Bio ch. 6
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
An Introduction to Metabolism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Metabolism
maintenance system run by energy transfers, anabolism and catabolism

Metabolism (pic)
Kinetic energy
energy in motion
Thermal energy
kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules
Heat
thermal energy in transfer from one object to another
Potential energy
energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure
Chemical energy
potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed or transferred
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
The total energy in the universe remains constant, but the amount of HIGH QUALITY energy decreases and LOW QUALITY increases
Entropy
degree of disorder
Free-energy
The porton of a system’s energy that can perform work
Chemical Equilibrium
G is at its lowest possible value in that system; a system at equilibrium cannot spontaneously change, so it can do no work
Exergonic reaction
energy exits, G decreases, spontaneous, cellular respiration (Delta G = -686 kcal/mol)
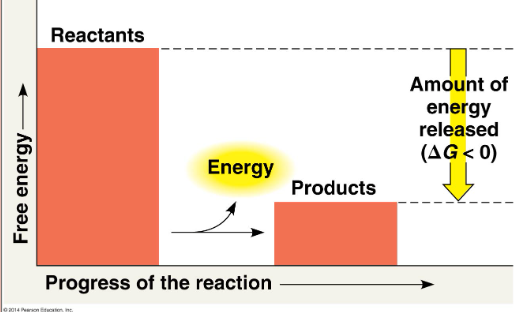
Exergonic reaction (pic)
Endergonic reaction
absorbs free energy, energy enters (non-spontaneous), G increases, photosynthesis (686 kcal/mol)
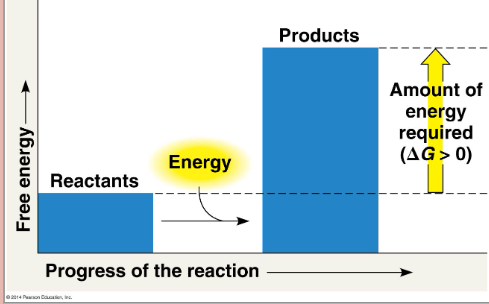
Endergonic reaction (pic)
ATP
powers cellular work by coupling exergonic reactions with endergonic reactions
ATP (types of work)
chemical work: pushing of endergonic reactions that would not happen spontaneously; transport work: pumping of substances against concentration gradient; mechanical work: movement
Enzymes (identity)
proteins, act as catalyst (speed up reactions), lower amount of activation energy required, cannot change Delta G, cannot make endergonic exergonic
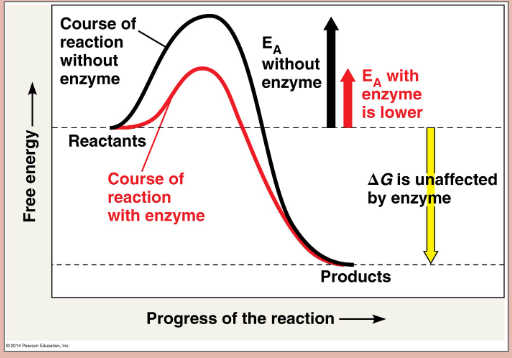
Enzyme (pic)
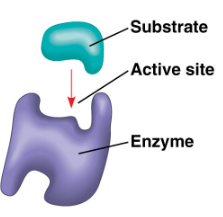
Enzyme binding (pic)
Enzymes (functioning)
If an enzyme becomes saturated with substrate, then add more substrate; all enzymes have optimal pH and temp.
Cofactors
non-protein enzyme helpers
Coenzyme
Organic cofactor
Types of Enzyme Inhibition
Competitive, non-competitive, feedback
Enzyme Inhibition
can be helpful or harmful, covalent bond=permanent or hydrogen bond=temporary
Competitive Inhibition
resembles substrate and competes with substrate for active site; if inhibitor binds, substrate cannot; slows the rate of reaction
Non-competitive Inhibition
inhibitor binds to allosteric site and makes active site change shape; covalent bond=enzyme is “dead”, hydrogen bond=inhibitor is “switch”
Feedback Inhibition
metabolic pathways, final product of pathway is allosteric inhibitor for first enzyme in pathway, hydrogen bond
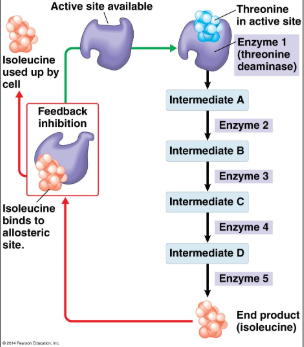
Feedback Inhibition (pic)
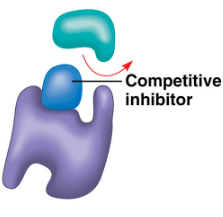
competitive inhibition
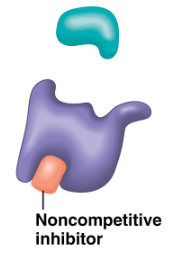
non-competitive inhibition (pic)