Chapters 3 & 9: Cell Adaptation, Inflammation, and Repair
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
atrophy
cell decreasing in size
hypertrophy
cell increasing in size
hyperplasia
increase in cell number
metaplasia
population of protective cells replace less protective cells (normal body process)
dysplasia
pre-cancerous, alteration in cell/tissue growth
examples of hypertrophy
left ventricle due to hypertension, bladder wall due to enlarged prostate
hyperplasia examples
breast cells during pregnancy, endometrium during ovulation
metaplasia examples
squamous cells replacing glandular cells in the cervix, glandular cells replacing squamous cells in the esophagus
stressed cells may fill up with (3):
normal body substances, abnormal endogenous substances, abnormal exogenous substances
injurious agents (5)
physical, radiation, chemical, biologic agents, nutritional imbalances
free radicals
chemicals with an unpaired electron in the outer electron shell
hypoxia causes ___
ATP depletion
Cells maintain cytosolic calcium at a ____ level.
low
apoptosis
cell suicide to stop damage from getting worse
necrotic cell death
unregulated death caused by injuries to cells
dry gangrene
lack of arterial blood supply but venous flow can carry fluid out of tissue
wet gangrene
lack of venous flow lets fluid accumulate in tissue
gas gangrene
hydrogen sulfide bubbles in muscle
How do cells change with aging?
the telomeres become short so that the cell can no longer divide
hydropic change
swelling, accumulation of water
types of radiation injuries
ionizing, nonionizing
inflammation
an innate automatic response to cell injury
inflammation effects (4)
neutralizes harmful agents, removes damaged and dead tissue, generates new tissue, promotes healing
first line of immune defense
barriers to entry (skin, saliva, mucus, tears)
second line of immune defense
non-specific immunity (anti-microbial substances, phagocytic WBCs, NK cells)
third line of immune defense
specific immunity, T & B cells
granulocytes
basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils, mast cells
agranulocytes
monocytes, T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes
inflammation 5 cardinal signs
