Sample exam 2 questions
2.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:37 AM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
What is the correct order of the following emulsion instability problems in terms of severity (mild -→ severe)
\
a. Flocculation -→ creaming -→ coalescence -→ breaking
b. Creaming -→ flocculation -→ coalescence -→ breaking
c. Coalescence -→ flocculation -→ creaming -→ breaking
d. Creaming -→ coalescence -→ flocculation -→ breaking
e. Coalescence -→ creaming -→ flocculation -→ breaking
\
a. Flocculation -→ creaming -→ coalescence -→ breaking
b. Creaming -→ flocculation -→ coalescence -→ breaking
c. Coalescence -→ flocculation -→ creaming -→ breaking
d. Creaming -→ coalescence -→ flocculation -→ breaking
e. Coalescence -→ creaming -→ flocculation -→ breaking
a
\
Flocculation is a step before coalescence, so any choice in which this is reversed is incorrect. Also, flocculation is less severe than creaming
\
Flocculation is a step before coalescence, so any choice in which this is reversed is incorrect. Also, flocculation is less severe than creaming
2
New cards
All of the following are characteristics of microemulsions, EXCEPT
\
a. From a physical stability standpoint, they are stable indefinitely
b. Visually, they appear as clear solutions
c. Surfactant % in these preparations can reach up to 50% or even higher
d. Preparation of microemulsions is more economical than that of emulsions
e. The particle size of the dispersed phase is 100 nm and up
\
a. From a physical stability standpoint, they are stable indefinitely
b. Visually, they appear as clear solutions
c. Surfactant % in these preparations can reach up to 50% or even higher
d. Preparation of microemulsions is more economical than that of emulsions
e. The particle size of the dispersed phase is 100 nm and up
e
\
The Particle size of the dispersed phase is between 10-100 nm
\
The Particle size of the dispersed phase is between 10-100 nm
3
New cards
The reason why tablets are considered the most stable of all oral preparations is
\
a. They are processed with high degree of compression
b. They are typically coated, and consequently protected from the external environment
c. A drug in a tablet form has the smallest exposed surface area
d. They are typically wrapped individually
e. None of the above
\
a. They are processed with high degree of compression
b. They are typically coated, and consequently protected from the external environment
c. A drug in a tablet form has the smallest exposed surface area
d. They are typically wrapped individually
e. None of the above
c
\
(a) They are processed with a high degree of compression, which doesn’t make them the most stable. (b) They are typically coated, and consequently protected from the external environment, but not all tablets are coated. (c) A drug in tablet form has the smallest exposed surface area. (d) They are typically wrapped individually: not unique for stability
\
(a) They are processed with a high degree of compression, which doesn’t make them the most stable. (b) They are typically coated, and consequently protected from the external environment, but not all tablets are coated. (c) A drug in tablet form has the smallest exposed surface area. (d) They are typically wrapped individually: not unique for stability
4
New cards
An oral tablet may be sugar-coated for the following reasons
\
a. To protect a drug that is susceptible to atmospheric oxygen
b. To protect a drug that is sensitive to moisture content
c. To enhance the bioavailability of a drug that is sensitive to the gastric digestive enzymes
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. To protect a drug that is susceptible to atmospheric oxygen
b. To protect a drug that is sensitive to moisture content
c. To enhance the bioavailability of a drug that is sensitive to the gastric digestive enzymes
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
e
\
(a) To protect a drug that is susceptible to atmospheric oxygen: true, (b) To protect a drug that is sensitive to moisture content: true, (c) To enhance the bioavailability of a drug that is sensitive to the gastric digestive enzymes: sugar coating doesn’t protect from gastric juices
\
(a) To protect a drug that is susceptible to atmospheric oxygen: true, (b) To protect a drug that is sensitive to moisture content: true, (c) To enhance the bioavailability of a drug that is sensitive to the gastric digestive enzymes: sugar coating doesn’t protect from gastric juices
5
New cards
Airborne is a vitamin C-containing effervescent tablet formulation. Which of the following is/are correct about this pharmaceutical dosage form
\
