World History Mid-Term Study Guide
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Renaissance
"rebirth"; a movement that centered on the revival of interest in the classical learning of Greece and Rome

Protestant Reformation
A religious movement of the 16th century that began as an attempt to reform the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the creation of Protestant churches.

Indulgences
Selling of forgiveness by the Catholic Church. The practice led to the Reformation.

Counter Reformation
Catholic Church's attempt to stop the protestant movement and to strengthen the Catholic Church

Martin Luther
German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church. He wrote 95 theses.

John Calvin
religious reformer who believed in predestination and a strict sense of morality for society. Created the Calvinist (protestant) church.

Divine Right
Belief that a monarchs/ rulers authority comes directly from god.

Absolute Monarchy
A government in which the king or queen has absolute power

Restoration
the re-establishment (bringing back/ restoring) of the British monarchy

Constitutional Monarchy
A system of governing in which the monarch's power is limited by law or parliament

Czar
A Russian emperor/ king
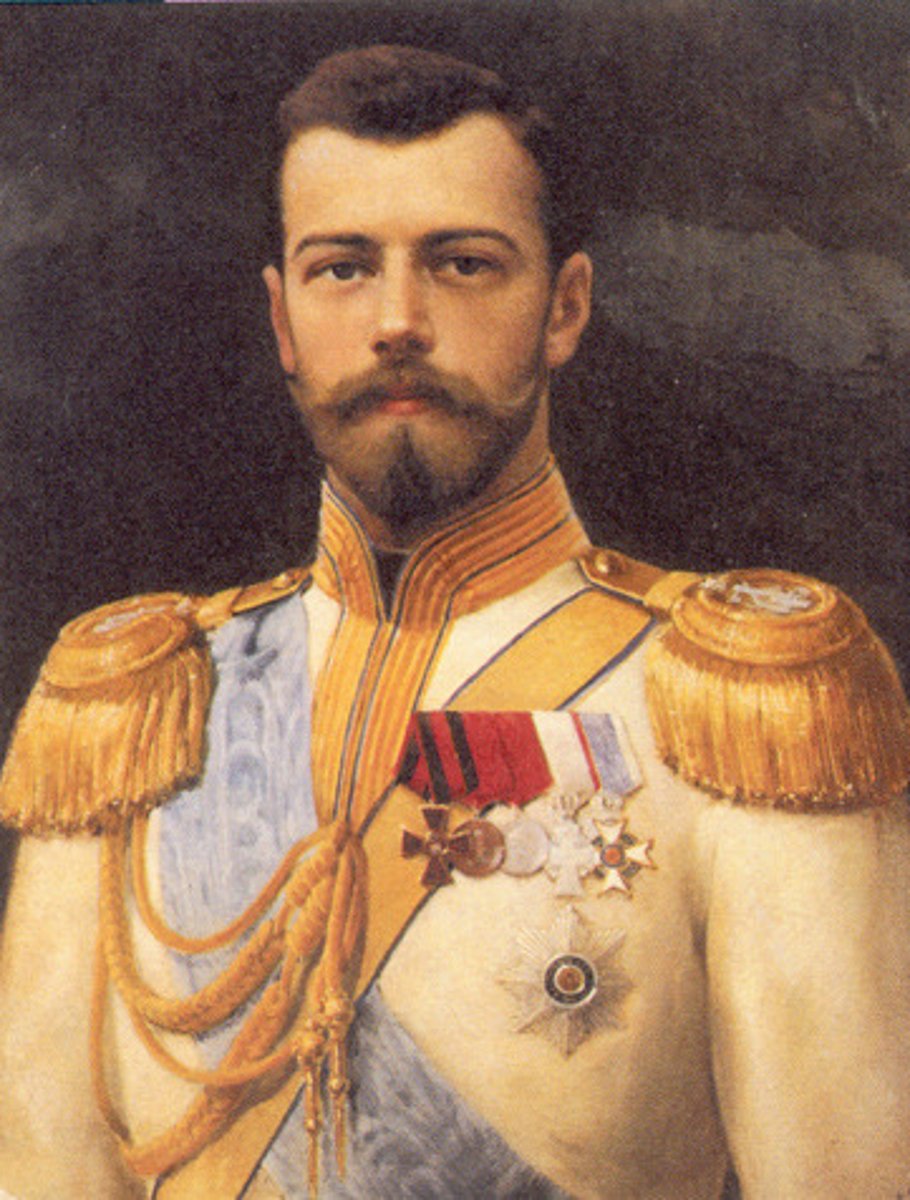

Philip II (2)
King of Spain who helped lead the Counter Reformation by persecuting Protestants in his holdings. Also sent the Spanish Armada against England.
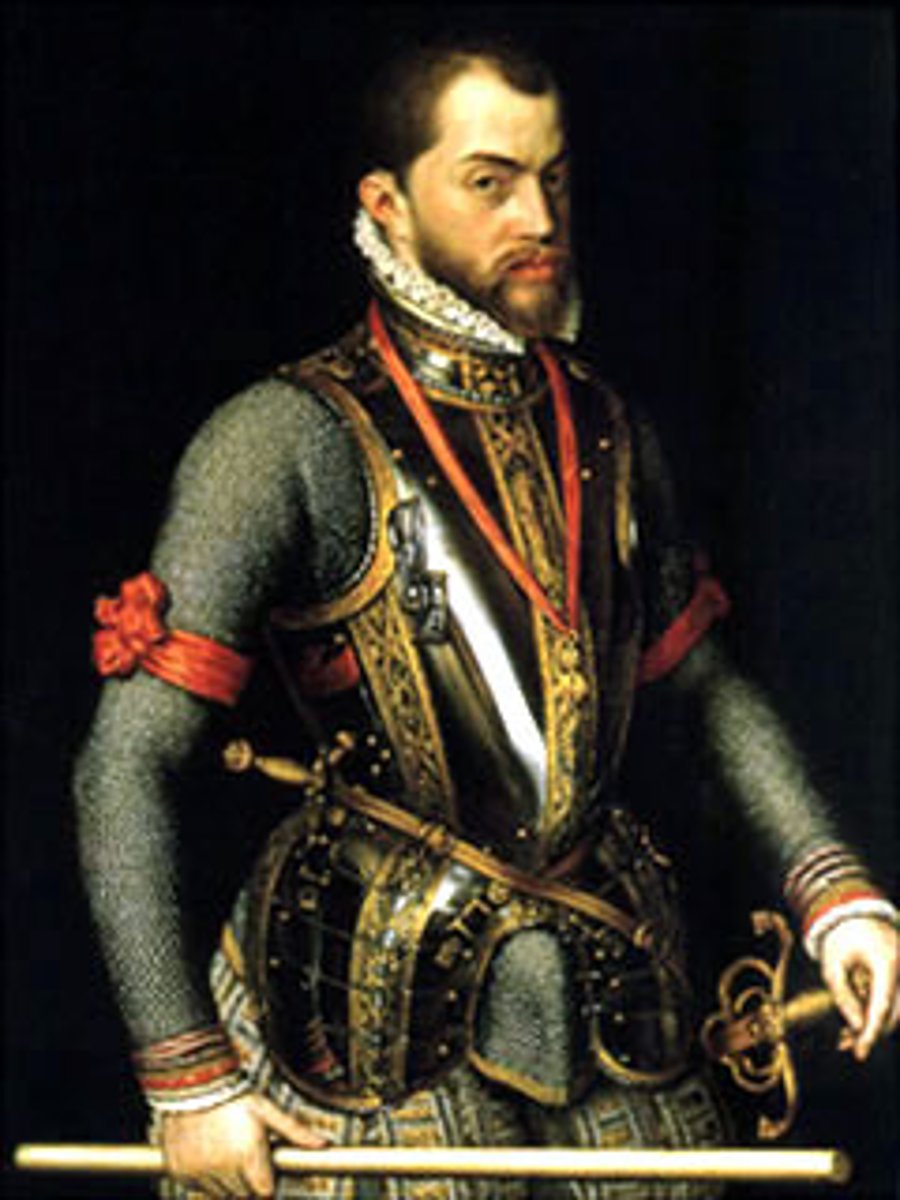