rubor, tumor, calor, dolor, functio laesa (redness, swelling, heat, pain, temporary loss of function)
phases of inflammation
vascular phase, cellular phase, leukocyte activation and phagocytosis
vascular phase of inflammation (exudation)
extravascular influx of fluids with high concentration of proteins, salts, cells; fluid brings antibodies and chemotactic substances to injured area
cellular phase of inflammation
adhesion, diapedesis, chemotaxis, phagocytosis
opsonization
coats surface of microbes with antibodies to prevent spread
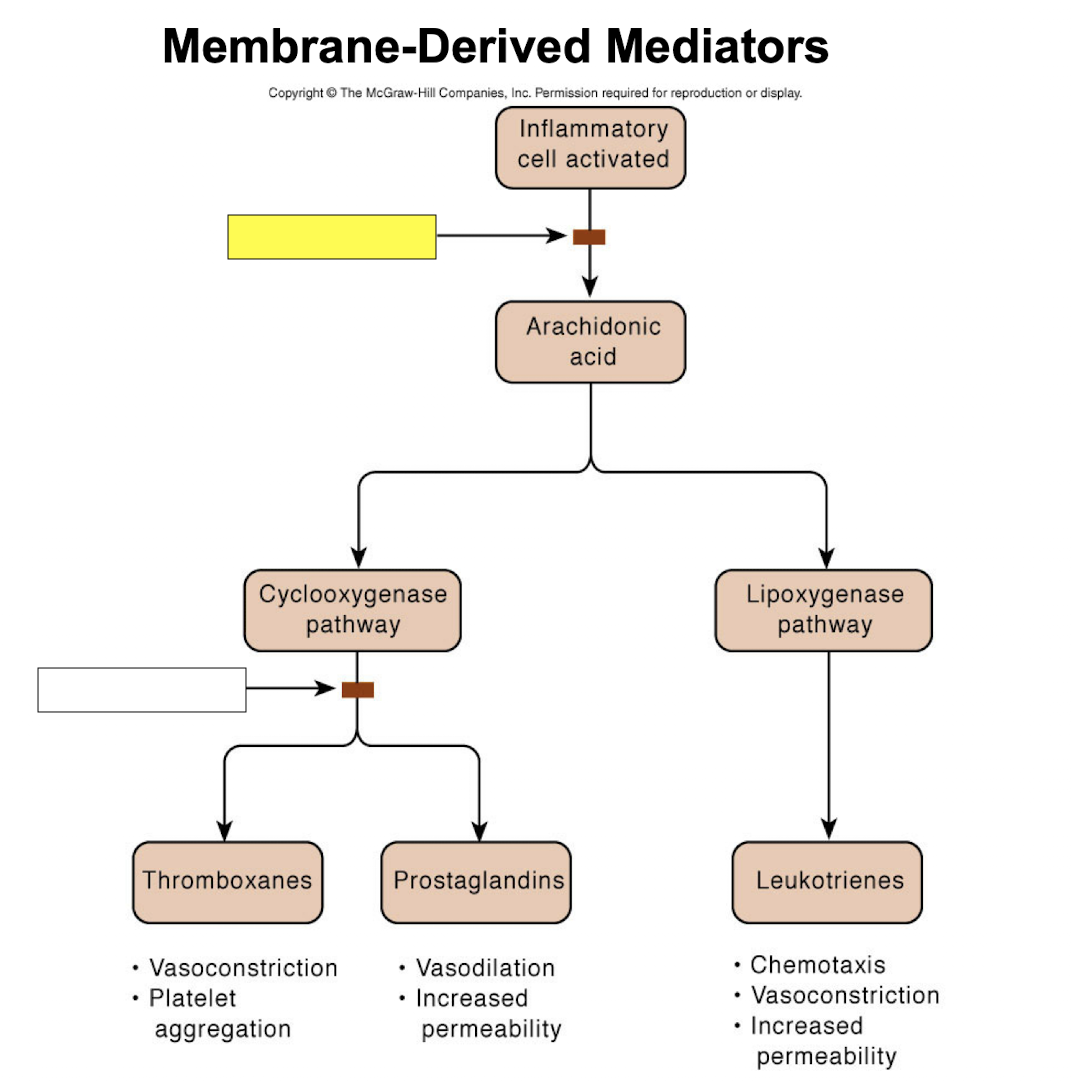
corticosteroids
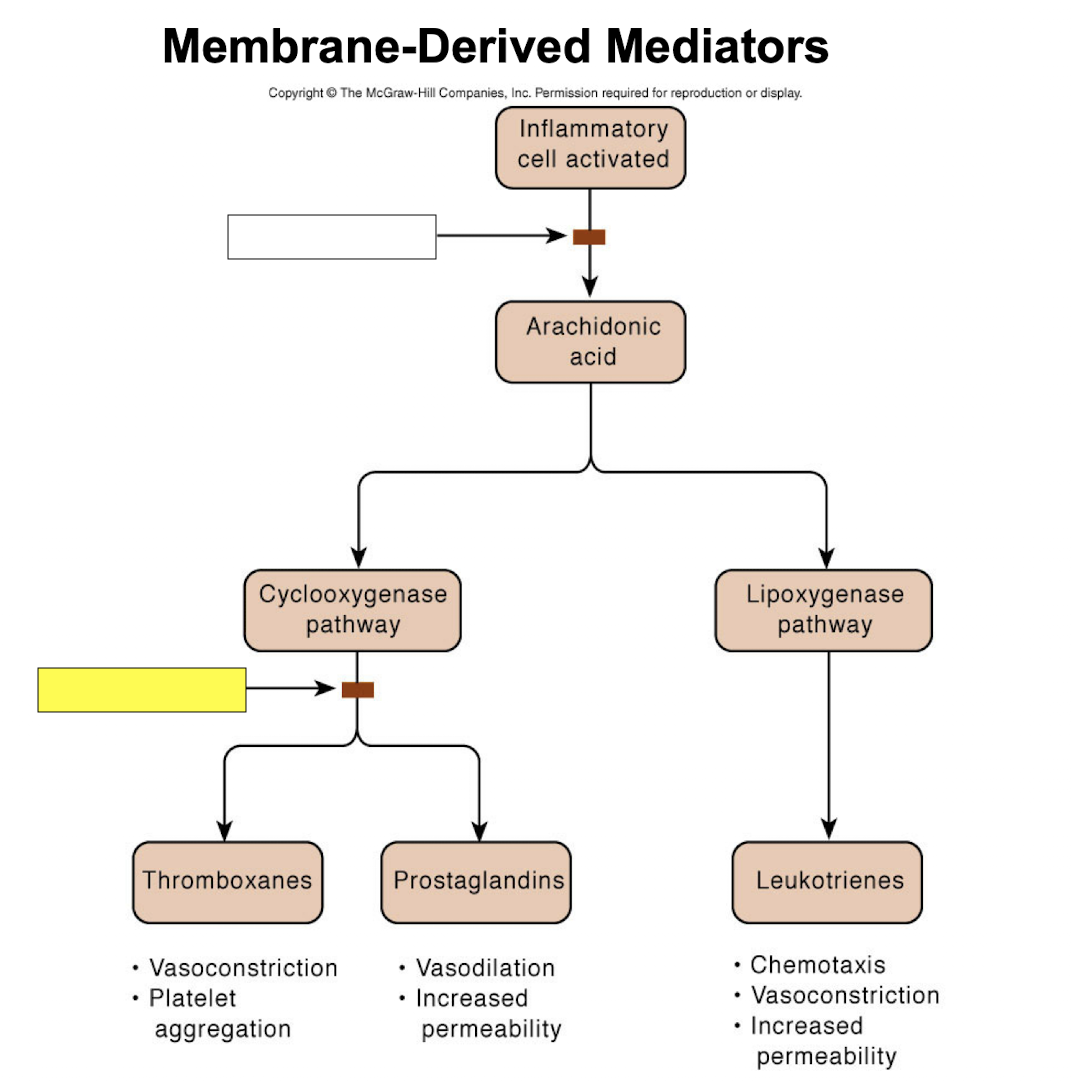
NSAIDs
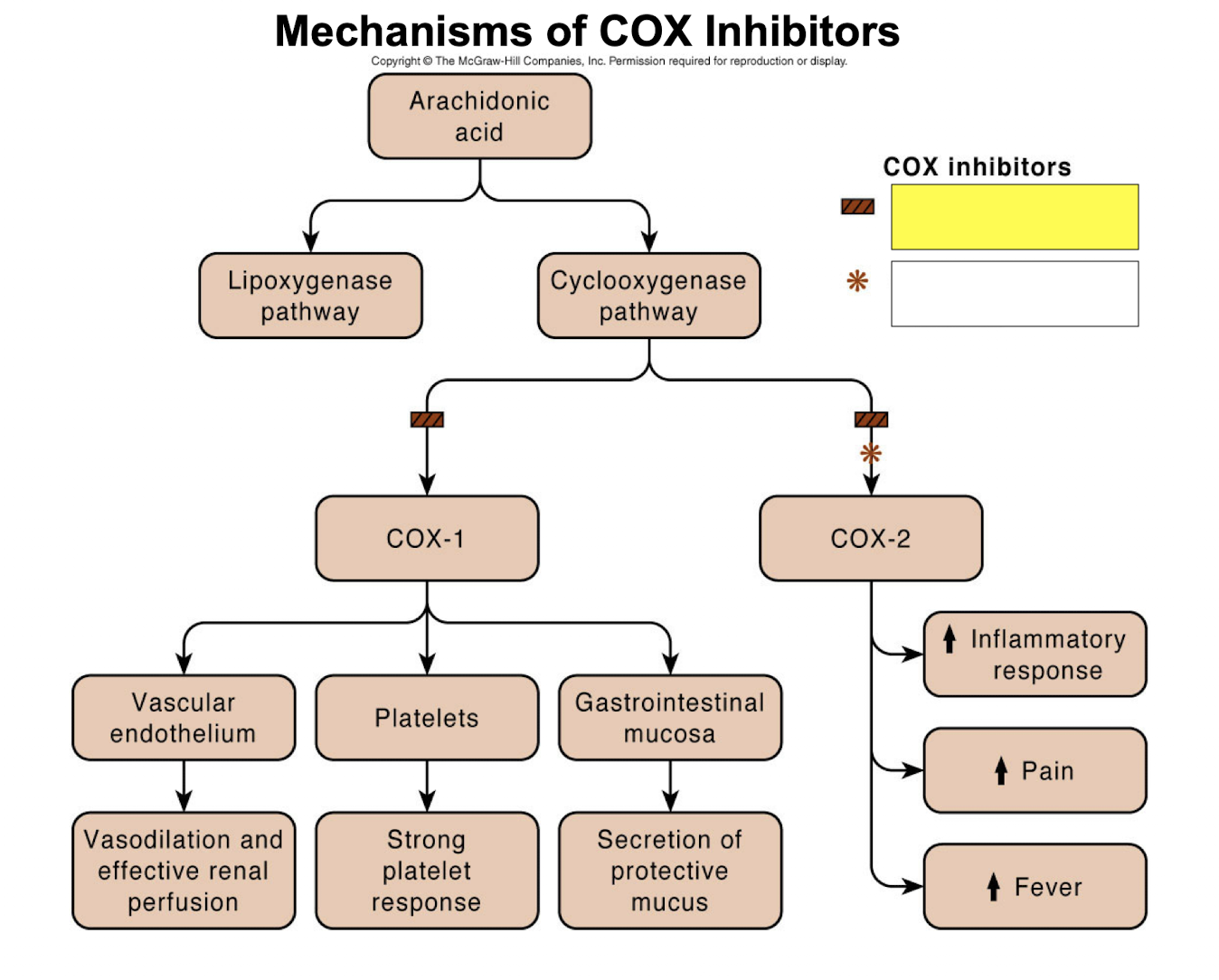
nonselective COX inhibitors
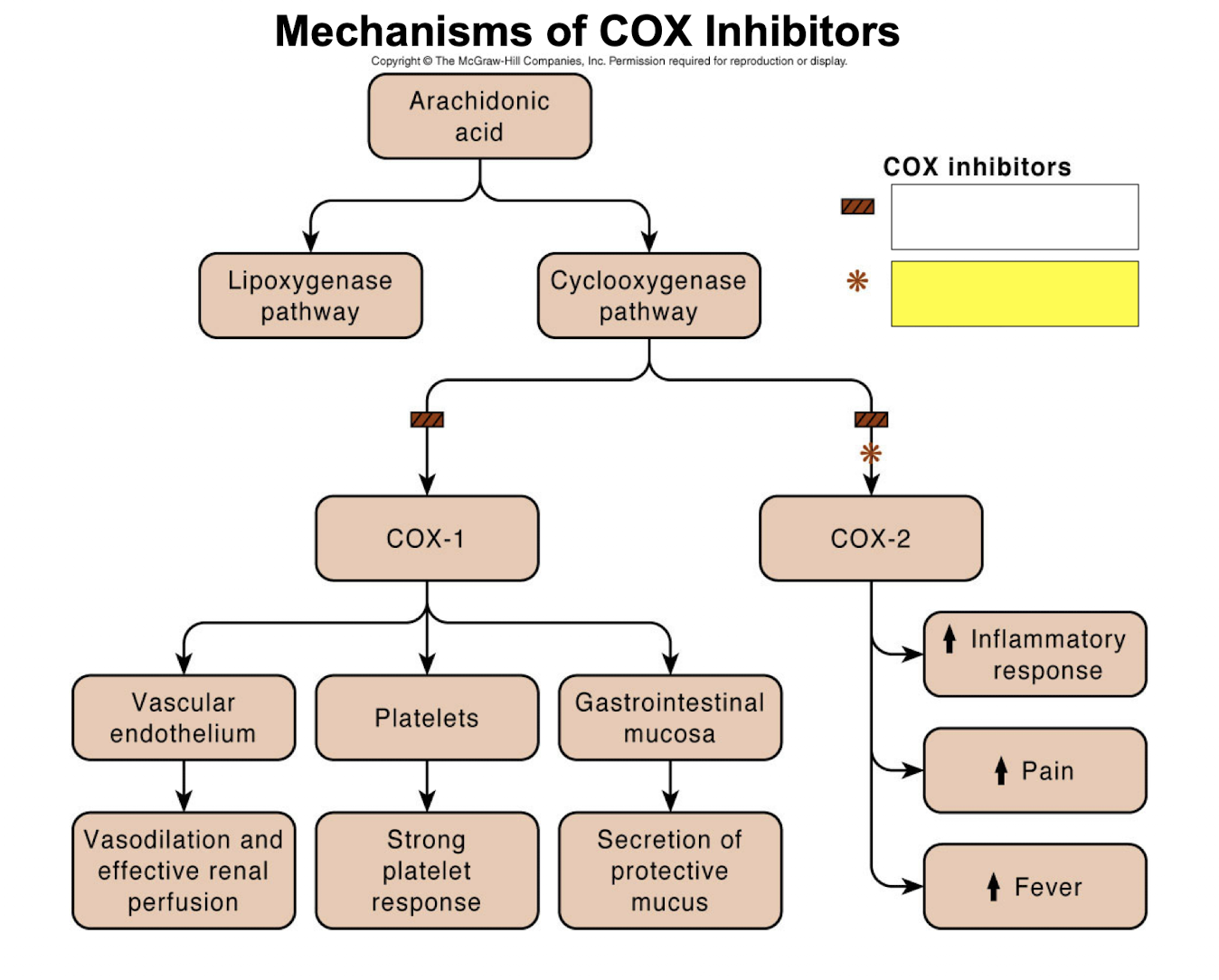
COX-2 selective inhibitors
granuloma
area of tissue that has undergone chronic inflammation, not purposeful or helpful
principle components of a granuloma (6)
lymphocytes, fibroblasts, macrophages, epithelioid cells, multinucleated giant cells, fibrous connective tissue
regeneration
replacing damaged cells
repair