a. It possesses an enhanced psychological perception over an ordinary tablet
b. It is necessary for this dosage form to be kept away from moisture during storage
c. Clear label should indicate the requirement to mix the tablet with water before ingestion
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. It possesses an enhanced psychological perception over an ordinary tablet
b. It is necessary for this dosage form to be kept away from moisture during storage
c. Clear label should indicate the requirement to mix the tablet with water before ingestion
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
d
\
(a) It possesses an enhanced psychological perception over an ordinary tablet: similar to carbonated beverages, (b) It is necessary for this dosage form to be kept away from moisture during storage, because it contains water sensitive excipients (c) Clear label should indicate the requirement to mix the tablet with water before ingestion: because it is hazardous to try to ingest
\
(a) It possesses an enhanced psychological perception over an ordinary tablet: similar to carbonated beverages, (b) It is necessary for this dosage form to be kept away from moisture during storage, because it contains water sensitive excipients (c) Clear label should indicate the requirement to mix the tablet with water before ingestion: because it is hazardous to try to ingest
6
New cards
Determination of tablet weight is necessary in which of the following quality standards tests
\
a. Weight variation test
b. Friability test
c. Tablet hardness
d. a and b only
e. a and c only
\
a. Weight variation test
b. Friability test
c. Tablet hardness
d. a and b only
e. a and c only
d
7
New cards
Which of the following pharmaceutical excipients is an example of super disintegrant that is employed in tablet manufacturing
\
a. Dicalcium phosphate
b. Magnesium stearate
c. Sucrose
d. Starch
e. Sodium starch glycolate
\
a. Dicalcium phosphate
b. Magnesium stearate
c. Sucrose
d. Starch
e. Sodium starch glycolate
e
\
Sodium starch glycolate (super disintegrant swells up to 200 - 400X its original volume allowing for rapid disintegration)
\
Sodium starch glycolate (super disintegrant swells up to 200 - 400X its original volume allowing for rapid disintegration)
8
New cards
True or False: In tablet manufacturing, the key difference between direct compression, as compared to either wet or dry granulation, is that the formation of granules is unneccessary
\
a. True
b. False
\
a. True
b. False
a
9
New cards
An ideal drug candidate for formulation into a conventional capsule dosage form would be
\
a. A solid drug that is susceptible to hydrolysis upon exposure to moisture
b. A solid drug that is stable in the liquid state but possesses a bitter taste
c. A solid drug agent that lacks proper compression characteristics
d. A solid drug that is sufficiently stable in the liquid state
e. A solid drug for which the release is required to be delayed by 3 hours
\
a. A solid drug that is susceptible to hydrolysis upon exposure to moisture
b. A solid drug that is stable in the liquid state but possesses a bitter taste
c. A solid drug agent that lacks proper compression characteristics
d. A solid drug that is sufficiently stable in the liquid state
e. A solid drug for which the release is required to be delayed by 3 hours
c
\
(a) A solid drug that is susceptible to hydrolysis upon exposure to moisture (can be used as coated tablet), (b) A solid drug that is stable in the liquid state but possesses a bitter taste (can be masked in a coated tablet), (c) A solid drug agent that lacks proper compression characteristics (only one which can’t be formulated as tablet), (d) A solid drug that is sufficiently stable in the liquid state (can be formulated as solution or suspension), (e) A solid drug for which the release in required to be delayed by 3 hours (can be formulated into enteric coated tablet)
\
(a) A solid drug that is susceptible to hydrolysis upon exposure to moisture (can be used as coated tablet), (b) A solid drug that is stable in the liquid state but possesses a bitter taste (can be masked in a coated tablet), (c) A solid drug agent that lacks proper compression characteristics (only one which can’t be formulated as tablet), (d) A solid drug that is sufficiently stable in the liquid state (can be formulated as solution or suspension), (e) A solid drug for which the release in required to be delayed by 3 hours (can be formulated into enteric coated tablet)
10
New cards
In the commercial production of hard gelatin capsules, the quality of the final product is carefully monitored throughout the production. That includes the evaluation of
\
a. Capsule size
b. Capsule moisture content
