Key Brain Structures and Their Functions - AP Psychology Study Guide
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
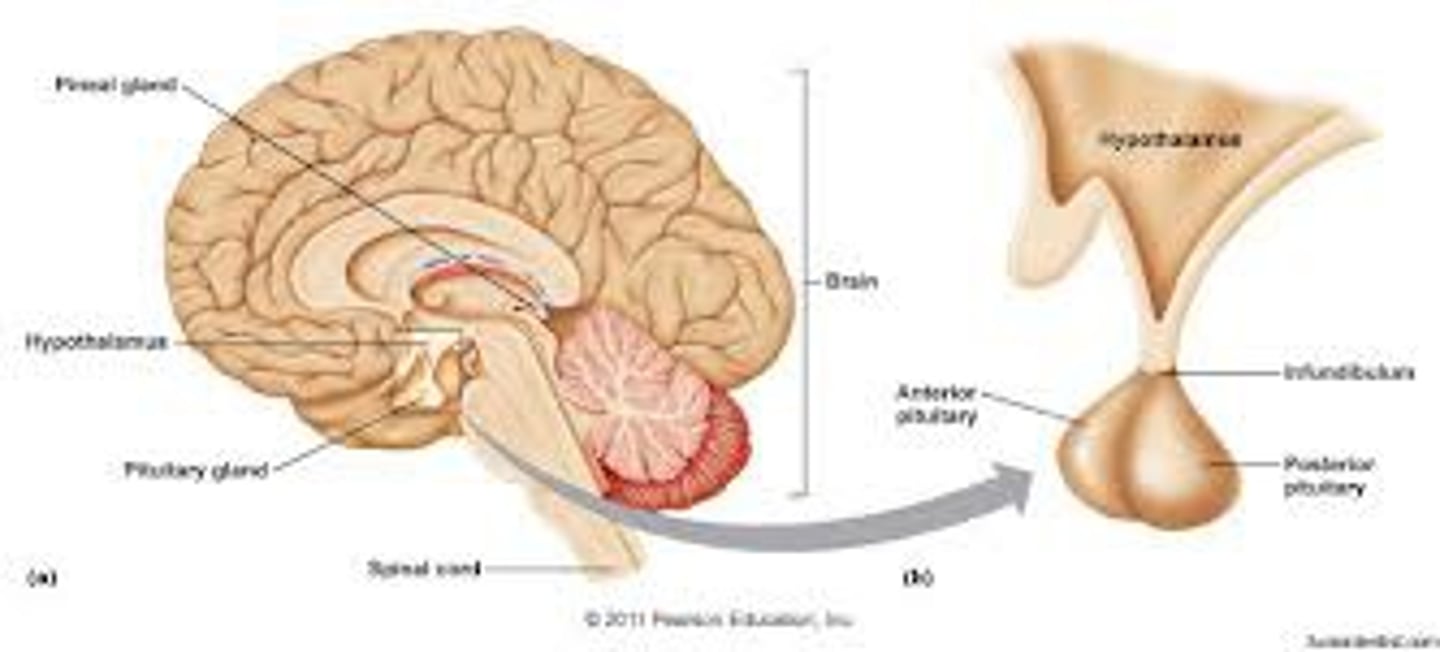
Pituitary Gland
Known as the master gland because it regulates the activity of several other glands. It is under the control of the hypothalamus.
Medulla
Controls vital life functions such as breathing, circulation, and swallowing.
Pons
Known as the bridge, it is located above the medulla. It is responsible for sleeping, walking, and dreaming.
Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain, it is responsible for coordinating fine muscle movement and maintaining posture and equilibrium.
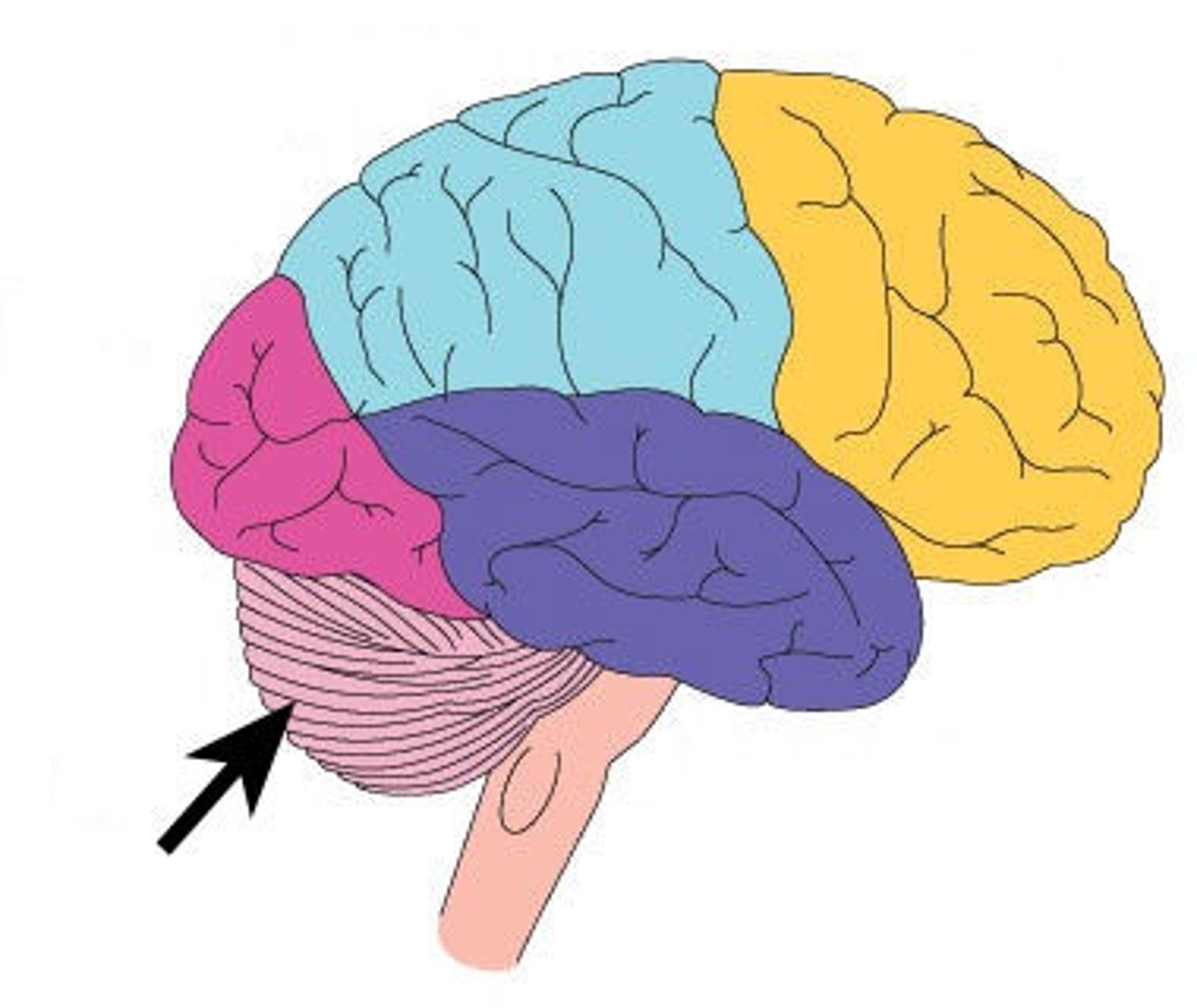
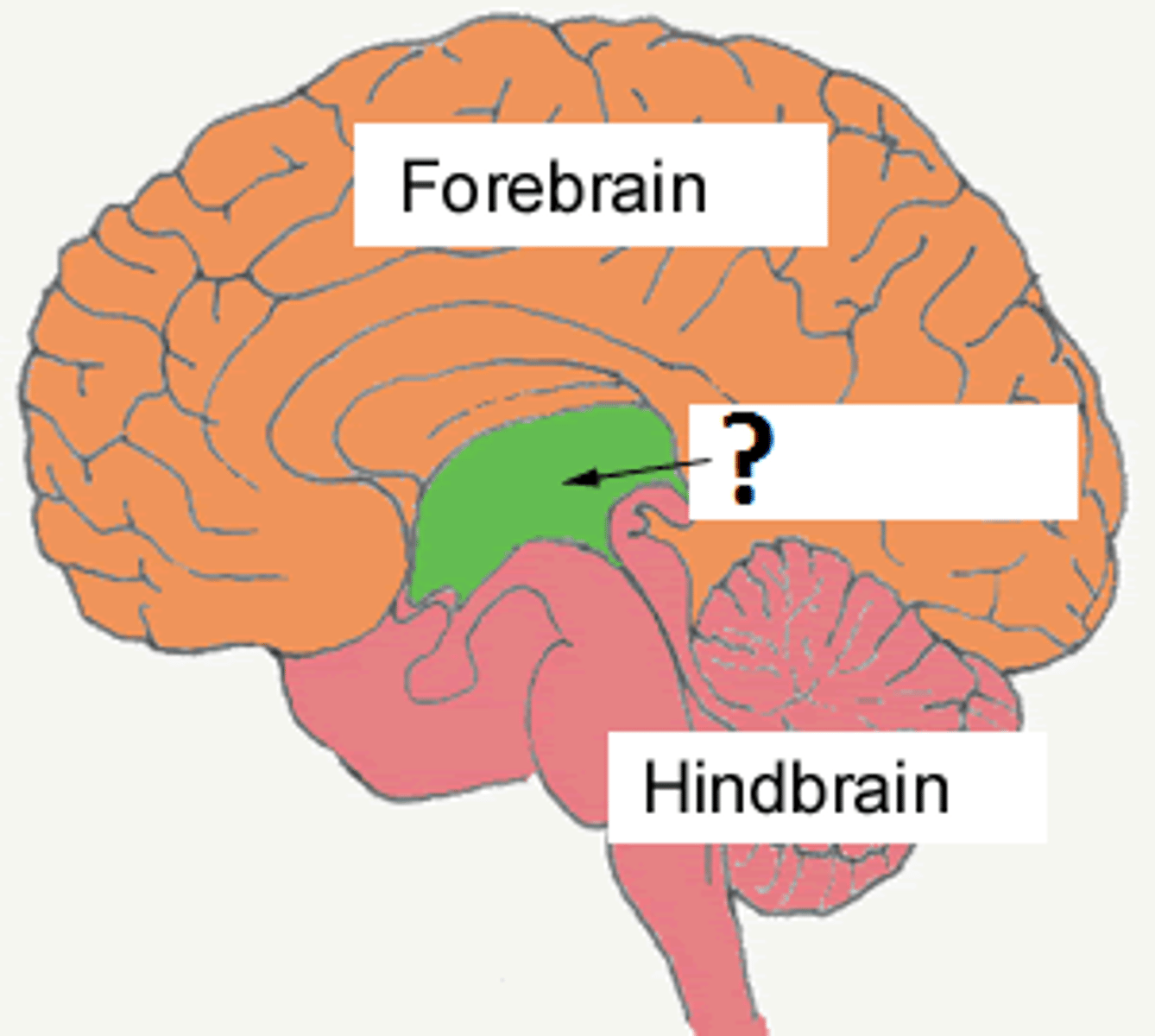
Midbrain
A small area in the brain located just above the spinal cord and below the forebrain. The midbrain integrates auditory and visual sensory information and muscle movements.