Louis XIV (14)
Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France. He built the palace at Versailles.
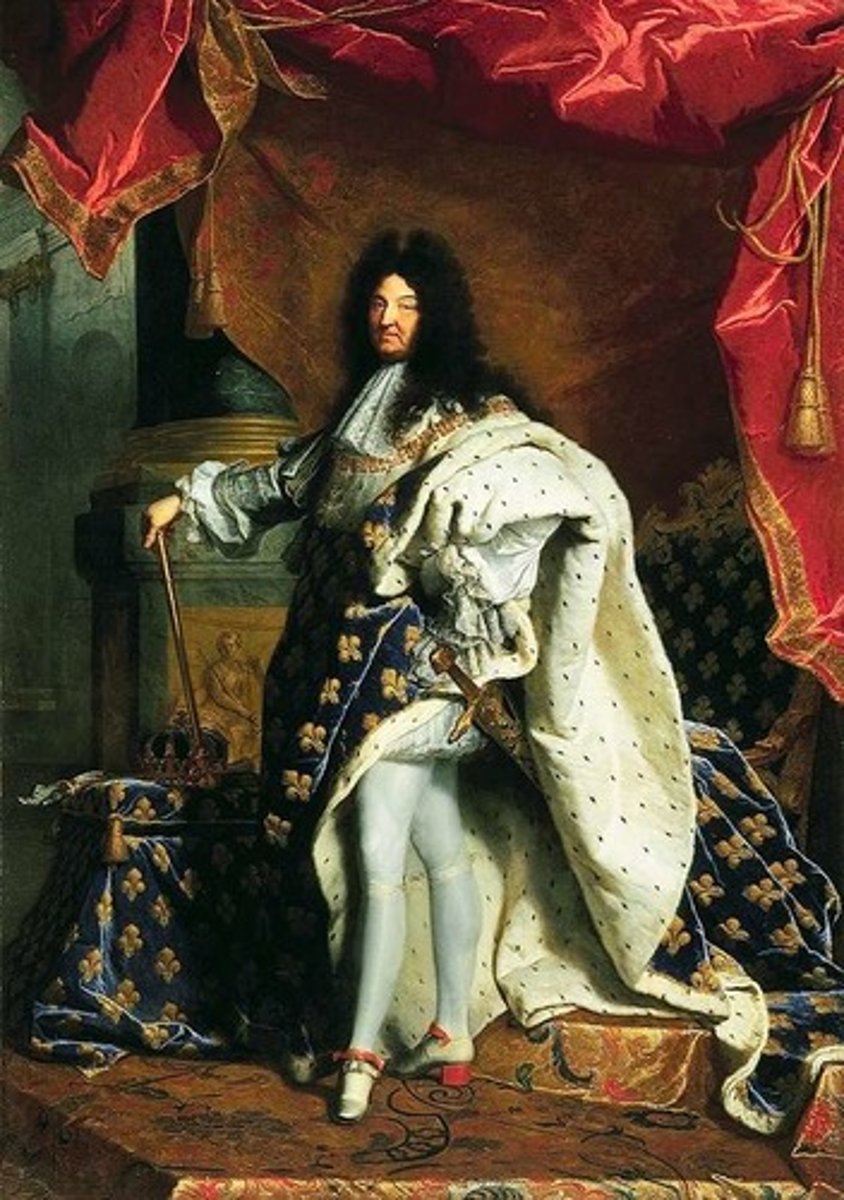