c. Weight of the drug-filled capsule
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. Capsule size
b. Capsule moisture content
c. Weight of the drug-filled capsule
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
e
\
(a) Capsule size and (b) Capsule moisture content are tested but since the drug is not filled yet we don’t do (c) Weight of the drug-filled capsule
\
(a) Capsule size and (b) Capsule moisture content are tested but since the drug is not filled yet we don’t do (c) Weight of the drug-filled capsule
11
New cards
Capsule sealing provides a tamper-evident dosage form and therefore, it is a must in the commercial production of capsules
\
a. True
b. False
\
a. True
b. False
b
\
Capsule sealing provides a tamper-evident dosage form and therefore, it is a must in the commercial production of capsules. It is not a must it is rare in special cases
\
Capsule sealing provides a tamper-evident dosage form and therefore, it is a must in the commercial production of capsules. It is not a must it is rare in special cases
12
New cards
Which of the following statements is/are correct about modified-release dosage forms
\
a. To be described as a delayed-release dosage form, the drug product needs to demonstrate extended-release characteristics
b. An extended-release dosage form is also known as a controlled-release dosage form
c. An extended-release drug product indicates that the release of the medicinal agent is sustained beyond what is expected from an immediate-release product
d. a and c only
e. b and c only
\
a. To be described as a delayed-release dosage form, the drug product needs to demonstrate extended-release characteristics
b. An extended-release dosage form is also known as a controlled-release dosage form
c. An extended-release drug product indicates that the release of the medicinal agent is sustained beyond what is expected from an immediate-release product
d. a and c only
e. b and c only
c
\
(a) To be described as a delayed-release dosage forms, the drug product need to demonstrate extended-release characteristics (delayed release (DR=enteric coated) is a different class not related to MR), (b) An extended-release dosage form is also known as a controlled-release dosage form (CR is a subclass of MR, so all CR is a type of MR but not every MR is CR), (c) An extended-release drug product indicates that the release of the medicinal agent is sustained beyond what is expected from an immediate-release product (maintains same plasma conc over an extended time)
\
(a) To be described as a delayed-release dosage forms, the drug product need to demonstrate extended-release characteristics (delayed release (DR=enteric coated) is a different class not related to MR), (b) An extended-release dosage form is also known as a controlled-release dosage form (CR is a subclass of MR, so all CR is a type of MR but not every MR is CR), (c) An extended-release drug product indicates that the release of the medicinal agent is sustained beyond what is expected from an immediate-release product (maintains same plasma conc over an extended time)
13
New cards
An osmotic pump can be enteric-coated to further modify drug release. In this case, which of the following contributes to the overall release characteristics of the drug from the dosage form
\
a. Osmotic pressure of the push layer
b. The thickness of the semi-permeable membrane of the pump
c. The time it takes for the enteric coat to dissolve
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. Osmotic pressure of the push layer
b. The thickness of the semi-permeable membrane of the pump
c. The time it takes for the enteric coat to dissolve
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
d
14
New cards
Mucoadhesive drug delivery
\
a. Is a technology in which extended drug release is achieved
b. The drug layer can be in the form of a microcapsule, film, tablet, or disc
c. The release of the drug can be directed to towards the oral mucosa
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. Is a technology in which extended drug release is achieved
b. The drug layer can be in the form of a microcapsule, film, tablet, or disc
c. The release of the drug can be directed to towards the oral mucosa
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
d
\
(a) is a technology in which extended drug release is achieved (one of the types of MR systems), (b) the drug layer can be in the form of a microcapsule, film, tablet or disc (different forms), (c) the release of the drug can be directed to towards the oral mucosa (by coating using an impermeable membrane to force the release towards the buccal pouch)
\
