1.3 Bonding 1.5 Structure CCEA
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Metallic Bonding definition
The attraction between layers of cations and a sea of delocalised electrons
Structure of metallic bonding
A metallic lattice ( regular arrangement of ions )
Properties of metals
Electrical conductivity
High melting and boiling point
Malleable and ductile
Hardness
Metallic electrical conductivity
Electrons in metal delocalised they free to move and carry charge through lattice in certain direction when potential difference applied thus metals can conduct in solid and liquid state
High melting points
Large amount of energy is requires ro break the strong attractions between the positive ions and the negative electrons
why does sodium have a higher melting/boiling point than potassium
smaller ions with a high charge attract the electrons more strongly - higher melting points than larger ions with a lower charge .
Na has smaller cations than K - so Na has higher Mp and Bp
why does magnesium and have a higher melting/boiling point than soduim
Mg cations have a higher charge than Na so Mg has higher Mp and Bp
Malleable and ductile
Layers of positive ions can slide over each other without disrupting the bonding
Hardness in metallic bonding
Strong attraction between positive ions and negative electrons, and strong regular structure
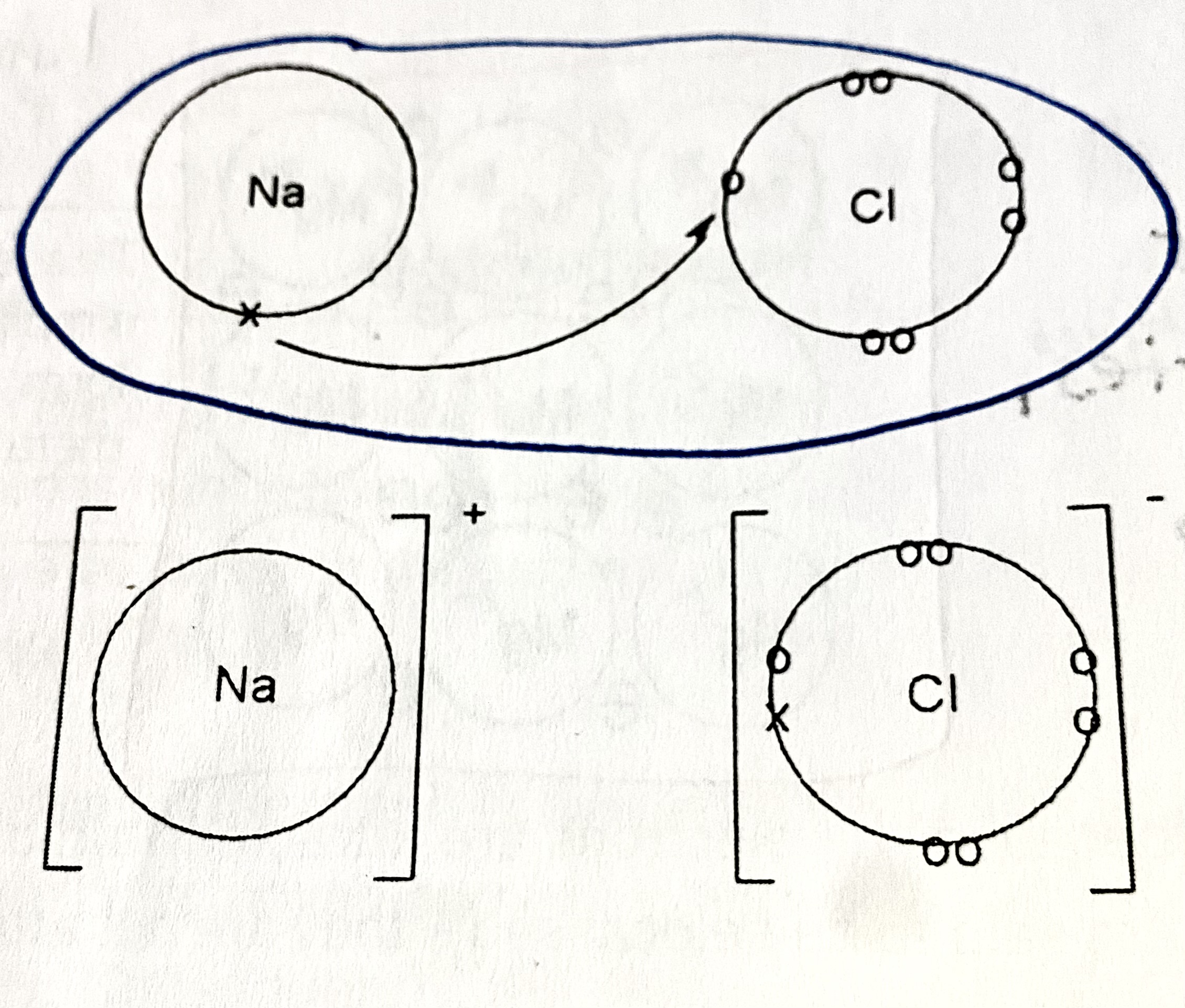
Ionic bonding
The electrostatic force of attraction between ions of opposite charge in a reuglar ionic lattice.
Metal atoms to non-metal atoms
Structure of ionic bodning
an ionic lattice
ionic bonding
Electrostatic forces increase in strength as
the charge on the ions increases
the size of the ions decreases
Properties of ionic compounds
High melting and boiling points
Can’t conduct electricity in solid state, can molten or aqueous
Usually white, crystalline solids
High melting points of ionic compounds
Requires lots of energy to break strong electrostatic forces of attraction between ions of opposite charge
Conductivity in ionic compounds
Not in solid state but when molten or aqueous
Ions are not free to move about in the solid state but are free when the solid is melted or dissolved in water
Usually white, crystalline solid
Ionic compounds exist as regular arrangements of ions in a giant ionic lattice.
Regular arrangement leads to hard crystal structure being formed
Covalent bond
The electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of bonded atoms
Structure of covalent bonds
There are two types of covalent structure (simple covalent) and giant covalent.