Charles I (1)
son of James I who was King of England and Scotland and Ireland
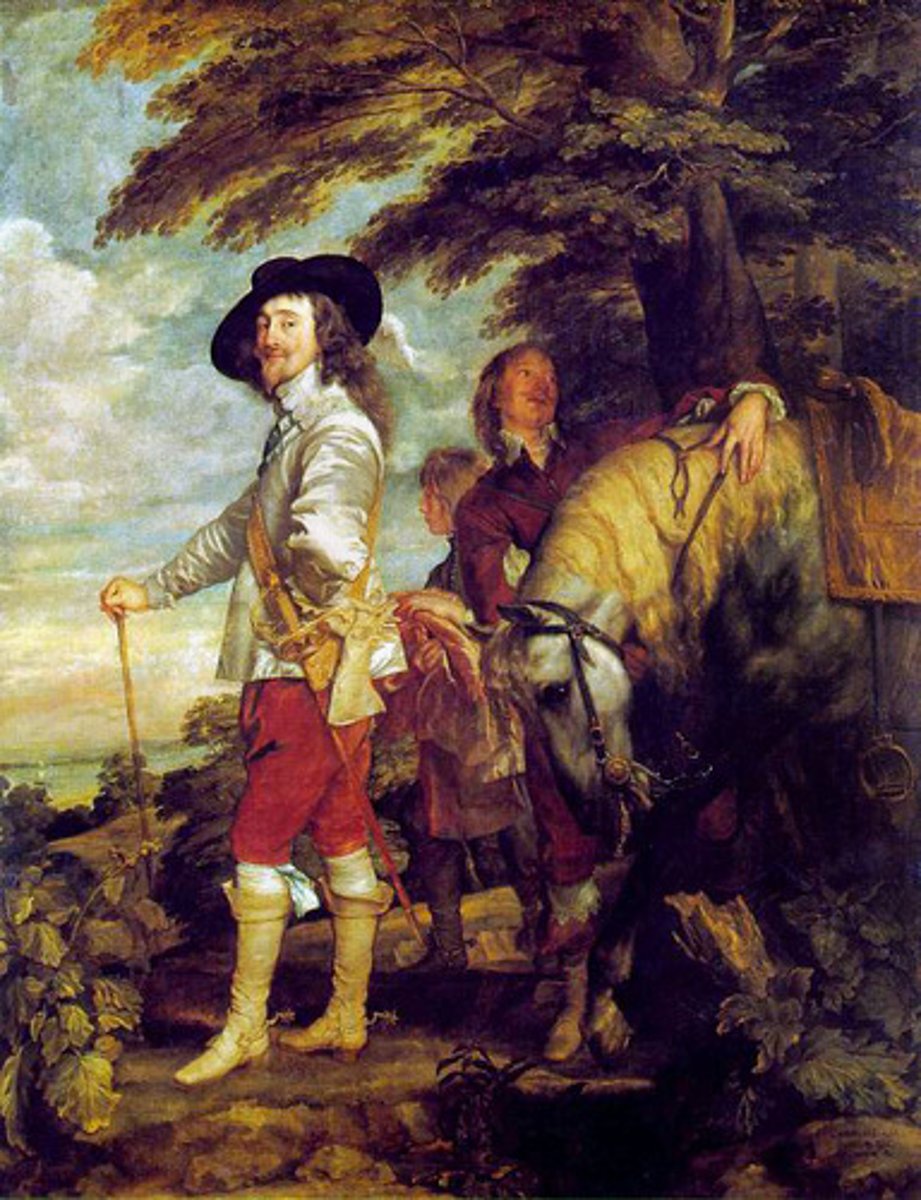

Peter the Great
Czar of Russia that Westernized Russia and built up a massive Russian army.

Catherine the Great
Empress of Russia who greatly increased the territory of the empire

Scientific Revolution
The series of events that led to the birth of modern science

