Fichas de aprendizaje Klausur CPS | Quizlet
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Agent Based modeling bottom up diagram
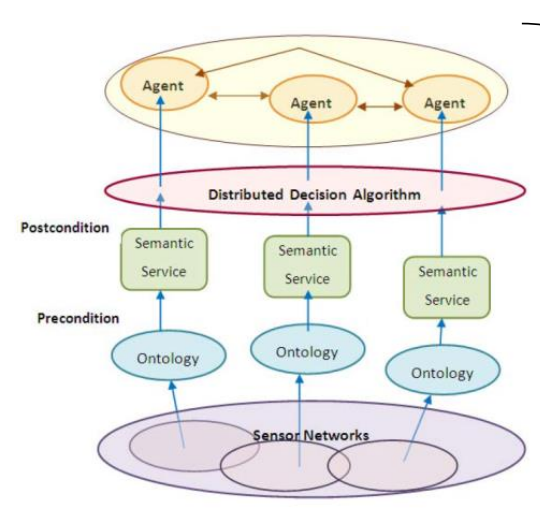
Name the software aproach for concurrency and predictability
PTIDES: Programming Temporally Integrated Distributted Embedded Systems
What is PTIDES for
Alternative programming model that structures real time softwares as an interconnection of actor communicating using timestamped events.
Characteristics of PTIDES programming
- Global distributed time model
- Coherent global temporal semantics
- Actor based communication
- Integration of technical system regarding real time
- Validation of satisfactory of temporal semantics
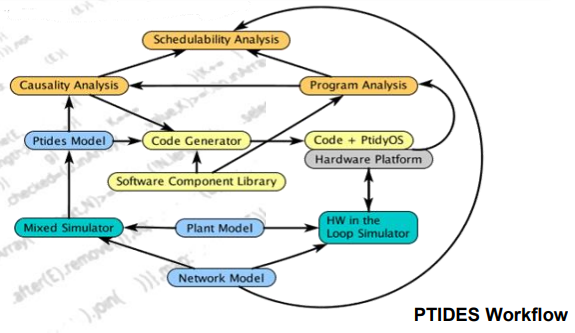
Describe PTIDES workflow map
Concurrency and time predictability hardware approach:
PTARM
What does PTARM stand for
Precision Timed ARM
What is PTARM
is a realization of Precision Timed (PRET) machines that provides timing predicatbility and composability without sacrificing performance.
PTIDES is the programming model
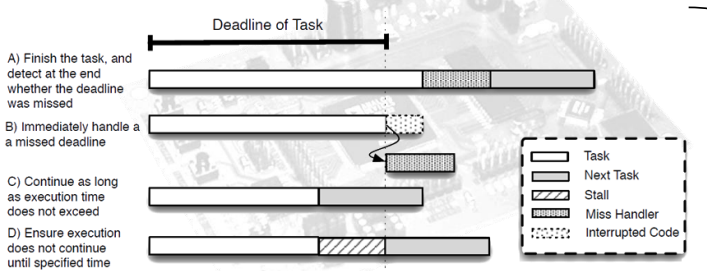
Describe PTARM diagram
How is Heterogeneity in CPS represented
- CPS have to adapt to new, unknown situations from different domains
- Dynamic changing paticipants and environments require a flexible communication
What is the response of CPS to Heterogeneity
They go from adaptability to transformability through a Semantic Gap
What does Semantic interoperability do?
Packages the data (syntax) and simultaneously transmits its meaning (semantics)
What does GUT stand for (Communication and Interoperability top down approach)
Grand Unified Theory
What is GUT about
developing a modeling language and conceptual frameworks into which heterogeneous modeling languages and frameworks can be translated.
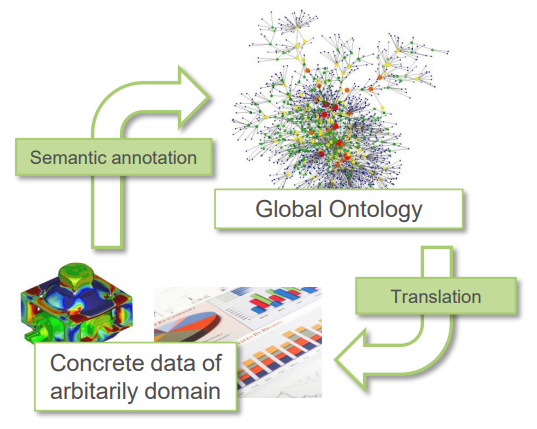
Describe the GUT diagram
Describe the CL/NLP diagram
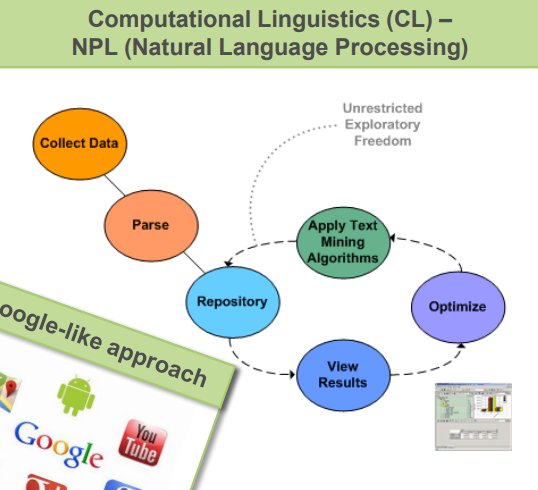
What does CL/NLP stand for?
