Exam 1: Human Anatomy
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
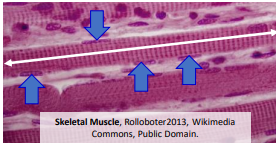
_muscle has long, unbranched, uninucleate cells with distinct actin-myosin lines and it voluntary
Skeletal
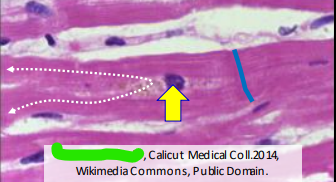
_ muscle has short, branched, uninucleate cells with distinct lines and is involuntary
Cardiac
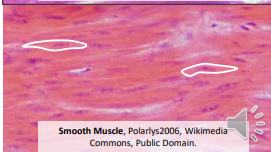
_muscle is short, unbranched, uninucleate cells without distinct lines and is involuntary
Smooth
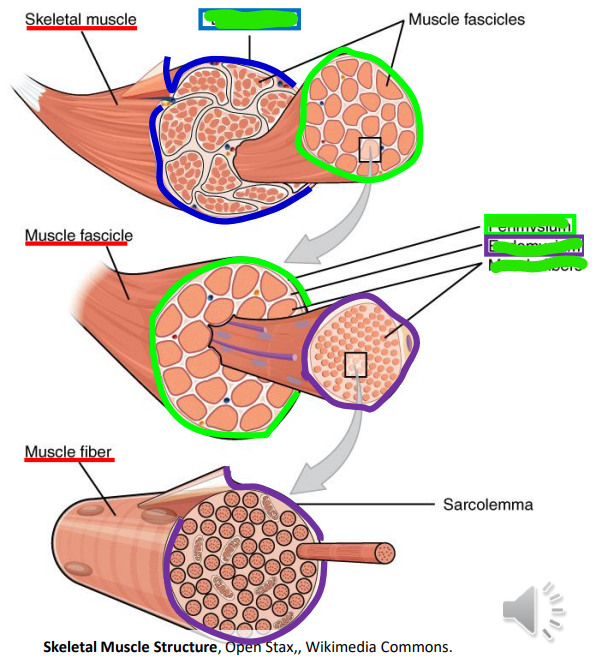
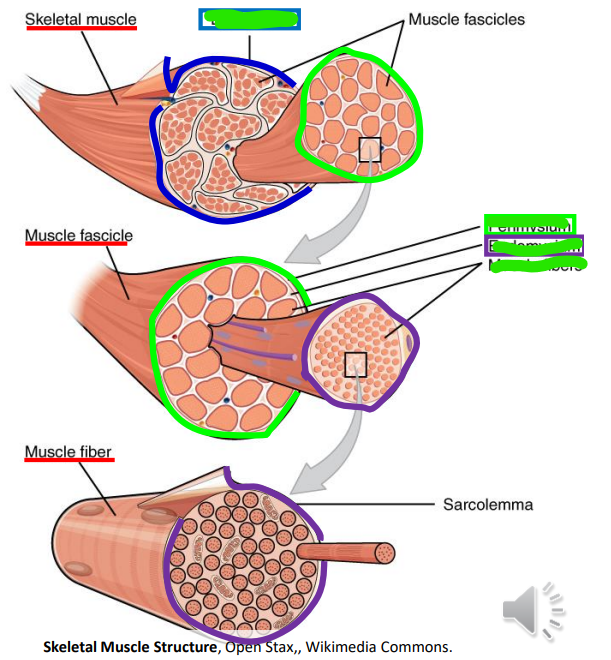
Muscle cells wrapped by _ into fibers, wrapped by _ into fascicles, wrapped by the _ into muscles
Endomysium; Perimysium; Epimysium
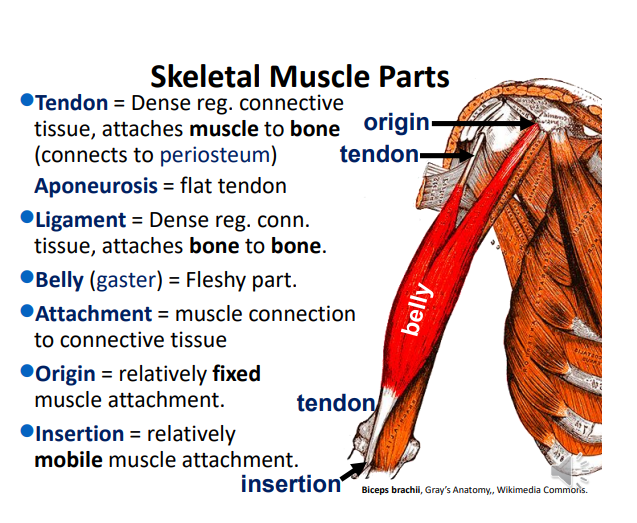
Tendons are _ _ connective tissue that attaches muscles to bone. It connects to the periosteum, which is around the bone.