What is a lone pair
A pair of unshared electrons
Why do covalent bonds happen
the electrons are more stable when attracted to two nuclei than when attracted to only one
What is a coordinate bond/ dative covalent
A shared pair of electrons between two atoms with both electrons shared by one atom
Why is a coordinate bond formed
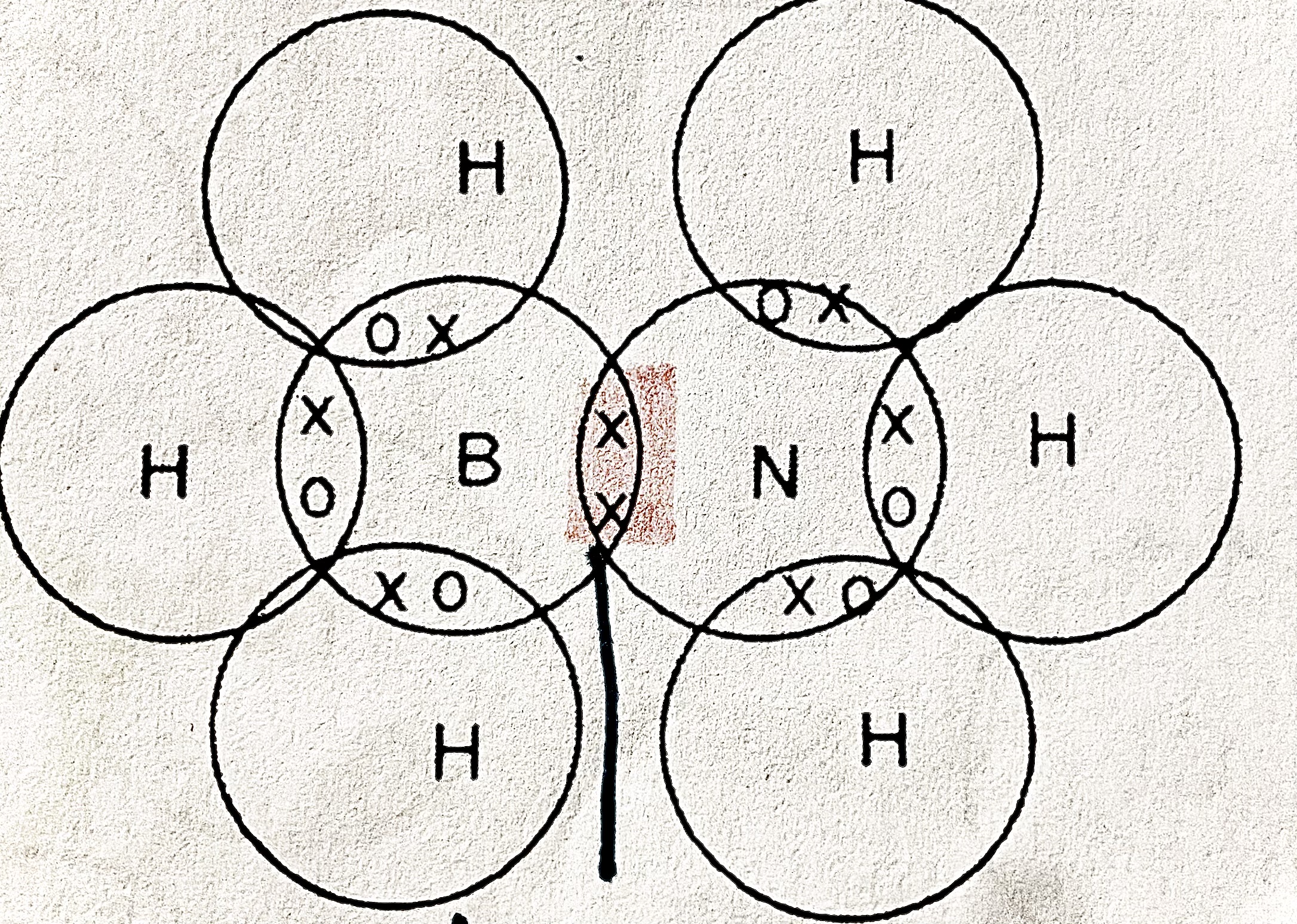
Because nitrogen shares a pair of electrons

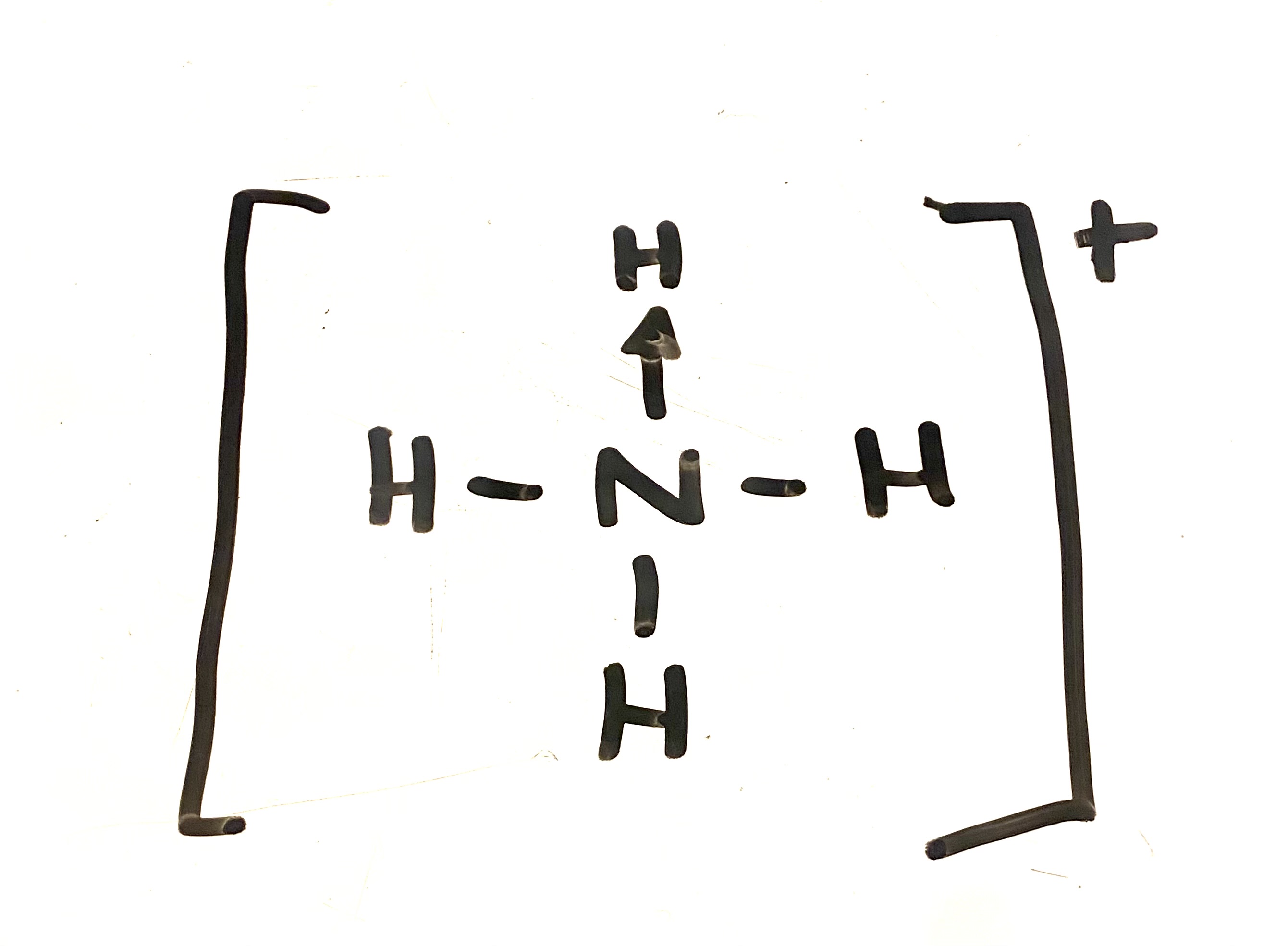
ammonia bond
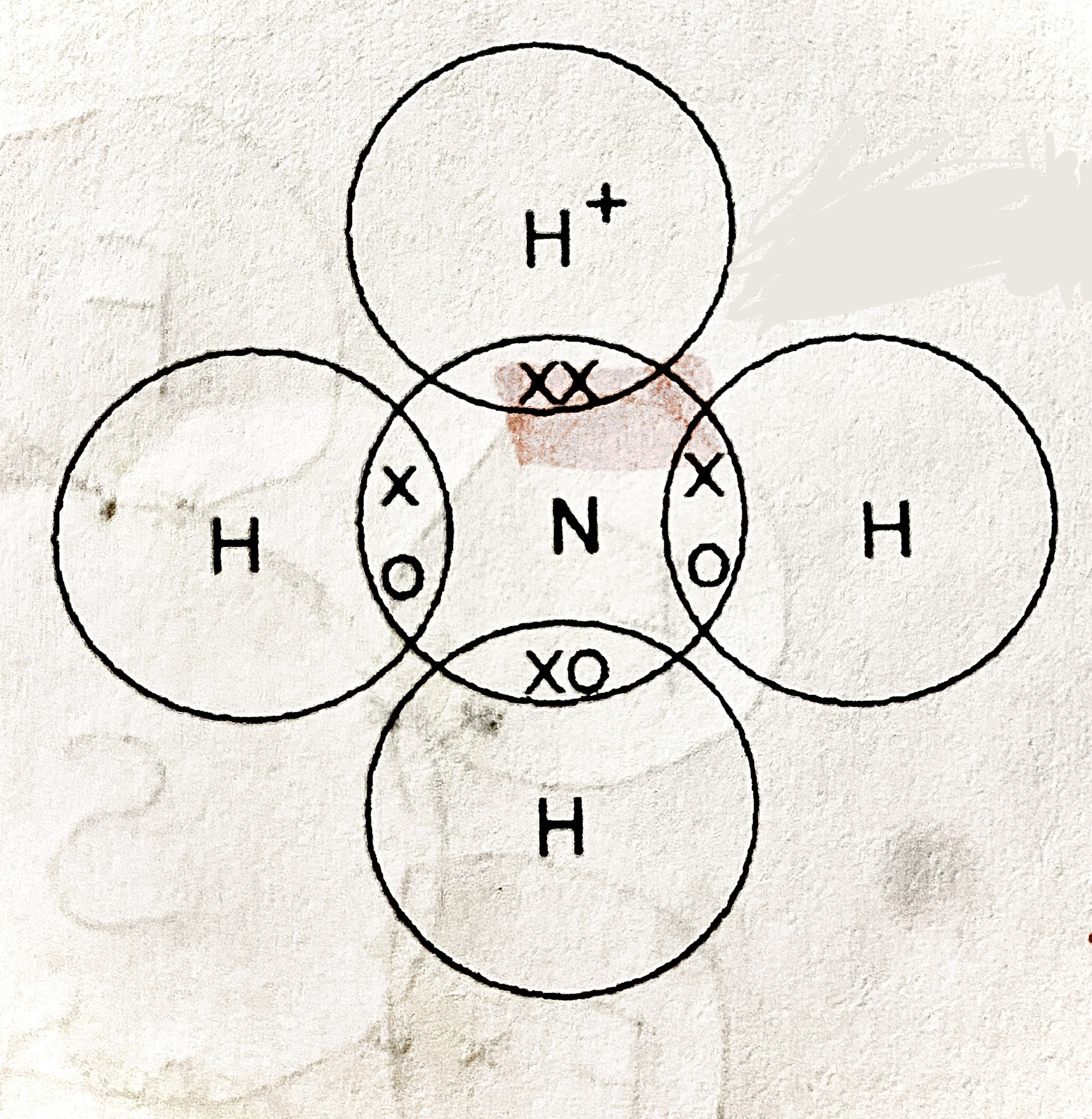
ammonium ion diagram
dirrection of arrow shows where the 2 electrons have come from
What is the octet rule
When reacting, an atom tends to gain, lose or share electrons to achieve eight in its outer shell.
contraction of the octet rule + examples
has less than 8 electrons in outer shell
BeCl2, BF3
Expanision of the octet rule
Has more than 8 electrons in the outer shell
PCl5, SF6
Propeties of moelcular covalent sturctures
Do not conduct elecitricty
Low melting and boiling points
Solubility
Molecular covalent compounds conductivity
They cant as they do not contain ions or delocalised electrons
Low melting and boiling points in molecular covalent compounds
Little energy required to break the weak Van der Waals forces between molecules. Attractive forces between molecules containing larger molecules - S8, P4, or heavier atoms such as I2 , are much greater than the attrcitve forces between molecules such as N2. Consequently sulfur and iodine have higher m.p and are more likly to be solids or liquids at r.t.p
Solubility in molecular covalent compounds
Molecular substances containing polar molecules - ammonia dissolve in polar solvents such as water. Molecular substances containing less polar molecules - sulfur or iodine dissolve in less polar solvents such as hexane.
