Module Two: Plant Ecology
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What traits do all land plants have?
Alternation of generations, embryos, cuticle
What species of land plants do not have stomata?
Liverworts
In what species is the sporophyte not the dominant generation?
Bryophytes (mosses), Liverworts
which species of plants have a vascular system?
Lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms, angiosperms
Gametophyte
The haploid generation, produces gametes through mitosis
Sporophyte
Diploide generation, produces spores by meiosis
Spore
Produces via meiosis and typically dispersed (excepto in seed plants). Grow into gametophyte via mitosis
Gamete
Haploid reproductive cell; fuses during fertilization to form a zygote
Meiosis
Cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half (produces spores in plants)
Mitosis
Cell division that produces identical cells; used for growth
Bryophytes
Non-vascular plants (ex: Liverworts, Hornworts, Mosses). Gametophyte dominate
Liverworts
Type of bryophyte; have pores, but no stomata
Hornworts
A type of bryophyte; have longer-lived sporophyte than other bryophytes
vascular system
System of tissues (xylem and phloem) that transports water and nutrients; allow for larger, branched sporophytes
Xylem
Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, and also provides structural support.
Phloem
Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting sugars (food) during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant like roots, fruits, and growing tissues
Seeds
Fertilized ovule
—> like human zygotes/embryo
Fruit
Structures derived from ovary
Gymnosperm
“Naked seed” plants (ex: pines, conifers); pollen delivered directly to the ovule
Angiosperms
Flowering plants; seeds enclosed within a carpel/ovary; make fruits
Flower
Reproductive structure of an angiosperm
Sporophyll
A modified leaf specialized for reproduction
Carpel (pistil)
Female reproductive organ; made of stigma, style and ovary
Ovary
Base of the carpel; contains the ovules; develops into fruit after fertilization
—> like human uterus
Ovule
Structure inside the ovary; contains the female gametophyte; develops into the seed after fertilization
—> like human egg
Stigma
Receptive tip of the pistil; the landing pad for pollen; held up by the style
—> like human vagina
Style
Stalk connecting the stigma to the ovary
Stamen
The male reproductive organ; made of the anther and filament
Anther
Part of the stamen; where pollen (male gametophytes) is produced
Filament
Stalk that holds up the anther
Pollen Grain
The male gametophyte in seed plants; typically three cells (tube cell and two sperm cells)
Pollination
The process of moving pollen from the anther to the stigma
Pollen tube
Tube that grows from the pollen grain down the style to deliver sperm to the ovule
Megastore Mother Cell
Diploid cell in the ovule that undergoes meiosis to create mega spores (female spores)
Microspore Mother Cell
Diploid cell in the anther that undergoes meiosis to create microspores (male spores)
Endosperm
The food supply for the embryo within an angiosperm seed
Double fertilization
Unique to angiosperms; Involves to fusion events: 1) Egg + Sperm = Zygote (diploid 2n), 2) Second sperm + Polar nuclei = endosperm (triploid, 3n)
Polar nuclei
The two nuclei in the large central cell of the female gametophyte; fuse with one sperm to form the endosperm
Germination
The process where a seed initiates growth
Radicle
The embryonic root; the first structure to emerge from the seed (grows downward to anchor and acquire water/nutrients)
Cotyledons
Embryonic leaves; provide early photosynthesis/nutrition until mature leaves develop
Hypocotyl
Embryonic stem; pulls cotyledons out of the soil
Eudicots (dicots)
Plant group whose embryos produce two cotyledons (ex: beans)
Monocots
Plant group whose embryos produce one cotyledons (ex: corn)
Meristem (Meristematic Tissue)
Undifferentiated tissue (similar to human stem cells) that allows for continuous growth. Found in buds and root/shoot tips.
Indeterminant Growth
The ability of a plant to grow continuously throughout its life from its meristems (unlike animals)
Bud
Cluster of meristem tissue that can grow and make new plant parts
Apical Bud
Bud located at the tip of a shoot or root; responsible for primary growth
Auxiliary Bud
Bud located in the axis (crook) where a leaf meets the stem
Primary Growth
Growth that results in the elongation of shoots and roots, and the production of leaves/flowers
Secondary Growth
Growth that results in making the plant wider/thicker (ex: forming the woody trunk of a tree)
Root cap
Protective layer of cells covering the apical meristem at the root tip
Zone of Cell Division
Location of the apical meristem; cells are undifferentiated and actively undergoing mitosis (cell division)
Zone of Elongation
Zone where cells move after division; cells grow much longer due to water uptake. This process also pushed the root tip further into the soil
Zone of Differentiation
Zone where cells finish elongating and become mature, specialized tissues. Their function is determined by their location.