Dense regular
If a tendon connects to the cartilage rather than the bone, then it connects to the _. (flat tendon)
Aponeurosis
Ligaments are made from _ _ connective tissue and attaches bone to _.
Dense regular; bone
Muscle that most causes a movement
Prime mover/agonist
Assists a prime mover
Synergist
Muscle reverses another movement
Antagonist
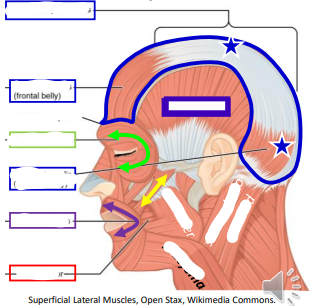
Label the facial muscles
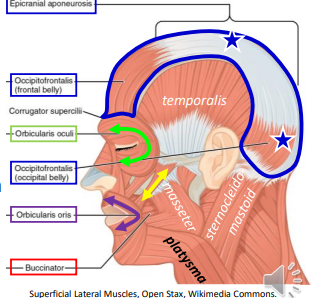
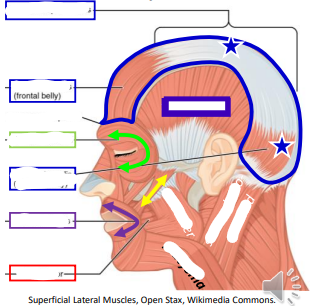
The Occipitofrontalis muscles originates on (4 places) and inserts on the _.
occipital, occipitalis belly, epicranial aponeurosis, frontalis belly; skin
What is the action of the Orbicularis Oculi?
Closes eye
What is the action of the Orbicularis Oris?
Purses the mouth
The Zygomaticus originates on the _, and inserts on the corner of the _.
Zygomatic; mouth
What is the action of the Zygomaticus?
Smile
The _ originates on multiple on the underside of the skull and inserts on the _.
Buccinator ;Orbicularis oris
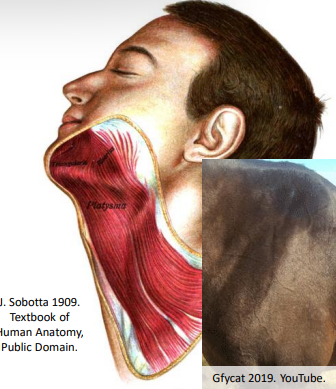
The _ is superficial and extends from the lower face down anterior neck to shoulders.
Platysma
The Platysma originates and inserts on the _.
Dermis (skin)
The Masseter muscle originates on the _ & _ (zygomatic arch) and inserts on the lateral _.
Zygomatic; Temporal; Mandible
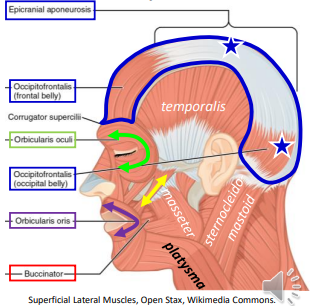
The Temporalis muscle originates on the _ (+frontal and parietal) under the zygomatic arch and inserts on the _ process of the mandible
Temporal; Coronoid
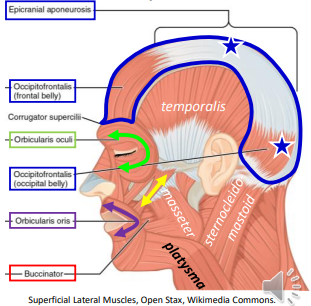
The lateral and medial Pterygoideus originates on the underside of the _, and inserts on the medial _.
Cranium; Mandible
What are the jaw closing muscles?
Masseter, Temporalis, Pterygoideus
What are the jaw opening muscles?
Hyoid stabilizes and Mandible depressor
What are the hyoid stabilizers? (4)
Omohyoid; Sternothyroid; Thyrohyoid; Sternohyoid
What are the Mandible Depressors (primary movers) (3)?