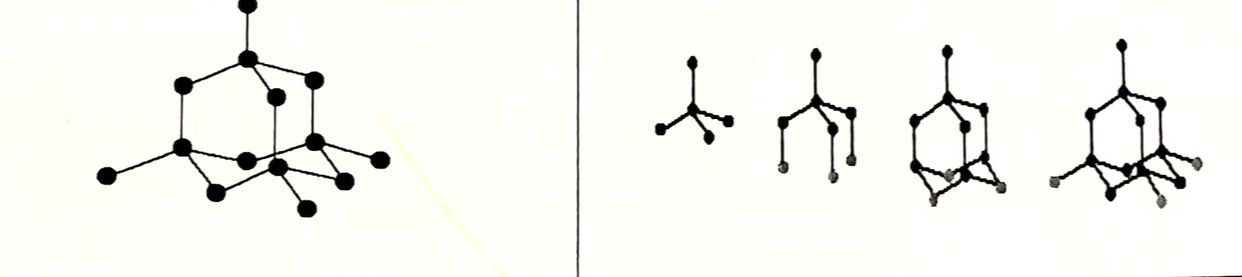
Structure of diamond (allotrope of carbon)
Each carbon atoms is covalently bonded to four others in a tetrahedral arrangement, to form a rigid three-dimensional structure
Diamond diagram
Properties of diamond
High melting and boiling point
Poor conductivity
Hard, strong and brittle
High melting and boiling point meaning behind diamond
SInce strong covalent bonds must be broken before any atoms can be sepearted which requires a large amount of energy
Diamonds poor conductivity
There are no ions or delocalised electrons, so there is little electrical conductivity in either solid or liquid state.
Diamonds hardiness, strong and brittle
The covalent bonds are strong and directional, lots of energy needed to break the bonds. Hardest substance - used n drills and glass-cutting.
Graphites structure
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three others. The spare delocalised electron occupies space above and below each layer, All atoms in same layer held together by strong covalent bonds, and the different layers are held together by intermollecular forces.
Properties of graphite
High melting point
Good electrical conductivity
Hardness
Graphite high melting point reason
Lots of energy required to break the strong covalent bonds
Graphite good electrical conductivity reason
due to delocaliseded electrons in each plane, graphite is very good conducutor of electricity within each layer, even in the solid state (ususally for a non-metal)
Graphite hardness
Graphite much softer than diamond since different planes can slip over eachother fairly easily. Used in pencils and industrial lubricant.