Computationial Linguistics - Natural Language Processing
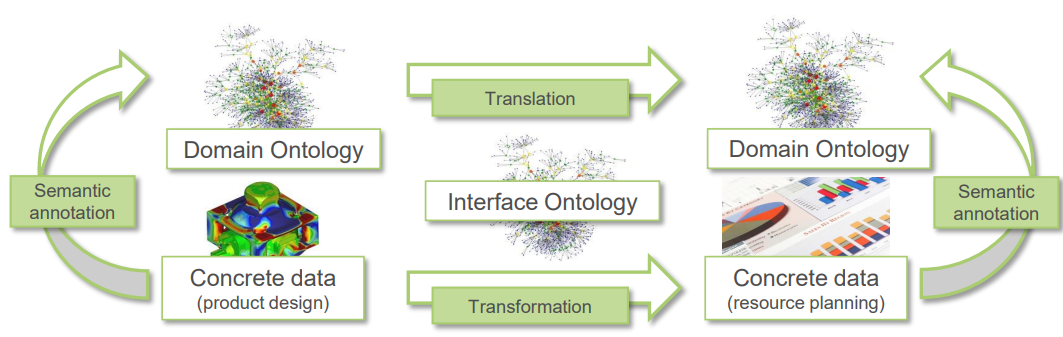
What is Abstract semantics about
developing interaces between heterogeneous modeling languages
Describe the Abstract Semantics for domains and Translations diagram
Define CPS as an engineering diescipline
A discipline focused on technology with foundation in mathematical abstractions to cojoin them for modeling physical processes.
Name the 8 fields of CPS (diagram)
- Hybrid models
- Wireless Sensing and Actuation
- Validation and Verification
- Application of CPS
- Scalability and complexity management
- Cyber Security
- Control Systems
- Concurrency. Communication and Interoperability
What is interoperability
Ability of two or more systems or components to exchange information and use the information that has been exchanged.
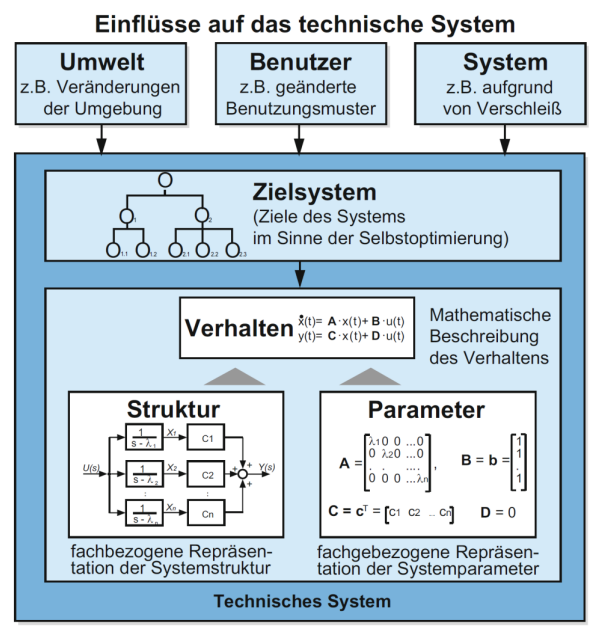
Define Selbstoptimierende Systeme
Endogenous adaptation of system's goals to changing influences and rule based autonomous adaptation of the parameters.
They inherit independently reactive intelligence and flexible adaptation to changing operatinig conditions.
How is the Aspekte eines Selbstoptimierenden Systems diagram like
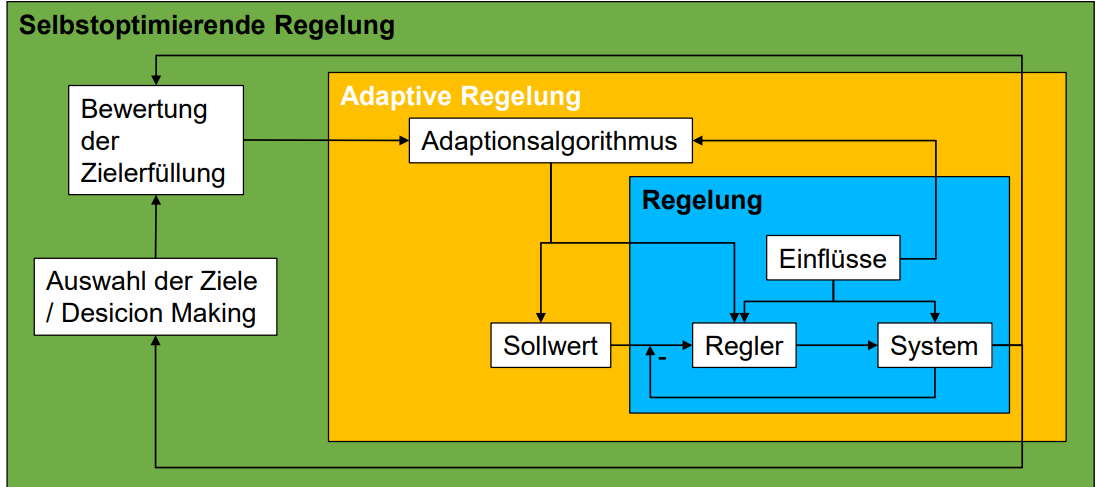
How is the Adaptive Regelung diagram like
Expansion of closed loop and adaptive controls to self-optimizing controls
What is Interdisziplinäre Produktentwicklung about?