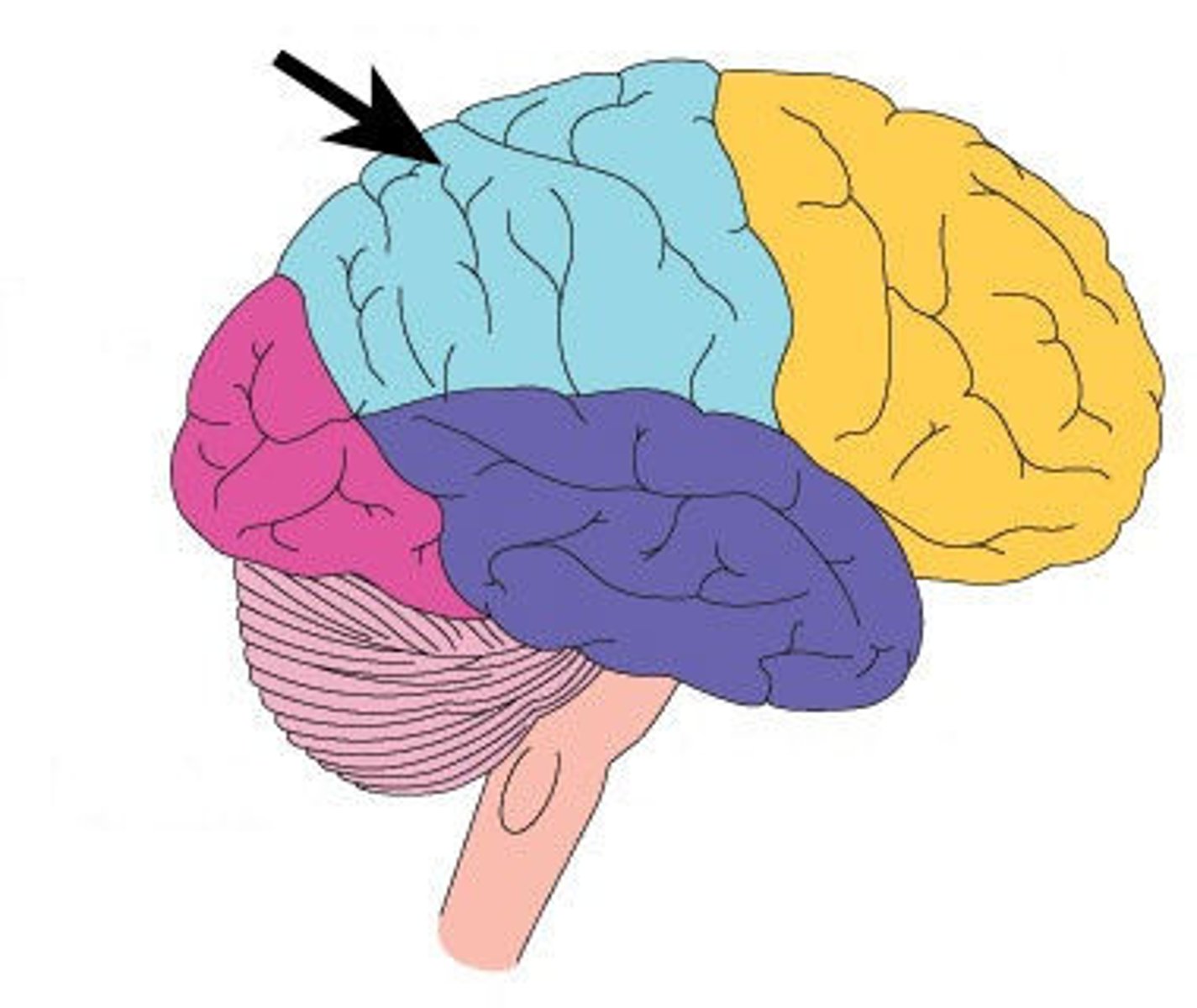
Frontal Lobe
Located directly behind the forehead and is responsible for abstract thought and emotional control.
Parietal Lobe
Receives and interprets bodily sensations such as pressure, temperature, touch, pain, and the location of body parts.
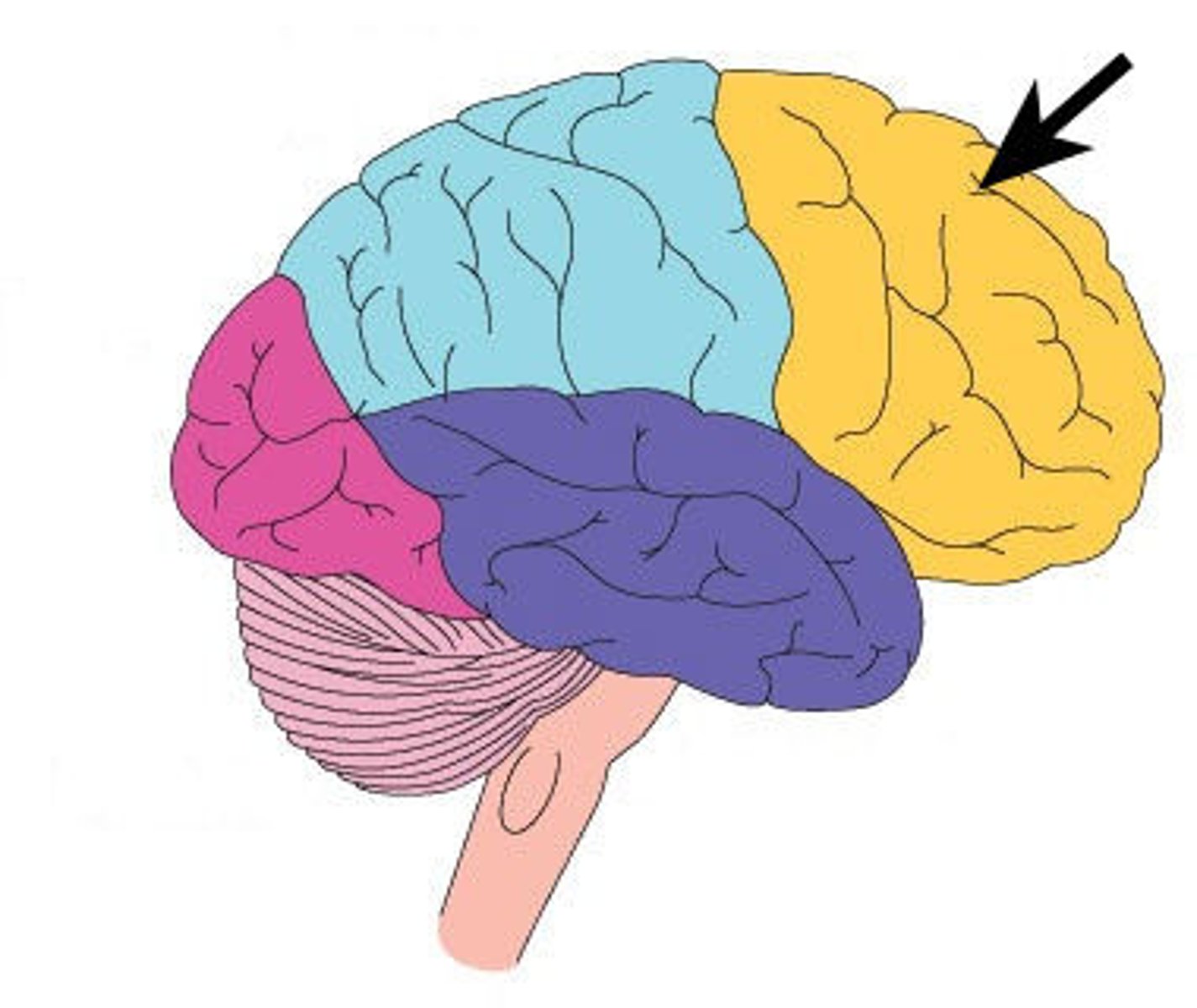
Occipital Lobe
Located at the back of the brain, it's responsible for vision and visual perception.