What is electronegativity
The extent to which an atom attracts the bonding electrons in a covalent bond
What two factors affect electronegativity
-As the size of the nuclear charge increases, increased attraction between nuclear charge and pair of electrons in the covalent bond, so electrongeavity increases
-as Size of atom increases pair of electrons in covalent bond further away from the nucleus , there will be decreased attraction from nuclear charge so electronegativity decreases
Electronegativity across period
Increases , nuclear charge increases size of atoms decreases hence greater attraction between the nucleus and the pair of electrons in the covalent bond
Electronegativity down a group
Decreases - pair of electrons in covalent bond further from nuclear so decreased attraction from nuclear charge. inner electrons also shield the pair of electrons in the bond from the nuclear charge
electronegativity values of two atoms same/similar
pair of electrons shared equally and a covalent bond is nonpolar e.g I2, O2
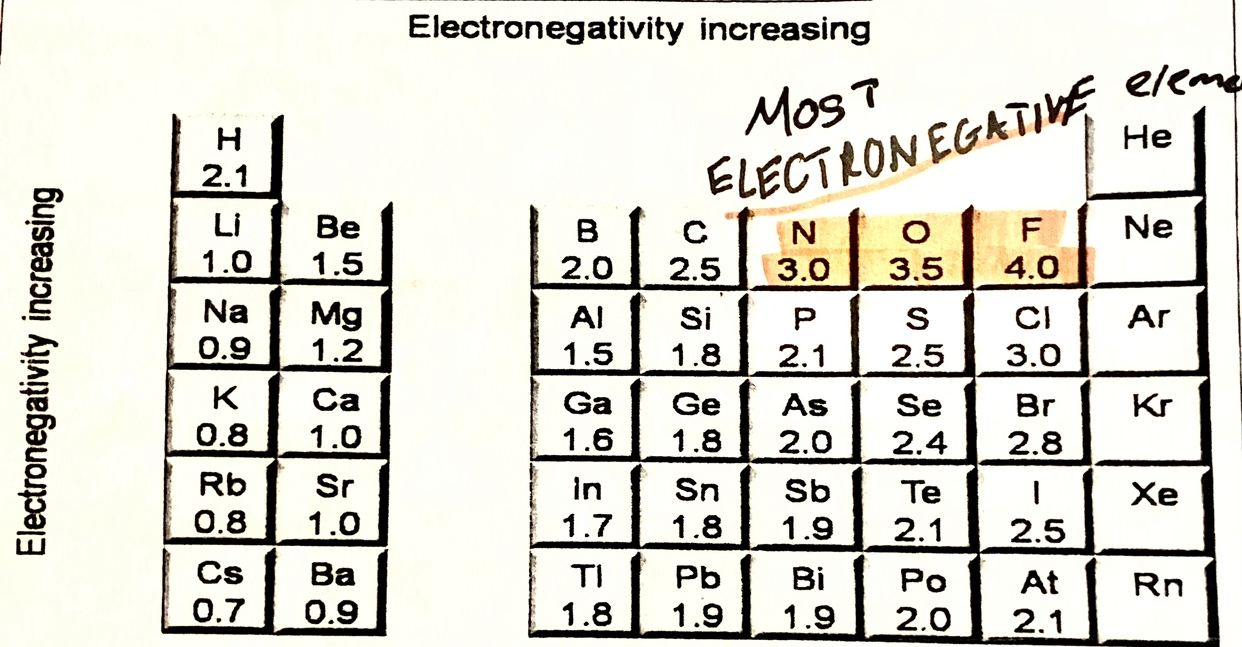
Electronegativity of N, O , F
N- 3.0
O- 3.5
F- 4.0
ELECTRONEGATIVTY TABEL
What is a polar bond