Mylohyoid; Anterior and Posterior Diagastric
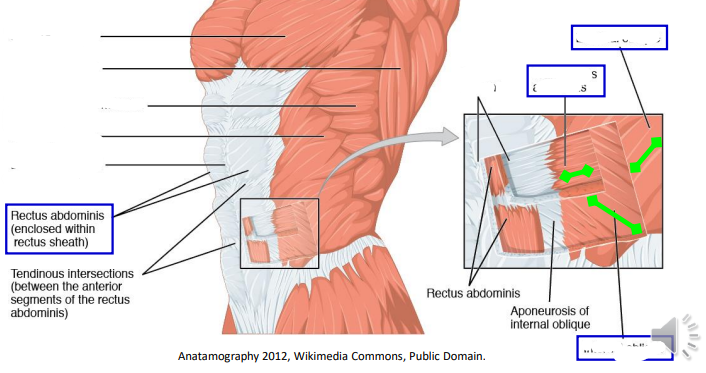
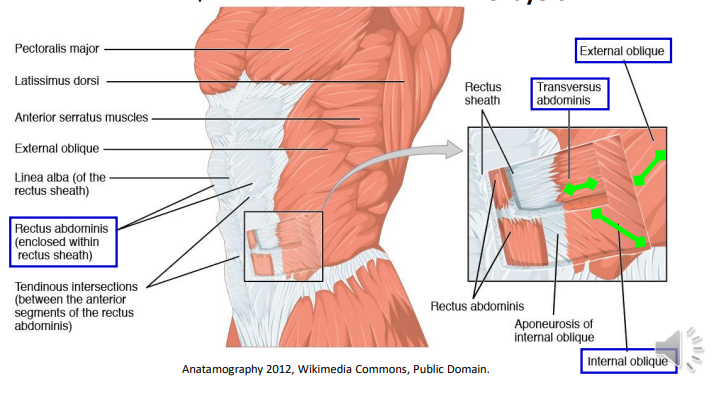
Label the abdominal muscles
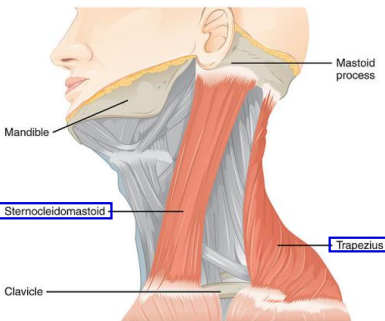
The _ bends the head forward and to the side
Sternocleidomastoid
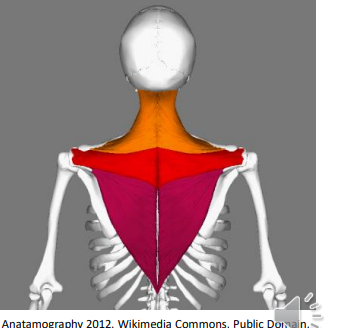
The _ upper portion pulls the head back; The middle and lower portions move the _.
Trapezius; Scapula
The _ , _ , & _ intercostals bewteen the ribs life and contract rib cage while breathing
External, Internal, Innermost
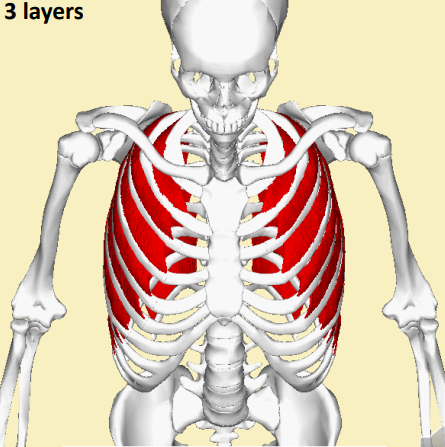
The intercostal muscles are overlain by muscles moving the _ & _(2 words)
Arms; Pectoral girdle
What muscles move the scapula(pectoral girdle muscles)? (4)
Rhomboideus minor & major; Levator scapulae; Trapezius; Serratus anterior
The Rhomboideus minor (superior) and major (inferior) originator on the _ processes of the vertebrae and insert on the _ scapula; They’re deep
Spinous; Medial
The _ _ originiates on the cranium and inserts the the superior scapula
Levator scapulae
The trapezius originates on the _ process of the vertebrae and inserts on the _&_ scapula; Superficial
Spinous; Dorsal;Medial
The serratus anterior originates on the _ ribs and inserts in the inferior lateral scapula. It moves the scapula _.
Anteriolateral; Laterally
The latissimus dorsi originates in the _ process of the vertebrae and inserts on the inferior had of the _
Spinous; Humerus
The skeletal system provides the _ for the human body and composes about 14% of your weight.
framework
The tissues that primarily compose the skeletal system are bone, cartilage, dense regular connective tissue, and Dense _ Connective Tissue (periosteum)
Irregular
The skeletal system provides support, facilitation of movement, and _.
protection
Bone matrix calcium and phosphorus are used to maintain _ levels.
blood
Red bone marrow cells are responsible for _.
blood cell production (hematopoiesis)
Yellow bone marrow cells store and release _ for energy.
fat
Compact bone is _, hard bone with osteons around blood vessels.
dense
Spongy (cancellous) bone consists of bone _ (trabeculae).
struts
_ form bone, osteocytes maintain bone, and osteoclasts dissolve bone.
osteoblasts
Bone is well _ and innervated.
vascularized
The _ is the long shaft of a long bone.
diaphysis
The _ are the bone ends, often with articular cartilages.
epiphysis
The _ is located between the epiphysis and diaphysis.
metaphysis
Projections on bones include bumps, processes, protuberances, tubercles, and _ (rounded, articulates).
condyles
A rough bump on a bone is called a _.
tuberosity
A hole in a bone is called a _.