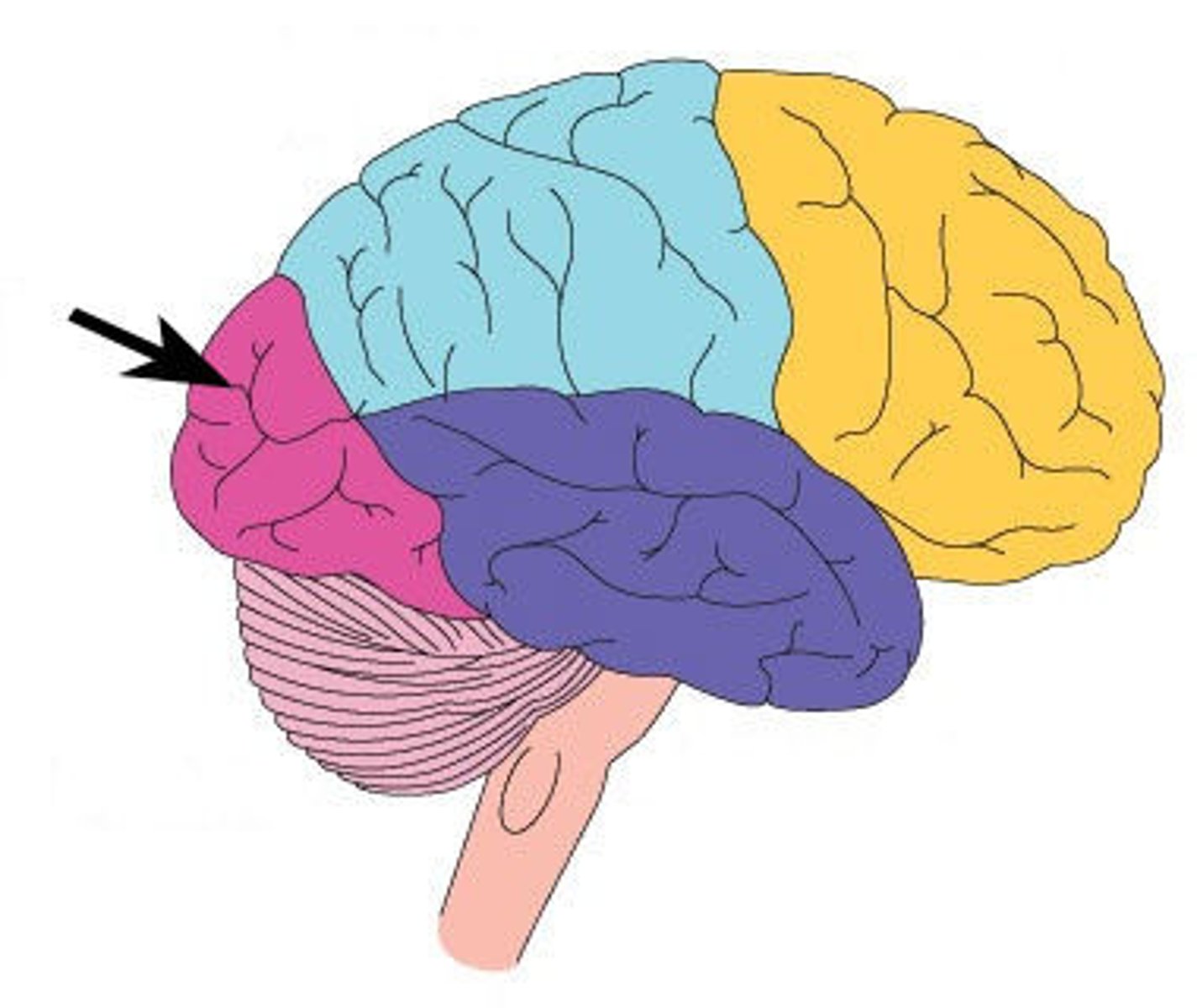
Temporal Lobe
Located on each side of the brain above the ears and involves processing involving sensory information from the ears.
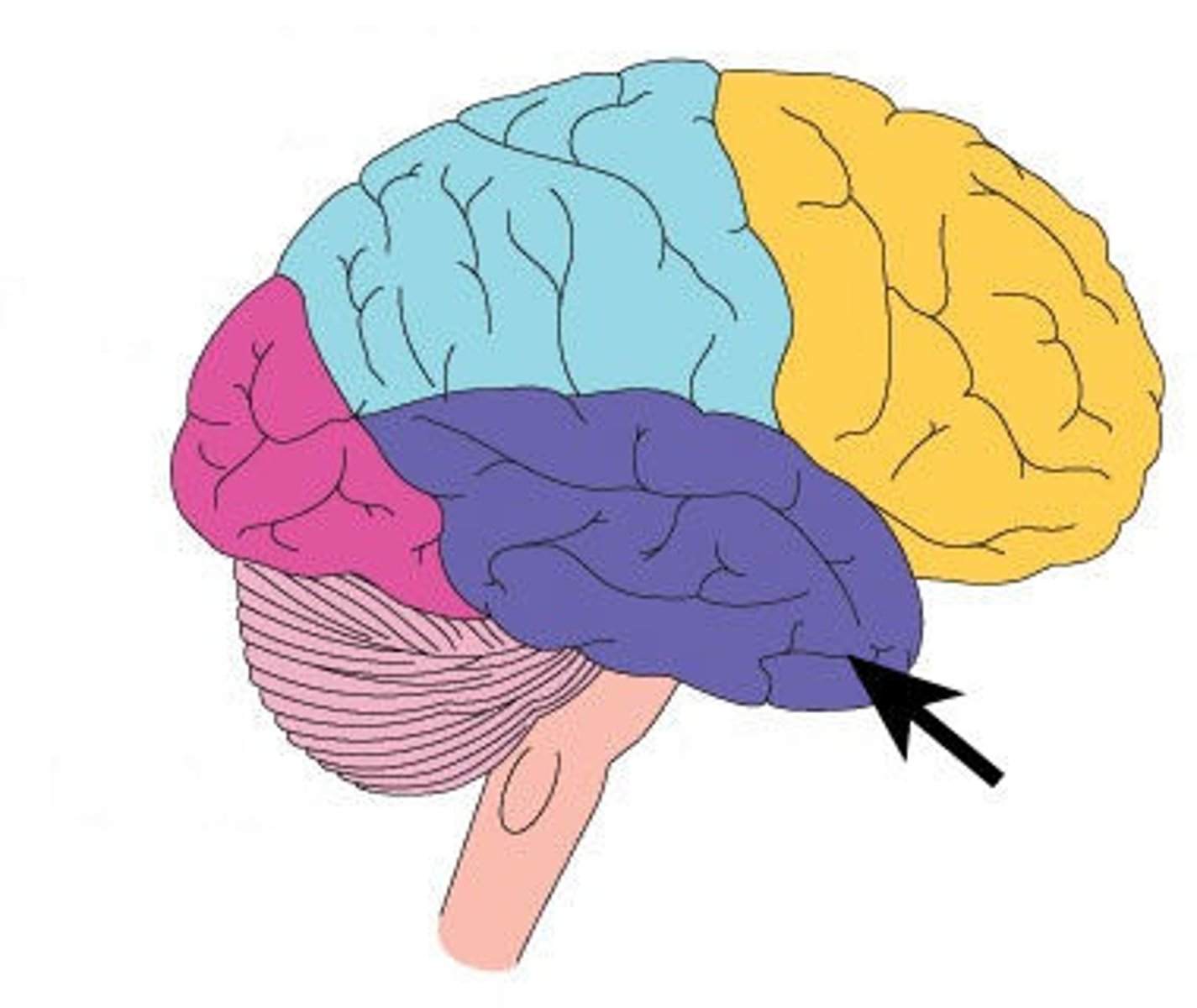
Thalamus
Located at the top of the brainstem, it receives input from all the senses, except smell, and directs this information to the appropriate cortical areas.