A covalent bond in which there is an unequal sharing of bonding electrons.
What is partial charges
Delta negative δ-, and delta positive (less electronegative)
How is a bond dipole formed
Seeration of charge that develops between atoms in polar covalent bond
size increases as difference in electronegativity values increases
Why does a polar bond cancel
The shape of the molecule is symmetrical and the polarities of the bond cancel out
different electronegativities cancel out
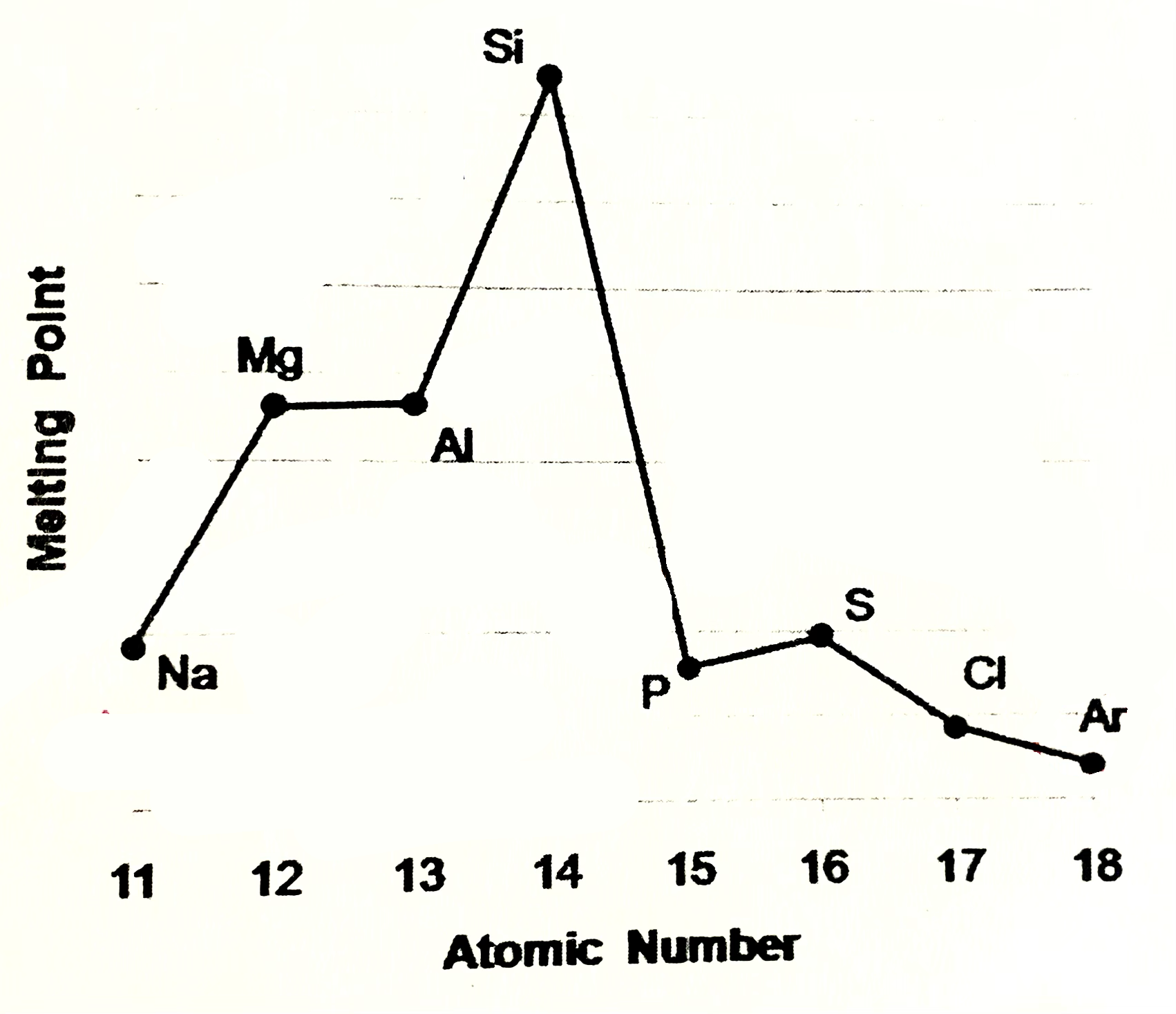
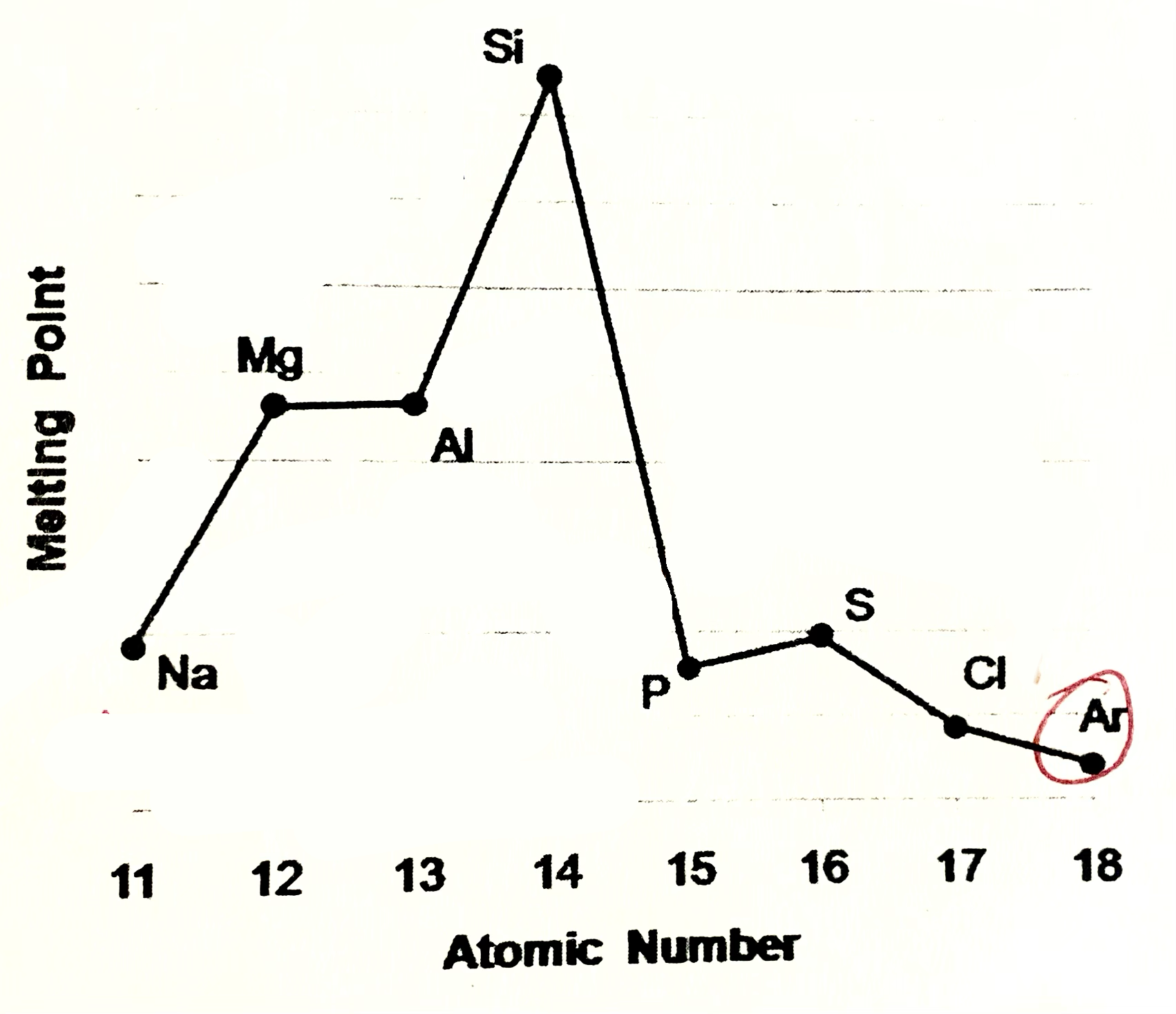
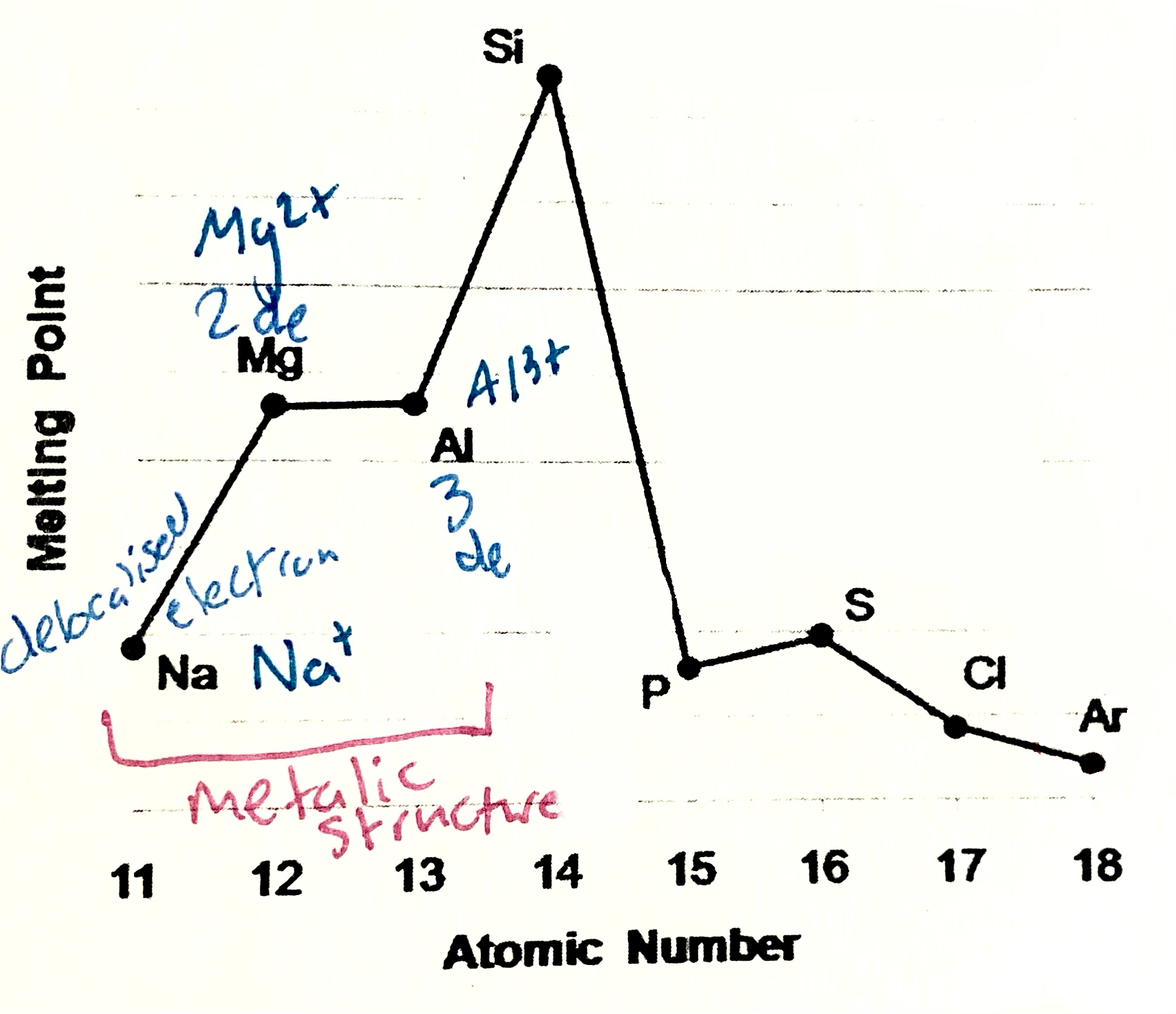