(a) is a technology in which extended drug release is achieved (one of the types of MR systems), (b) the drug layer can be in the form of a microcapsule, film, tablet or disc (different forms), (c) the release of the drug can be directed to towards the oral mucosa (by coating using an impermeable membrane to force the release towards the buccal pouch)
15
New cards
The release of a lipophilic drug in the rectum
\
a. Is fast from a cocoa butter suppository base since cocoa butter melts rapidly
b. Can be enhanced if the drug is incorporated into a hydrophilic suppository base
c. Is independent of the nature of suppository base used
d. Will continue to increase upon increasing the initial drug load in the suppository
e. None of the above
\
a. Is fast from a cocoa butter suppository base since cocoa butter melts rapidly
b. Can be enhanced if the drug is incorporated into a hydrophilic suppository base
c. Is independent of the nature of suppository base used
d. Will continue to increase upon increasing the initial drug load in the suppository
e. None of the above
b
\
(a) is fast from a cocoa butter suppository base since cocoa butter melts rapidly (not fast because release of a lipophilic drug from lipophilic base is not efficient), (b) can be enhanced if the drug is incorporated into a hydrophilic suppository base (true because release of lipophilic drug from hydrophilic base is efficient), (c) is independent of the nature of suppository base used (false), (d) will continue to increase upon increasing the initial drug load in the suppository (false because the surface area for absorption and aqueous medium is limited)
\
(a) is fast from a cocoa butter suppository base since cocoa butter melts rapidly (not fast because release of a lipophilic drug from lipophilic base is not efficient), (b) can be enhanced if the drug is incorporated into a hydrophilic suppository base (true because release of lipophilic drug from hydrophilic base is efficient), (c) is independent of the nature of suppository base used (false), (d) will continue to increase upon increasing the initial drug load in the suppository (false because the surface area for absorption and aqueous medium is limited)
16
New cards
Which of the following is the reason why cocoa butter is the ideal suppository base
\
a. It is a faint, chocolate like odor
b. It is completely miscible with water
c. Is independent of the nature of suppository base used
d. Will continue to increase upon increasing the initial drug load in the suppository
e. None of the above
\
a. It is a faint, chocolate like odor
b. It is completely miscible with water
c. Is independent of the nature of suppository base used
d. Will continue to increase upon increasing the initial drug load in the suppository
e. None of the above
d
\
(a) It has a faint, chocolate like odor (doesn’t make it ideal), (b) It is completely miscible with water (it is lipophilic), (c) If polymorphism is exhibited, it is reversible since the unstable polymorph will eventually convert back to the most stable form (polymorphism id not reversible), (d) It melts at 30 – 36°C; just below body temperature (this allows release of drug), (e) It can be efficiently used to incorporate both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs (false because it is hard to incorporate a hydrophilic drug in a lipophilic base)
\
(a) It has a faint, chocolate like odor (doesn’t make it ideal), (b) It is completely miscible with water (it is lipophilic), (c) If polymorphism is exhibited, it is reversible since the unstable polymorph will eventually convert back to the most stable form (polymorphism id not reversible), (d) It melts at 30 – 36°C; just below body temperature (this allows release of drug), (e) It can be efficiently used to incorporate both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs (false because it is hard to incorporate a hydrophilic drug in a lipophilic base)
17
New cards
PEG-based suppositories are typically stored at
\
a. 4℃
b. 2-8℃
c. 10-15℃
d. Controlled room temperature
e. Usual room temperature
\
a. 4℃
b. 2-8℃
c. 10-15℃
d. Controlled room temperature
e. Usual room temperature
e
18
New cards
Advantages of transdermal drug delivery include all of the following, EXCEPT
\
a. Avoidance of oral absorption related issues
b. Allows for moderately high drug concentrations to be maintained in the body
c. It is non-invasive route of drug administration
d. Permits self-administration of the medicinal agent
e. Drug therapy can be easily terminated by removal of the delivery system
\
a. Avoidance of oral absorption related issues
b. Allows for moderately high drug concentrations to be maintained in the body
c. It is non-invasive route of drug administration