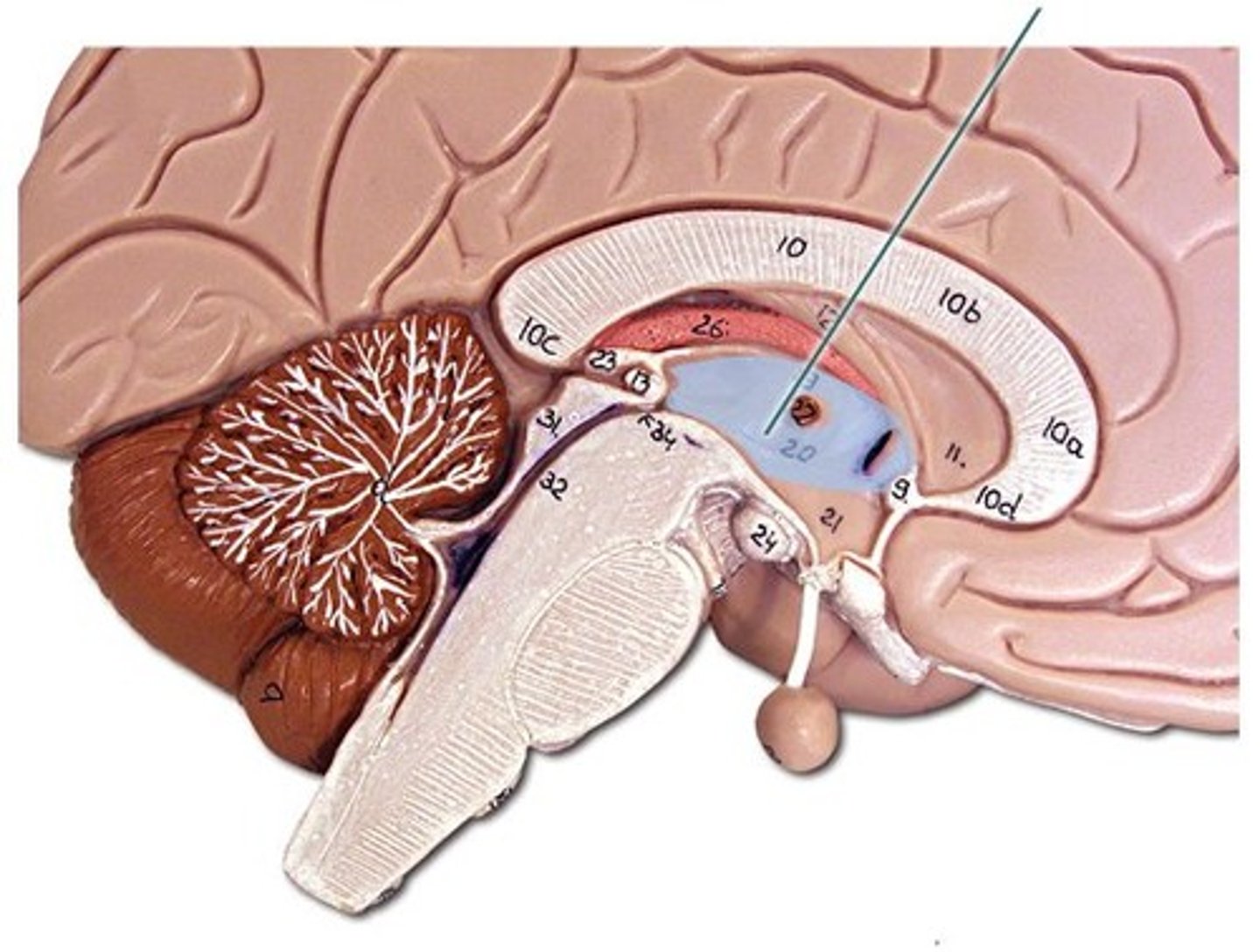
Hypothalamus
Located under the thalamus and regulates key functions such as hunger and thirst.
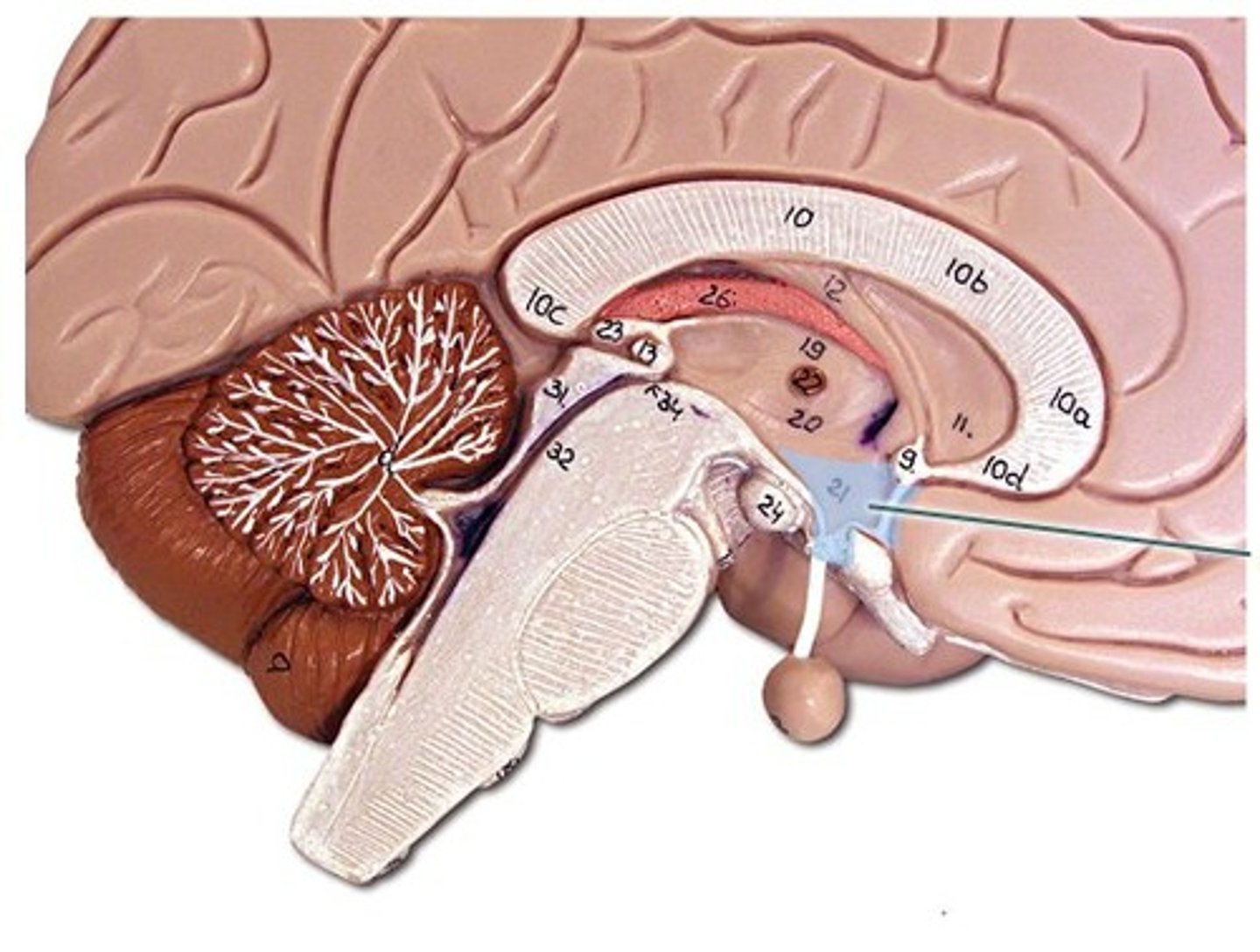
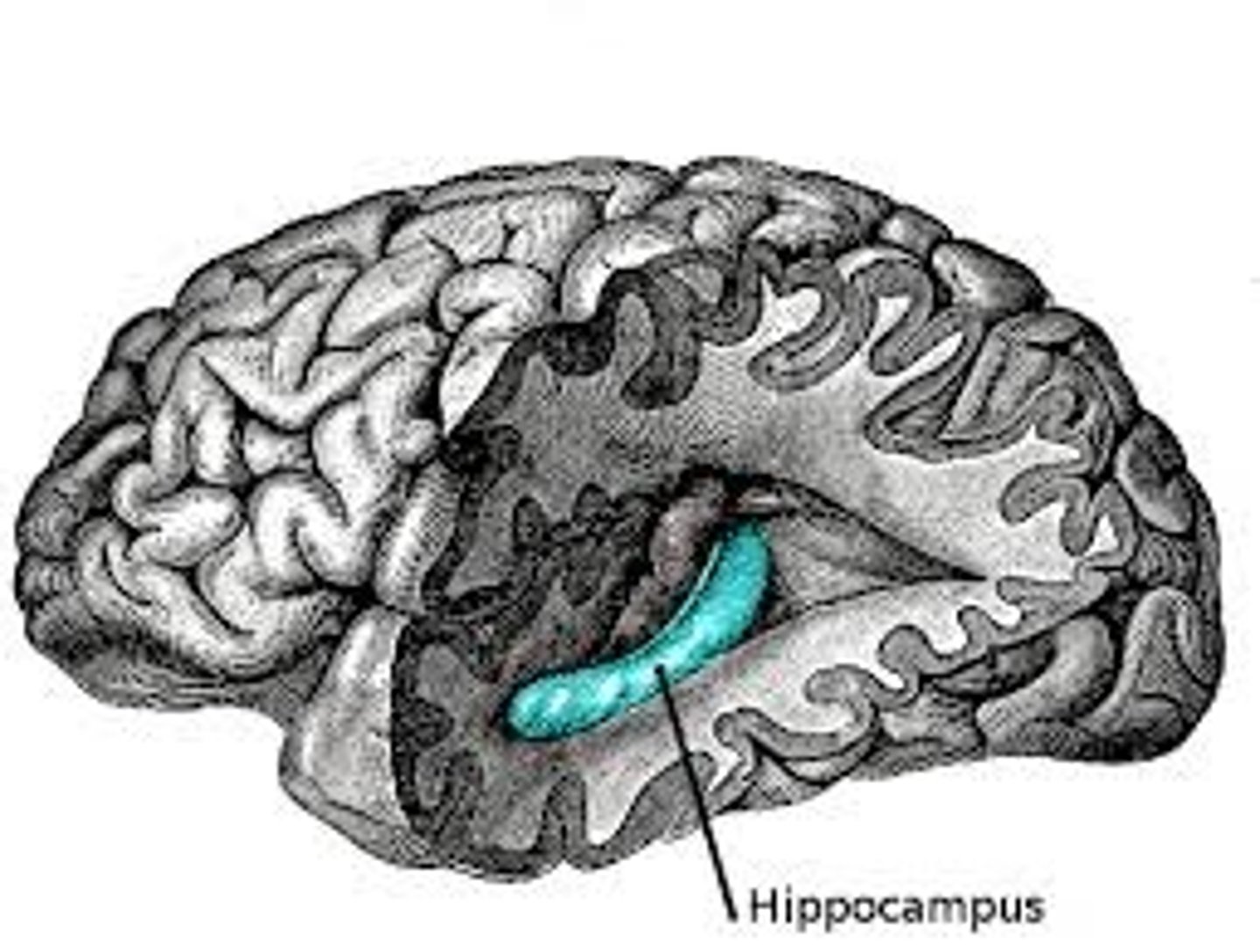
Hippocampus
Plays a key role in forming new memories of events and information.
Amygdala