foramen
Bone types include long, flat, irregular, short, and _.
sesamoid
_ is the formation of bone.
ossification
In endochondral ossification, bone replaces _ (hyaline).
cartilage
In intramembranous ossification, bone replaces collagen-rich _.
connective tissue
A fracture is a _ bone.
broken
In a _ fracture, the skin is intact.
closed
In an open/_ fracture, the broken end projects from the skin.
compound
The _ is the largest human organ
Skin
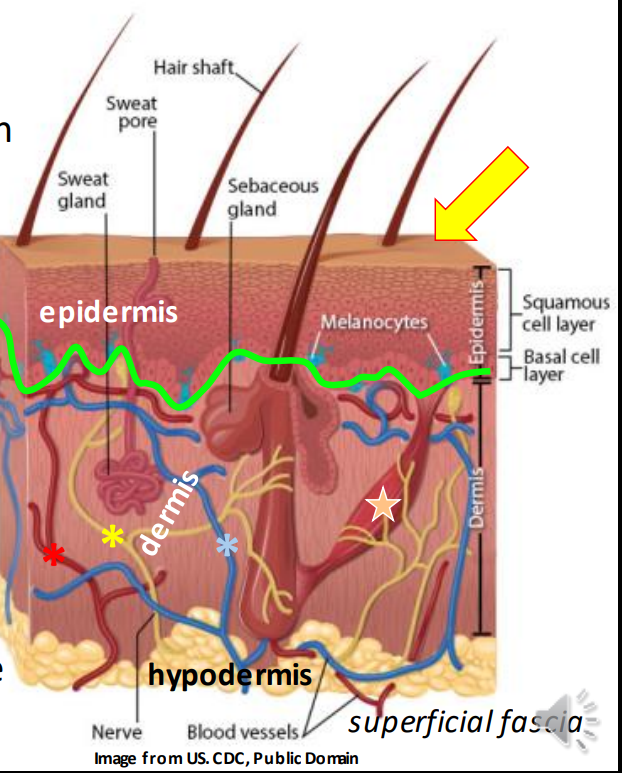
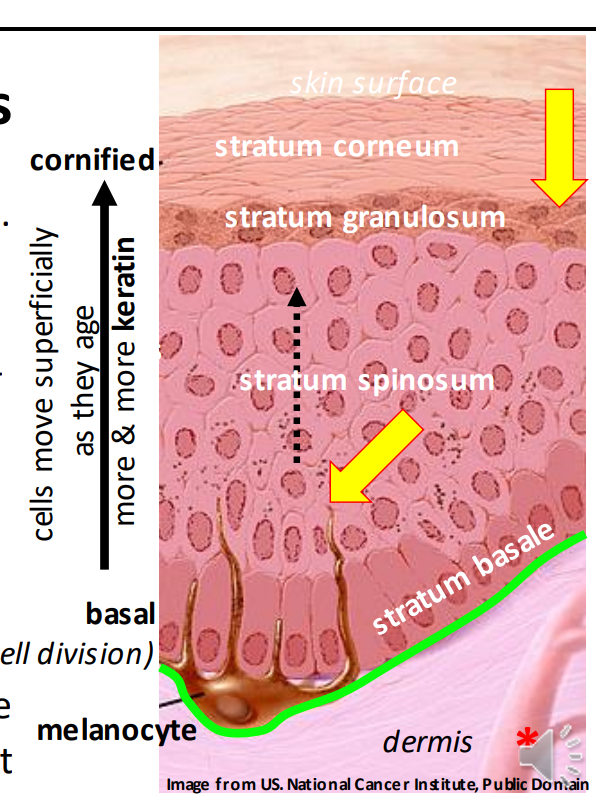
The epidermis is the _ layer of the skin and is made up of _ _ epithelium
Stratified squamous
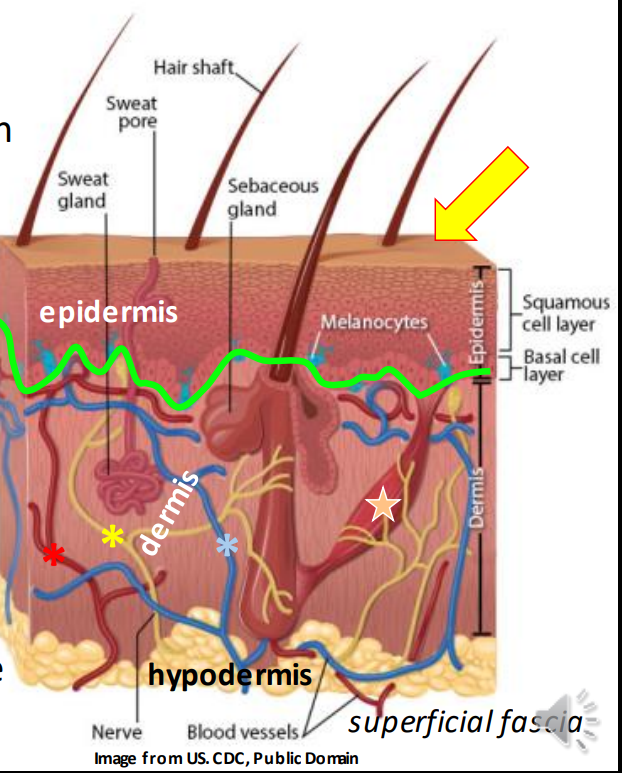
The epidermis is full of dead surface cells filled with _ protein>
Keratin
The dermis is made up of _ and _ irregular connective tissue
Loose, Dense
The hypodermis is made up of _ _ connective tissue
loose irregular
_ gives the surface of the skin its durability.
