Earth Science Chapter 1
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Earth science is the name for all the sciences that collectively seek to understand Earth and its neighbors in space. It includes geology, oceanography, meteorology, and astronomy. Throughout its long existence, Earth has been changing. In fact, it is changing as you read this page and will continue to do so into the foreseeable future. Sometimes the changes are rapid and violent, as when severe storms, landslides, and volcanic eruptions occur. Conversely, many changes take place so gradually that they go unnoticed during a lifetime. Scales of size and space also vary greatly among the phenomena studied in Earth science.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
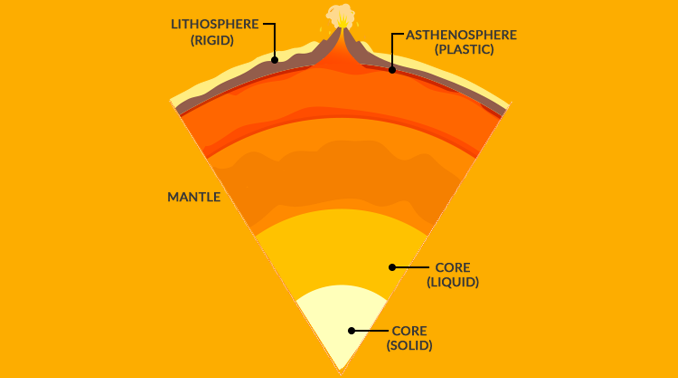
Asthenosphere
The mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. 80 and 200 km below the surface, and extends as deep as 700 km.
Atmosphere
the layer of gases, like nitrogen and oxygen, that surrounds a planet, held in place by gravity, providing air to breathe, regulating temperature, and shielding life from harmful solar radiation
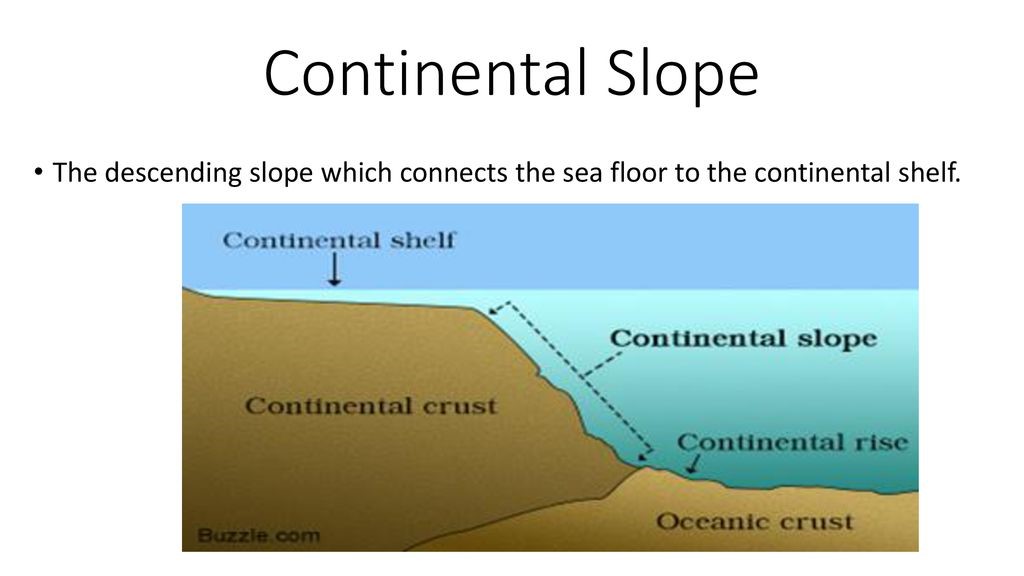
Continental slope
a wide, gentle incline from a deep ocean plain (abyssal plain)
Crust
the outermost, solid, and thinnest layer of the planet, representing less than 1% of its volume. It is a rocky, relatively brittle shell composed of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
geologic time
the extensive 4.6-billion-year span representing Earth's entire history, from its formation to the present
hydrosphere