Linked to the production and regulation of emotions such as aggression, fear, and disgust.
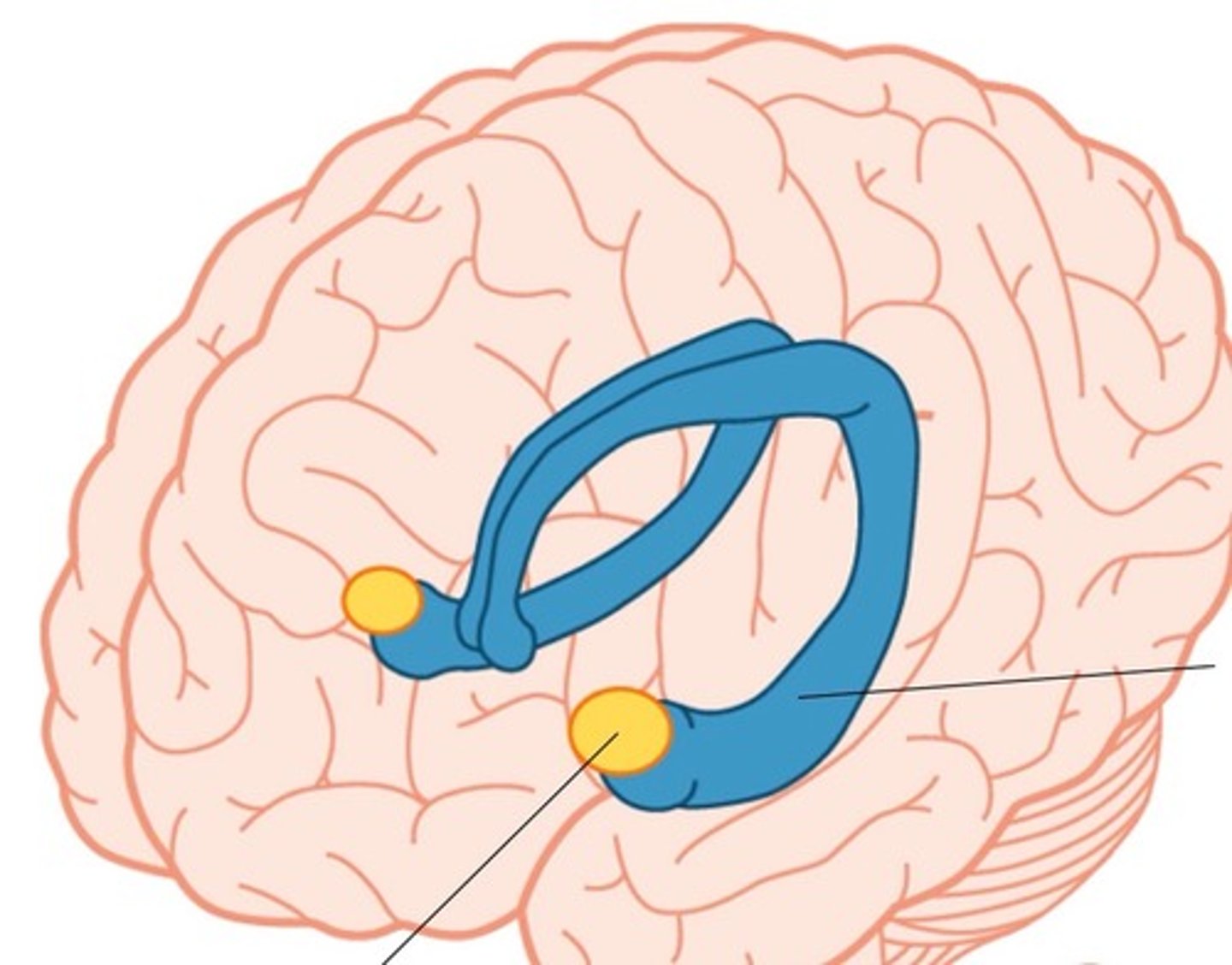
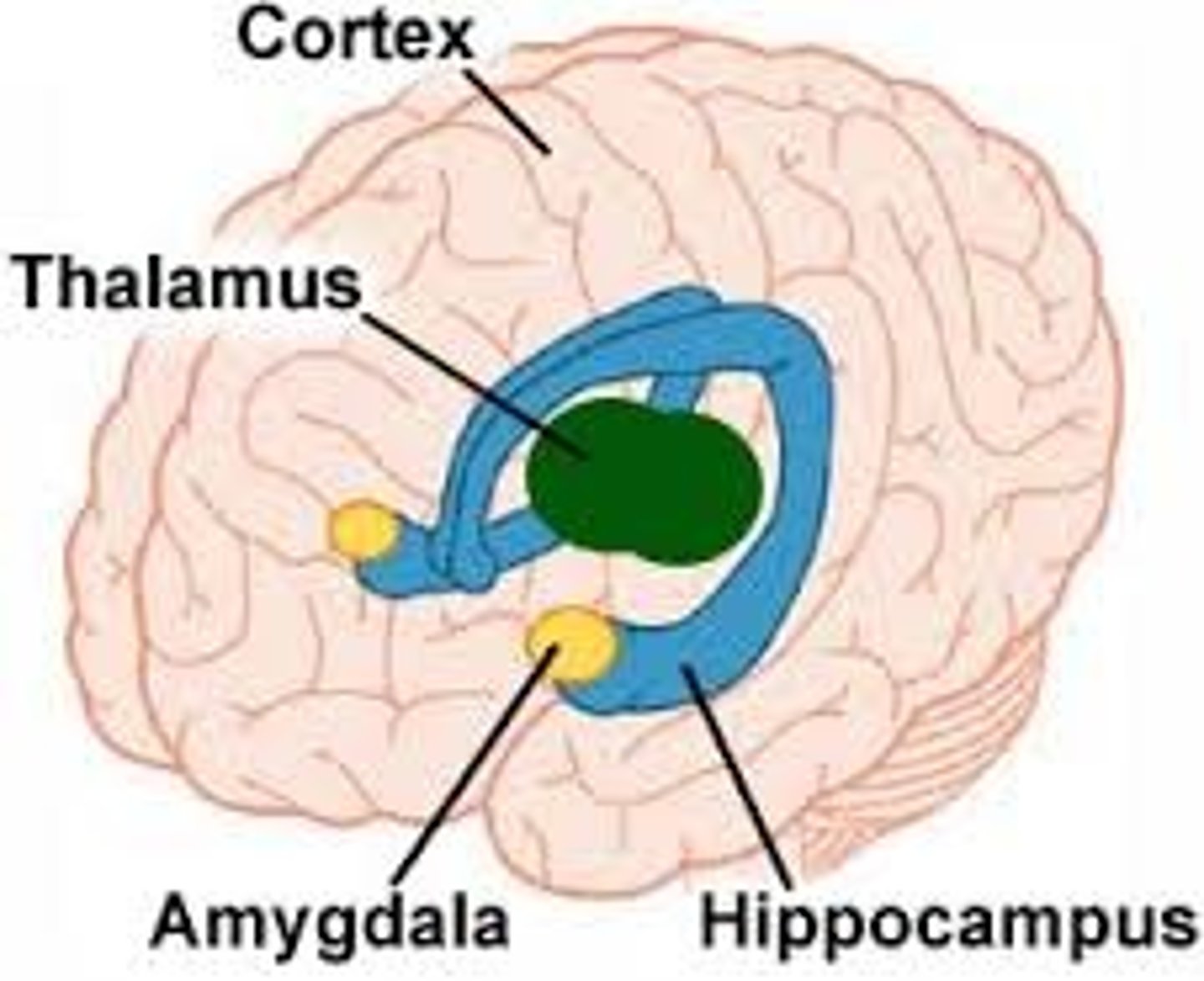
Limbic System
The hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus make up the this system and play a key role in the experience of emotions.