Sodium, magneisum and aluminium meaning
Sodium magneisum and aluminium are metals (metalic structure). Strenght of metalic bonding depends upon the number of delocalsied electrons in metalic structure. Soidum has one, Mg 2, Al 3. Hence M.P and B.P increase from sodium to aluminium
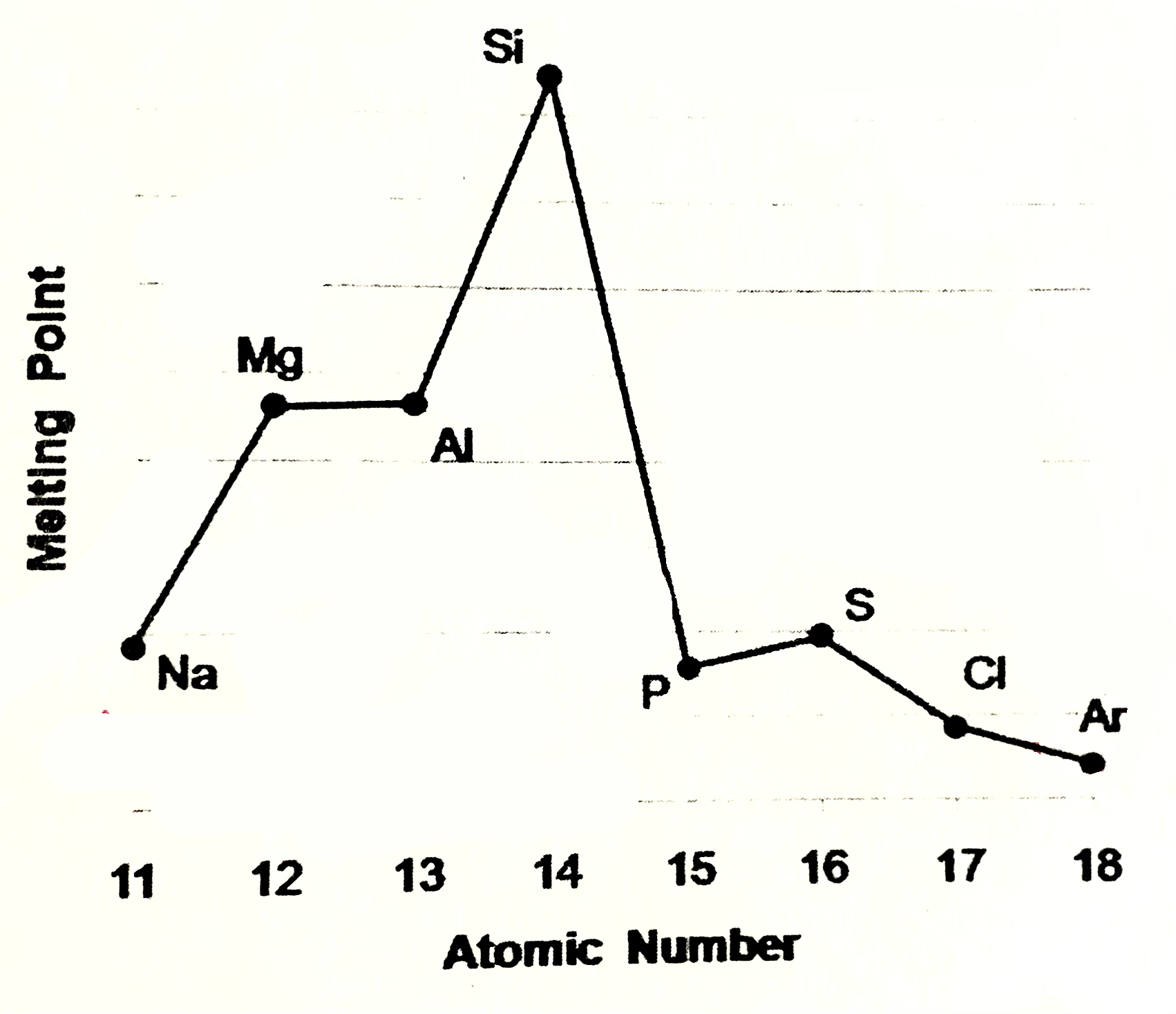
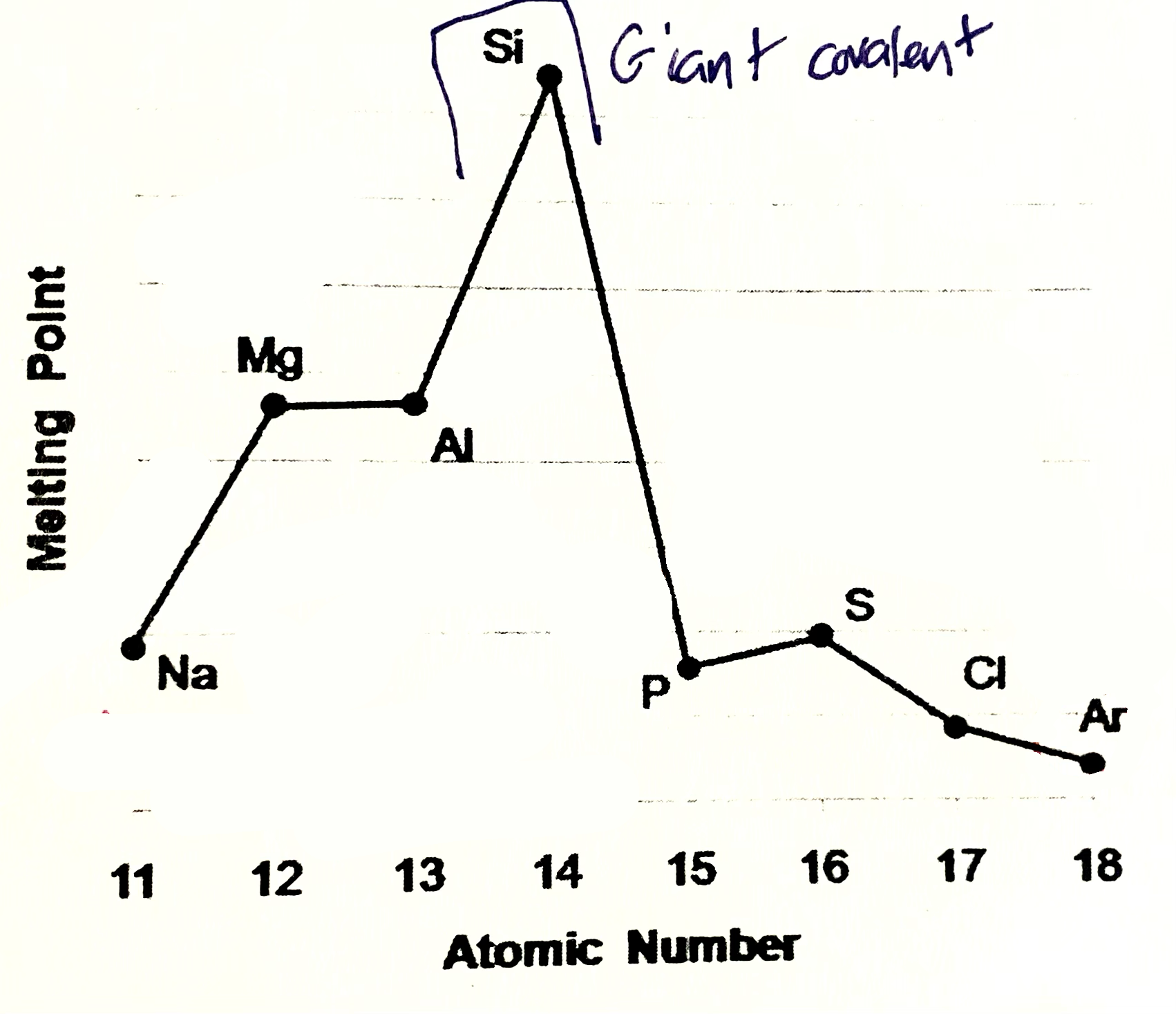
Silicone meaning
Silicone exists as giant covalent strucutre. Great number of strong covalent bonds betweent the atoms have to be broken so high M.P and B.P
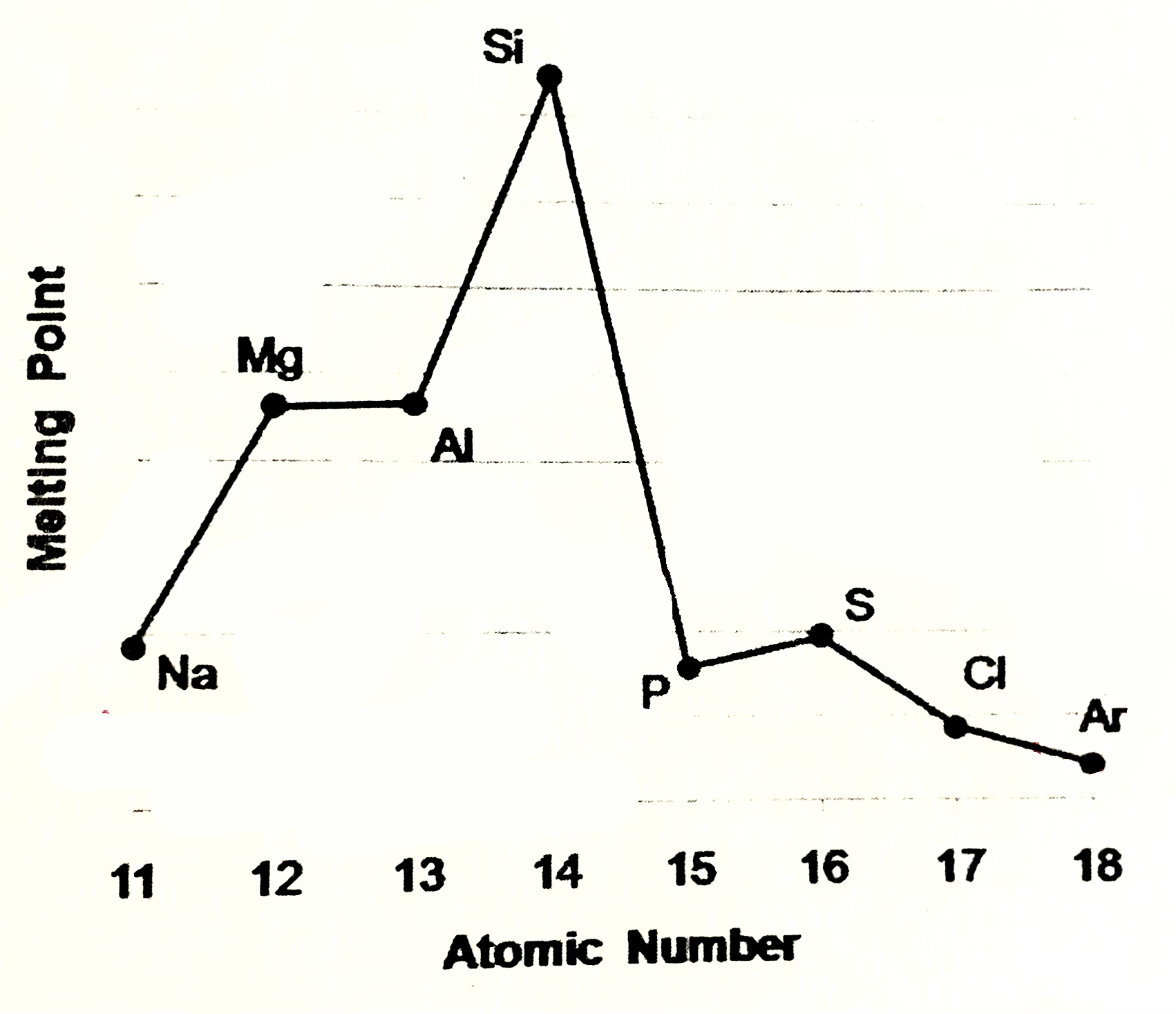
Phosphorus, sulfur, chlroine