d. Permits self-administration of the medicinal agent
e. Drug therapy can be easily terminated by removal of the delivery system
b
\
(a) Avoidance of oral absorption related issues, (b) Allows for moderately high drug concentrations to be maintained in the body (it doesn’t maintain drug conc), (c) It is a non-invasive route of drug administration (true), (d) Permits self-administration of the medicinal agent (true) (e) Drug therapy can be easily terminated by removal of delivery system (true)
\
(a) Avoidance of oral absorption related issues, (b) Allows for moderately high drug concentrations to be maintained in the body (it doesn’t maintain drug conc), (c) It is a non-invasive route of drug administration (true), (d) Permits self-administration of the medicinal agent (true) (e) Drug therapy can be easily terminated by removal of delivery system (true)
19
New cards
Which of the following molecules has the best chance to permeate through the intercellular route of the skin
\
a. A molecule with molecular weight of 900 g/mole and log Km of 0.5
b. A molecule with molecular weight of 450 g/mole and log Km of 0.5
c. A molecule with molecular weight of 900 g/mole and log Km of 2.9
d. A molecule with molecular weight of 450 g/mole and log Km of 2.9
e. All of the above molecules will demonstrate comparable ability of permeating through the intracellular route of the skin
\
a. A molecule with molecular weight of 900 g/mole and log Km of 0.5
b. A molecule with molecular weight of 450 g/mole and log Km of 0.5
c. A molecule with molecular weight of 900 g/mole and log Km of 2.9
d. A molecule with molecular weight of 450 g/mole and log Km of 2.9
e. All of the above molecules will demonstrate comparable ability of permeating through the intracellular route of the skin
d
\
A molecule with molecular weight of 450 g/mole and log Km of 2.9, because its molecular weight is less than 500 and highest Km which indicates better portioning and permeation into skin
\
A molecule with molecular weight of 450 g/mole and log Km of 2.9, because its molecular weight is less than 500 and highest Km which indicates better portioning and permeation into skin
20
New cards
The stratum corneum layer of the skin is characterized by which of the following
\
a. It represents the rate-limiting step in the transdermal permeation process
b. Under normal conditions, it has a pH of 4.5-6
c. Due to the presence of the liquid domain as well as the moisture content, the stratum corneum is amphiphilic in nature
d. a and b only
e. a and c only
\
a. It represents the rate-limiting step in the transdermal permeation process
b. Under normal conditions, it has a pH of 4.5-6
c. Due to the presence of the liquid domain as well as the moisture content, the stratum corneum is amphiphilic in nature
d. a and b only
e. a and c only
d
\
(a) It represents the rate limiting step in the transdermal permeation process and (b) Under normal conditions, it has a pH of 4.5 – 6 (are true) but (c) Due to the presence of the lipid domain as well as the moisture content, the stratum corneum is amphiphilic in nature (lipophilic not amphiphilic)
\
(a) It represents the rate limiting step in the transdermal permeation process and (b) Under normal conditions, it has a pH of 4.5 – 6 (are true) but (c) Due to the presence of the lipid domain as well as the moisture content, the stratum corneum is amphiphilic in nature (lipophilic not amphiphilic)
21
New cards
Which of the following application sites in the human body has the highest rate of percutaneous drug absorption
\
a. Scalp
b. Forearm (ventral side)
c. Back
d. Ankle
e. Forearm (dorsal side)
\
a. Scalp
b. Forearm (ventral side)
c. Back
d. Ankle
e. Forearm (dorsal side)
\
\
a
\
Scalp (3.5) > Back (1.7) > Forearm (ventral side) (1.1) > Forearm (dorsal side) (1) > Ankle (0.42)a
\
a
\
Scalp (3.5) > Back (1.7) > Forearm (ventral side) (1.1) > Forearm (dorsal side) (1) > Ankle (0.42)a
22
New cards
Chemically, penetration enhancement can be achieved by
\
a. Modification of the diffusion coefficient of the permeating drug
b. Modification of the partition coefficient of the permeating drug
c. Altering the degree of keratin swelling
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. Modification of the diffusion coefficient of the permeating drug
b. Modification of the partition coefficient of the permeating drug
c. Altering the degree of keratin swelling
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
d
\
Chemical enhancers can improve skin penetration through Km modification, - D enhancement, - SC perturbations: - Keratin swelling
\
Chemical enhancers can improve skin penetration through Km modification, - D enhancement, - SC perturbations: - Keratin swelling
23
New cards
All of the following statements regarding iontophoresis are correct, EXCEPT
\
a. It involves the delivery of charged molecules across the skin by applying an electrical current
b. Drug reservoir is placed on the skin under the active electrode
c. Due to the application of the electrical current, iontophoresis is considered an invasive technique
d. Transdermal permeation rate can be controlled by controlling the applied current
e. This technique can be effectively employed to enhance transdermal permeation of amino acids
\
a. It involves the delivery of charged molecules across the skin by applying an electrical current
b. Drug reservoir is placed on the skin under the active electrode
c. Due to the application of the electrical current, iontophoresis is considered an invasive technique
d. Transdermal permeation rate can be controlled by controlling the applied current
e. This technique can be effectively employed to enhance transdermal permeation of amino acids
c
24
New cards
Below is the formula for rose water ointment, USP. Based on its composition, what category of ointment bases does Rose water ointment, USP belong to
_________________________________________
Cetyl Esters Wax 125 g
White Wax 120 g
Almond Oil 560 g
Sodium Borate 5 g
Stronger Rose Water 25 mL
Purified Water 165 mL
Rose Oil 200 uL
__________________________________________
\
a. Oleaginous
b. Anhydrous absorption base
c. W/O emulsion type
d. O/W emulsion type
e. Water-soluble
_________________________________________
Cetyl Esters Wax 125 g
White Wax 120 g
Almond Oil 560 g
Sodium Borate 5 g
Stronger Rose Water 25 mL
Purified Water 165 mL
Rose Oil 200 uL
__________________________________________
\
a. Oleaginous
b. Anhydrous absorption base
c. W/O emulsion type
d. O/W emulsion type
e. Water-soluble
c
\
Water content is 190 mL which represents \~ 20 % content → W/O emulsion
\
Water content is 190 mL which represents \~ 20 % content → W/O emulsion
25
New cards
As a compounding pharmacist, you have been consulted on the appropriate selection of a medicated ointment base. If a rapid release rate of the drug is desirable, and the patient expressed discomfort towards the greasy-feeling of some topical application, then the best ointment base to choose in this case would be
\
a. Oleaginous
b. Anhydrous absorption base
c. W/O emulsion type
d. O/W emulsion type
e. Water-soluble
\
a. Oleaginous
b. Anhydrous absorption base
c. W/O emulsion type
d. O/W emulsion type
e. Water-soluble
e
26
New cards
Most gels, as medicated topical preparations
\
a. Are single-phase
b. Contain the gelling agent at a concentration of 0.5-2%
c. Contain a large proportion of the solid drug (25%)
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. Are single-phase
b. Contain the gelling agent at a concentration of 0.5-2%
c. Contain a large proportion of the solid drug (25%)
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
e
27
New cards
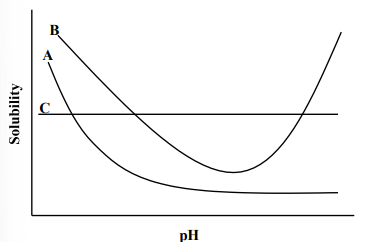
If the following figure represents the relationship between the solubility and pH for three new chemical entities (NCEs); A, B and C in an aqueous solution, which of the following statements is/are correct
\
a. “A” represents a typical weakly basic drug
b. “B” represents a typical weakly acidic drug
c. “C” most likely represents a neutral drug molecule
d. a and b only
e. a and c only
\
a. “A” represents a typical weakly basic drug
b. “B” represents a typical weakly acidic drug
c. “C” most likely represents a neutral drug molecule
d. a and b only
e. a and c only
e
28
New cards
The correct order of the following relative terms of solubility is
\
a. Freely soluble > soluble > slightly soluble > sparingly soluble
b. Very soluble > soluble > freely soluble > slightly soluble
c. Sparingly soluble > slightly soluble > very slightly soluble > practically insoluble
d. Very soluble > soluble > slight soluble > sparingly soluble
e. Very soluble > freely soluble > very slightly soluble > sparingly soluble
\
a. Freely soluble > soluble > slightly soluble > sparingly soluble
b. Very soluble > soluble > freely soluble > slightly soluble
c. Sparingly soluble > slightly soluble > very slightly soluble > practically insoluble
d. Very soluble > soluble > slight soluble > sparingly soluble
e. Very soluble > freely soluble > very slightly soluble > sparingly soluble
c
29
New cards
In preparing an oral solution for a solid drug, all of the following can be applied successfully to improve the dissolution rate EXCEPT
\
a. Heating up the preparation if heat is expected to evolve upon dissolution
b. Trituration of the solid drug particles
c. Use of a vortex mixer that allows for vigorous shaking
d. Heating the preparation if the drug solubilization is an endothermic process
e. Cooling down the preparation if the drug solubilizing is an exothermic process
\
a. Heating up the preparation if heat is expected to evolve upon dissolution
b. Trituration of the solid drug particles
c. Use of a vortex mixer that allows for vigorous shaking
d. Heating the preparation if the drug solubilization is an endothermic process
e. Cooling down the preparation if the drug solubilizing is an exothermic process
a
\
Heating up the preparation if heat is expected to evolve upon dissolution, this means it is an exothermic reaction (similar to Ca (OH)2) heating results in slowing rate of dissolution
\
Heating up the preparation if heat is expected to evolve upon dissolution, this means it is an exothermic reaction (similar to Ca (OH)2) heating results in slowing rate of dissolution
30
New cards
Syrups, as a pharmaceutical dosage form, are characterized by the following
\
a. If sucrose-based, the risk of crystallization of the sugar component is obsolete due to the highly solubility of sucrose in water
b. Contrary to powders, they have the advantage of easy administration to infants/children
c. Due to their high sugar content, they are quite resistant to microbial growth
d. a and c only
e. b and c only
\
a. If sucrose-based, the risk of crystallization of the sugar component is obsolete due to the highly solubility of sucrose in water
b. Contrary to powders, they have the advantage of easy administration to infants/children
c. Due to their high sugar content, they are quite resistant to microbial growth
d. a and c only
e. b and c only
c
\
(a) If sucrose-based, the risk of crystallization of the sugar component is obsolete due to the high solubility of sucrose in water (not true) , (b) Contrary to powders, they have the advantage of easy administration to infants/children (not true, they are not easy to administer to infants, (c) Due to their high sugar content, they are quite resistant to microbial growth (correct 60 – 85% prevents microbial growth
\
(a) If sucrose-based, the risk of crystallization of the sugar component is obsolete due to the high solubility of sucrose in water (not true) , (b) Contrary to powders, they have the advantage of easy administration to infants/children (not true, they are not easy to administer to infants, (c) Due to their high sugar content, they are quite resistant to microbial growth (correct 60 – 85% prevents microbial growth
31
New cards
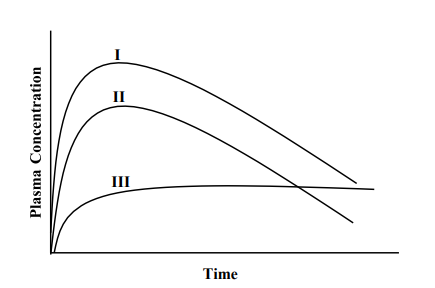
If the figure below represents the plasma concentration vs. time profile for a given drug, which of the following statements is/are correct
\
a. I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution and an oral suspension of the drug, respectively, given at the same dose
b. III represents the profile for a controlled-release oral tablet of the drug
c. I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution of the drug given at doses of 8 mg and 6 mg, respectively (assuming the drug follows linear pharmacokinetics within this dosage range)
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution and an oral suspension of the drug, respectively, given at the same dose
b. III represents the profile for a controlled-release oral tablet of the drug
c. I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution of the drug given at doses of 8 mg and 6 mg, respectively (assuming the drug follows linear pharmacokinetics within this dosage range)
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
d
\
(a) I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution and an oral suspension of the drug, respectively, given at the same dose (because the amount of drug reaching blood from an oral solution is much higher than from suspension), (b) III represents the profile for a controlled-release oral tablet of the drug (follows typical profile for CR). (c) I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution of the drug given at doses of 8 mg and 6 mg, respectively (because the amount of drug reaching blood from an oral solution 8 mg is higher than from that containing 6 mg)
\
(a) I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution and an oral suspension of the drug, respectively, given at the same dose (because the amount of drug reaching blood from an oral solution is much higher than from suspension), (b) III represents the profile for a controlled-release oral tablet of the drug (follows typical profile for CR). (c) I and II may represent the PK profiles for an oral solution of the drug given at doses of 8 mg and 6 mg, respectively (because the amount of drug reaching blood from an oral solution 8 mg is higher than from that containing 6 mg)