Corpus Callosum
A bundle of nerve fibers that connect the brain's left and right hemispheres.
Broca's Area
Plays a crucial role in speech production, which involves the muscle movement needed for speech.
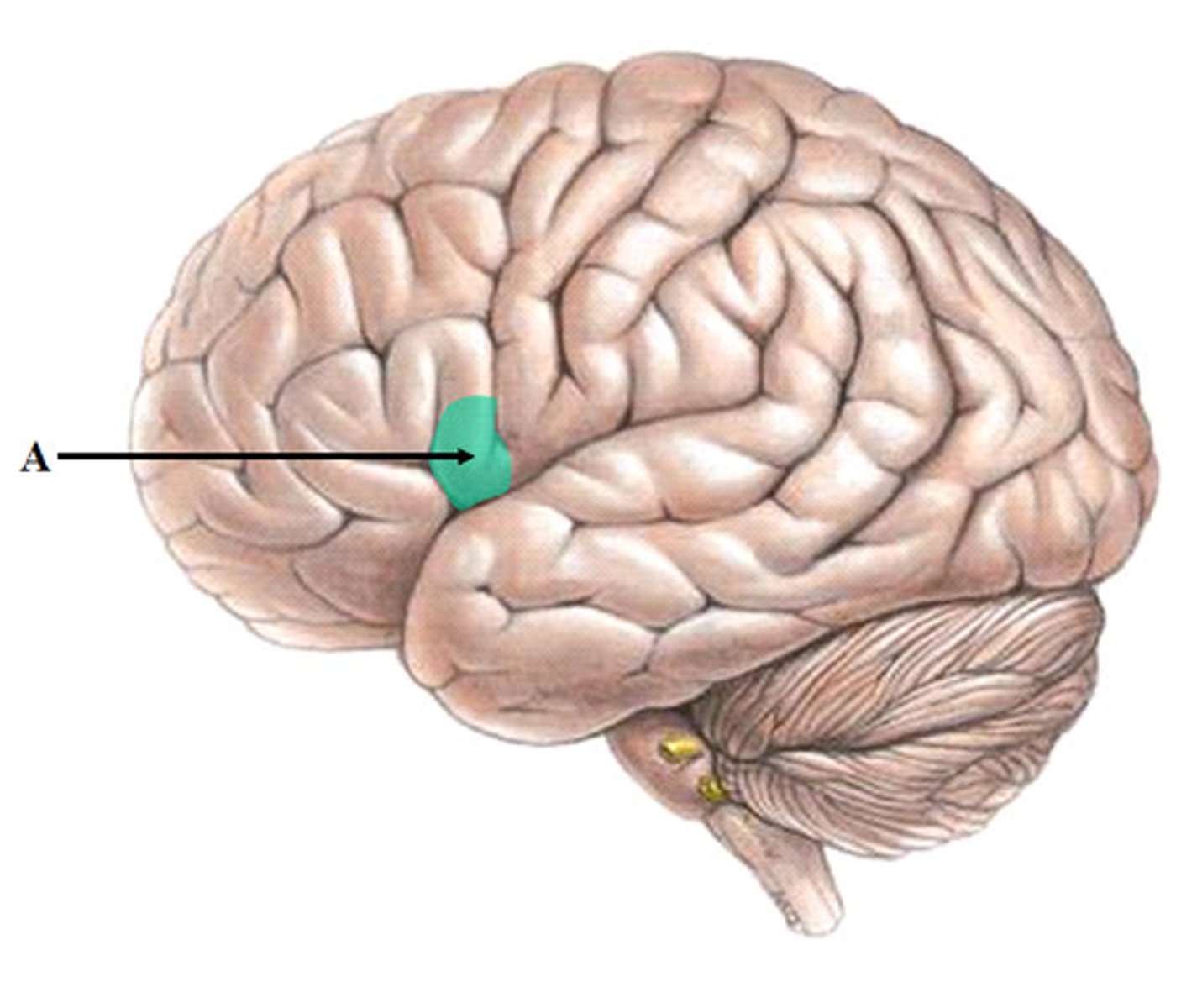
Wernicke's Area
Plays a crucial role in language development, which involves the comprehension of spoken requests.
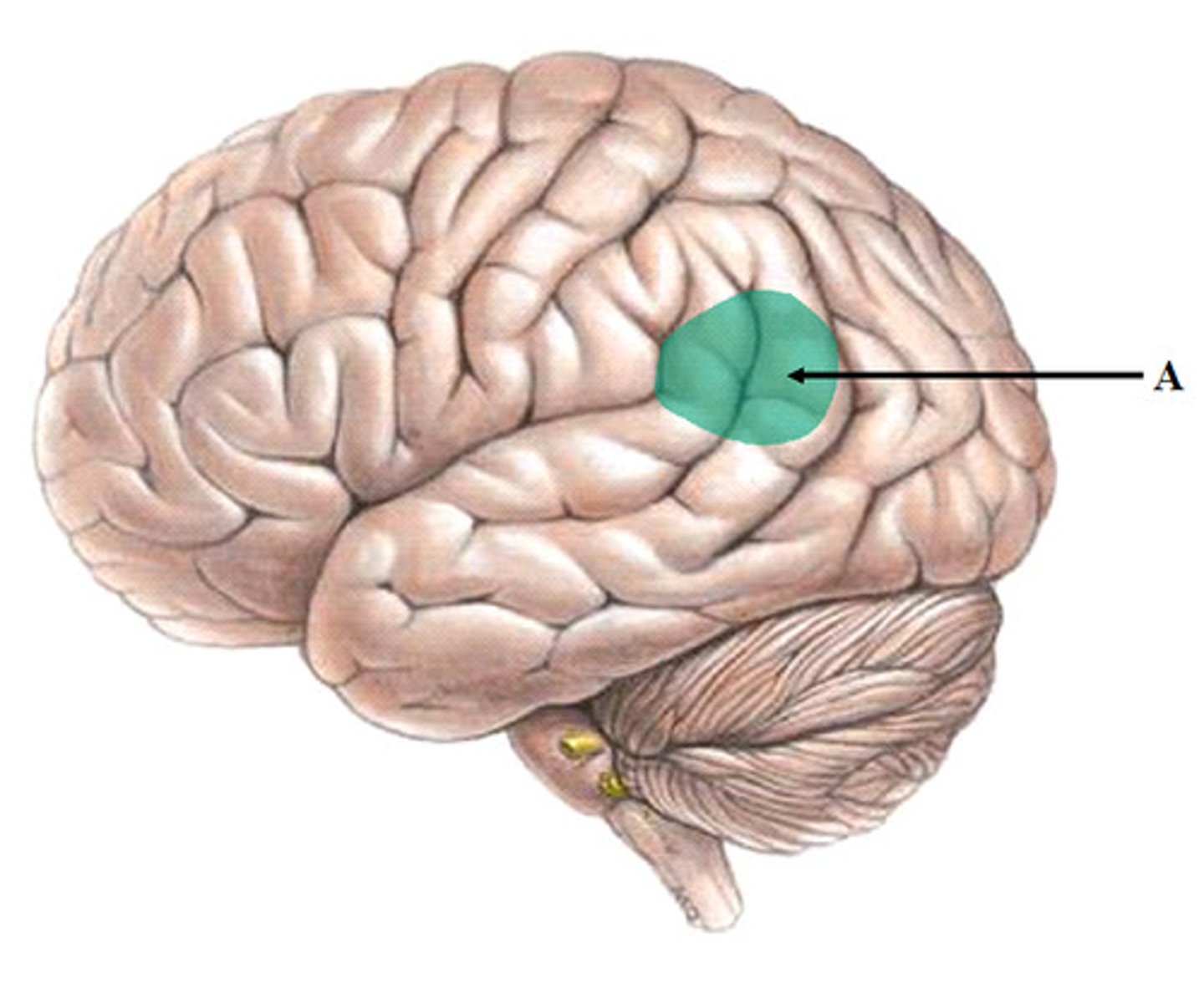
Visual Cortex
The most important area of the brain's occipital lobe, which receives and further processes visual information.