Dermal Tissue
The outermost layer; includes the epidermis and cuticle
Epidermis
The protective outer layer of cells
Cuticle
Waxy layer on the epidermis of shoots/leaves; reduces water loss
Ground Tissue
All tissues other than vascular and dermal; functions include storage, support, and photosynthesis
Secondary Growth
Growth that results in the increase in girth of stems and roots. Occurs mainly in dicots
Cortex
Ground tissue outside vascular bundles; often used for sugar storage
Pith
Ground tissue inside the ring of vascular bundles (in dicot stem)
Endodermis
Ground tissue layer around the vascular bundles in roots; acts as a barrier
Vascular Bundle
Strand containing both xylem and phloem tissues
Mesophyll
Ground tissue in leaves; specialized for photosynthesis (palisade and spongy layers)
Guard Cells
Dermal cells surrounding a stoma; open and close to regulate gas exchange
Vascular Cambium
A type of lateral meristem that forms a ring in the stem; produces secondary xylem (to the inside) and secondary phloem (to the outside)
Cork Cambium
A type of lateral meristem that forms to the outside of the vascular cambium; produces bark/cork
Secondary Xylem
Wood; Tissue produced to the inside of the vascular cambium; makes up the majority of a woody plants girth; forms annual rings in temperature climates
Secondary Phloem
Part of the bark; tissue produced to the outside of the vascular cambium
Bark
All tissues external to the vascular cambium (includes secondary phloem and periderm/cork)
Tropism
A growth response that results in the curvature or turning of a plant organ in response to an environmental stimulus
Positive Tropism
Growth towards the stimulus
Negative Tropism
Growth away from the stimulus
Phototropism
Growth response to light
Compare number of cotyledons (embryonic leaves) between monocots and dicots
Monocots: one
Dicot: two
Compare the stem vascular bundles of monocots vs dicots
Monocots: vascular bundles are scattered randomly throughout the stem
Dicots: vascular bundles are arranged in a ring
Do monocots or dicots have a cortex and pith?
Dicots
Do monocots or dicots exhibit secondary growth?
Dicots
Compare root structures of a monocot and a dicot
Monocots: usually have fibrous roots, which are shallower and great for preventing soil erosion (like grass)
Dicots: usually have taproot (central, thick primary root), which is better for deep water access and anchoring large structures (ex: trees)
What does the Calvin Cycle do?
Takes CO2 out of the air and creates sugar
What process do all photosynthesizing plants take part in?
C3 photosynthesis
What fixes CO2 in C3 photosynthesis?
RuBicCO
What fixes CO2 first in C4 photosynthesis?
PEP-C
What process does C4 photosynthesis eliminate?
Photorespiration
Why do some plants not do C4 photosynthesis?
It is more costly to perform C4 photosynthesis
Why do plants need water?
Photosynthesis and other hydrolysis reactions (<1%)
Growth and expansion of cells (<5%)
Transpiration- evaporation of water from leaves (~95%)
Provides transport og nutrients from roots to leaves
Cools leaves
Allows stomata to remain open for CO2 absorption
Is relative humidity generally (almost always) higher inside or outside of the leaf?
inside
As relative humidity increases, the transpiration rate…
decreases
As relative humidity decreases, the transpiration rate…
increases
Stomatal Conductance
Function of stomatal density and stomal aperture
What do guard cells do?
Govern aperture (they open and close stomata)
Adaptations that have contributed to the success of plants in terrestrial environments include seeds, long-lived sporophyte, stomata, and alternations of generations. List these adaptations in the order in which they appeared in the fossil record
alternations of generations, stomata, long-lived sporophyte, seeds
A trait of the common ancestor of charophytes and land plants that was exapted by land plants and allowed them to invade land was…
They were dispersed by spores
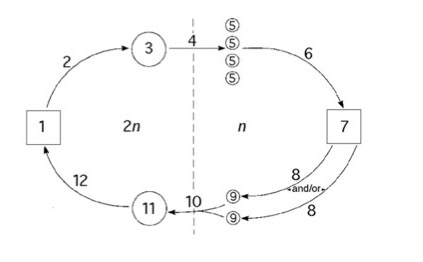
Which number could represent a multicellular embryo?
1
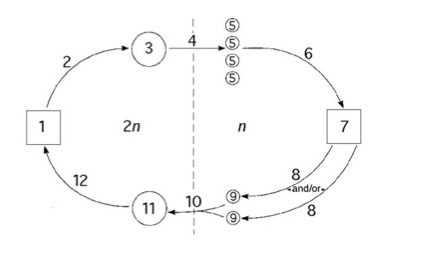
Which plant species exhibit this life cycle?
Bryophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms do, but charophytes do not
Stomata _______ in response to INCREASING light intensity
Open
Stomata ______ in response to DRY soil
Close