End-to-end, distributed, interdisciplinary process support, integration across product life cycle, domains and supply chain based on virtual models.
What are the three axes of Interdisziplinäre Produktentwicklung?
Cross Domain, Produktlebenszyklus (integriert) and förderiert
What are the components of the Cross Domain axis on Interdisziplinäre Produktentwicklung?
Dienstleistungen (Services)
Software
Elektronik
Mechanik
What are the 7 components of the Produktlebenszyklus axis on Interdisziplinäre Produktentwicklung?
Anforderungsdefinition (Definitino of requirements)
Produktplanung
Entwicklung
Prozessplanung
Produktion
Betrieb (Operation)
Recycling
What is the component of the förderiert axis on Interdisziplinäre Produktentwicklung?
Lieferkette Verschiedene Unternehmen/Standorte
Supply chain on various companies/locations
Describe the Interdisziplinäre Produktentwicklung chart
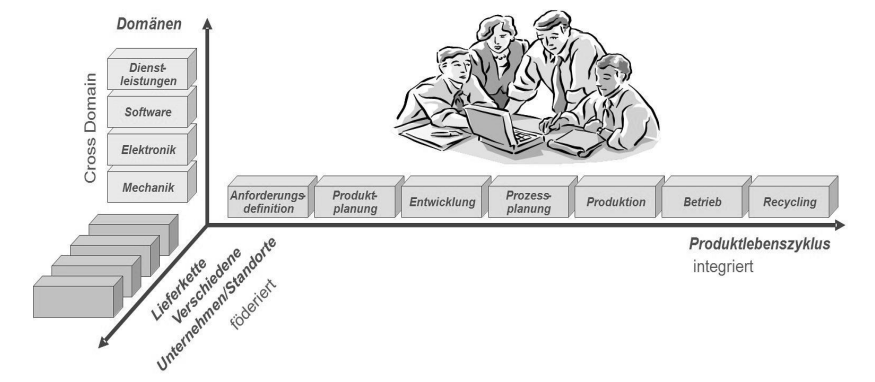
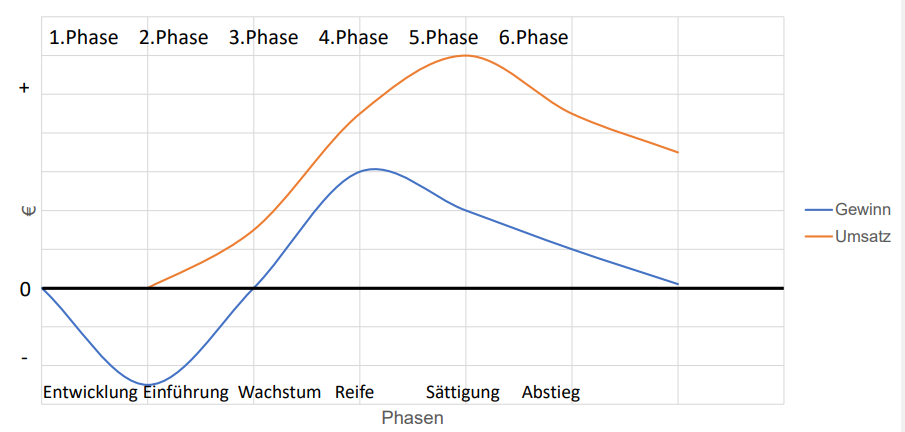
How many phases does the Produktlebenszyklus has?