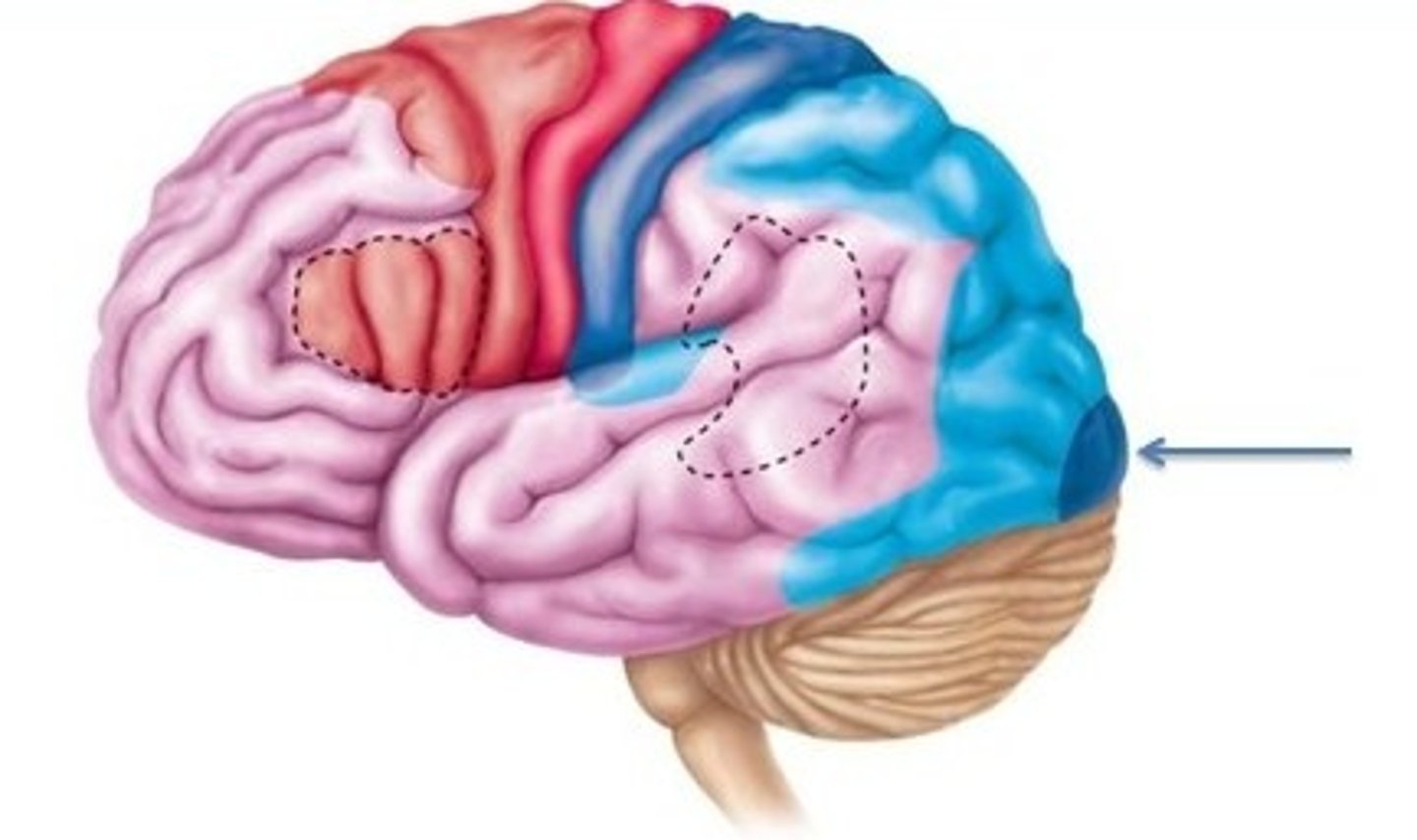
Auditory Cortex
In the temporal lobe, receives information from the thalamus. Where the detection of complex features of auditory information, such as patterns, takes place.
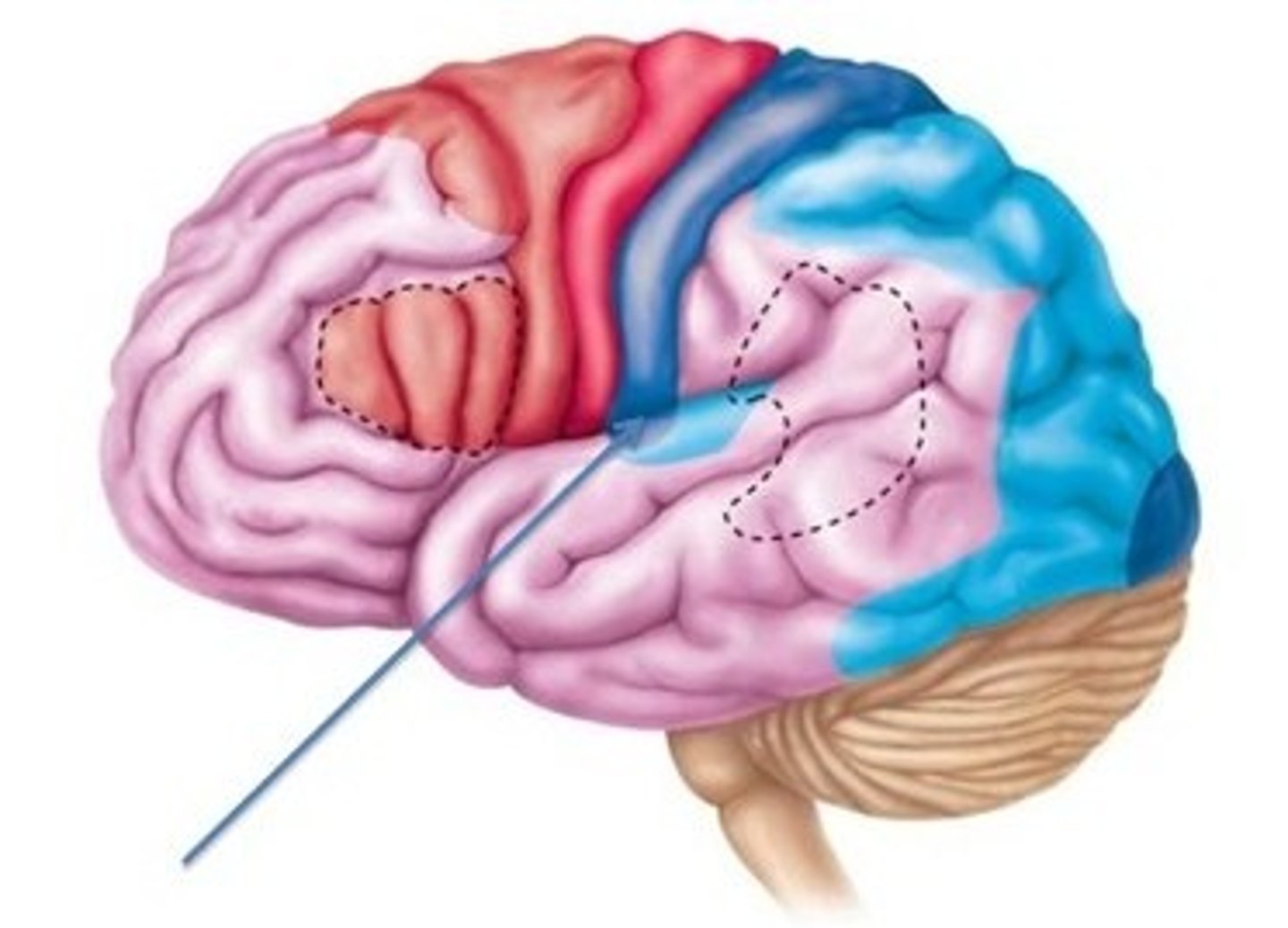
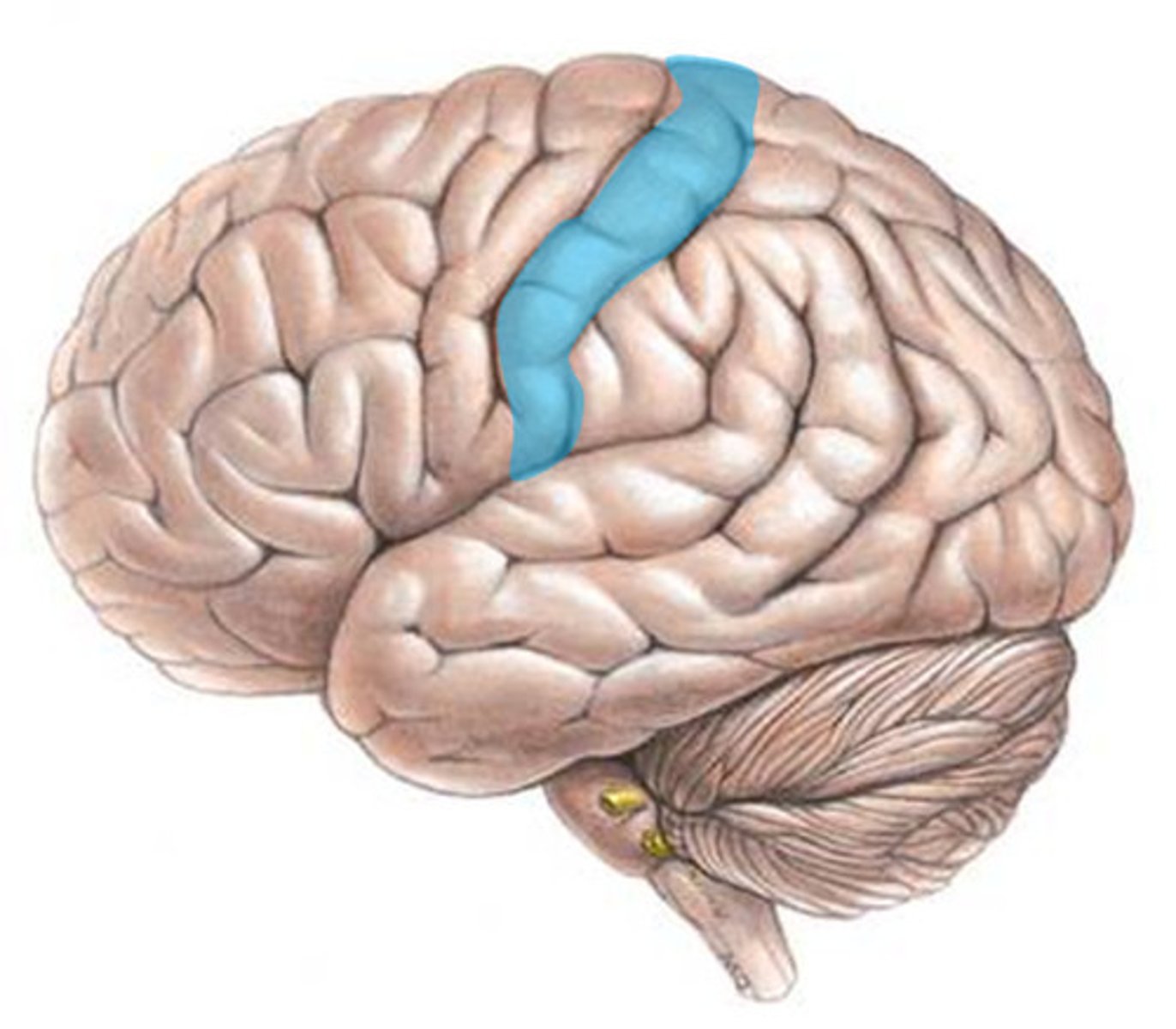
Motor Cortex
A thin, vertical strip at the back of the frontal lobe. Controls voluntary movements, sends signals to muscles. Top of the body is controlled by neurons at the bottom, visa versa.
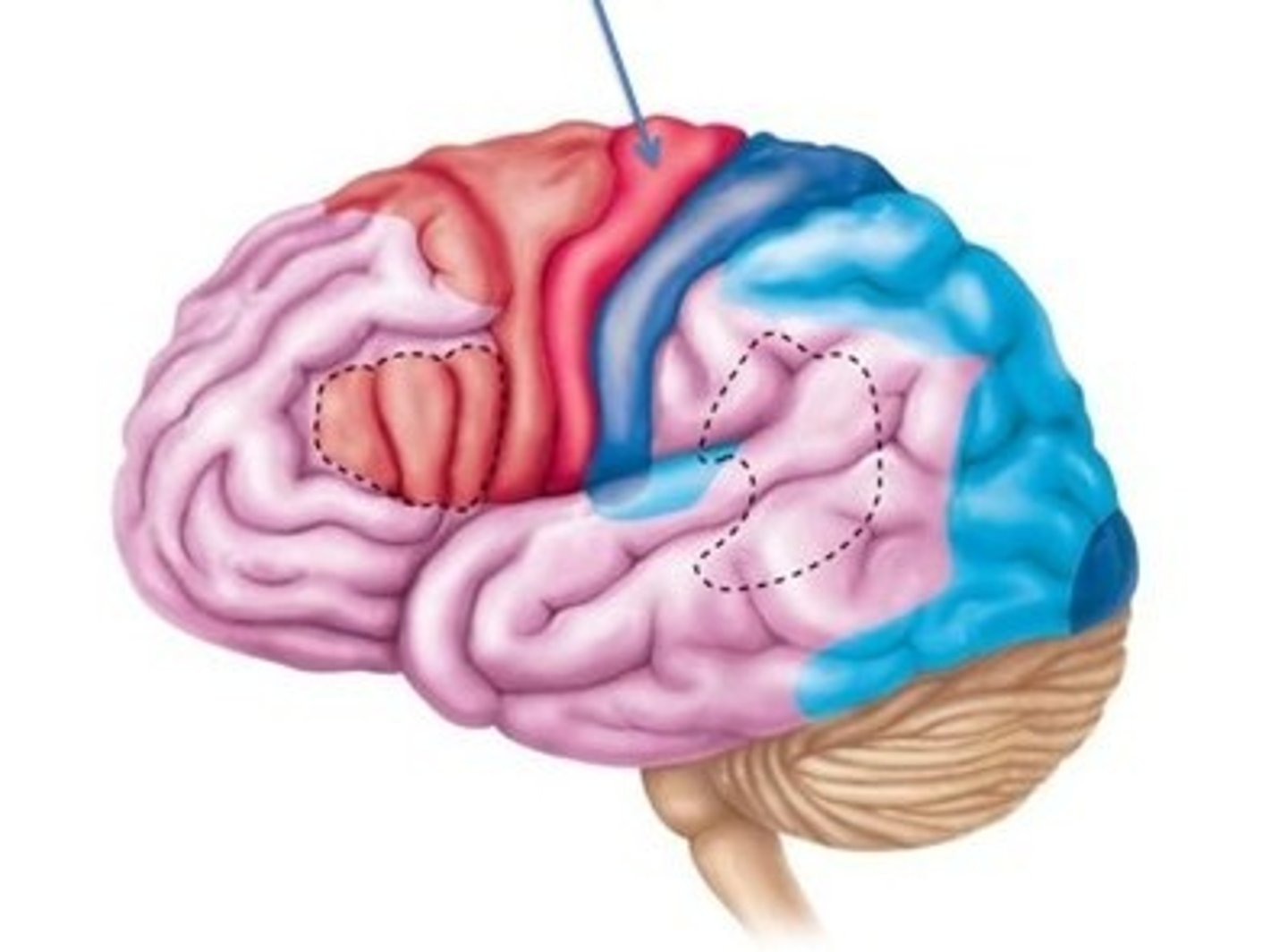
Left Hemisphere
Specializes in verbal and analytical functions.
Right Hemisphere
Focuses on nonverbal abilities, such as visual recognition tasks and music.
Achetocholine (ACh)
controls voluntary movement
lack of leads to Alzheimer's
Dopamine
Lack of leads to Parkinson's disease, too much leads to schizophrenia
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter (speeds things up); involved in memory
Seratonin
A neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal; linked to depression
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, slows things down, helps with anxiety
nonepinephrine
neurotransmitter (not serotonin) also linked to depression
somatosensory cortex
area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations