MSE-2015 L7 Case 6 3 Year Old Orphan
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Haemophilia A
A genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in factor VIII, leading to increased bleeding.
X-linked recessive disorder, therefore rare in females
most common cause: inversion within FVIII gene where it breaks during meiosis at intron 22, causing exons 1-22 to reattach in wrong direction
rare in females, but can be due to
Turner’s syndrome (where one X is absent)
homozygous FVIII deficiency (both X chromosomes carry the mutation)
inappropriate lyonisation (random X inactivation leading to a significant proportion of cells expressing the mutated X).
FVIII
Factor VIII, a blood-clotting protein that is deficient in Haemophilia A.
gene located on long arm of X chromosome
part of intrinsix tenase complex which activates FX
X-linked recessive disorder
A type of inheritance where the gene causing the condition is located on the X chromosome.
Haemophilia B
A genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in factor IX, also known as Christmas disease. Also an X-linked recessive disease.
FIX
Factor IX, a blood-clotting protein that is deficient in Haemophilia B.
also located on the long arm of X chromosome, near FVIII gene
plays a crucial role in the coagulation cascade, activating factor X in the presence of factor VIII and calcium ions
Haemophilia clinical presentation
haematuria
purpura
bruising
epistaxis (nose bleed)
haemorrhage
haemarthrosis (bleeding into joints)
Haemophilia Treatment
Recombinant FVIII.FIX produced using tissue culture techniques
Clotting factor concentrates e.g. cryoprecipitates
Desmopressin
Gene therapy
Von Willebrand Factor (vWF)
Produced by endothelial cells, platelets and sub-vascular connective tissue
has 2050 amino acids, found in plasma as large multimers
binds and protects inactive FVIII
binds to both exposed collagen and platelets
binds to thrombin
Thrombocytopenia
A condition characterized by a reduction in platelet count, which can lead to bleeding.
Desmopressin
A treatment for von Willebrand disease that stimulates the release of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor. For minor Haemophilia A disease also.
Prothrombin Time (PT)
A blood test that measures the time it takes for blood to clot, used to assess coagulation factors.
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
A blood test that assesses the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade, prolonged in haemophilia.
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
A condition characterized by low platelet counts and purpuric rash, often due to autoimmune mechanisms.
Megakaryoblast
A large bone marrow cell from which platelets are derived.
Thrombopoiesis
The process of platelet production, including pre-endomitosis and post-endomitosis phases.
Pre-endomitosis begins with initial differentiation of common myeloid progenitor, TPO (Thrombopoietin) is a early driver
Endomitosis is mitosis without telophase and cytokinesis phase, RUNX1 key to suppress Rho signalling
Terminal differentiation (post-endomitosis) = distinct morphological cells, appear within bone marrows e.g. megakaryoblast
Thrombocytopoiesis
aka platelet shedding, reduction in platelet count
also regulated by TPO, with roles for IL-6 and Il-11
Demarcation system = megakaryocyte ultrastructure feature
membrane lined channels that reach from cell membrane into cytoplasm
delineates final mature thrombocytes
Megakaryocyte will produce proplatelet process which can cross the endothelium
sinusoidal capillaries within bone marrow facilitate this
Minor/moderate reduction in platelets doesnt always = increase in haemorrhage risk as spontaneous bleeding risk is high when platelet count is ~20 x109 cells/L.
Acquired or hereditary
Cryoprecipitate
A blood product used to treat clotting disorders by providing fibrinogen and other clotting factors.
Adenovirus Mediated Gene-transfer - Gene Therapy
Involves delivering a functional copy of the FVIII to the patient's liver cells.
By using an adenovirus vector to carry the normal FVIII gene, it is possible to enhance the production of factor VIII in the body, helping to restore proper blood clotting function.
This approach aims to provide a long-term solution for managing the disorder, reducing the need for regular clotting factor injections.
Factor-poor plasma
Plasma that has been depleted of specific coagulation factors to create a baseline for testing so activity of specific coagulation factors can be assessed without interference from other factors.
Clotting Factor Test
Pt plasma mixed with factor-poor plasma and PT/APTT test undertaken. If pt has good quality/quantity of factor it will correct the clotting time of factor-poor plasma.
monoclonal antibodies also used for quantitative factor count, may be preferred for specificity and sensitivity in quantifying coagulation factors, allowing for more precise measurements.
some labs prefer traditional testing methods, due to their established protocols and historical reliability, even if they may be less specific than monoclonal antibody methods.
Ristocetin
A test that causes platelet aggregation, used to evaluate von Willebrand factor activity.
Requires vWF to cause platelet aggregation
Platelet aggregation
The clumping together of platelets in the blood, essential for the formation of a clot.
Thromboelastography (TEG)
A method to test platelet function and clot strength by measuring changes during coagulation.
also detect aberrant fibrinolysis
blood slowly agitated around a wire to initiate coagulation
measured by…
R time - time to start forming a clot, 5-10mins, shows problem with coagulation factor. Treat with FFP
K time and A angle - time until clot reaches fixed strength, 1-3mins. Shows problem w fibrinogen, treat with cryoprecipitate
Maximum Amplitude (MA) - highest vertical amplitude of TEG, problem with platelets. Treat with platelets or DDAVP
LY30 - percentage of amplitude reduction 20mins after MA, problem with excess fibrinolysis
Turner’s Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder that can lead to haemophilia A in females due to abnormal X chromosome inheritance.