all the water on, under, and above Earth's surface, including oceans, rivers, lakes, glaciers, groundwater, and atmospheric water vapor
system
a set of interacting components (like land, ocean, air, life) that work together as a whole
core
The innermost part of Earth
Meteorology
the scientific study of Earth's atmosphere, focusing on weather, atmospheric phenomena (like wind, rain, storms), and weather forecasting, using principles of physics and math to understand and predict short-term atmospheric changes
Biosphere
the global ecological system integrating all living organisms and their relationships with the physical environment, including the air, water, and land
hypothesis
a proposed, testable explanation or educated guess for an observation or phenomenon, serving as a starting point for scientific investigation or inquiry, often stated as an "if-then" prediction about the relationship between variables that can be proven true or false through experiments or data collection
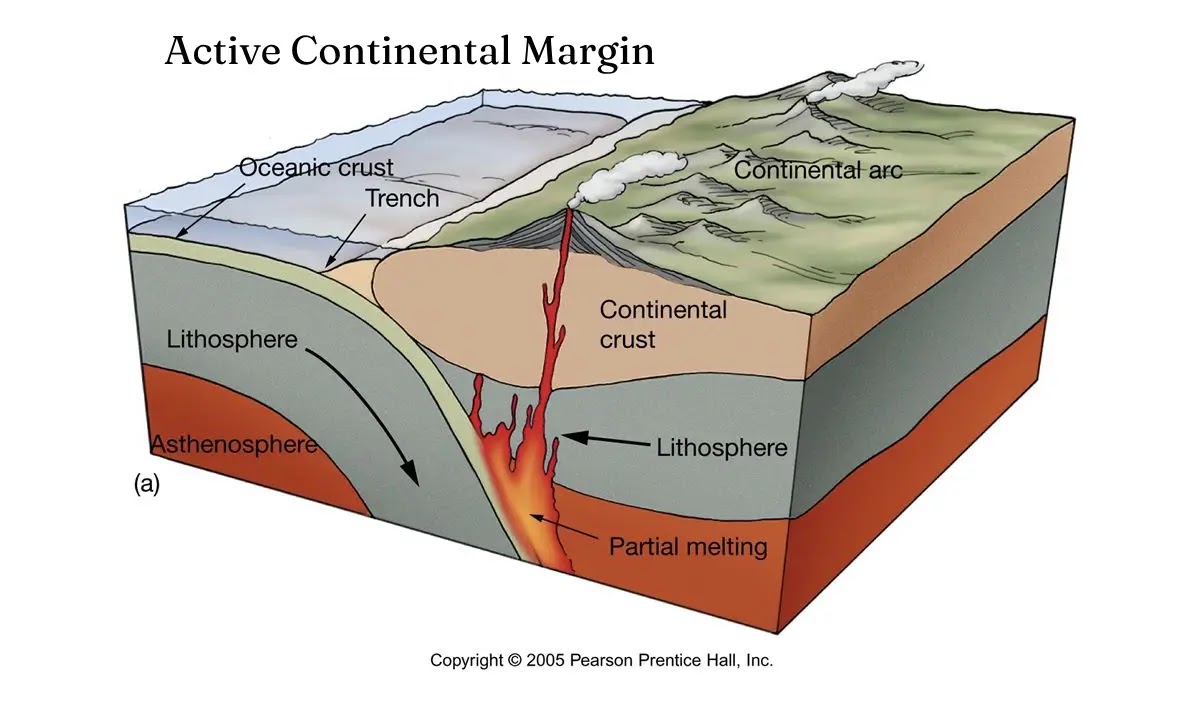
continental margin
the underwater edge of a continent—the zone where continental crust transitions into oceanic crust.

Lithosphere
Earth's rigid, rocky outer layer, encompassing the crust and the uppermost, solid part of the mantle, forming the tectonic plates that move around the surface, broken into sections like continents and ocean floors, and it's the "land" part of Earth's systems
Geosphere
the solid, rocky components of Earth, spanning from the surface crust down to the inner core, including mountains, soil, and mineral deposits
Continental shelf
the edge of a continent that lies under the ocean