Name them
6:
Entwicklung
Einführung (Implementation)
Wachstum (Growth)
Reife (Maturity)
Sättigung (Satiation)
Abstieg (Descence)
Describe the Produktlebenszyklus Phasen chart
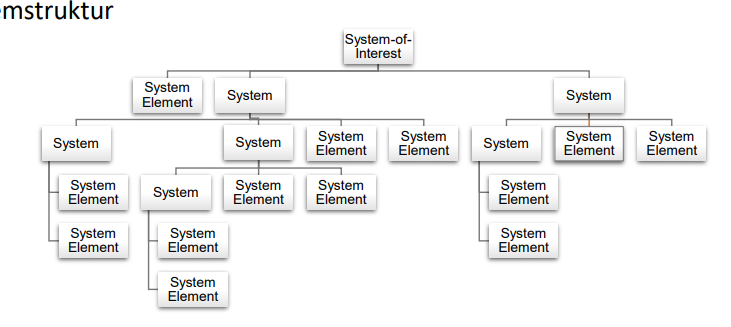
Describe the Systemstruktur of the System of interest based on several integrating systems
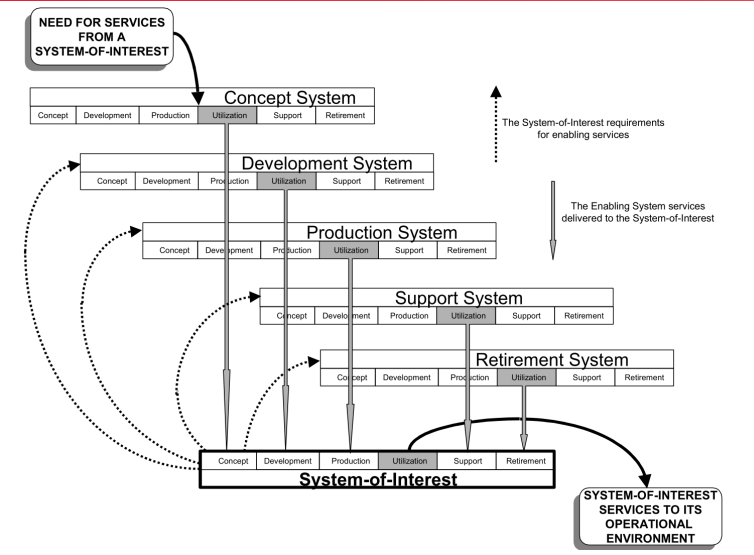
Systems Engineering Diagram
What are the three basic principles that determine the systematic approach to product development
Strukturierung in Phasen
Von Groben zum Detail (from rough to detailed)
Problemlösezyklus (Problem solving cycle)
What are the steps of Evaluation and selection of product development
Stufe:
Qualitative rough evalutaion based on experience
Qualitative fine evaluation based on rough research
Quantitative evaluation based on extensive detailed research
What are the expected times for each Step of the product development process.
Stufe 1: Direkt nach der Ideenfindung
Stufe 2: nach ca 2 Wochen
Stufe 3: innerhalb von 3 bis 6 Monaten
Describe the selection process of the product development process

What does SMSDA stand for
Smart Manufacturing Systems Design and Analysis
What are the four fields of SMSDA
Modellierungsmethoden zur Analyse von Fertigungssystemen
Predictive Analytics
Performance measurement für Fertigungssystemen
Service-based manufacturing and service composition
What are the three domains of the development of analytical skills by linking domain-specific viewpoints and what are they based on.
Domänen:
Domänen Ontologie
n - Viewpoints
Problem Domäne
Problem formulation Metamodel
Objective Model
Analytische technische Domäne
Tool Metamodel
Analytical Capability
Describe the development of analytical skills by linkin domain-specific viewpoints structure
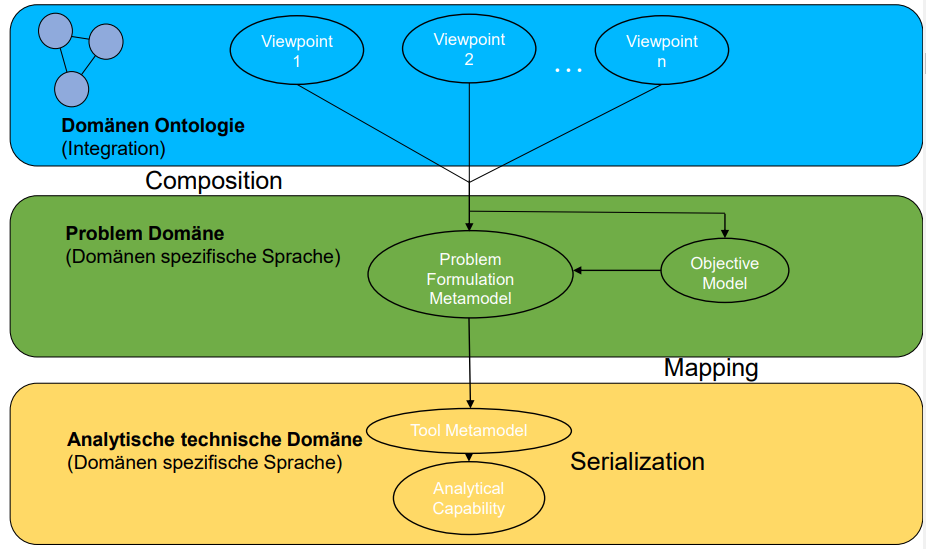
What are the questions of the performance measurement for smart manufacturing
Welche Metriken werden verwendet, um eine bestimmte Leistung zu charakterisieren?
