BOC Hematology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
In order for hemoglobin to combine reversibly with oxygen, the iron must be
In the ferrous state
Which description fis the Donath Landsteiner antibody
IgG biphasic hemolysin
(Specific) secondary granules pf the neutrophilic granulocyte
Appear first at the myelocyte stage
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells are capable of producing
Lymphoid and myeloid stem cells
Auer rods are characterized by
Fused primary granules
Which is a characteristic of cellular changes as megakaryoblasts mature into megakaryocytes in the bone marrow
Nuclear division without cytoplasmic maturation
True statement of megakaryocytes in bone marrow
An average 5-10 should be found in each low power field (10x)
After the removal of red blood cells from the circulation hemoglobin is broken down in
Iron, heme, globin
Which cells are involved in inmediate hypersensitivity reactions
Basophils
A Wright Stained peripheral blood smear reveals blue, ring shaped inclusions with red chromatin dots in several of red blood cells. These inclusions are consistent with
Malarial parasites
HGB 11.5 g/dL
HCT 34%
MCV 89 fL
MCH 29pg
MCHC 29%
Normocytic, hypochromic erythrocytes
Multiple myeloma
Roleaux
Automated hematology analyzers calculate the hematocrit using which following
MCV and RBC
Analogy: MCV = HCT/RBC x 10
A false elevation in a manual hematocrit (microhematocrit) determination may result from
Trapped plasma
Increased MCHC
Spherocytes
Amount hemoglobin in red blood cells
MCH
RDW-CV and RDW-SD provide
Index of distribution of rbc volumes
MCV 55fL
MCHC 25%
MCH 17pg
Microcytic, hypochromic
Calculate MCV
RBC 2.00 × 10^6 uL
HCT. 24%
HGB 6.8 g/dL
Retic 0.8%
MCV = HCT/RBC x 10
24/ 2 × 10=120 fL
MCH formula
HGB/RBC x 10
MCH calculation
HCT 20%
RBC 2.4 × 10^6 uL
HGB 5 g/dL
5/2.4 × 10=20.833 > 21pg
MCHC
HGB/HCT x 100
MCV formula
HCT/RBC x 10
The calculated erythrocyte indices on adult man are
MCV= 89fL
MCH: 29pg
MCHC: 38%
The calculations have been rechecked; erythrocytes on the peripheral blood smear appear normocytic and normochromic with no abnormal forms. The next stop is:
Repeat hemoglobin and hematocrit
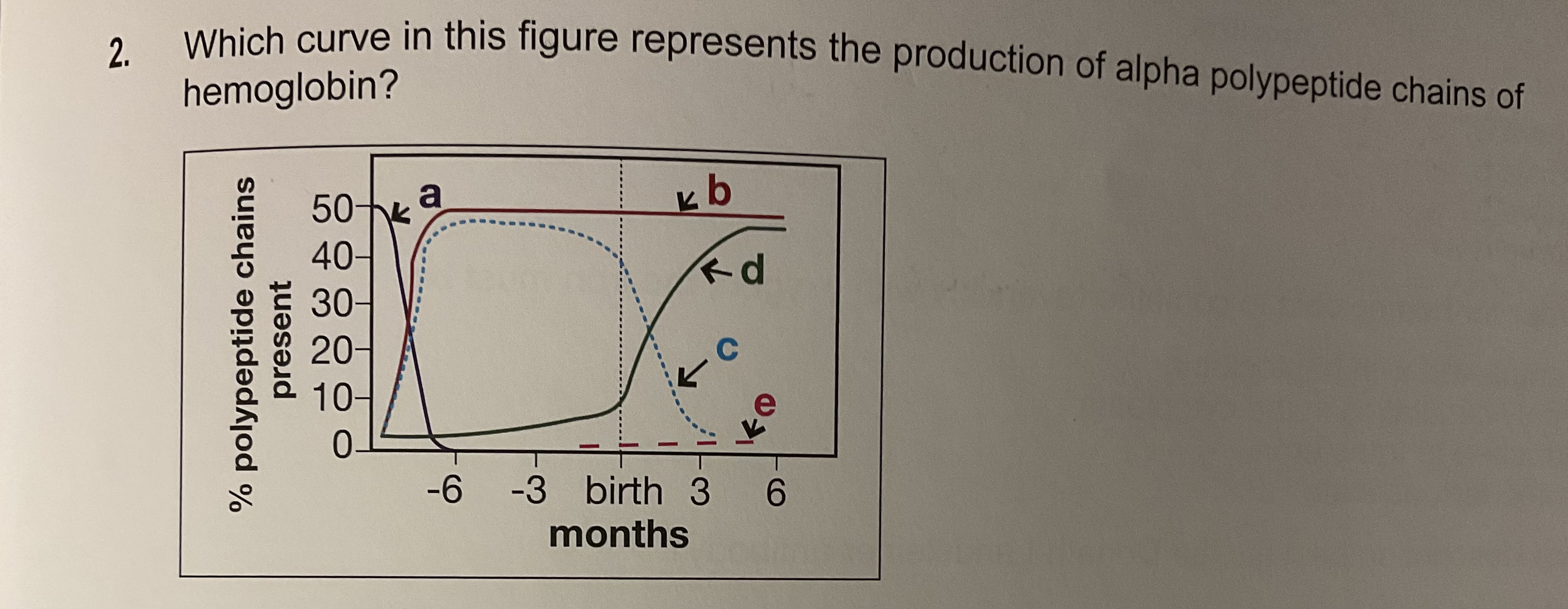
B
Alpha es lo mas que hay en adultos 95-98% y aumenta a medida que creces porque de bebé tienes mas HgF
