types and symptoms of anxiety
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what is anxiety
complex combination of negative emotions and physical sensations
examples of negative emotions commonly occuring in anxiety
fear
apprehension
worry
examples of physical sensations commonly occuring in anxiety
palpitations
nausea
chest pain
shortness of breath
dizziness
insomnia
how does abnormal anxiety differ from normal anxiety
abnormal anxiety is persistent, excessive, and interferes with daily functioning, often without a clear or proportional threat
what are the main types of anxiety
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Panic Disorder
Phobias (specific & social)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD – historically classified as anxiety)
what is GAD
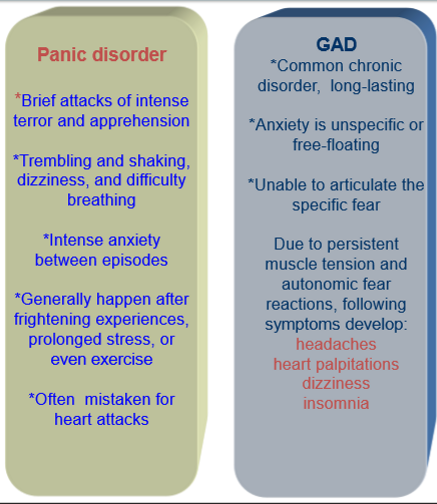
common, chronic, long-lasting disorder characterised by unspecific or free-floating anxiety
what does free floating anxiety mean in GAD
when the individual is unable to identify or articulate a specific cause for their anxiety
what causes physical symptoms in GAD
persistent muscle tension and autonomic fear reactions
name some symptoms of GAD
Headaches
Heart palpitations
Dizziness
Insomnia
what is a panic disorder
characterized by brief attacks of intense terror and apprehension
what symptoms occur during a panic attack
trembling and shaking
dizziness
difficulty breathing
how do individuals feel between panic attacks
they experience intense anxiety between episodes
what can trigger panic attacks
Frightening experiences
Prolonged stress
Physical exercise
why are panic attacks often mistaken for heart attacks
due to chest discomfort, palpitations, breathlessness, and dizziness which are similar symptoms of heart attacks too
what is OCD
characterised by obsessions or compulsions
what are obsessions
distressing, repetitive thoughts or images that a person recognises as senseless
what are compulsions
repetitive behaviour performed to reduce anxiety caused by obsessions
examples of compulsions
extreme cleanliness
constant checking and rechecking of doors
how is OCD classified in DSM-5
OCD is now classified under ‘Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders’, not anxiety disorders, although anxiety remains a core feature
what are the 4 main OCD categories
checking
contamination/mental contamination
hoarding
ruminations and intrusive thoughs
what is checking driven by (hint: fear of what?)
fear of damage, fire, leaks, unlocked doors, or harm
what is contamination driven by
Fear that contamination will cause illness or death to oneself or loved ones
what are ruminations in OCD
persistent intrusive obsessional thoughts, often misunderstood (e.g. body shape thoughts in eating disorders)
what is a phobia
strong, irrational fear and avoidance of specific object or situation
how do phobias differ from GAD and panic disorders
phobias are triggered by a specific stimulus, unlike the generalized or unpredictable anxiety seen in GAD or panic disorder
how do people with phobias perceive their fear
usually recognise the fear is excessive and unreasonable but cannot control it
what is a specific phobia
intense fear of something that poses little or no actual danger
examples of common specific phobias
height
enclosed spaces
blood
flying
dogs
water
what happens when someone with specific phobia faces feared object
may experience panic attack or severe anxiety, even thinking about it can trigger symptoms
what is social phobia known as
social anxiety disorder
what charactises social phobia
overwhelming anxiety and excessive self-consciousness in social situations
what is the main fear in social phobia
fear of being watched, judged, embarrassed or humiliated
how does social phobia affect daily life
can interfere with work, school and ordinary activities
how far in advanced do individuals with social phobia worry
days or weeks before a feared social situation
what does DSM stand for
diagnosis and statistical manual of mental disorders
what is DSM used for
classifies mental health disorders
how were anxiety disorders classified in DSM-II
grouped together as “anxiety neurosis”, without subdivisions
what change occured in DSM-III
formal distinction between GAD and other anxiety disorders
how does DSM-IV define GAD?
excessive anxiety and worry on most days for 6 months or more
how many symptoms are required for GAD diagnosis (DSM-IV)
at least 3 symptoms or 1 in children
what is a the prevalence of GAD
1-year prevalence: 3%
Lifetime prevalence: 5%
what role does family history play in anxiety disorders
family history increases likelihood of developing anxiety disorder
difference between panic disorders and GAD
name the common types of eating disorders
bulimia nervosa
anorexia nervosa
binge eating disorder
what is bulimia nervosa
binge eating and purging (self-inducing vomiting, over-exercising, usage of diuretics and laxatives)
what is anorexia nervosa
extreme food restriction to the point of starvation and excessive weight loss
what is binge eating disorder
without subsequent purging episodes