Wie quantifiziert man diese Metrik mit realisierbaren Messungen?
What does Sustainability in Production mean? (3)
Environmentally friendly processes
conserving energy and natural resources
Economically healthy and safe for employees, communities and consumers
Why is sustainably production a challenge?
The reduction of resource consumption and environmental impact must be weighed against other factors such as punctuality, quality, productivity and costs.
What are the approaches on sustaiable processes?
ASTM E60.13 Stadard Guide for Evaluation of Sustainability of Manufacturing Processes
ASTM E60.13 Guide for Characterizing Environmental Aspects of Manufacturing Processes
Standardizes the methods for characterizing the performance of manufacturing processes as building blocks for system analysis with a special focus on sustainability assesment
What does SMOPAC stand for?
Smart Manufacturing Operations Planning and Control
What are the key research areas that SMOPAC is based on:
Digital Thread
System analysis integration
Wireless Systems
Cybersecurity
Prognosis, maintenance and control
What is the digital thread of SMOPAC based on?
Explain the diagram
Design
Analysis
Fabrication
Inspection
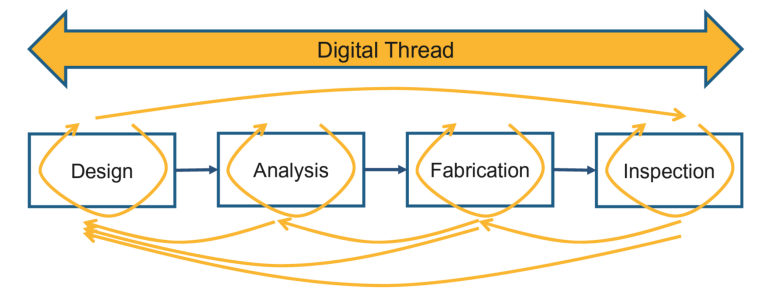
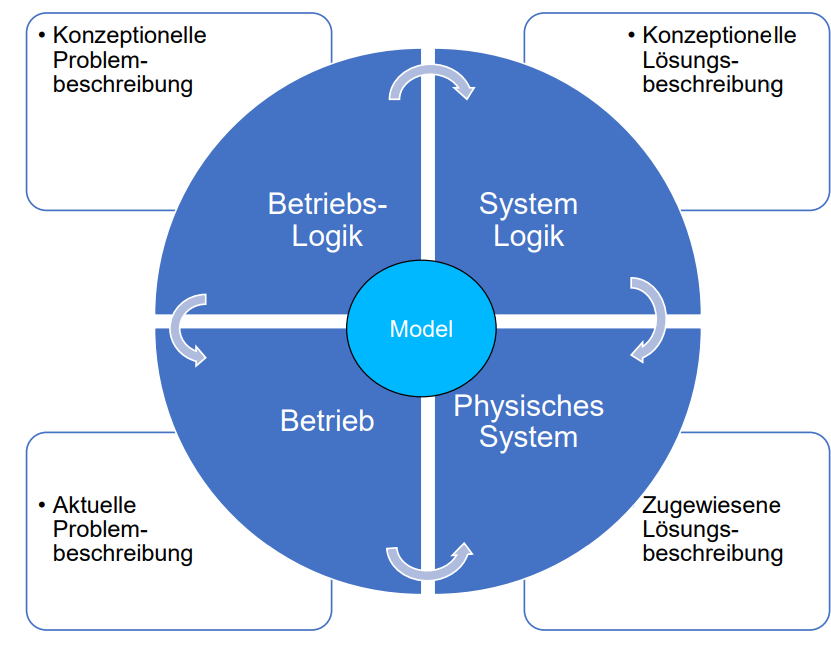
What are the 4 basis of Model based Engineering:
System Logic
Betrieb
Betriebs Logik
Physisches System
What are the Model-Based Engineering fields based on?
Betriebs-logik:
Description of conceptual problems
System Logik
Description of conceptual solutions
Physisches System
Assigned solution description
Betrieb
Description of the actual problem
Describe the Model- Based Engineering chart
Describe the model based engineering of supervisory controllers diagram
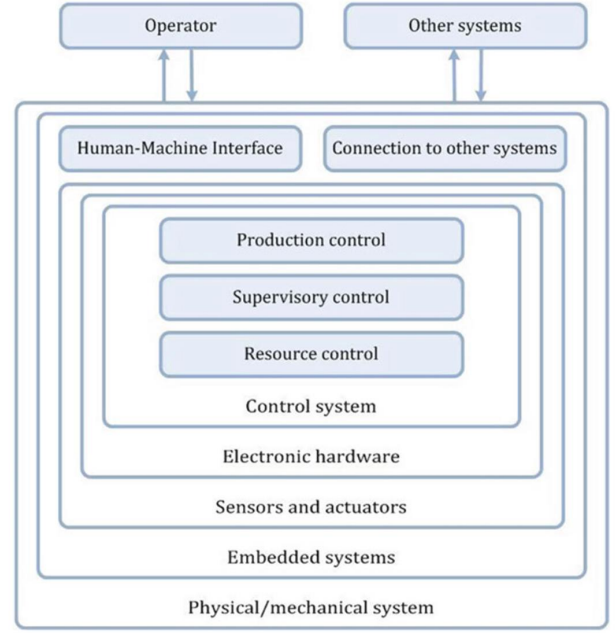
Describe the design process (Entwurfsablauf) of model based engineering
Develop hybrid automaton models of system components
The uncontrolled discrete event system can be abstracted from the uncontrolled hybrid system
Requirements models are then defined in the form of extended finite automata or state-based expressions
Simulation and simulation-based visualization can be used to validate the higher-level control system against the uncontrolled hybrid system
The higher-level controller together with the unregulated discrete-event system, known as the controlled system, can be subjected to verification.