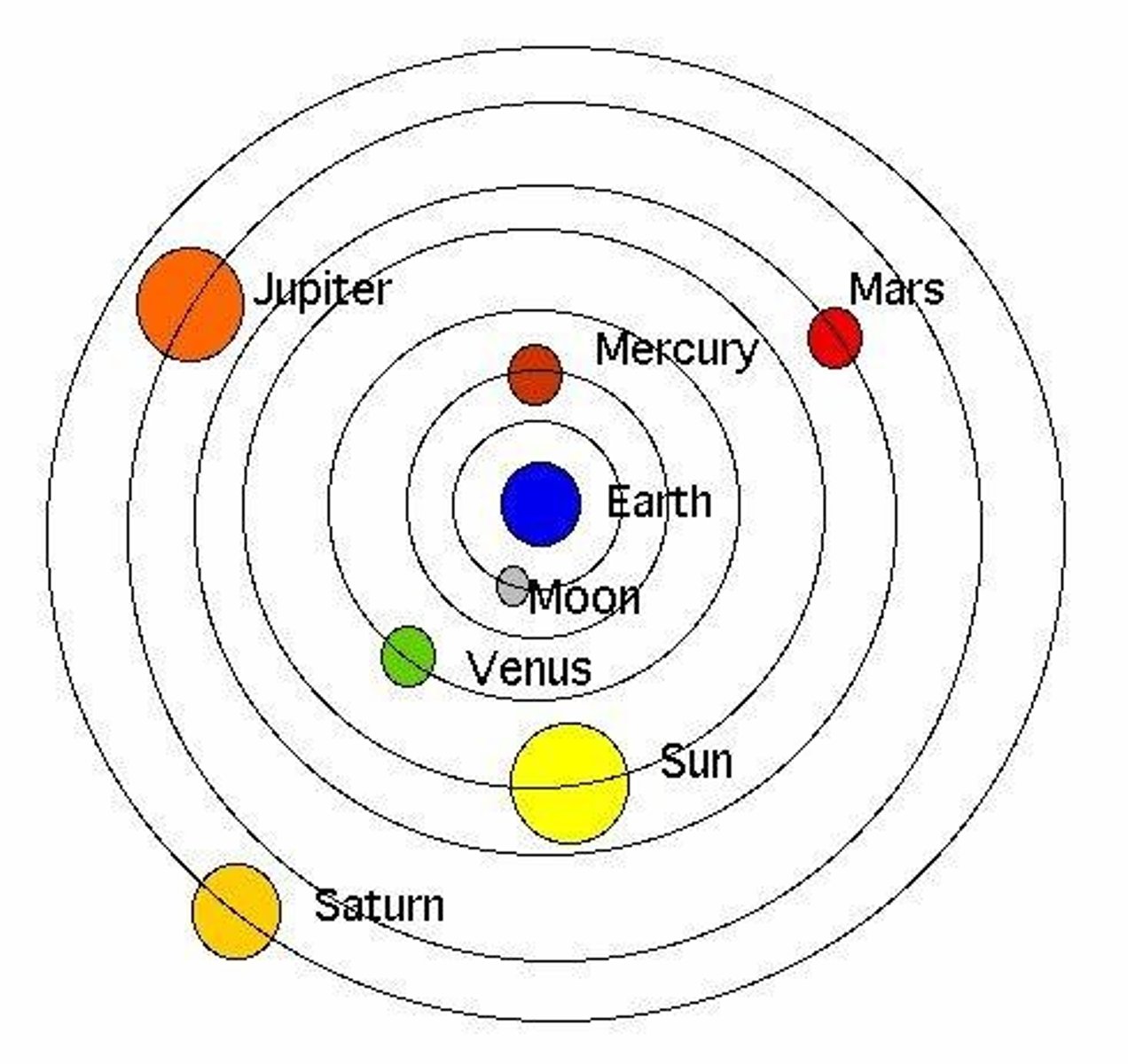
Geocentric Theory
Earth is the center of the Universe and planets revolve around Earth
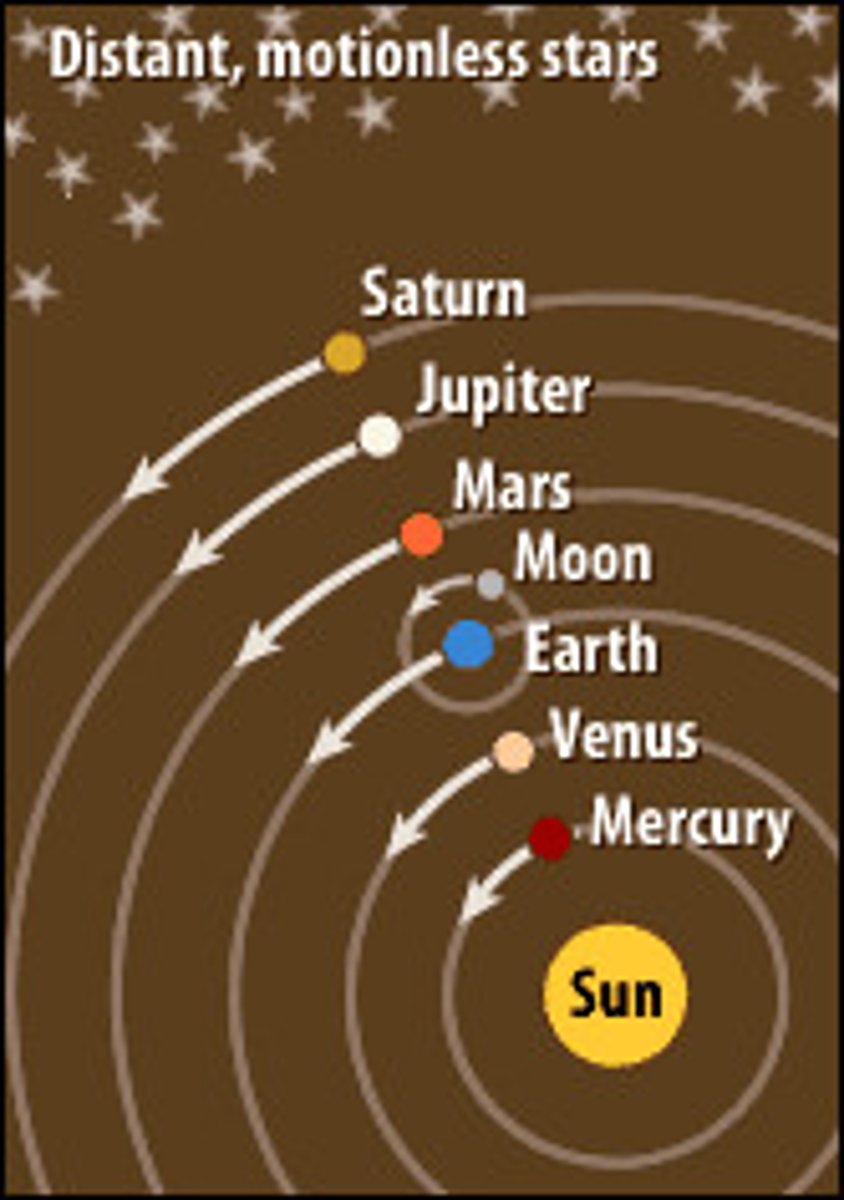
Heliocentric Theory
Sun is the center of the universe and planets revolve around Sun
Enlightenment
a movement that emphasized science and reason as guides to help see the world more clearly

Social Contract
An agreement between the people and their government that their consent to be governed

American Revolution
the revolution of the American colonies against Great Britain

Galileo Galilei
Italian astronomer and mathematician who was the first to use a telescope to study the stars

Nicholas Copernicus
Created the Heliocentric model of the Universe
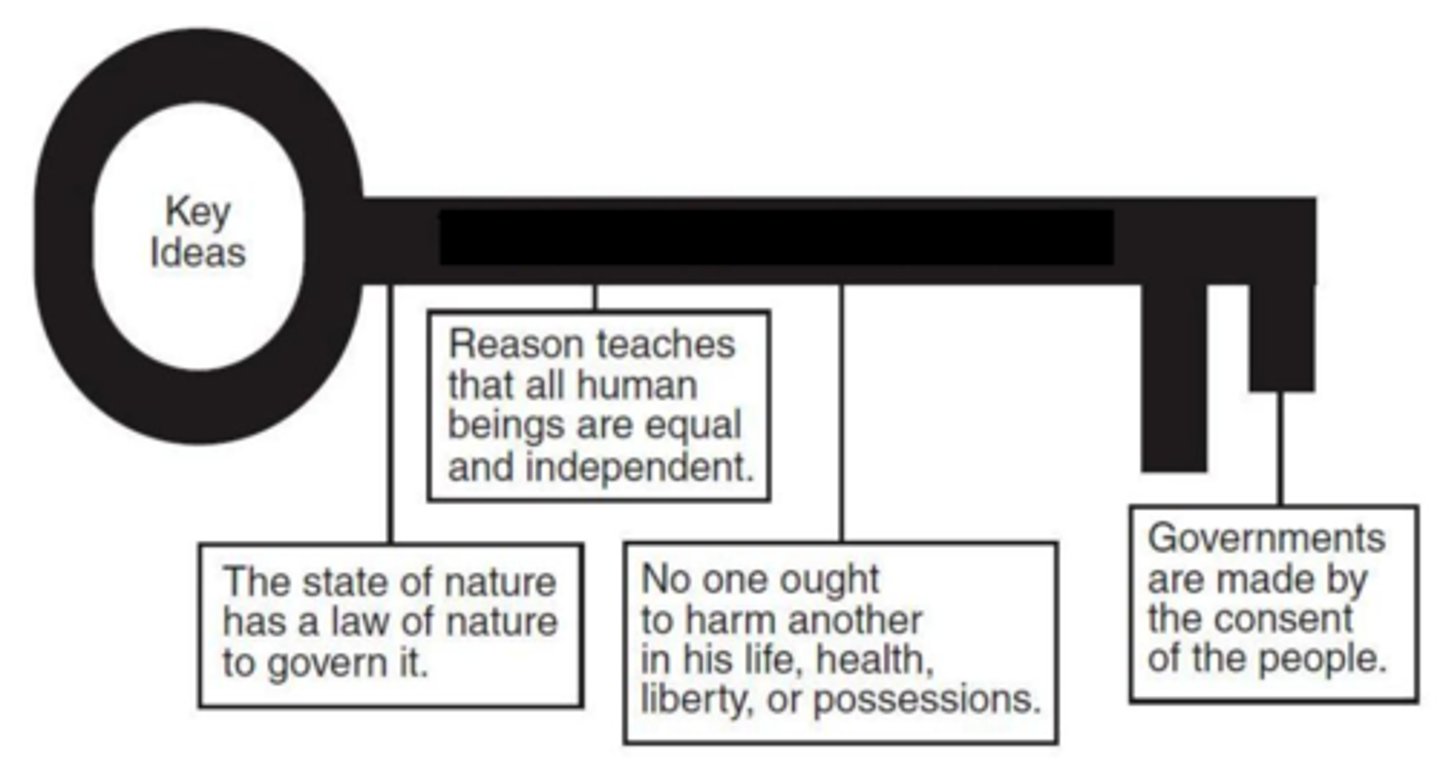
John Locke
English philosopher who argued that people have natural rights and the government protects/ locks those rights
Rousseau
believed people were basically good but that they were corrupted by the evils of society, especially the uneven distribution of property