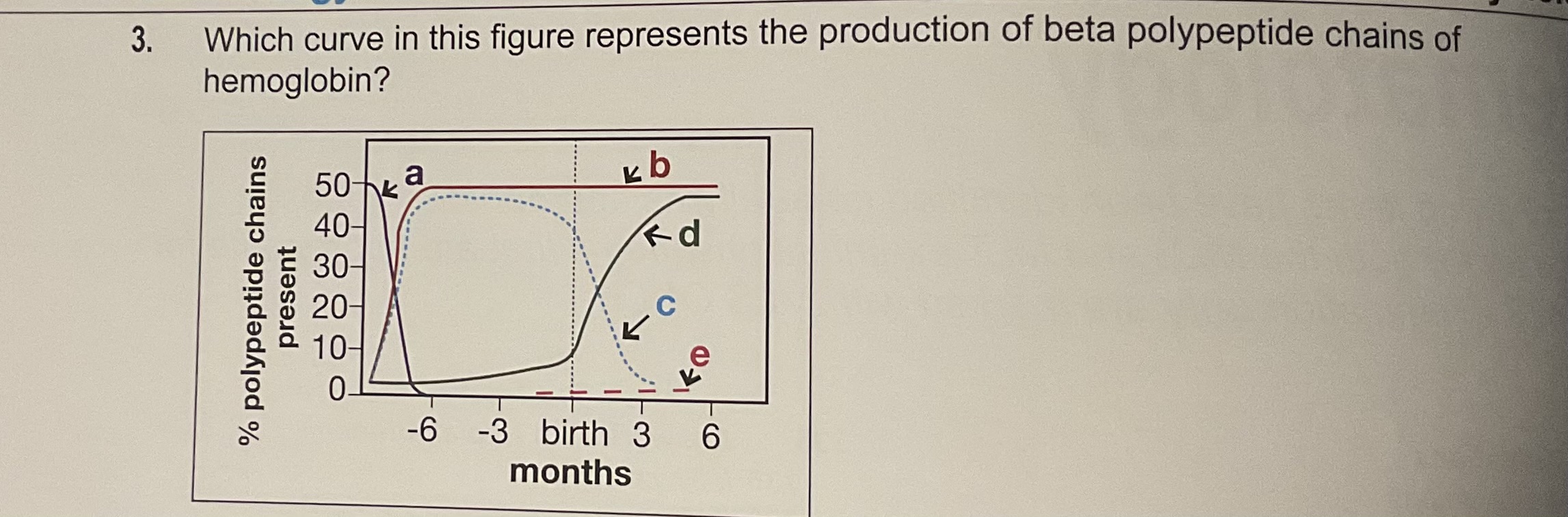
D
Increases after 30 week of gestation so aumenta a medida que uno crece (pensemos)
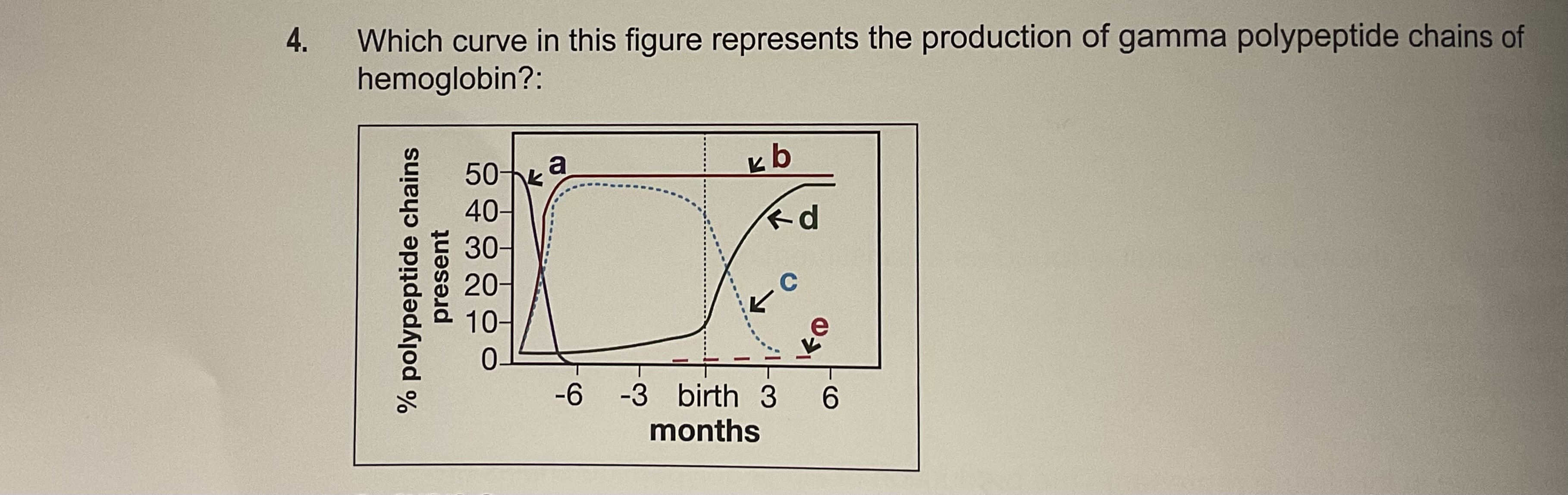
C
Gamma se desarrolla en liver y BM (elevada) y luego va disminuyendo después que naces
Pernicious anemia is
Macrocytic (B12 defiency)
Hemolysis in Paroxymal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) is:
Caused by a red cell membrane
Associated to idiopathic hematomachrosis
Iron overload in tissue
A patient with policytemia vera is most likely to develop deficiency of
Iron
DAT can help to distinguish
Inherited shperocytosis from acquired spherocytosis
Anemia of chronic inflammation is characterized by:
Decreased serum iron levels
Factors common involved in causing anemia in patients with chronic renal disease include:
Inadecuate erythropoiesis
The hypoproliferative red cell population in bone marrow of uremic patients its caused by:
Decreased levels of circulating erythropoietin

Anemia of chronic inflammation
Iron levels decreased
TIBC decreased
Severy hypochromic microcytic anemia patient with history of chronical bleeding.
Which result set would be expected in this case?