Observer-based monitoring can be derived from the higher-level control system and the hybrid observer
In addition, the supervisory controller model can be used for model-based testing.
Describe the Valuation model (Bewertungsmodell) for Cyber Physical Production Systems
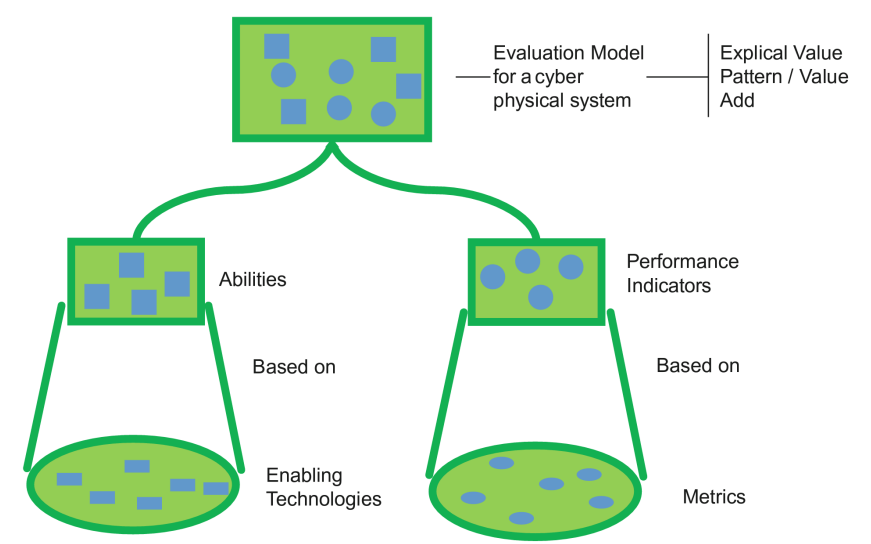
Describe the Categories and Capabilities of IOT diagram

What are the 4 IT Integration capabilities when it comes to I4.0 Components?
Can be used as an entity
individually known
anonymously known
unknown
How are the I4.0 components classified?
Can be used as entities
individually known
Describe the Klassifikation von I4.0 Komponenten diagram
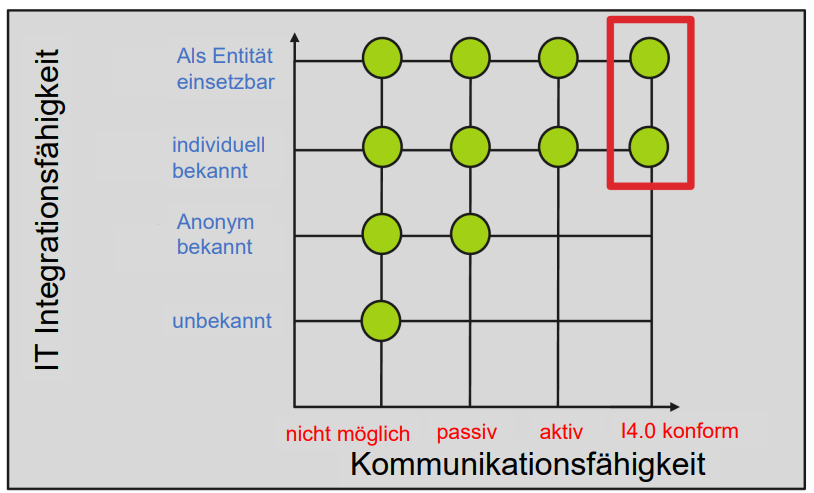
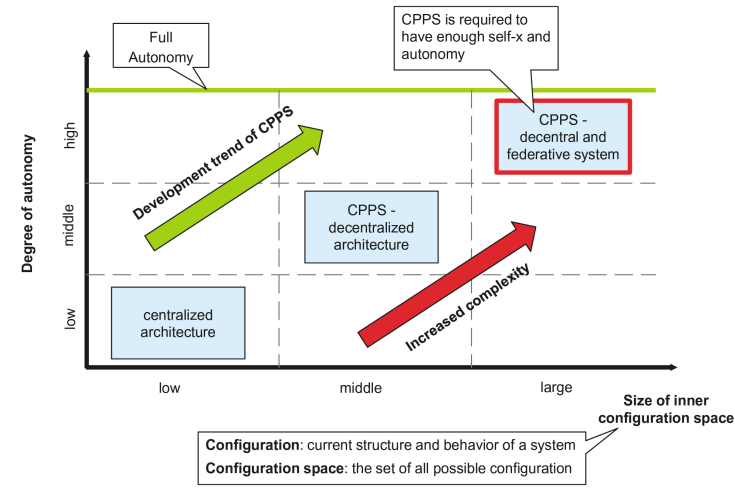
What does CPPS stand for?
