IR Spectroscopy Signals
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
if you don't remember these by evening kill yourself
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
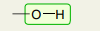
Single Bond: O-H
3200-3600 (broad)
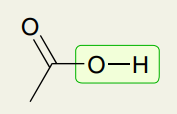
Single Bond: Carboxylic Acid O-H
2200-3600 (very broad)
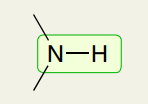
Single Bond: Amine
3350-3500
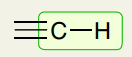
Single Bond: Triple Bond C-H (sp)
~3300
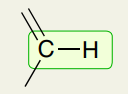
Single Bond: Double + Single Bond C-H (sp2)
3000-3100
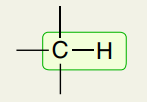
Single Bond: 3 Single Bonds C-H (sp3)
2850-3000
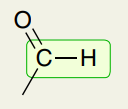
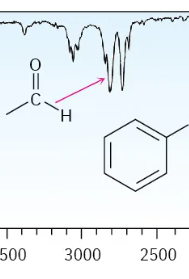
Single Bond: Double Bond to O, Single Bond C-H Aldehyde
2750 and 2850 (two weak signals)
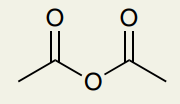
C=O Double Bond: Anhydride
~1820 and ~1760
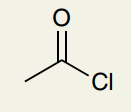
C=O Double Bond: Acyl Chloride
~1790
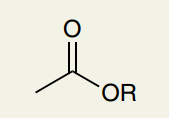
C=O Double Bond: Ester
~1735 (can’t differentiate from aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids)
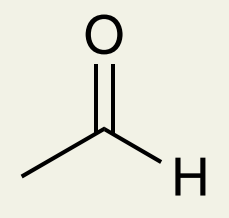
C=O Double Bond: Aldehyde
~1730 (can’t differentiate from esters, ketones, carboxylic acids)
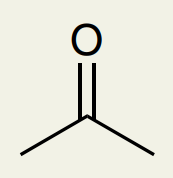
C=O Double Bond: Ketone
~1720 (can’t differentiate from esters, aldehydes, carboxylic acids)
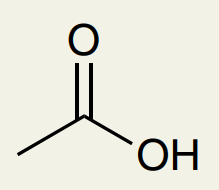
C=O Double Bond: Carboxylic Acid
~1715 (can’t differentiate from esters, aldehydes, ketones)
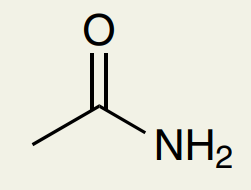
C=O Double Bond: Amide
~1650
If the C=O bond is conjugated, will the frequency (cm^-1) be lower or higher?
Lower, since the resonance structures give the compound more single-bond character
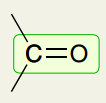
Double Bonds: C=O
~1650-1820 (strong)
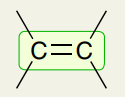
Double Bonds: C=C
1600-1700
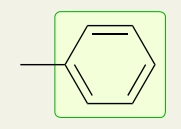
Double Bonds: Benzene/Aromatic Rings
1450-1600 (peaks for the C=C bonds) and 1650-2000 (overtones, combination bands)

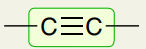
Triple Bonds: C≡C
2100-2200
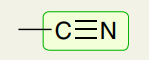
Triple Bonds: C≡N
2200-2300
Amines: Primary
3350 and 3450
Amines: Secondary
3350-3500
Double Bonds Region
1600-1850
Triple Bonds Region
2100-2300
Z-H Bonds Region
2700-4000