Serum iron decreased
TIBC increased
Storage iron decreased
Which is the most closely associated with iron deficiency anemia
Chronic blood loss
Defect in thalassemia:
Quantitative deficiency in RNA result in decreased globin chain production
20 yrs old African American has peripheral blood changes suggesting thalassemia minor. The quantitative A2 level is normal, but the HbF level is 5% (normal <2%) This is most consistent with:
Delta- beta thalassemia minor
TIP» Si es major es 100% HbF
Anemia secondary to uremia and chronic renal disease characteristically is:
Normocytic, normochromic
Laboratory findings consistent with hemolytic anemia:
Increased serum lactate dehydrogenase (L D)
Increased catabolism of heme
Deficiency of this enzyme associated with moderate-severe hemolytic anemia after exposure to certain drugs and with cell inclusions of hemoglobin denature
G6PD
Patient with G6PD deficiency are least likely to have hemolytic episodes in which of the following situations:
Spontaneously
Characteristics of autoimmune hemolytic anemia
DAT +
(abnormal production of antibodies)
Pernicious anemia
Macrocytosis and Pancytopenia
Macrocytosis and pancytopenia
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Folic acid deficincy anemia characteristic:
Macrocytic
Megaloblastic asynchronous development in bone marrow indicates:
Impaired DNA synthesis
Associated with megaloblastic anemia
Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia
Characteristic features of iron metabolism in patients with anemia of chronic inflammation
Serum iron decreased
Transferrin saturation decreased
TIBC normal or decreased
Characteristic of morphologic feature of Hemoglobin C
Target cells
Thalassemia are characterized by:
Deceased rate of globin chains

Thalassemia minor
Laboratory findings in hereditary spherocytosis:
Decreased RBC band 3 protein
Which of the types of policytemia vera a severly burned patient most likelt have:
Relative polycythemia associated with dehydration
Lead poisoning
Basophilic stippling
Pernicious anemia white blood cell feature
Hypersegmentation
Parameter abnormal in hereditary spherocytosis
MCHC
Protein defective in hereditary elliptocytosis
Spectrin
Most common mechanism in hereditary stomatocytosus
Abnormal Na/K permeability
Basic mechanism associated with sideroblastic anemia:
Enzymatic defect in heme synthesis causes iron accumulation
Individuals with Fanconi anemia characteristically show:
Increased HbF
Fanconi is a autosomal recessive disorder of normocytic anemia
Features: short stature, microcephaly, and hyperpigmentation
Abnormal rcb morphonoly in Pyruvate Kynase Deficiency
Echinocytes (Burr cells)
Hemoglobin D y G