Montesquieu
French political philosopher who advocated the separation of powers
George Washington
1st President of the United States; commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution

Old Order
the political and social system in place in France before the Revolution (3 estates and the king)
National Convention
revolutionary government that abolished France's monarchy, declared the First Republic, and ruled during the Reign of Terror

Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen
French Revolution document that outlined what the National Assembly considered to be the natural rights of all people and the rights that they possessed as citizens

Reign of Terror
a violent phase of the French Revolution where the government, led by Robespierre and the Committee of Public Safety, executed thousands of "enemies to the revolution" using the guillotine

Congress of Vienna
Meeting of representatives of European monarchs called to reestablish the old order after the defeat of Napoleon

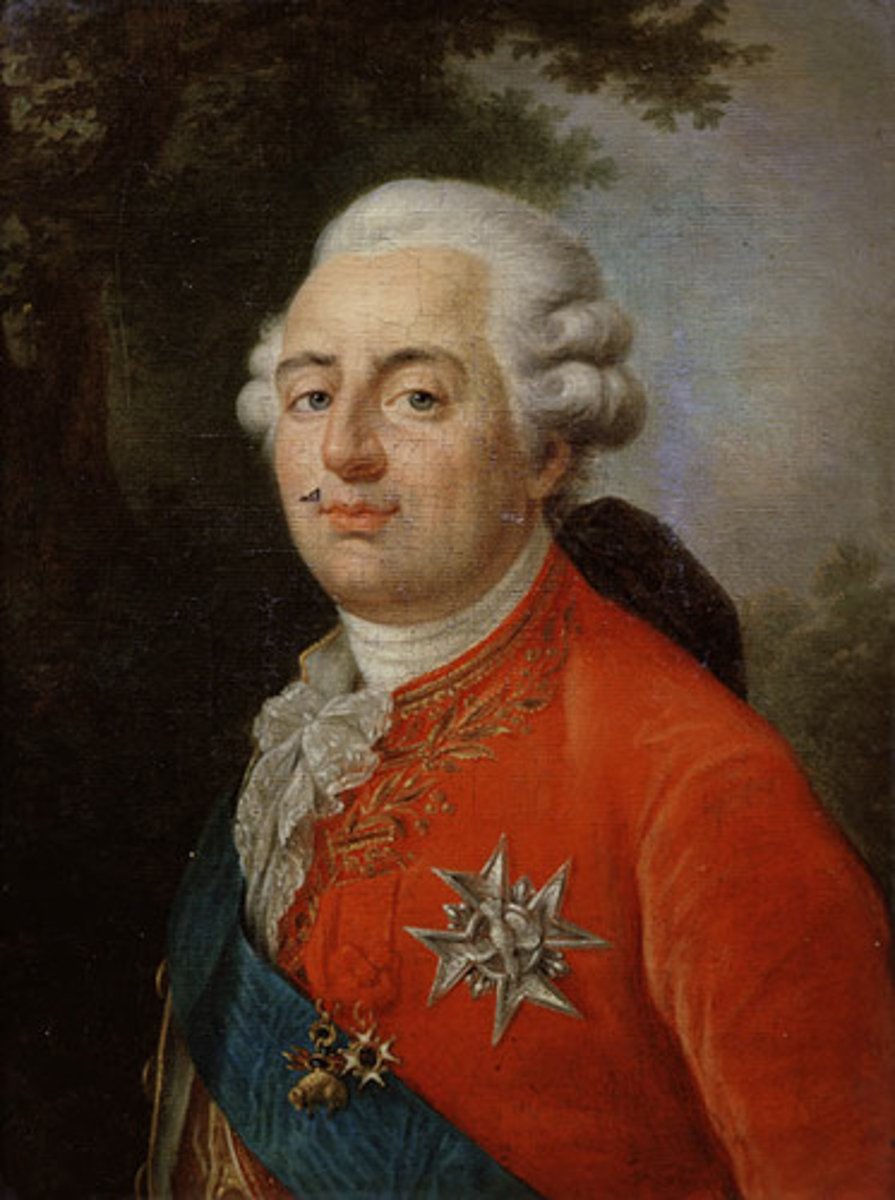
Louis XVI
King of France during the French Revolution and he and his wife (Marie Antionette) were executed