are simple molecular species (molecular covalent). P consists of P4 molecules, S - S8 molecules, Cl - Cl2 molecules. Forces between molecules are weak Van der Waals forces, so these elements have low melting and boiling points. Strength of VDW forces increases as size of the molecules increases more energy is needed to break these forces, so M.P and B.P increases from Cl2 , P4, S8
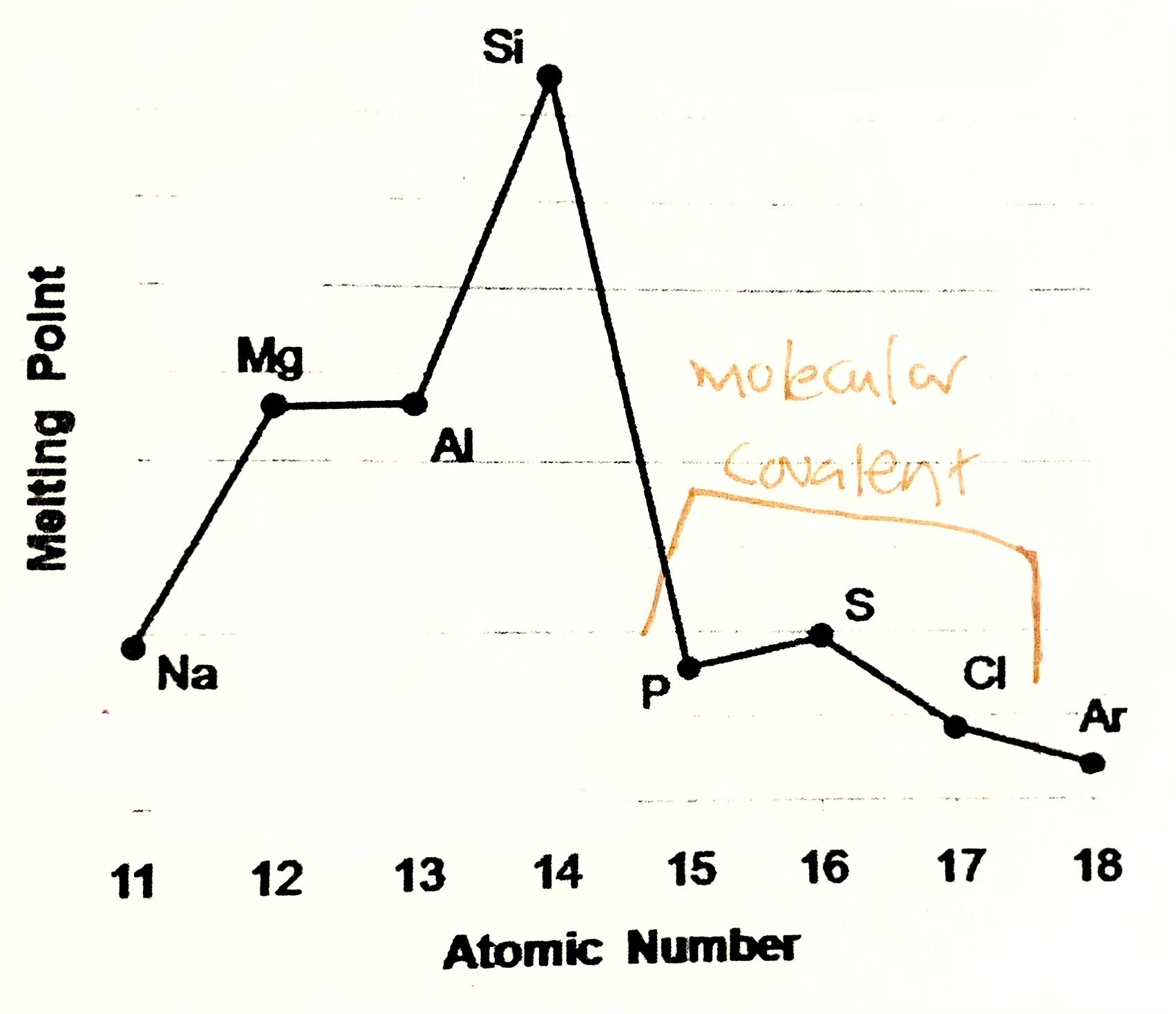
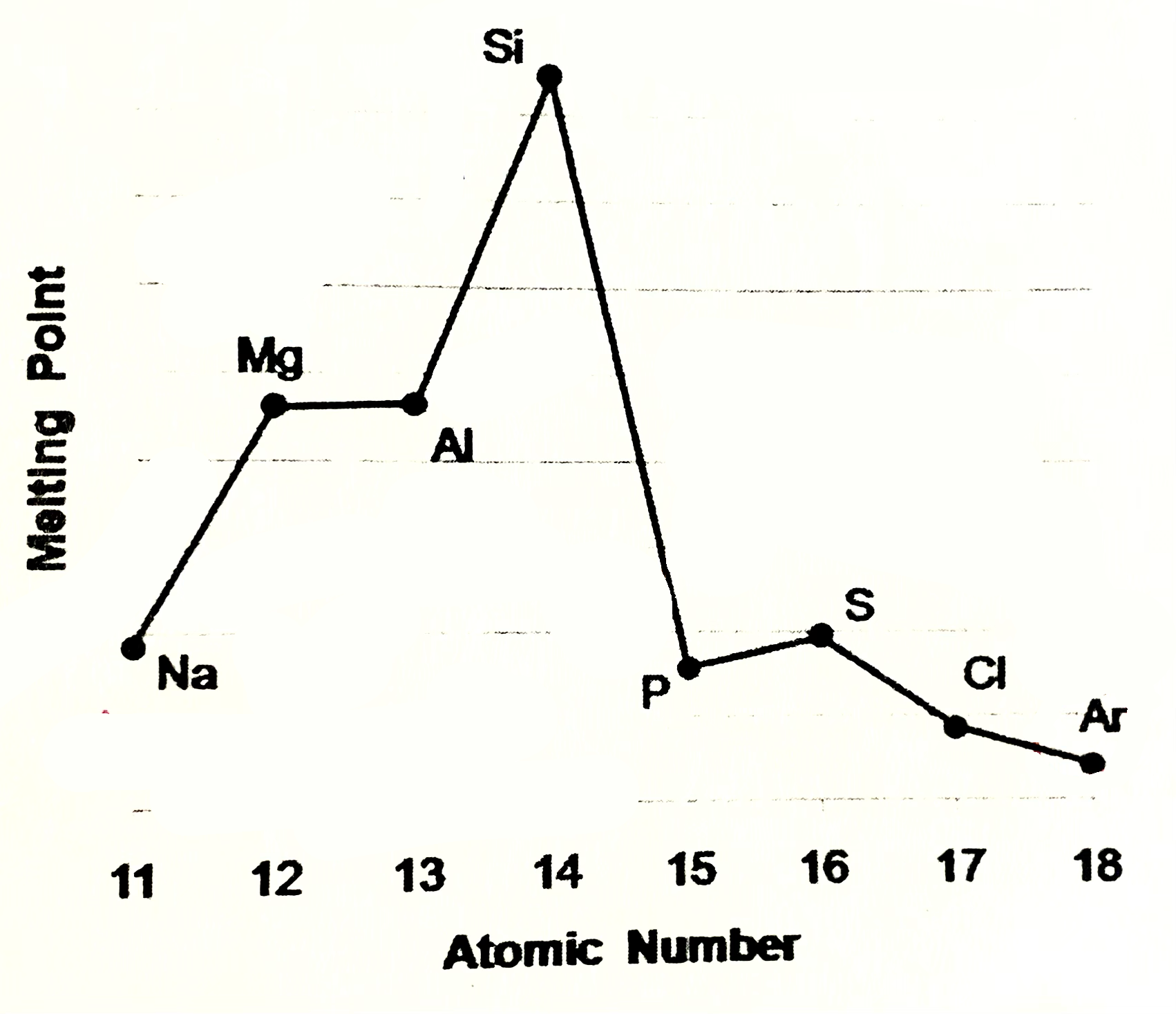
Argon
Argon exists as isolated atoms (monotamic) with weak Van der Waals forces between the atoms. therefore Ar has lowest M.P and B.P in period.