Lysosomes and Endocytic Transport
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
digestion and recycling of intra/extracellular macromolecules, organelles, or microorganisms occurs in -
lysosomes
lysosomes are enclosed by a single membrane whose lipids are highly - on the lumenal side for -
glycosylated, protection
ATP-driven H+ pump maintains a pH of around - inside the lysosome
5
lysosomes contain about 40 types of hydrolytic enzymes that all require a pH of - for optimal activity, such as -
5, acid hydrolases
damage to cell/animal is avoided in two ways
degradative enzymes are isolated in a - compartment, the -
enzymes that can leak into the cytosol/extracellular space are - at pH -
separate, lysosome, inactive, 7.2
lysosomal acid hydrolases are --tagged in the cis-golgi for delivery to lysosomes
M6P
How are lysosomal acid hydrolases M6P tagged?
lysosomal acid hydrolases are made on - and transported into the -
in there, - occurs
once moved to cis-golgi, a signal patch in the sequence is recognized by -
the same enzyme transfers - to terminal mannose of the precursor sugar with a - bond
then the GlcNAc is -, leaving the lysosomal acid hydrolase with a M6P tag on the - sugar ring at -
RER, RER lumen, glycosylation, GlcNAc phosphotransferase, GlcNAc, phosphodiester, removed, mannose, C6
How do M6P-receptors work?
M6P transmembrane receptors are found in -
receptors bind to - (golgi side) and - proteins (cytosol side)
--coated vesicles bud from - and are delivered to early endosomes
in early endosomes, there is - (lower/higher) pH, causing - of M6P-hydrolase:receptor complex
acid hydrolase is - and remains in early endosome, moved to -
M6P receptor is recycled back to the - via - pathway
trans-golgi, M6P-tagged cargo, clathrin coat, clathrin, TGN, lower, dissociation, dephosphorylated, lysosome, TGN, retrieval
lysosomal storage diseases are caused by - in one or more of the -
genetic defects, lysosomal acid hydrolases
accumulation of - in defective lysosomes has severe pathological consequences, particularly in the -
undigested substrates, central nervous system
inclusion-cell disease is when all the acid hydrolase enzymes are missing from the - of fibroblasts but are found circulating in the -
mutations occur in the GlcNAc phosphotransferase gene resulting in a lack of -
instead hydrolases are defaulted to be transported - of the cell via constitutive secretory pathway
lysosomes, blood
M6P-tagging
out
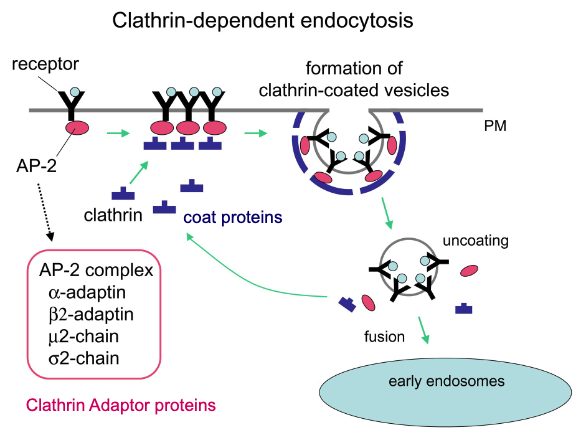
if this is endocytosis, which side is extracellular and cytosolic? why?
top is extracellular, lower is cytosolic
coat proteins are always cytosolic
three fates of endocytosed macromolecules
recycling
transcytosis
processing/degradation
transcytosis is when receptor:ligand complexes can be endocytosed on one side of the cell, transported - the cell and released through the - membrane
across, opposite
if receptor and/or ligand molecules are not diverted into recycling transport vesicles from endosomes, they will end up in an endolysosome to be - or -
processed, degraded
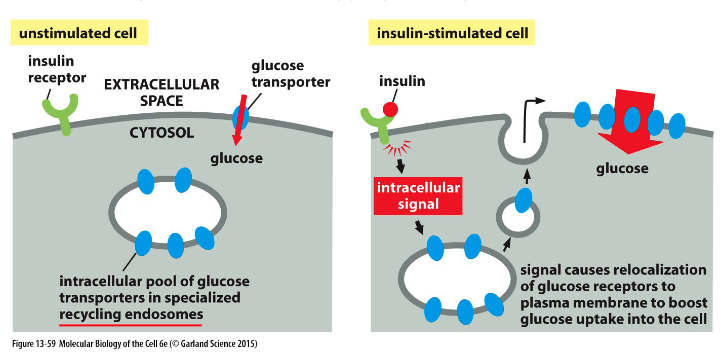
How are glucose transporters regulated?
when there is an - (increase/decrease) in concentration of glucose and insulin in the bloodstream, insulin binds to its -
budding of transport vesicles from -
delivers - back to the PM
increases - uptake
increase, receptor, recycling endosomes, glucose transporters, glucose
How does receptor-mediated endocytosis work?
signals cause - in the PM to pre-assemble into - coated vesicles
extracellular ligands bound are therefore selectively - into the cell
transmembrane receptors, clathrin, endocytosed
endocytic vesicles fuse to form -, which can fuse to form -
early endosomes, recycling endosomes
early and recycling endosomes bud - that recycle endocytosed cargo back to the - or biosynthetic cargo back to the -
retrieval vesicles, PM, trans golgi
early endosomes invaginate to evolve into - (MVB), which fuse with existing late endosomes or with each other to form (new) -
evolving endosomes and MVBs “motor” along - toward the interior of the cell
multivesicular bodies, late endosomes, microtubules
late endosomes fuse with existing lysosomes into - or mature into -
endolysosomes, new lysosomes
endosomes represent the cellular compartments where outside and inside macromolecules often -
meet
three pathways to lysosomal digestion
endocytosis
phagocytosis
autophagy
endocytosis is when extracellular macromolecules enter cells by - and are delivered to an -
if extracellular molecules are not retrieved from -, they will eventually end-up in - for processing or degradation
endocytosis, early endosome
early endosomes, endolysosomes
phagocytosis occurs when - (four types) cells ingest microorganisms and dead cells
macrophages, neutrophils, mast, and dendritic
autophagy is used for the - of a cell’s - or - inside
natural turn-over, intracellular macromolecules, organelles
opsonization is when antibodies that coat microbes also bind - on these cells and trigger -
Fc receptors, phagocytosis
LPS of bacteria is directly recognized by a - (TLR4) on phagocytic cells
apoptotic cells that flip - to the - lipid bilayer are also recognized by phagocytic cells
pathogen-associated molecular pattern receptor
phosphatidyl serine, outer
phagocytic cells extend - that engulf the target cell, enclosing the ingested cell inside a -
autophagosomes form inside the cytosol to engulf and digest expired -
pseudopods, phagosome
organelles
autophagy occurs when auto/phagosomes fuse with - and their contents are degraded by the various -
intracellular lysosomes, acid hydrolases