4.1.4.5 Economies and diseconomies of scale
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
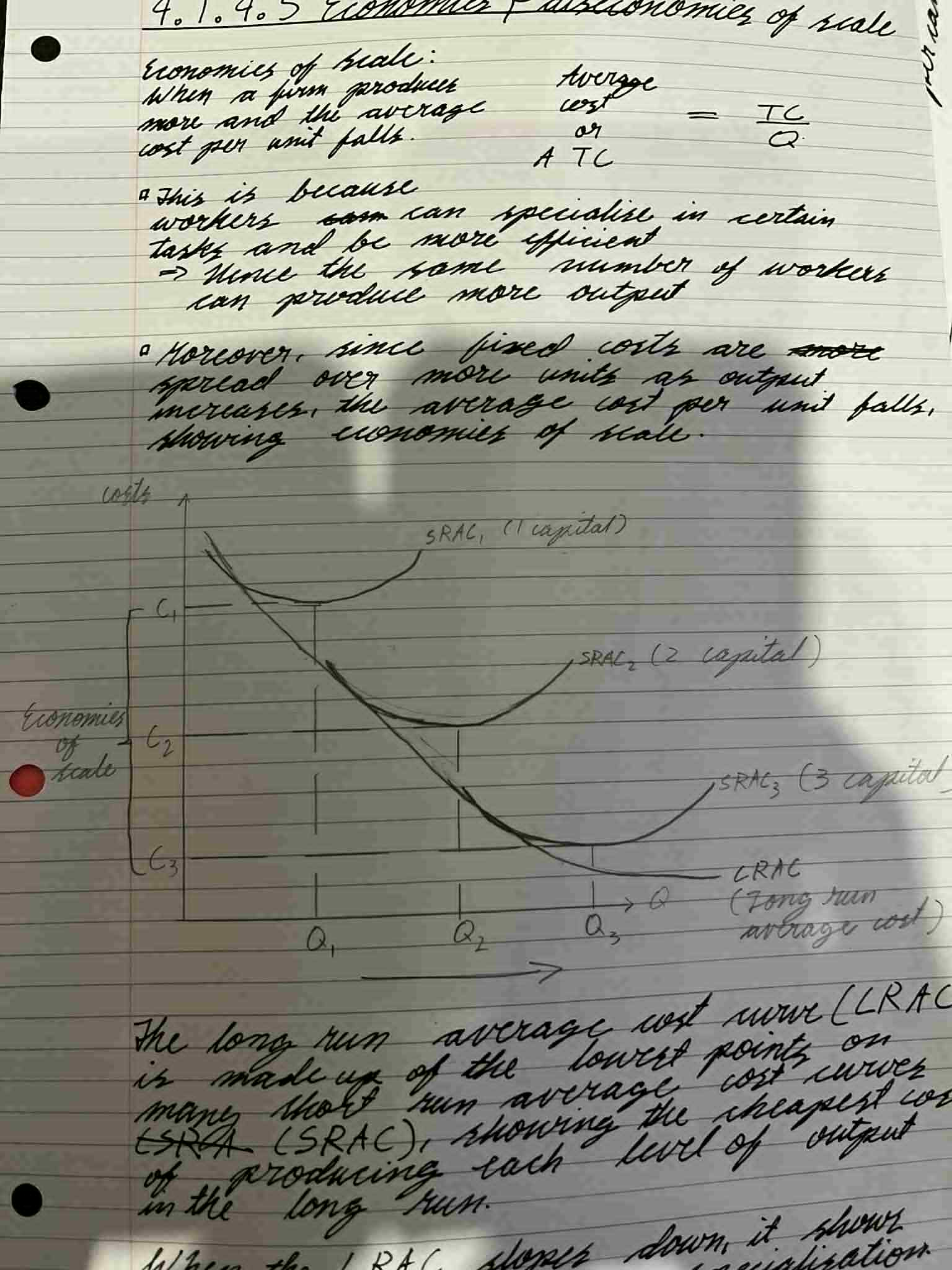
economies of scale
when a firm produces more and the average cost per unit falls
TC/Q
formula for average cost or ATC
specialise, efficient, same, more
economies of scale occur when workers can __________ in certain tasks and be more ________, hence the ____ number of workers can produce _____ output.
fixed costs are spread over more units as output increases
What allows the average cost per unit to fall in economies of scale?
long run average cost(LRAC)
made up of the lowest points on many short run average cost curves(SRAC)
cheapest cost of producing each level of output in the long run
What does the LRAC show?
down, specialisation
When the LRAC slopes ____ it shows economies of scale from ___________
technical, managerial, purchasing, risk-bearing, financial, marketing
What causes of Economies of Scale?
technical EofS
occurs when bigger firms can use better machines or production methods
Large-scale production allows the use of advanced technology which small firms cannot afford
big factories can buy robots => more efficient => cost of robots is high but spread across thousands of cars => cost per car becomes small
Application for technical EofS
car making, steel, or energy, where specialised equipment increase productivity
technical economies are especially vital in industries such as
output rises, ATC falls => helping firms compete more effectively
Analyses for technical EofS
Managerial EofS
when large firms employ specialist manager for different jobs(i.e. production, finance market)
Tesco
Application for Managerial EofS
Each manager build expertise in their area => firm more efficient / small firms =>less effective => only rely on 1-2 people — cost of manager spread across large output, => ATC falls
Analyses for Managerial EofS
Purchasing EofS
when a large firm buys raw materials or stock in bulk and suppliers give discounts
Primark = > orders millions of item at once and pays less per unit
Application for Purchasing EofS
Bulk buying => reduces cost per unit => one large order cheaper than buying many small ones => cost advantage over small firms => explains why supermarket and large chain dominate in competitive markets
Analyses for Purchasing EofS
financial EofS
when large firms can borrow money more easily and at a lower interest rate.
Banks see big firms as safer as they have assets and good reputation
Apple can borrow billions at a low interest rate, while small start up must pay higher rates or may even be refused a loan
Application for Financial EofS
lower borrowing costs => helps large firms keep ATC lower => large firm can expand/invest in new projects more cheaply(sell shares in stock market, which small firms can’t do)
Analyses of Financial EofS
Marketing EofS
when advertising or promotion costs are spread over a large output
Coca-Cola pays for global ad campaigns => TC is high but spread across billions of cans sold => ATC is low
Application for Marketing EofS
large firms may use reputation to negotiate cheaper shelf space or better advertising deals => advantage over small firms in attracting customers while keeping ATC per unit low
Analyses for Marketing EofS
Risk-bearing EofS
when large firms can spread risks across many products, markets or regions
Unilever makes food, cleaning, and personal care products
application for Risk-Bearing EofS
large firms operate in many countries => one market slows another can support the firm => less uncertainty and more confident planning => decreased ATC since loses are balanced out by gains
Analyses for Risk-bearing EofS