Keratin
Most fat is stored in the _.
Hypodermis
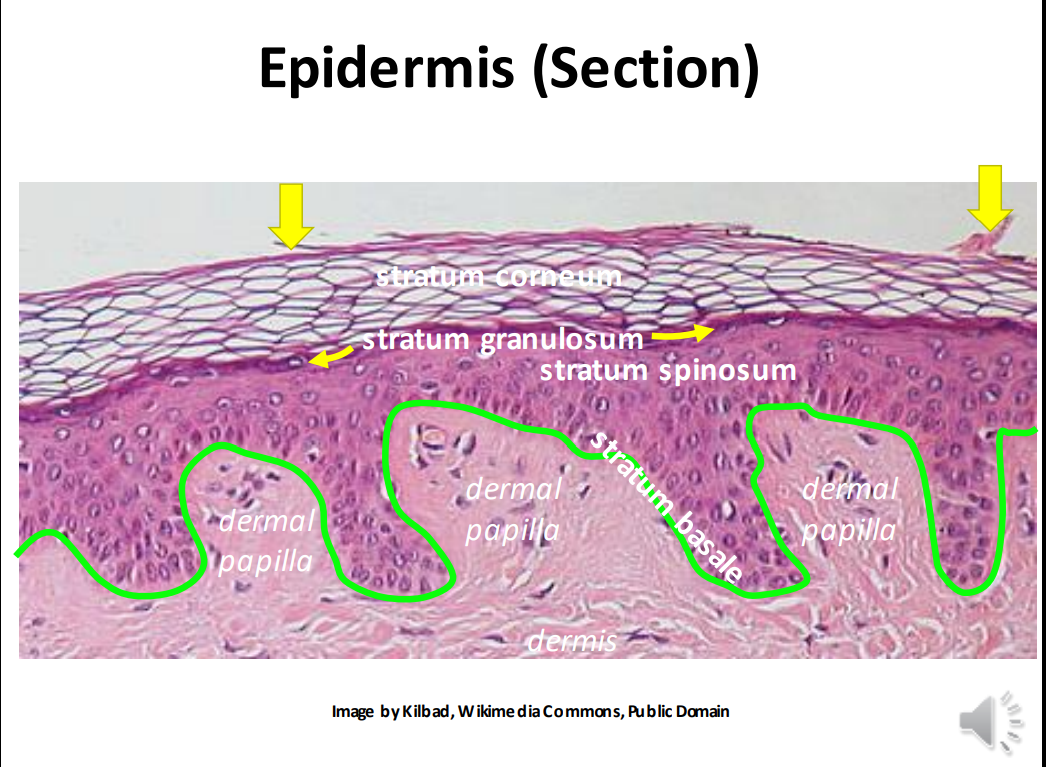
The layers of the epidermis from deep to superficial are:
Stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum
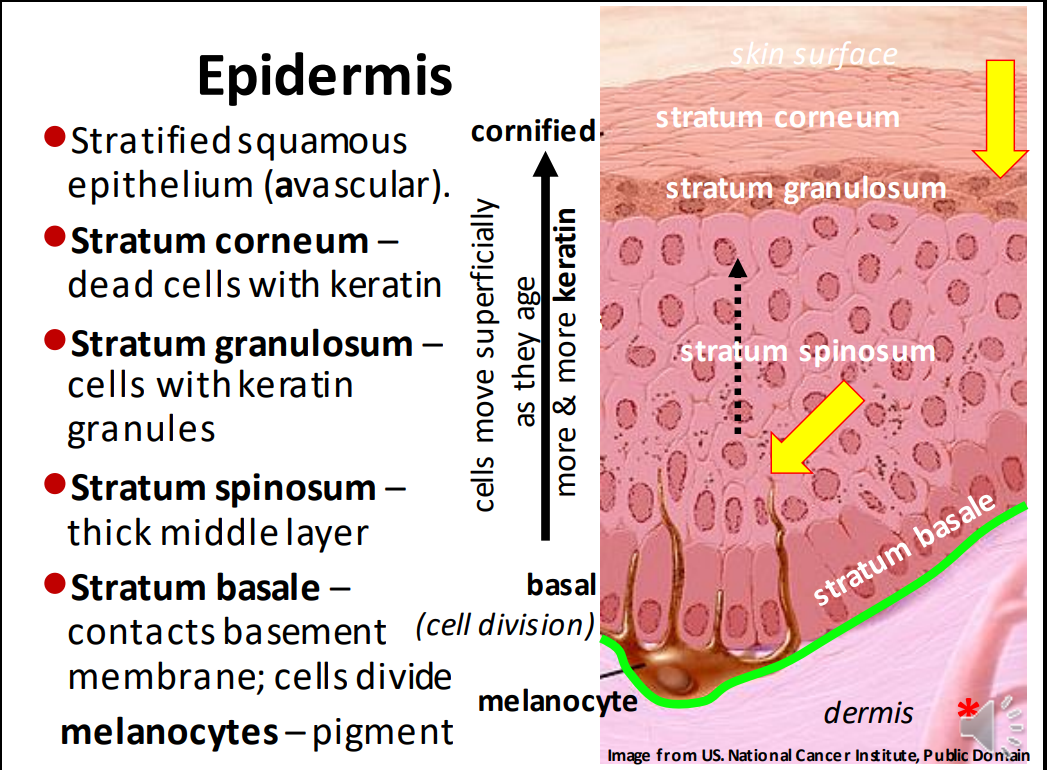
Is the epidermis vascular or avascular?
