gomphosis
Holds teeth in their sockets (fibrous type)
Symphysis
Compromised of fibrous cartilage (i.e. pubis) (cartilaginous type)
Synchondrosis
Compromised of hyaline cartilage (i.e. epiphyseal growth plates -LExt) (cartilaginous type)
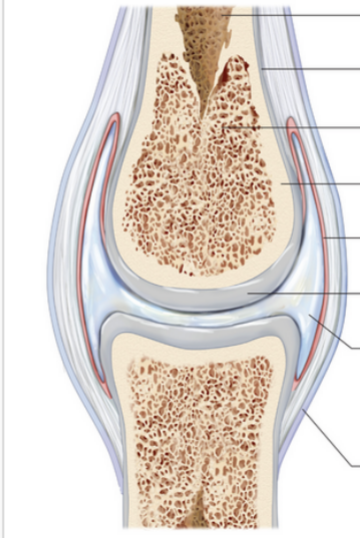
Synovial Joint
Allows for free movement between bones with no friction (i.e. shoulder, knees)
Compartments, fascia
Muscles are typically found in __ and are separated by __
Striations, voluntary
Skeletal muscle
Long tubular cells with __
Found in __-moving muscles
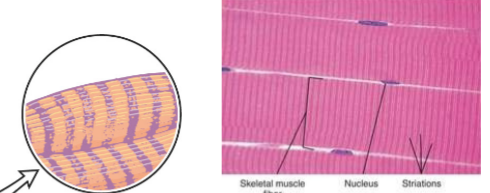
Y, heart
Cardiac muscle
_-shaped cells found in the __
involuntary
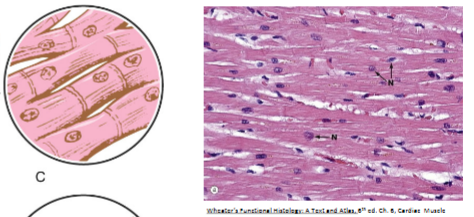
Spindle, internal
Smooth muscle
__-shaped cells in walls of __ organs
involuntary
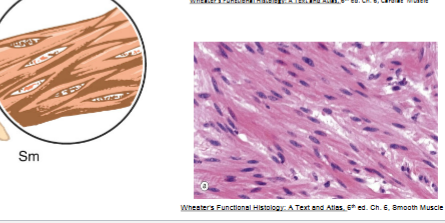
Joint, bone, contraction
Muscles cross at least one __, attach to __
Muscle __ pulls the insertion to the origin
Origin
Region of bone that is stationary with attached muscle
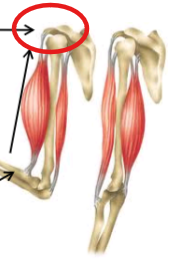
Insertion
Region of bone that is mobile with attached muscle
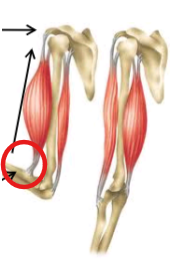
Agonist
Prime mover of a joint or structure
Synergist
Muscles that work together (with agonist) to produce movement
Fixator
Muscles that hold the joint steady so agonists and synergists can allow movement
Antagonist, speed
An __ performs the opposite action as agonist to control the __ of movement
Fascia
Contains cells, fibers, and ground substance for surrounding muscles
Fat, collagen
Superficial fascia contain mostly __ and loosely arranged __ fibers
Deep, compartments
__ fascia encircles muscles and forms __. Also envelops nerves, arteries, and lymphatics.
Oxygenated, away, smaller
Arteries carry __ blood __ (toward/away) heart and have branches that get __
Deoxygenated, toward, larger
Veins carry __ blood __ (toward/away) heart and have branches that get __
Narrow, no, media, more
In arterial circulation
__ (narrow vs large) lumen
__ (have vs no) valves
Tunica __ thickest
__ (more vs less) elastic
Large, have, externa, less
In venous circulation
__ (narrow vs large) lumen
__ (have vs no) valves
Tunica __ thickest
__ (more vs less) elastic
Tunica Media
Smooth muscle in arteries that affects blood pressure
Skeletal muscle pump
Muscle in veins that aids in venous blood return and prevent backflow of blood
Veins, arteries, tunica media
__ (arteries/veins) increase in diameter from small to larger
__ (arteries/veins) decrease in diameter from larger to small
Capillaries are tiny and only have the __ __ layer