Cyber Physical Prooduction Systems
What are the 3 Autonomy configurations
Centralized Architecture
CPPS - decentralized arrchitecture
CPPS - decentralized architeccture and federative system
Describe Autonomy and Configuration Space diagram (Complexity)
What aspects of a CPPS are part of the characteristics of overall system architecture?
Modularity
Complexity
Usability
What aspects of a CPPS are part of the characteristics of production operation?
Maintainability
Production Efficiency
Automatic Adaption
What aspects of a CPPS are part of the characteristics of Cyber Support?
Social interaction
Support of Decisions
What aspects of a CPPS are part of the characteristics of Changing Production Systems?
Automatic Planning
Reconfigurability
Describe the IIOT Characteristics diagram
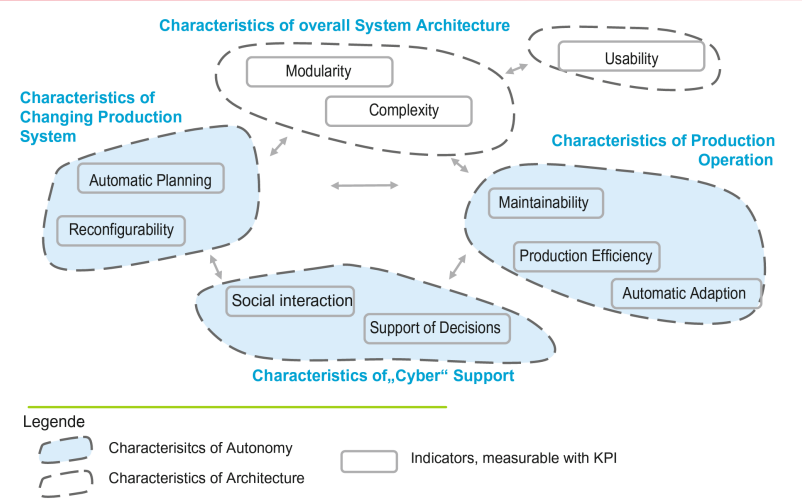
How are modularity, complexity and usability as characteristics of the overall system architecture of a CPS
Usability: of user-friendliness, it is linked to the system architectures
The characteristics of the changing production system are indicated by automatic planning as a reconfigurability indicator
Social interaction and decision support as special cyber indicators
The production operation is characterized by performance indicators, which are maintainability, production efficiency and automatic adaptation
Describe the Business Intelligence diagram
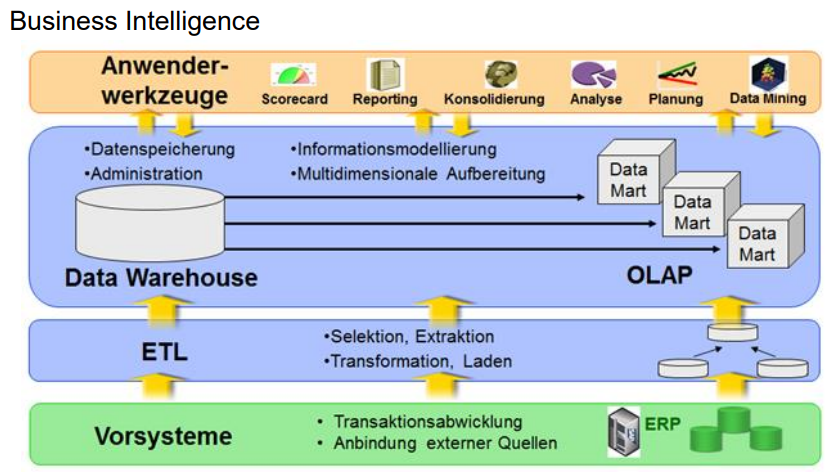
How many steps does the BI Process (Business Intelligence) have?
5
What are the BI Process Steps?
Data as source systems integrated and loaded into data warehouse or analysis repository.
Data sets organized in data models or OLAP blocks to prepare them for analysis
Analytics experts and business users run analytical queries against the data.
Query results integrated into data visualizations, dashboards, reports and online portals.
Decision Making and Strategic Planning based on the data.