scar-tissue formation—maintains structure but not function
parenchyma
functional tissue of an organ
stroma
organ maintenance (support tissue)
labile cells
divide whole life, constant cell division
stable cells
somewhat specialized, mostly stable in adulthood
permanent or fixed cells
very specialized cells
nerve cells require support from ____
neuroglia
phases of regeneration
inflammatory, proliferative, remodeling
phase of regeneration: inflammatory
hours to days: increased capillary permeability, diapedesis, coagulation
phase of regeneration: proliferative
days to weeks: budding capillaries, influx of macrophages, influx of fibroblasts & collagen
phase of regeneration: remodeling
weeks to months: tissue function/strength is close to, but does not exceed, original tissue
scars are produced by ____
fibrosis
collagen has ____ strength
tensile (doesn’t pull apart easily)
revascularization
angiogenesis
granulation tissue
pink/granular appearance as new blood vessels form
abrasion
scraping injury
primary intention
incision, severing
secondary intention
wound edges not closely apposed, more granulation tissue and wound contraction
How long does it take for cells from the basement membrane to reach the surface?
24-28 days
myofibroblasts
exist at edges of wound, pull the edges close together to minimize scar tissue formation
Epithelial cells are what kind of cells?
labile
Glandular cells are what kind of cells?
stabile
Nervous cells are what kind of cells?
permanent
Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are what kind of cells?
permanent
Smooth muscle cells are what kind of cells?
stabile
PNS healing is more efficient than CNS healing due to ____
Schwann cells
contracture
damage to large areas, collagen displays exaggerated wound contracting, limits mobility and lumen of organ
adhesions
union of serous membranes, restricts movement
dehiscence
wound breaking open due to pressure applies to healing tissues
keloids
excess transforming growth factor, excess fibroblast producgtion
proud flesh
excess granulation tissue, can interfere with surface restoration
most important factors affecting wound healing (6)
blood flow/oxygen, age, nutrition, immune status, infection, foreign bodies