32
New cards
Elixirs possess a better ability than syrups to solubilize lipophilic drug substances. This is due to their
\
a. Lower viscosity
b. Lower sugar content
c. Hydroalcoholic nature
d. Higher resistance to microbial growth
e. None of the above
\
a. Lower viscosity
b. Lower sugar content
c. Hydroalcoholic nature
d. Higher resistance to microbial growth
e. None of the above
c
\
Hydroalcoholic nature allows dissolving lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs
\
Hydroalcoholic nature allows dissolving lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs
33
New cards
All of the following are advantages of using aerosols as pharmaceutical preparations, EXCEPT
\
a. They are considered clean applications since little or no wash-up is required upon dose administration
b. Drug product can be efficiently protected, if it is moisture-sensitive
c. Their application results in minimal irritation to the applied area of the body
d. They are considered a more economic option compared to conventional therapies
e. A metered dose can be administered each time the product is used
\
a. They are considered clean applications since little or no wash-up is required upon dose administration
b. Drug product can be efficiently protected, if it is moisture-sensitive
c. Their application results in minimal irritation to the applied area of the body
d. They are considered a more economic option compared to conventional therapies
e. A metered dose can be administered each time the product is used
d
34
New cards
Which of the following could be a reason to prepare a three-phase aerosol system, instead of the more common two-phase system
\
a. Drug is sensitive to atmospheric oxygen
b. Drug is susceptible to hydrolysis in the aqueous phase
c. Drug does not have sufficient lipid solubility in the liquid propellant phase
d. When a combination of two drugs is desired
e. None of the above
\
a. Drug is sensitive to atmospheric oxygen
b. Drug is susceptible to hydrolysis in the aqueous phase
c. Drug does not have sufficient lipid solubility in the liquid propellant phase
d. When a combination of two drugs is desired
e. None of the above
c
35
New cards
Aqueous aerosol systems cannot be prepared by cold filling because
\
a. These systems will freeze at the low temperatures applied in this method
b. This method is costly and labor intensive
c. This method is only suitable for large-container aerosol preparations
d. Air trapped in container could not be displaced
e. None of the above
\
a. These systems will freeze at the low temperatures applied in this method
b. This method is costly and labor intensive
c. This method is only suitable for large-container aerosol preparations
d. Air trapped in container could not be displaced
e. None of the above
a
36
New cards
Drug solubility is a crucial factor in determining the overall intestinal absorption of medicinal agents. Based on that, which of the following statements is/are correct
\
a. The higher the aqueous solubility, the better is the intestinal absorption
b. The higher the liquid solubility, the better is the intestinal absorption
c. The higher the lipid solubility, the higher is the intestinal drug permeation
d. a and c only
e. b and c only
\
a. The higher the aqueous solubility, the better is the intestinal absorption
b. The higher the liquid solubility, the better is the intestinal absorption
c. The higher the lipid solubility, the higher is the intestinal drug permeation
d. a and c only
e. b and c only
c
\
The higher the lipid solubility, the higher is the intestinal drug permeation (not absorption, because lipophilicity improves the ability of drug to permeate through membranes but absorption profile for a drug in the intestinal tract is determined by the interplay of various processes such as motility, transit, solubility, dissolution, precipitation and stability)
\
The higher the lipid solubility, the higher is the intestinal drug permeation (not absorption, because lipophilicity improves the ability of drug to permeate through membranes but absorption profile for a drug in the intestinal tract is determined by the interplay of various processes such as motility, transit, solubility, dissolution, precipitation and stability)
37
New cards
Oral absorption of a drug from a solid dosage form depends on
\
a. The physiochemical properties of the drug
b. The physiology of the stomach
c. The type of drug formulation
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
\
a. The physiochemical properties of the drug
b. The physiology of the stomach
c. The type of drug formulation
d. All of the above
e. a and b only
d