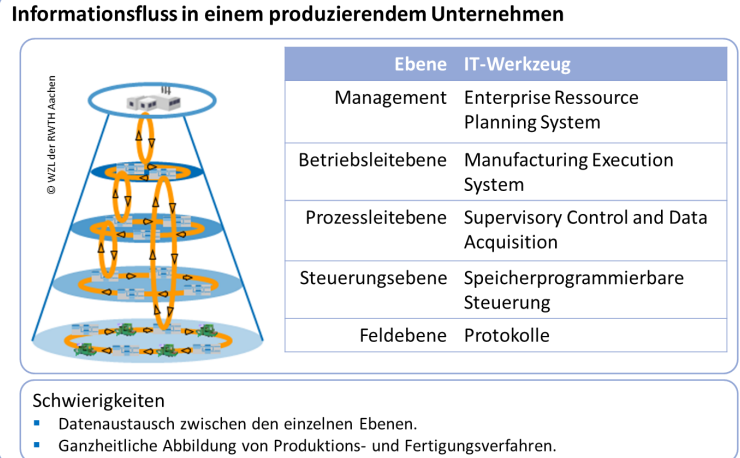
What are the levels through which the information flows in a producing Organization?
Management
Betriebsleitebene (Operating level)
Prozessleitebene (Process contol level)
Steuerungsebene (Control level)
Feldebene (Field level)
Which are the IT Tools each of the levels of information flow in a producing Organization use.
Management - Enterprise Ressource, Planning System
Operating Level - Manufacturing Excecution System
Process Control level - Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
Control level - Programmable Logic Controller
Field Level - Protocols
What are the difficulties of the information flow in a producing Organization?
Data Exchange between each level
Full-time mapping of production and manufacturing processes
Describe the graph of Informationsfluss in einem produzierendem Unternehmen.
What is EAI?
The process-oriented integration of application systems in heterogeneous IT application architectures
Keywords:
Process-oriented
Integration
application systems
heterogeneous application architectures
What does EII stand for?
Enterprise Information Integration
What is EII good for?
Integration of Data from different sources
Data consolidation
Data fusion
Data cleansing
ETL Process
What is BI good for?
Overall view of data
Monitoring and Reporting
Data Mining
When should EAI be active in comparison with EII and BI
During the data production process, afterwards EII and BI start
How is Autonomy defined as?
Freedom to restrict structure and access options to data or methods
What are the high levels of Autonomy in Cross Company systems?
Design autonomy
Interface autonomy
Access autonomy
Communication autonomy
How are the high levels of autonomy in cross company systems defined as?
Design autonomy - Free decisions about data format, model and schema
Interface autonomy - Freedom in the choice of technical access method
Access autonomy - Freedom via user rights
Communication autonomy - Free decision whether and when a request is answered
How is the distribution (Verteilung) of the Autonomy?
Physical distribution oof application or data source.
What are the types of Heterogenität Probleme in the integration?
Technical
Syntactic
Structural
Semantic
Define the types of Heterogenität Probleme in the integration of CPS
Technical - Differences in the ability to access data or applications
Syntactic - Differences in the technical presentation of information
Structural - Differences in the structural representation of information
Semantic - Differences in the meaning of terms and concepts used
Explain the Data level of integration methods
The data level is an event-driven exchange of data between different databases or other data stores
Explain the Data level of integration methods diagram

Explain the Application Interface Level of integration methods
Connection of in-house developments or standard applications based on existing interfaces (API) without manual intervention

Explain the Method Level of integration methods
Calling distributed methods for the use of business logic
Explain the User Interface Level of integration methods
The data is accessed from the user masks
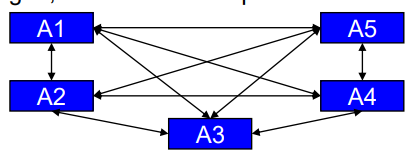
Explain the Peer-to-Peer integration topology
Decentralized message brokers receive, send and interpret messages
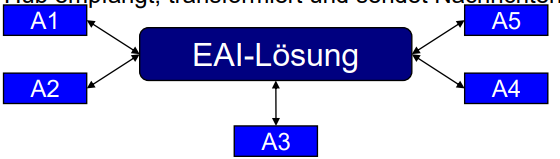
Explain the Hub-and-Spoke Integration topology
Central hub receives, transforms and sends messages
Explain the Bus/Pipeline/Publish and Subscribe Integration topology
Server Centric Topology
Messages shared through Bus system to which the software components are connected.
Boradcasting is possible
What does ESB stand for
Enterprise Service Bus
Name the EAI Components
Metadatabase
Middleware (Intermediary Software)
Adapter
Messages management
Process management
Describe the Functions of the Middleware as an EAI Component
Management of adapters for integration at data level
Management of resources and provision of additional services
Describe the funcitons of the Adapter as an EAI Component
Connecting the application and middleware
Differentiate static and dynamic adapters
Overcoming syntactic and structural heterogeneity
Describe the functions of the Metadata Dank as an EAI Component
Centralized storage of component distribution, security parameters and responsibilities, technological infrastructure, alignment schemes, transformation information, rules and logic for message processing, design and architectural information