Normal range for FVIII activity
70-150% in adults, essential for appropriate clotting function.
Von Willebrand’s disease
Common inherited bleeding disorder, characterized by a deficiency of von Willebrand factor.
Heterogenous, with different subtypes.
Most common inherited bleeding disorder
vWD Subtypes
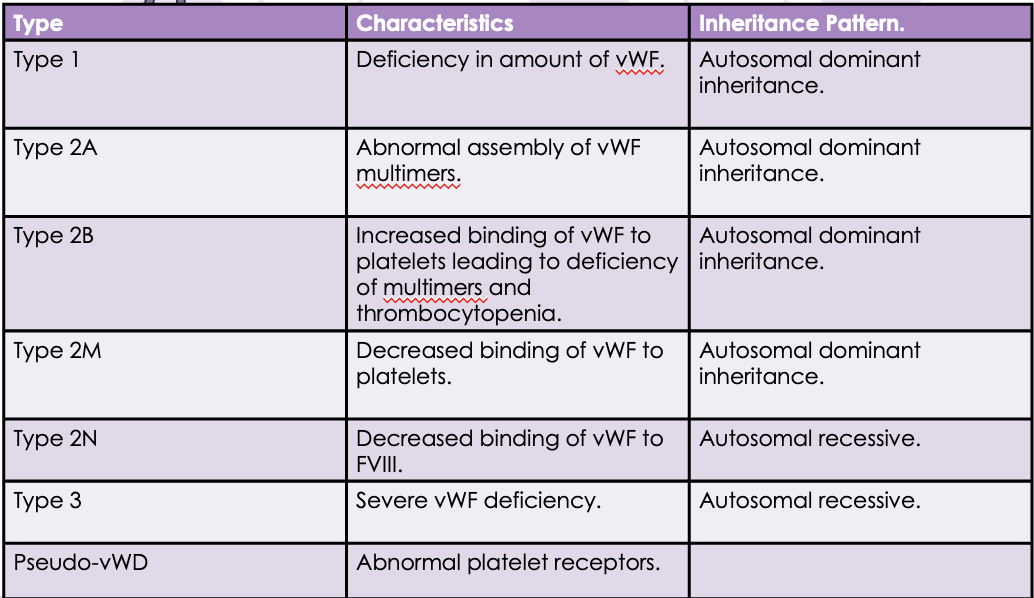
vWD
Desmopressin/Vasopressin - stimulates FVIII release from intra-cellular stores
stimulates vWF from platelet granules
cryoprecipitate
recombinant vWF
vWF Testing
Platelet aggregation (thromboelastography)
vW antigen
Ristocetin
Platelets and Homeostasis
Primary Platelet Plug: adhere to the site of vascular injury, becoming activated and aggregating to form a primary platelet plug, which is essential for initial hemostasis.
Reservoir of Coagulation Factors, act as a reservoir for various coagulation factors, such as factor V and factor VIII, which are secreted upon activation to facilitate the coagulation cascade.
Calcium in Coagulatio, ions released from platelets and surrounding tissue are crucial for several steps in the coagulation cascade, including the activation of clotting factors.
Haemodynamic Altering Compounds, release substances like thromboxane A2 and ADP that alter blood flow and vascular tone, promoting further platelet recruitment and aggregation
Platelet Investigations
FBC reveal number and size
important to keep in mind of EDTA mediated platelet clumping
dont inform whether platelets function
Function testing can including screening or diagnostic tests
Pre-analytical Variables of Platelet Testing
Medicines e.g. aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen
Diet e.g. garlic, turmeric, onions, ginger can reduce platelet function
Supplementation e.g. Vit C, E and B6
Others e.g. alcohol, smoking, caffeine
Platelet Screening Tests
Bleeding time test, 1mm incision damages capillaries only so no secondary haemostasis
TEG
Platelet function analyser aka PFA-100
Platelet Diagnostic Tests
Introducing agonists to pt platelets and measuring response, done by in two methods
PRP aka patient platelet rich plasma - relies on light transmission
whole blood method - relies on electrical charge in resistance
Platelet Disorder Mechanisms
Thrombocytopenia
impaired production
increased consumption
splenic sequestration
Platelet Function Disorders
Defect in surface receptors
Defect in granule function/number
Defect in metabolism
Phospholipid exposure
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Low platelet count and purpuric rash
purple regions on skin
do not blanche on pressure
bruising, epistaxis, menorrhagia
IgG produced targets glycoprotein IIb/IIIa on the platelet surface.
Integrin complex.
Receptor for vWF and fibrinogen
Platelets are opsinized by IgG.
Renders them susceptible to phagocytosis by splenic macrophages.
Good prognosis for young children
Spontaneous remission in 2months is common
ITP Haematology
Thrombocytopenia ( <150 x109 cells/L)
RBC decrease after bleeding
usually normal unless ITP is secondary to something else
important to establish true ITP from pseudo (EDTA)
ITP Treatment
For acute ITP no pro-coagulant needed, excessive bleeding very rare
Treat underlying infection, prevents antibody secretion
Monitoring platelet counts until stabilised
Platelets
Treatment for transfusion needs e.g. thrombocytopenia
Each unit contains ~250x109 cells/L.
More perishable than RBC
produced at 22 degrees, kept for 5 days
pooled or aphresis