Ambas migran con HbS en alkaline gel
Hemoglobinopathiy results from delta and beta gene
HbLepore
Consistent with heterozygous beta thalassemia
Increased red blood cell count
Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoblogin HPFH is due to a loss of expression of globin chain:
Gamma
Anti-I
Cold agglutinin disease
Most common presentation of paroxymal cold hemoglobinuria
Children with viral illnes
Anemia of hospitalized patients
Anemia of chronic inflammation
Increased red cell mas into 99 percentile
Serum erythropoeitin level below range
Which of following criteria confirm a diagnosis of polycytemia vera?
JAK2 V617F mutation
Spherocytes and policromasia
HDN and ABO incompatibility
Polycytemia vera M:E ratio
4:1
A patient has a tumor that concentrates erythropoietin. He most likely to have which of the following types of polycytemia?
Polycytemia associated with renal disease
Which type of polycythemia is most often associated with lung disease
Polycythemia, secondary to hypoxia
How does BM respond to anemic distress
Expand production, release RBC prematurely
Which of following conditions contribute lethargy, abdominal pain and hemoglobinuria in G6PD deficiency patients
Ingesting fava beans
The most likely cause of macrocytes that accompanies primary myelofibrosis is:
Folid acid deficiency
Giant, vacuoled, multinucleated erythroid precursors are present in which following:
Erythroleukemia
Significant feature in dyserythropoiesis
Megaloblastoid erythropoiesis
M: E ratio in erythroleukemia
Low
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia is a complication of:
CLL
Total granulocyte count 7.5 × 10³ uL is termed:
Absolute neutrophilic leukocytosis
Elevation of total white blood cells count above 11.0 × 10³ uL is termed:
Leukocytosis
Elevation of lymphocyte percentage above 45% is termed:
Relative lymphocytosis
Relative are %
Absolute are numbers
The mechanism causing catecholamine- induced neutrophilia includes:
A shift in granulocytes from the marginating pool to the circulating pool
What accounts for the smudge cells in CLL
Artifact due to fragile cells
M:E ratio in chronic myelocytic leukemia
Variable

Infectious mononucleosis
Abnormalities in erythroleukemia
Megaloblastoid development
Neutropenia is associated with:
Viral infection
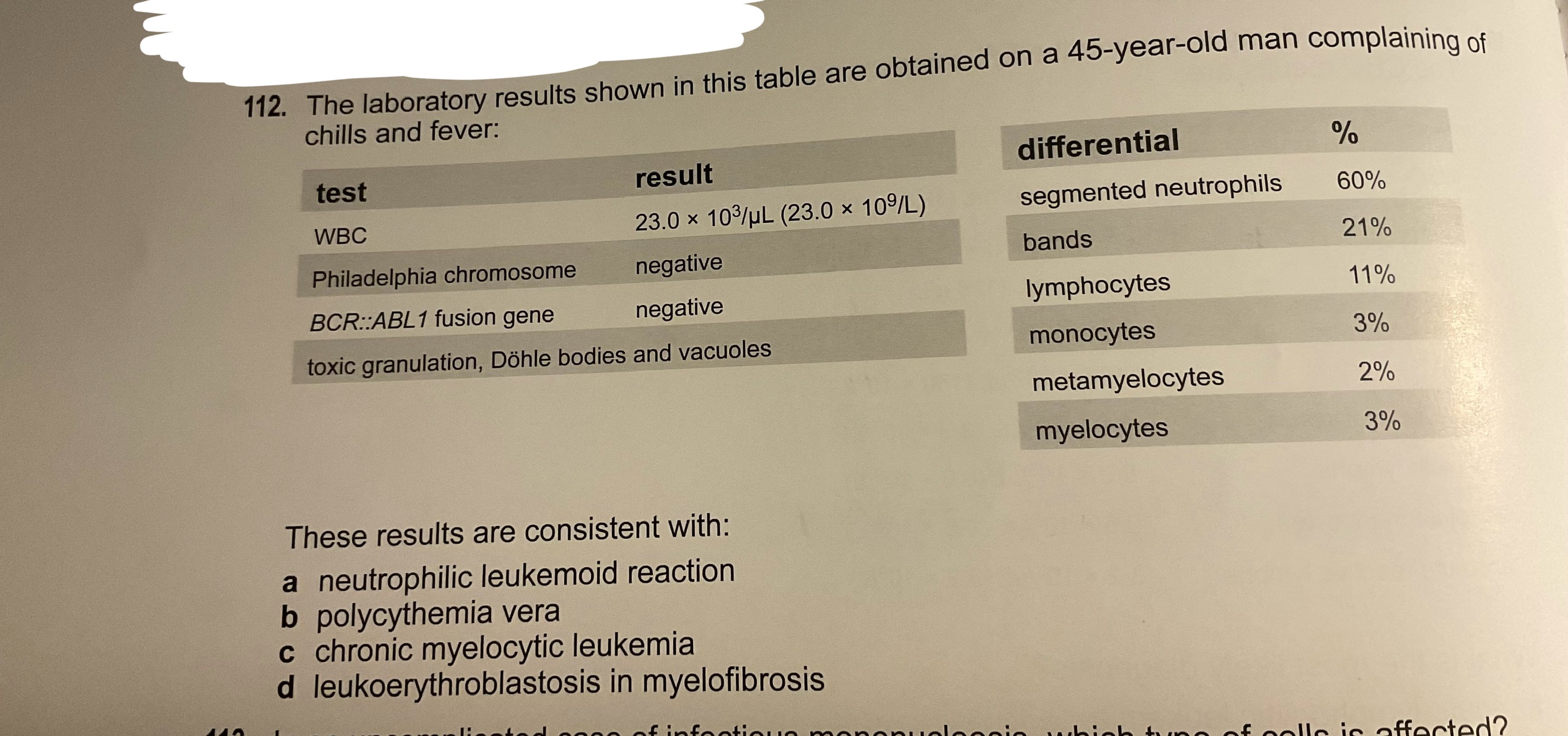
Neutrophilic Leukemoid reaction
Dwarf micromegakaryocytes may found in the peripheral blood of patients with:
Primary myelofibrosis
Pseudo pelger huët anomaly associated with:
Chronic myeloid leukemia
High levels of basohips are seen in which leukemia
CML
Hypercellular Bone Marrow with an M:E 6:1 is most commonly due to :
Granulocytic hyperplasia

Primary myelofibrosis