C1 - Atoms
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What do chemical reactions cause?
Atoms to change what they’re bonded to
Element
A substance containing only one type of atom
Compound
A substance containing two or more different types of chemically bonded
Conservation of mass
Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed
Mixture
Contains different substances not chemically bonded
Filtration
Removes large insoluble particles from a liquid
Evaporation
Leaves behind crystals of a dissolved substance (solute) if heated gently (crystallisation)
Distillation
Involves condensing the evaporated solvent and collecting it
Fractional Distillation
Can seperate liquids due to their different boiling points
Chromatography
Causes substances to rise up paper due to capillary action, lighter particles move further up
Solid → Gas
Sublimation
What is needed to overcome the electrostatic between particles, to melt / evaporate?
Heat
Physical Change
No new substance is made
Aqueous
In solution
1st atomic model
John Dalton
Solid spheres
2nd atomic model
JJ Thompson
Plum pudding model
Posistive sphere with electrons dotted randomly
3rd atomic model
Ernest Rutherford
Nucleus is small and positively charged
Most alpha particles went directly through a gold leaf, very few deflected back
4th atomic model
Niels Bohr
Electrons exist in shells
5th atomic model
James Chadwick
Discovered the neutron
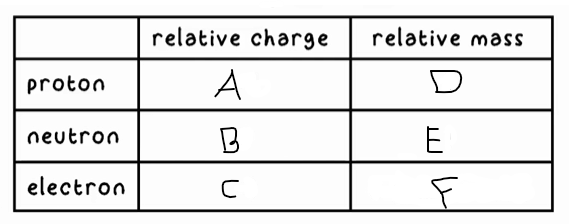
A?
+1
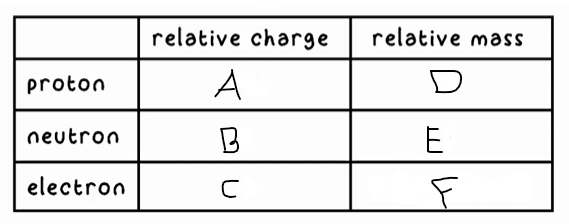
B?
0
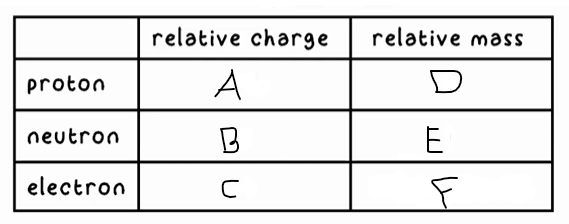
C?
-1
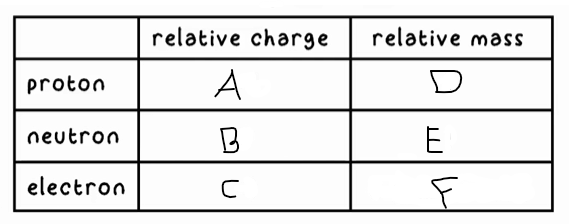
D?
1
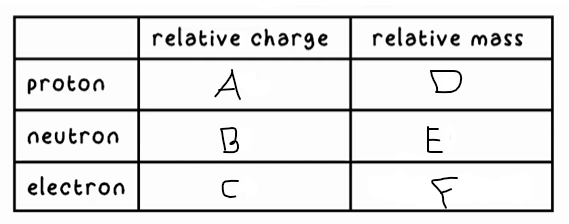
E?
1
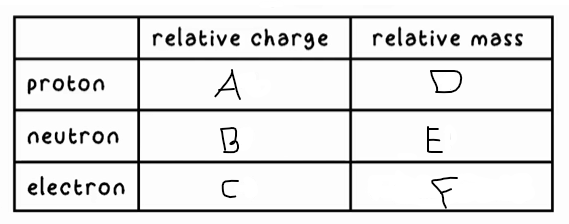
F?
0 (very small)
Isotope
Same element, same number of protons, different number of neutrons
Mass number
The number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus
Atomic number
(or relative atomic mass) is the number of protons in a nucleus. An atom must also have this number of electrons in order to be neutral, if not is is an ion
Why are some numbers on the periodic table not integers?
They are an average mass of all isotopes
Calculation for relative atomic mass
total mass of atoms / total number of atoms
How were elements initially ordered in the periodic table?
By atomic weight
What was Dmitri Mendeleev order his periodic table?
Reversed and swapped some elements and kept gaps for elements that had not yet been discovered
Group
Number of atoms in outer shell
What do metals always do to gain a full outer shell?
Donate electrons to form positive ions
What do non-metals always do to gain a full outer shell?
Accept electrons to gain a full outer shell, either become negative ions or share electrons
What are Group 1 know as?
The alkali metals
What happens when a group one metal reacts with water?
Produce an alkali
What do Group 1 metals do to gain a full outer shell?
Lose their outer electron, so their ions are always 1+
What happens to reactivity as you go down group one and why?
Gets more reactive because the outer electron is further away from thenucleus so is donated more readily
What are Group 7 elements known as?
Halogens
What do Group 7 elements do to gain a full outer shell?
Gain 1 electron to form 1- ions
What happens to the reactivity of group 7 elements as you go down the group?
Get less reactive
What happens to the boiling point of group 7 elements as you go down the group?
Increases
What is special about the noble gases?
They are unreactive as they already have a full outer shell
What is special about transition metals?
They can donate different numbers of electrons