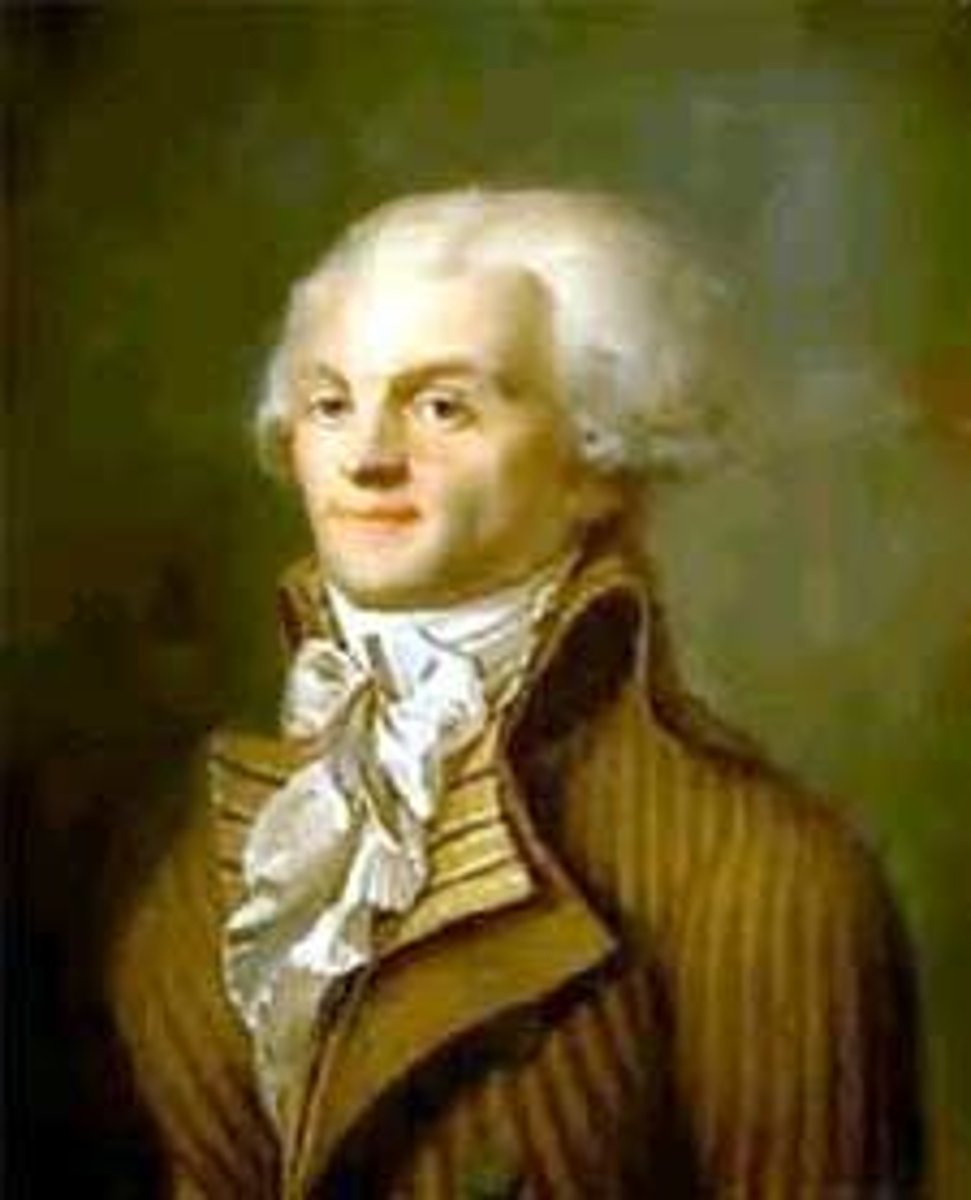
Maximillian Robespierre
Radical leader of the French Revolution and led the Committee of Public Safety and the Reign of Terror

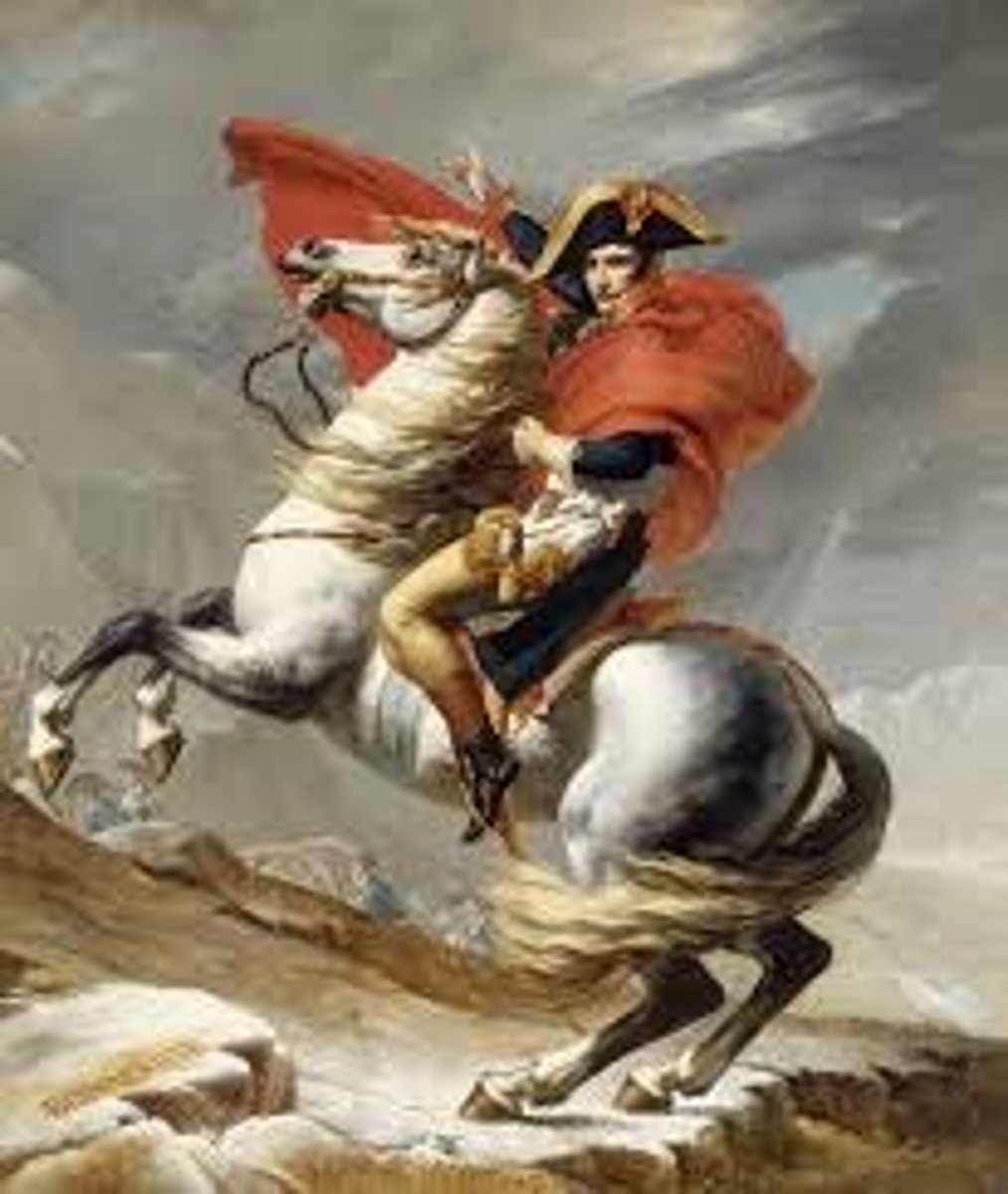
Napoleon Bonaparte
Overthrew the French revolutionary government (The Directory) in 1799 and became emperor of France in 1804