Avascular
The stratum basale contains the _ membrane and is the place where _ _ happens.
Basement, cell division
Melanocytes are produced in the stratum _.
Basale.
The stratum _ is the thick middle layer where cells mature.
Spinosum
As cells get older, they move more _
Superficially
The stratum _ starts making a ton of _ and gets ready to die
Granulosum, keratin
As cells age, they acquire more and more _ (cornified)
Keratin
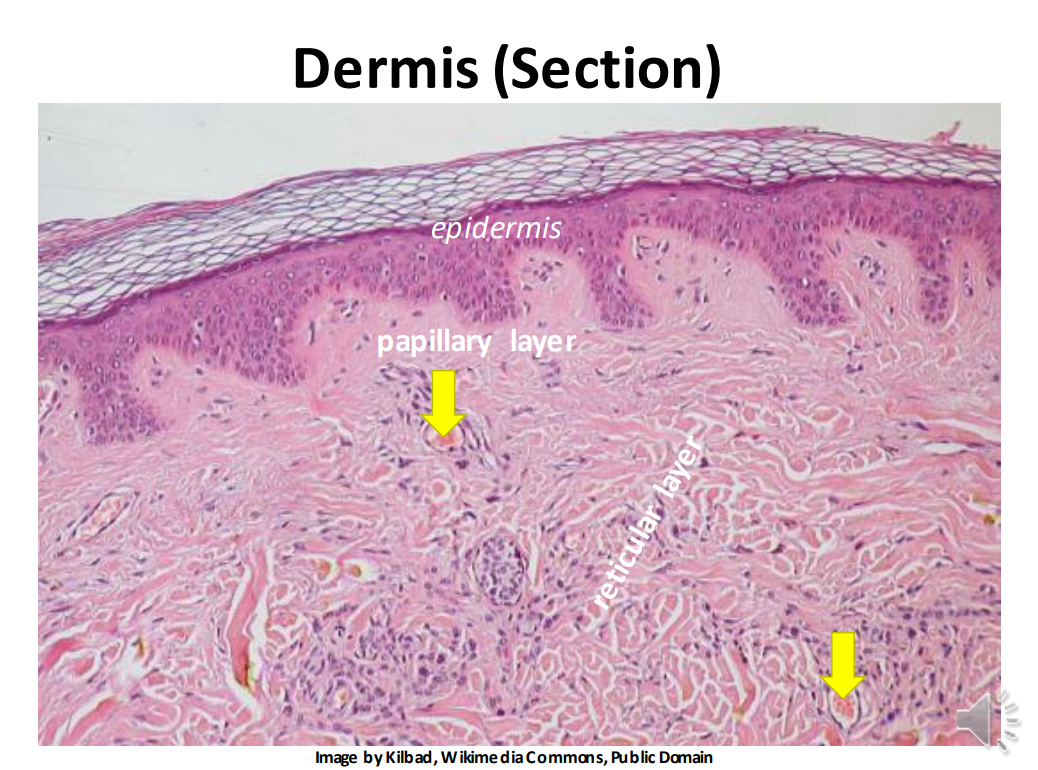
The dermis is made up of _ & _ connective tissue (vascular)
Loose, dense
The _ layer (stratum laxum) of the dermis is superficial and forms papillae
papillary
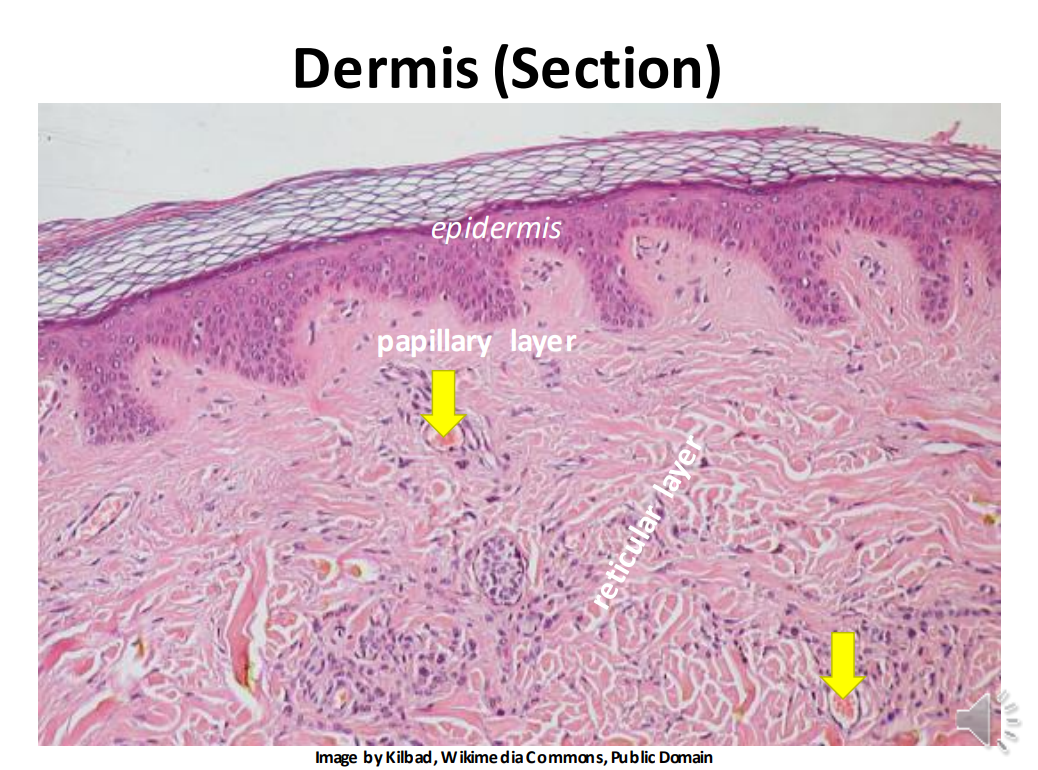
The _ layer of the dermis (stratum compactum) is deep and dense
Reticular
_ is a pigment cell that contains melanin (brown-black protein) in _.
Melanocyte; melanosomes
