EXAM 3 - Mesencephalon
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what part of the mesencephalon contains the superior and inferior colliculi
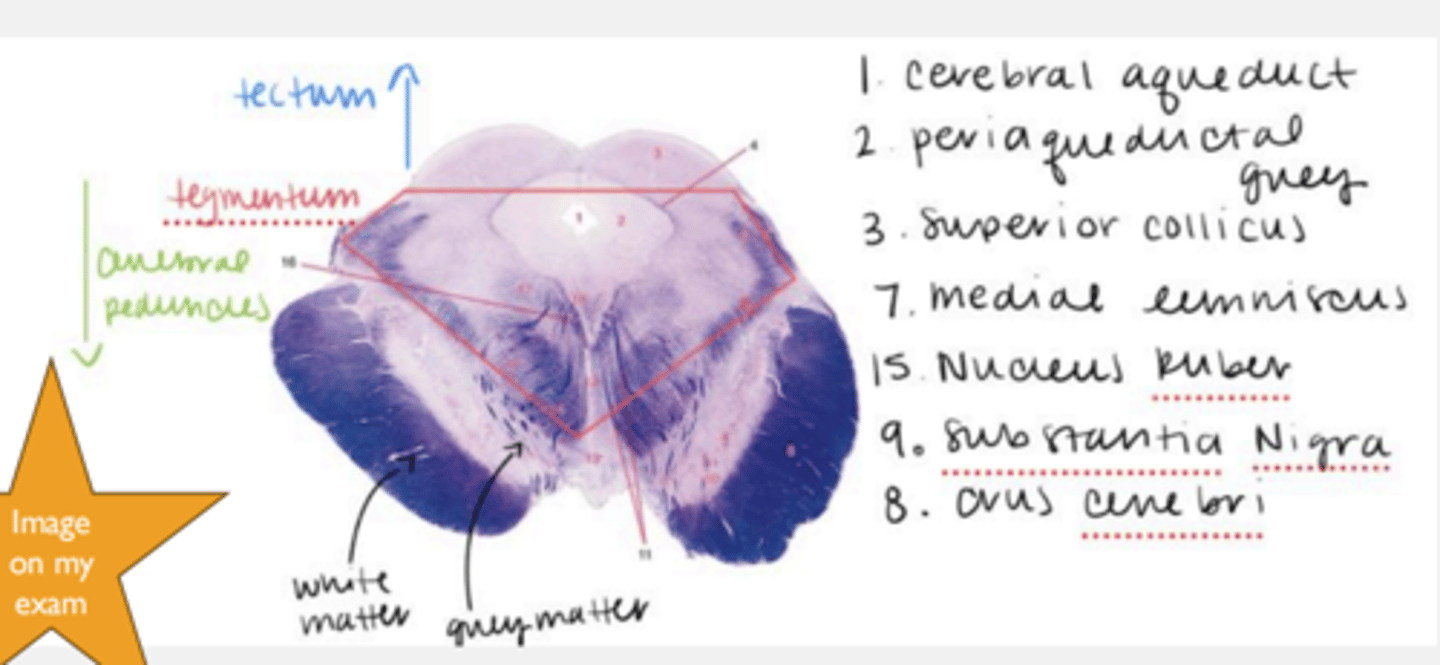
tectum
what surrounds the cerebral aqueduct
periaqueductal gray
what is posterior to the cerebral aqueduct
tectum
what is anterior to the cerebral aqueduct
cerebral peduncles
what CN origins are found in the periaqueductal gray
3 and 4
what structures are included in the cerebral peduncles
tegmentum, substantia nigra, and crus cerebri
what part of the cerebral peduncle is white matter
crus cerebri
what part of the cerebral peduncle is gray matter
substantia nigra
know this diagram of the mesencephalon
what type of reflexes are associated with the superior colliculi
visual
is superior colliculi reflex voluntary or involuntary
involuntary
what tract arises form the superior colliculus and what does it do
tectospinal, move head away from objects moving rapidly through field of vision
what muscles are contracted via tectospinal tract
traps and SCM
will damage to the tectum result in loss of vision
NO, decrease ability to respond to objects moving through vision field
what info do the inferior colliculi relay? where?
auditory info to the thalamus
what is the opening for CSF to flow from 3rd to 4th ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
what is produced in the periaqueductal grey
endorphins and enkephalins
where is the apparent origin for CN 3
interpeduncular fossa
what muscles are controlled by the occulomotor nuclei
superior, medial, and inferior rectus, inferior oblique, and levator palpebrae superioris
what muscles are controlled by accessory occulomotor (Edinger-Westphal's)
ciliary muscles and sphincter pupillae
what muscle is supplied by the trochlear nerve (CN4)
superior oblique muscle
what is the origin of CN4
posterior side of brainstem
what is unique about the fibers of CN 4
left and right fibers cross at apparent origin
if superior oblique muscle is contracted, what movement occurs
eye will turn down and out
what parts of the midbrain contain periaqueductal grey
tectum and tegmentum
what CN are located in tegmentum in the periaqueductal grey
3 and 4
where is the reticular formation of the midbrain located
in tegmentum
what tract is found in the tegmentum that carries 2 pt touch, vib, kin info to the VPL of thalamus
medial lemniscus
what nucleus is found int he tegmentum
red nucleus
what is the parvocellular portion of the Red Nucleus
highly vascular, superior, extends into subthalamus
what is the magnocellular portion of the red nucleus
inferior, large, most fibers here, smaller in humans
the red nucleus receives input fibers from where
cerebellar nuclei (dentate and interposed (globose and emboliform))
what is the name of the gray matter between tegmentum and crus cerebri
substantia nigra
what is produced in the substantia nigra and what is it made from
dopamine from tyrosine
damage to the substantia nigra can result in what condition? what is a treatment?
Parkinson's, dopamine
can dopamine cross BBB
NO, use L-dopa
the substantia nigra acts as a place where information is exchanged between what two nuclei
caudate and putamen
what type of axons does Crus Cerebri contain
pyramidal axons (UMNs)
what is corticomesencephalic
cortex to midbrain to CN 3 and 4
what is corticopontine
cortex to pons
what is corticobulbar
cortex to medulla
what is corticospinal
cortex to spinal cord
what movement is initiated by corticomesencephalic fibers
voluntary eye movement because the fibers terminate on CN 3 and 4
what movement do axons of crus cerebri initiate
skilled voluntary movement