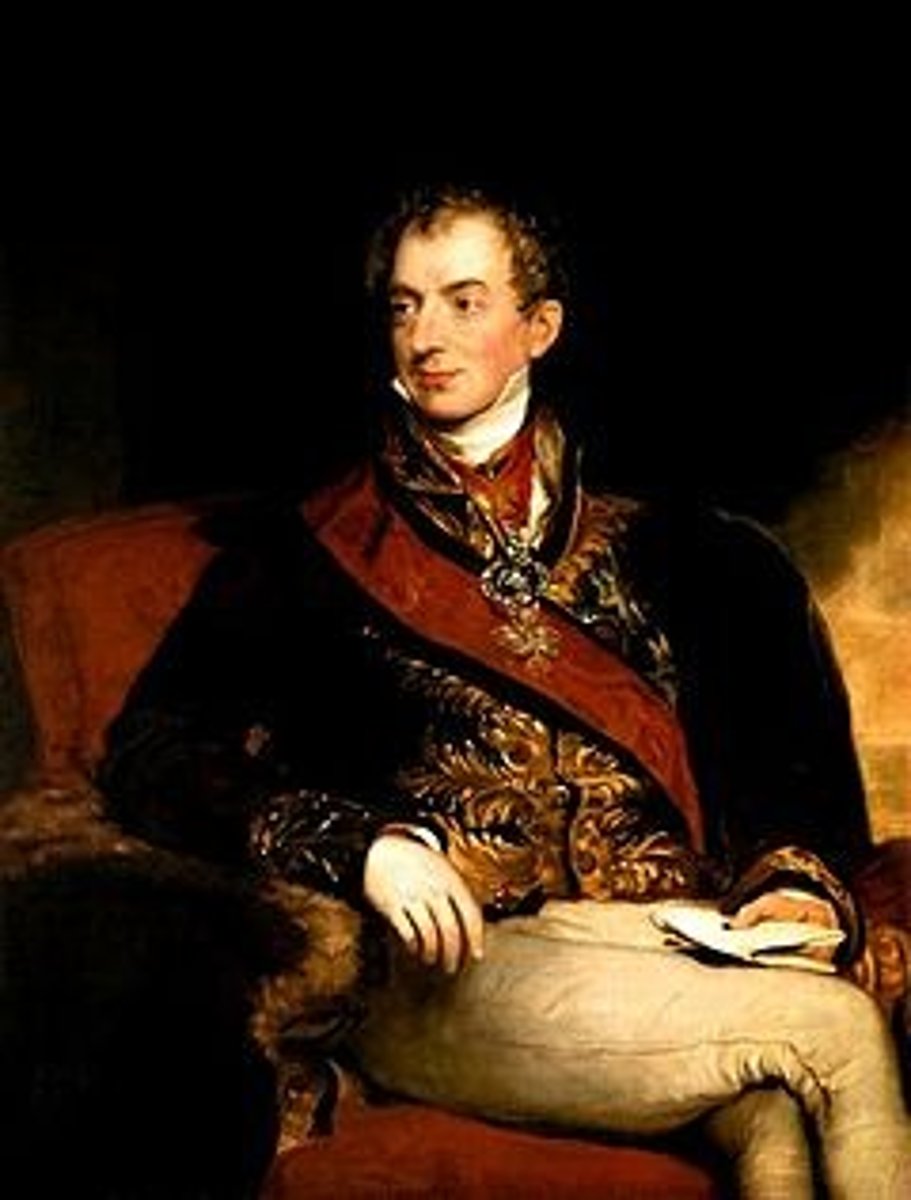
Prince Klemens von Metternich
Led Europe's big meeting (Congress of Vienna) to put kings back in charge, stop new revolutions, and keep peace