_ is a pigment in the dermis and hypodermis. It gives a light component to skin complextion
Carotene
Blushing occurs when blood vessels…
Expand and increase blood flow
Stratum _ cells are particularly active to produce the hair
basale
The epidermis dips into the dermis and forms _ and _ glands associated with hair follicles
Sweat; sebaceous
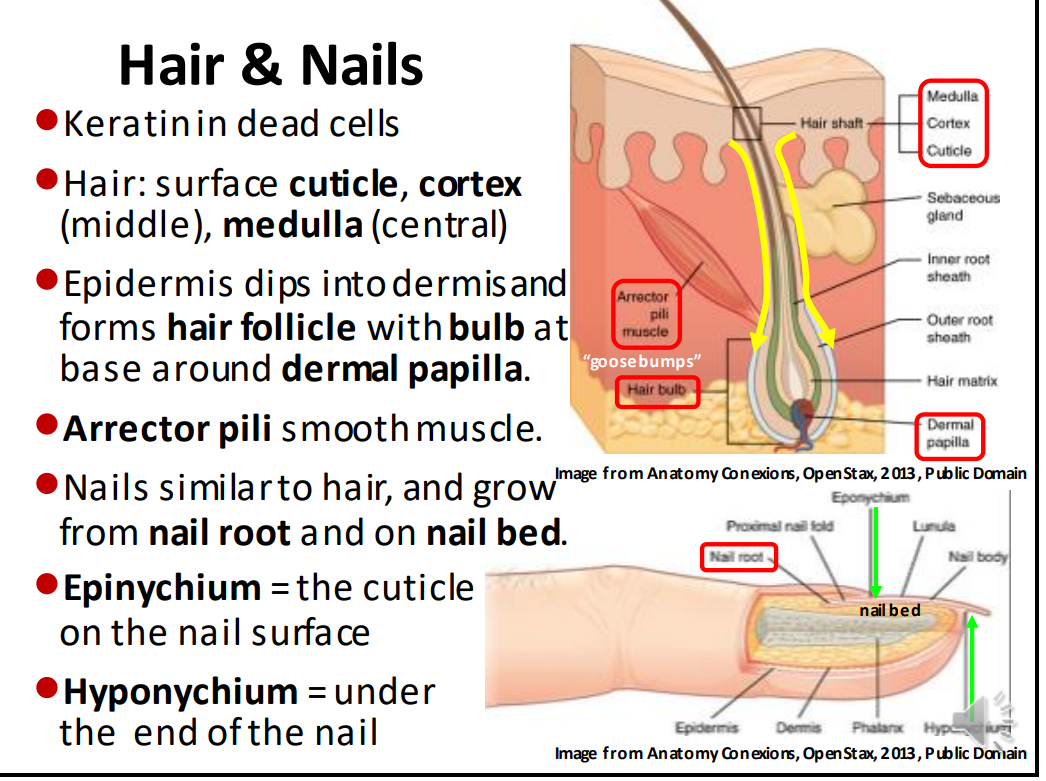
The hair and nails are composed of dead _ cells
Keratin
The layers of the hair from deep to superficial are:
Medulla, cortex, cuticle
The epidermis dips into the dermis and forms hair follicles with a bulb at the base around the _ _
Dermal papilla
The _ is the cuticle on the nail surface
epinychium
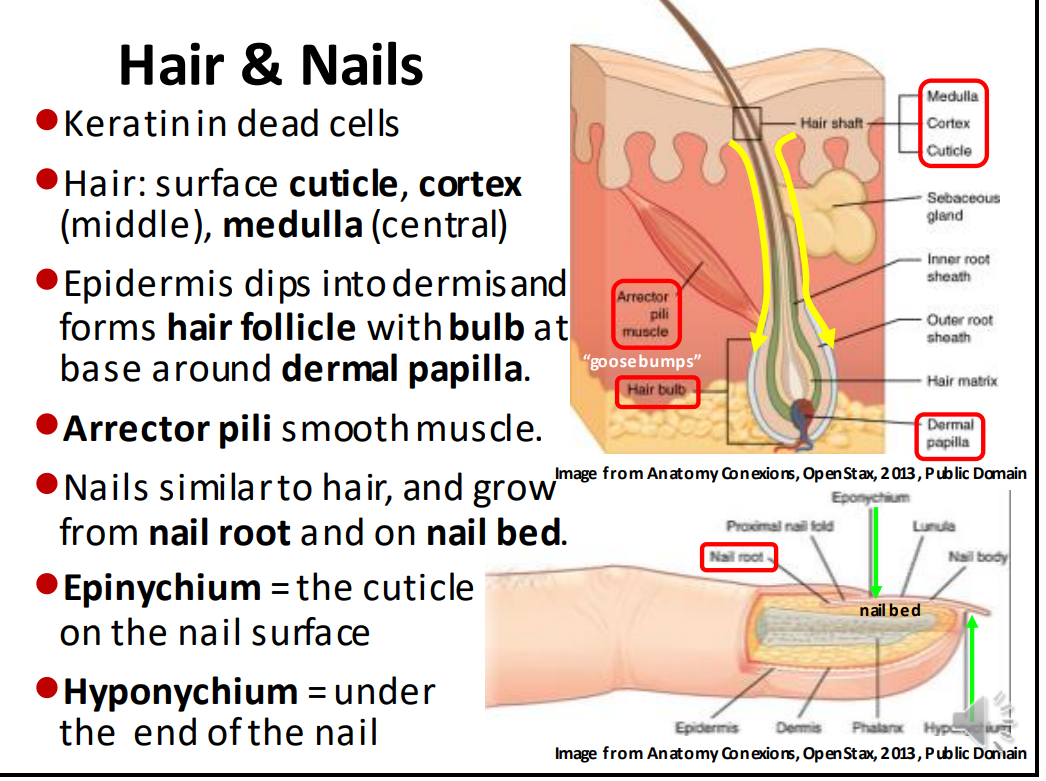
The _ is under the end of the nail
hyponychium
_ sweat glands make watery sweat
Eccrine
_ sweat glands make “smelly” sweat
Apocrine
_ glands make cerumen (earwax)
Ceruminous
_ glands can make milk
Mammary
What are the 4 functions of the skin?
Protection, Senses, Thermoregulation, and Vitamin D Synthesis
What does the stratum corneum protect the skin from? (4)
Drying, UV light, abrasion, and microorganisms
During _, walls of blood vessels in the dermis expand to _heat, and contract to _ heat.
Thermoregulation; radiate; conserve
_ occurs when there is a buildup of stratum corneum cells
Acne
A wound is repaired when a _ forms a scab and stratum _ cells divide and dermal fibroblasts repair _.
Blot clot; basale; collagen
Bedsores occur when a constant pressure blocks blood flow and then causes localized _ death
Cell
Calluses and Corns occur when frequent abrasion cause an increase in stratum _ division that thickens the skin, especially stratum _.
Basale; Corneum
_ occurs when melanocytes builds a mutation and becomes cancerous.
Melanoma