Biology- 9th grade
1/930
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
931 Terms
Enzymes are?
catalytic proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy through helping to either break down or build molecules
what is activation energy?
amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
when an enzyme has a specific shape it is…
the active site that will only allow a specific substrate to bind
molecules made in the chemical reaction are called?
products
products( of enzymes) usually end in..
a s e (Amylase, lactase)
enzyme will only work in…
a specific pH and temperatures ranges because they will denature (change shape)
denature
change shape
increasing substrate concentration…
increases the rate of reaction
the rate of reaction will remain the same once..
it reaches a certain concentration
enzyme activity will be the highest at…
an enzymes optimum pH
a pH too high or too low will…
cause the enzyme to denature or stop working
if the temperature is too high
the enzyme denatures (changes shape) and the enzyme activity stops
the enzyme activity is the highest at
the optimum temperature
enzyme
a protein that controls the rate of reactions
catalyze
adding a catalyst to cause a reaction to happen (breaking the toothpick)
substrate
the substance the enzyme is working on (toothpicks)
active site
where a chemical reaction takes place (bind and undergo a chemical reaction)
enzymes have a specifically shaped area called…
an active site where it binds with items called substrates, the bindings are very specific and made for that substrate
induced fit
the active site changes shape to perfectly fit the substrate, either building it up or breaking it down
the item resulted from an induced fit is called
a product
lactate is an
enzyme!
lactase breaks down
lactose into smaller parts so our bodies can digest it
people who don’t produce enough lactpse
dont have enough lactase
enzymes are called a catalyst because
they can be used over and over in the reaction (making things happen)
lipase
enzyme that breaks down lipids
enzyme sidekicks
cofactors + coenzymes
enzyme sidekicks may
bind to the substrate or the active site to help the enzyme break down or build up substrates into products
enzymes have
optimum pH levels and temperatures
substrate concentration means
the relative amount of substrate present in a solution
can an enzyme be used more than once?
yes
hydrolysis reaction?
the breakdown of a molecule into a polymer into monomers
dehydration synthesis
a type of reaction that involves building large molecules called polymers by joining together monomers
uses of enzymes
digestion, metabolism, respiration, eliminating toxins
can enzymes in denatured due to pH be brought back (yes or no)
Yes
monomer of proteins
amino acid
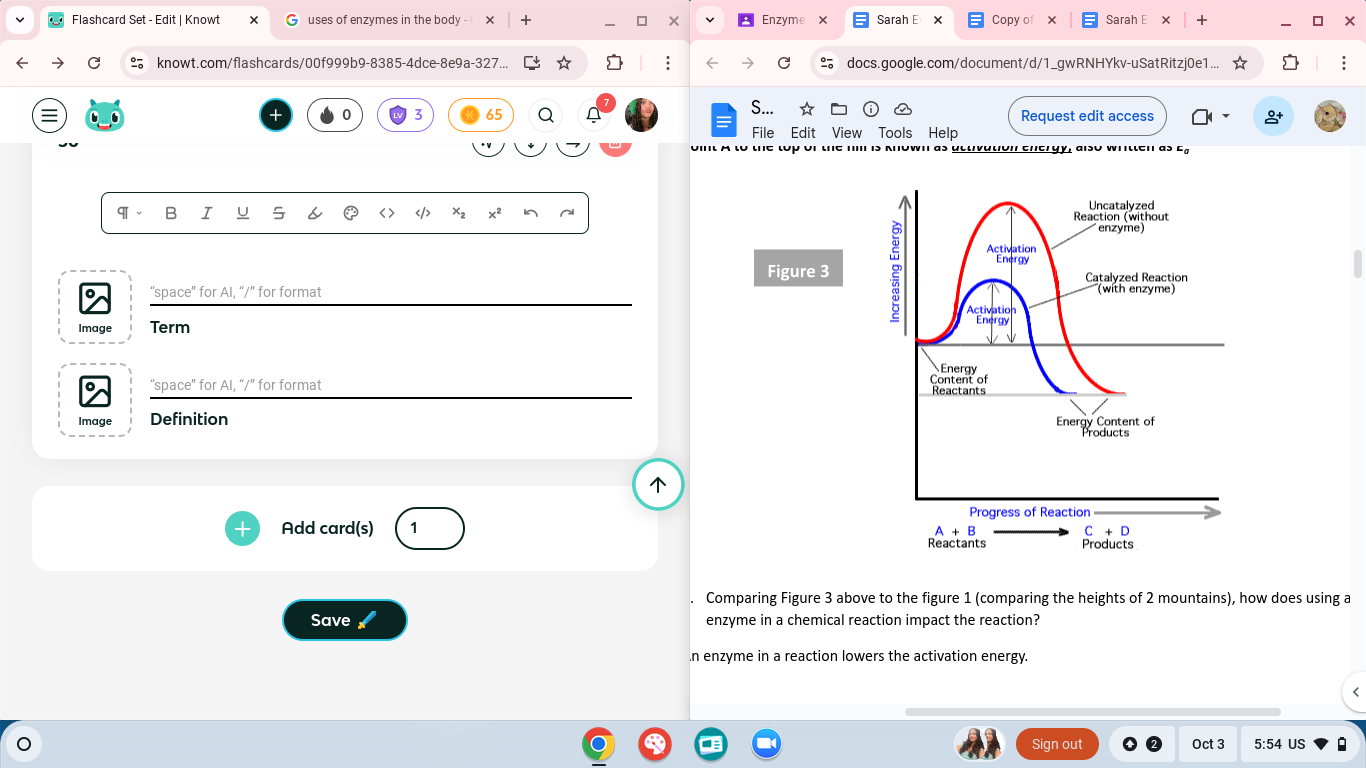
which has the enzyme catalyzing the reaction
the smaller one because enzymes LOWER activation energy because they make it go faster
optimum temperature for the human body
37 degrees
competitive inhibitor
prevents the enzyme from binding to the substrate by binding to the ACTIVE SITE
non competitive
attach to other parts of the enzyme NOT the active site to change their shape
activation energy is
the amount of energy needed to start a reaction
increasing enzyme concentration increases the rate of reactions because…
the substrate will have more enzymes to bond with
chewing or the stomach breaking down food is
mechanical digestion
does mechanical and chemical digestion take place in the stomach
yes
the small green structure in the liver is
the gallbladder
what helps food move down the GI track via smooth muscle contraction
peristalsis
carbohydrates are broken down into ___ and their main function is ___
monosaccharides, provide living things with energy
alimentary canal consist of
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
vital to brain structure and regulated by insulin and glucagon
glucose
NOT a function of a protein
provide long term storage
due to evolutionary needs it is much easier to gain than lose weight
true
villi in the small intestine is responsible for
absorption
the pancreas produces
enzymes
the large organ above the stomach
liver
six nutrients digestion breaks down
water, protein, carbs, lipids, minerals, vitamins
most of the excess water in food is absorbed in the ___ before undigested byproduct is packaged as waste
large intestine
mechanical digestion
chewing, squeezing, grinding, large pieces of food broken down into smaller pieces that can be processed
chemical digestion
various enzymes and other chemicals break down food into smaller and smaller molecules
mouth incluedes
teeth (mechanical digestion) saliva (moisten food and contains amylase an enzyme that breaks down food) tongue (forms bolus, a ball of food that can be swallowed
esophagus
