IGS 8a L16-18 (Exchange Rates)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IGS 8a Final Exam Study Deck
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
How do we buy things abroad?
Exchange our currency for the local currency via exchange rates
What is the exchange rate?
price at which we exchange one currency for another
exchange rate for home currency is its price in other currencies
Spot Rate
the price you must pay in order to get other currencies at that point in time
currency appreciation
when a currency becomes more valuable in terms of other currencies
currency depreciation
when a currency becomes less valuable in terms of other currencies.
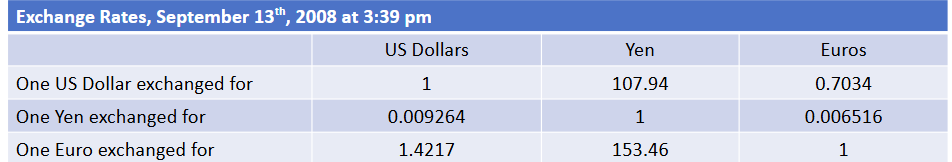
Movements in Exchange Rates EURO example
2008: .70 Euro per USD —> 2025: .93 Euro per USD
Euro depreciated. Used to by 1.42 USD now buys 1.07 USD
Impact of Exchange Rate Movements
When our currency appreciates, the price, in our home currency, of foreign goods, service, and assets goes down
when our currency depreciates, the price, in our home country, of foreign goods, services, and assets goes up
Forex market
Participants are transacting currencies
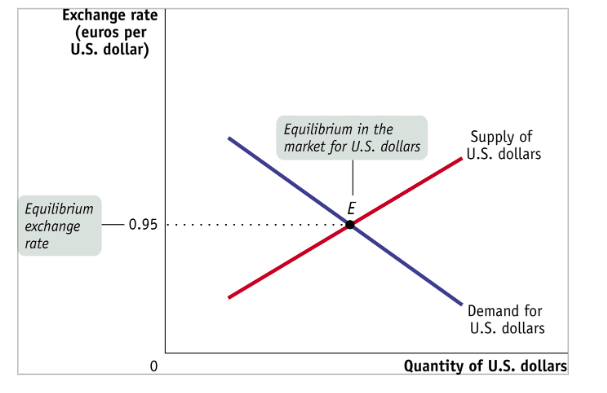
S and D of USD
D for USD comes from foreigners who want to by USD so they can buy US goods/services/assets
S for USD comes from US citizens who want to buy foreign goods/services/assets
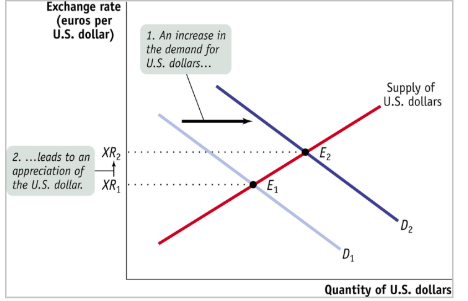
BofP and Supply and Demand for currency
BofP debits create supply in forex markets → push up exchange rate
BofP credits create demand in forex markets —> lowers exchange rate
BofP & ER: Sample
USD appreciated, Americans want more foreign goods (CA). foreigners want more assets (FA)
Effective Exchange rate
average of all the exchange rates that a country has with its trading partners
weights of different individual exchange rates given by trade shares
Real exchange rate
for USD vs Peso → Peso/$1 x Price US/Price Mexico
What shifts supply and demand for forex
Changes in relative income growth
price increases at home or abroad
changes in consumer preferences
changes in attractiveness of assets at home and abroad
changes in national confidence and outlook
3 Core Influences on ER
Prices
Monetary police and interest rates
Speculation
Prices (core influence on ER)
PPP hypothesis → nominal ER will adjust so that each currency has the same purchasing power everywhere
ER will offset change in prices
Real ER numerical meaning
If less than 1 → currency depreciation in real terms
if more than 1 → currency appreciation in real terms
real appreciation
your currency can buy more of another currency’s goods
akak how much stuff you can buy in another country
PPP decline
decline in Real ER for US means USD has depreciated in real terms
USD is now under-valued
PPP increase
increase in Real ER for Mexico means Peso has appreciated in real terms
Peso now over-valued
how to offset CA deficit
real appreciation of currency
Depreciation and CA deficit
Depreciation of a currency can lead to a worsening of the current account (CA) deficit, as it may increase the cost of imported goods, thereby affecting trade balances negatively.
J curve response in current account
A theory that illustrates how a country's current account balance initially worsens following a depreciation of its currency before improving over time as exports become more competitive.
monetary policy (core influence on ER)
Refers to actions by a central bank to control the money supply, interest rates, and inflation, which can significantly impact exchange rates (ER) and affect trade balances.
affects Financial Account
Speculation (core influences on ER)
Currencies are traded instantly and their value responds quickly to changes in sentiment/beliefs on how an economy will perform in the future
Exchange Rate regime
rule governing policy toward exchange rate
Fixed exchange rate
when government keeps exchange rate against some other currency at or near a particular target
floating or flexibly exchange rate
government lets exchange rate go wherever market takes it
exchange market intervention
government purchases or sales of its own currency in forex markets
benefit of fixing currency
stability and reduces currency risk
lowers transaction costs of trade
fixing currency and inflation expectations
must have lower inflation than other country to make sure their prices don’t go up faster than partner country
attempt to reduce inflation by fixing against USD
Fixed ER example
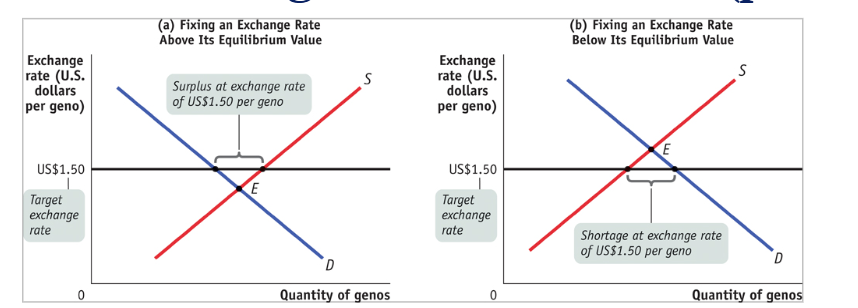
under-valued exchange rate (fixed)
government intervention by selling its own currency and acquiring USD to add stock to its foreign reserves
government can use monetary policy by lowering interest rate
government can impose foreign exchange controls to make it harder to buy their currency
over-valued exchange rate (fixed)
government can buy up surplus of currency
raise interest rates
limit citizens ability to exchange their currency for USD using foreign exchange controls
devaluation
reduction in value of currency that is set under a fixed exchange rate
revaluation
increase in value of currency that is set under a fixed exchange rate