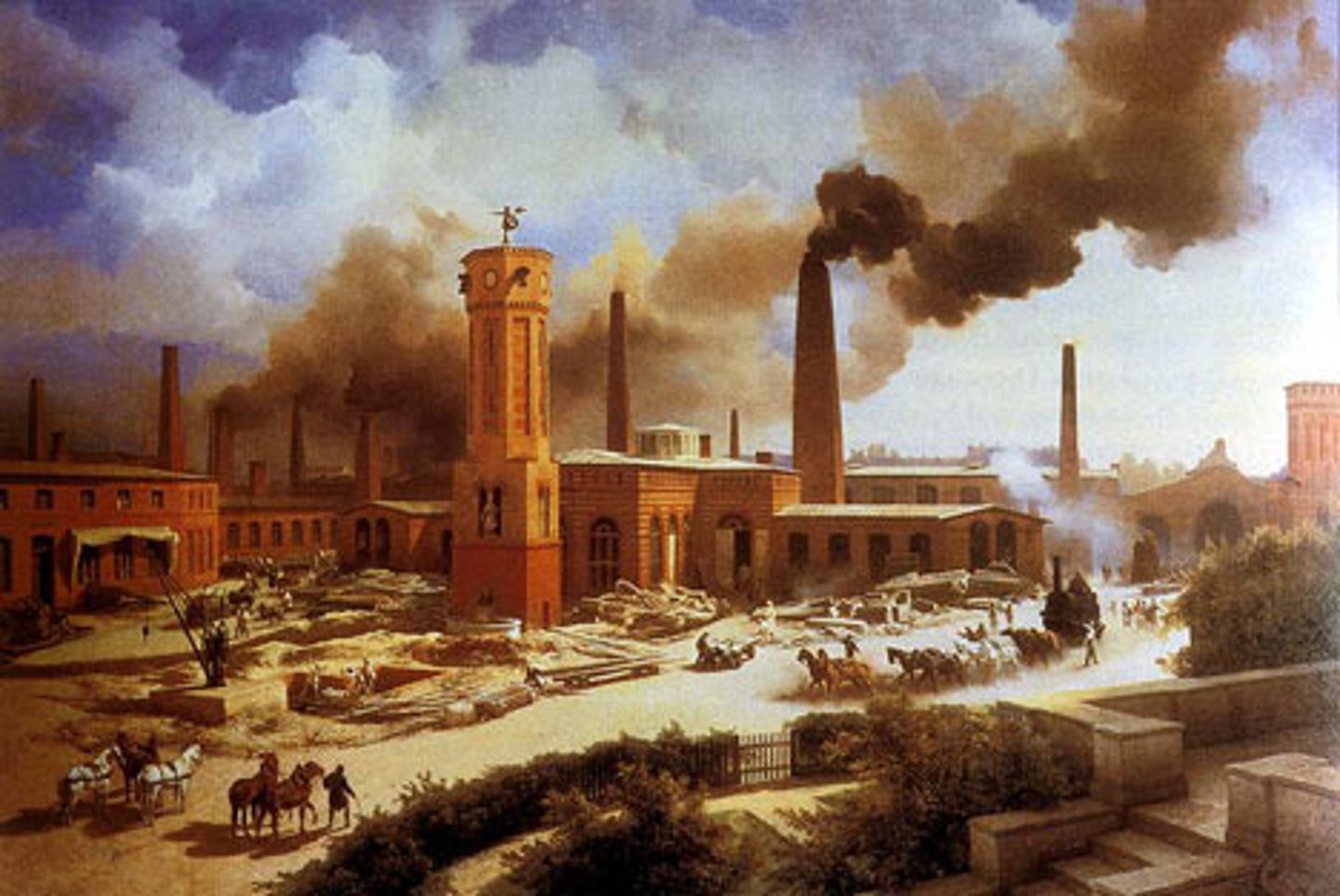
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods

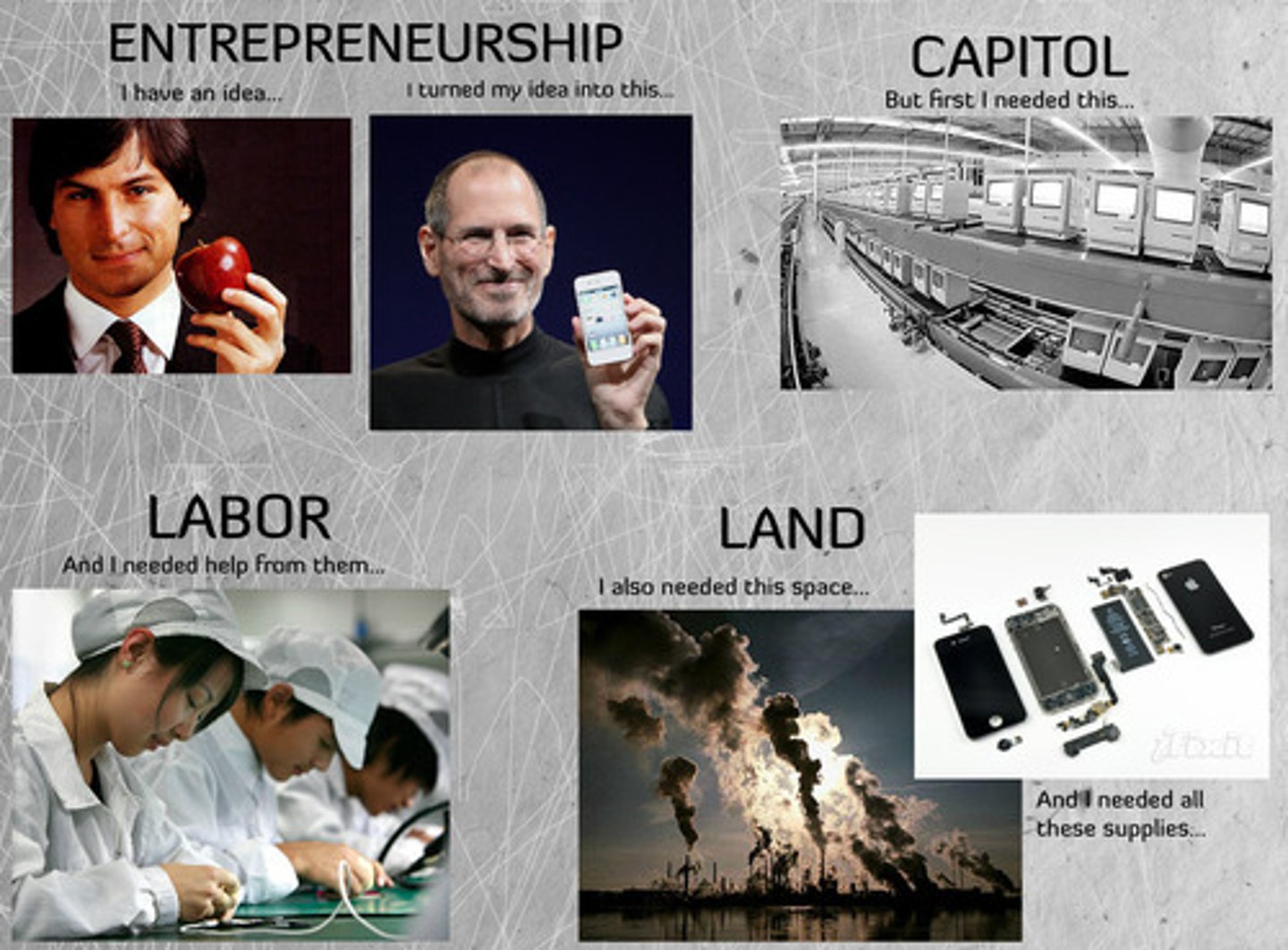
Factors of Production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
Cottage Industry
Manufacturing based in homes rather than in a factory, commonly found before the Industrial Revolution

Labor Union
An organization of workers that tries to improve working conditions, wages, and benefits for its members

Strike
to refuse to work in order to force an employer to meet certain demands

Robert Owen
a Utopian who set up a model community at his cotton mill in Scotland

Karl Marx
Father of Communism