food from mouth passes throat the pharynx to esophagus, food moves through the esophagus by muscle contractions called peristalsis
stomach
the muscular walls of the stomach churn food, stomach acids begin to break down the food and the pepsin enzyme begins to breakdown, proteins, the food is qualified into chyme
small intestine
receives enzymes from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder to further breakdown fats, proteins and carbohydrates, it is highly folded and contains villi for nutrients to be absorbed into the bloodstream
large intestine
water is absorbed into the blood, bacteria breaks down fiber and help with absorbing vitamins, waste is compacted into feces pushed out the rectum
pancreas
digestive functions include: pancreatic juice is secreted into small intestine, contains sodium bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid, contains various enzymes to break down macro nutrients
liver
Produces bile and sends it to the gallbladder and small intestine.
Bile is a fluid that breaks apart the fats found in fatty foods- mechanical digestion
enzymes can then break down the fats into individual molecules - chemical digestion
gallbladder
Stores, modifies and concentrates bile from the liver
Releases bile to the small intestine after meals
chewing or the stomach breaking down food is
mechanical digestion
does mechanical and chemical digestion take place in the stomach
yes
the small green structure in the liver is
the gallbladder
what helps food move down the GI track via smooth muscle contraction
peristalsis
carbohydrates are broken down into ___ and their main function is ___
monosaccharides, provide living things with energy
alimentary canal consist of
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
vital to brain structure and regulated by insulin and glucagon
glucose
NOT a function of a protein
provide long term storage
due to evolutionary needs it is much easier to gain than lose weight
true
villi in the small intestine is responsible for
absorption
the pancreas produces
enzymes
the large organ above the stomach
liver
six nutrients digestion breaks down
water, protein, carbs, lipids, minerals, vitamins
most of the excess water in food is absorbed in the ___ before undigested byproduct is packaged as waste
large intestine
mechanical digestion
chewing, squeezing, grinding, large pieces of food broken down into smaller pieces that can be processed
chemical digestion
various enzymes and other chemicals break down food into smaller and smaller molecules
mouth incluedes
teeth (mechanical digestion) saliva (moisten food and contains amylase an enzyme that breaks down food) tongue (forms bolus, a ball of food that can be swallowed
esophagus
food from mouth passes throat the pharynx to esophagus, food moves through the esophagus by muscle contractions called peristalsis
stomach
the muscular walls of the stomach churn food, stomach acids begin to break down the food and the pepsin enzyme begins to breakdown, proteins, the food is qualified into chyme
small intestine
receives enzymes from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder to further breakdown fats, proteins and carbohydrates, it is highly folded and contains villi for nutrients to be absorbed into the bloodstream
large intestine
water is absorbed into the blood, bacteria breaks down fiber and help with absorbing vitamins, waste is compacted into feces pushed out the rectum
pancreas
digestive functions include: pancreatic juice is secreted into small intestine, contains sodium bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid, contains various enzymes to break down macro nutrients
liver
Produces bile and sends it to the gallbladder and small intestine.
Bile is a fluid that breaks apart the fats found in fatty foods- mechanical digestion
enzymes can then break down the fats into individual molecules - chemical digestion
gallbladder
Stores, modifies and concentrates bile from the liver
Releases bile to the small intestine after meals
Enzymes are?
catalytic proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering activation energy through helping to either break down or build molecules
what is activation energy?
amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
when an enzyme has a specific shape it is…
the active site that will only allow a specific substrate to bind
molecules made in the chemical reaction are called?
products
products( of enzymes) usually end in..
a s e (Amylase, lactase)
enzyme will only work in…
a specific pH and temperatures ranges because they will denature (change shape)
denature
change shape
increasing substrate concentration…
increases the rate of reaction
the rate of reaction will remain the same once..
it reaches a certain concentration
enzyme activity will be the highest at…
an enzymes optimum pH
a pH too high or too low will…
cause the enzyme to denature or stop working