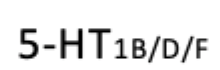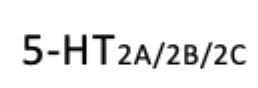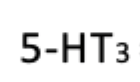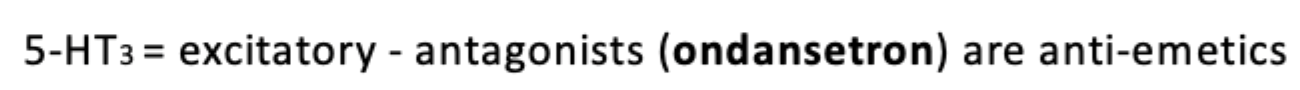Insomnia
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Insomnia
The most common sleep disorder in the with underlying mechanism not clearly understood.
Risk factors: stress, shift work, ageing, and drug/alcohol abuse
Synptoms: becoming more irritable, feeling tired, and having difficulty remembering. So concentration, reasoning, and reaction time can become severely impaired.
What is main focus of insomnia treatments?
Combination of pharmacological approaches and non-pharmacological measures like cognitive behavioural therapy and relaxation therapy.
1) Block wake promoting pathways
2) Enhance sleep inducing pathways
What pathways are relevant to sleep disorders?
-the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) involved in circadian rhythm
-hypothalamus involved in wakefulness
-brainstem reticular formation for arousal and consciousness.
What are the primary neurotransmitters to target, in the treatment of sleep disorders?
Histamine, GABA, dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin.
Where are histaminergic neurons located?
Tuberomammillary nucleus of the hypothalamus
What is the role of histaminergic neurons?
-Wake promoting pathway (arousal)
-Feeding
-Thermogenesis
-Learning
-Memory
What is the correlation between firing and arousal state?
Highest when alert, slower when asleep and silent during REM sleep
What types of neurons are found in outputs to the cortex involved in wakefulness?
Cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain
What other sites does the histaminergic neurons of the tuberomammillary nucleus communicate with?
Other pontine wake promoting nuclei like…
-locus coeruleus (NA)
-raphe nuclei (5-HT)
-ventral tegmental area (DA)
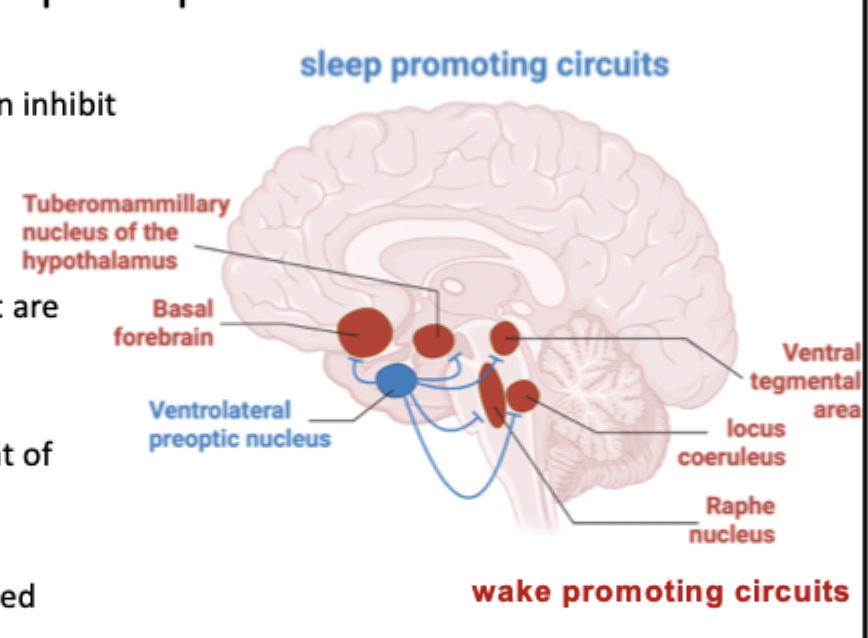
Where are inhibitiory inputs for sleep promoting centres?
In ventrolateral preoptic nucleus in hypothalamus
Which two histamine receptors are relevant to sleep?
H1 and H3
Diphenhydramine
Centrally acting antagonist of H1 receptor which is excitatory due to Gq coupling
clozapine
H1 antagonists produce sedation - side effect of anti-psychotics
Zolpidem
Z drug
Enhances GABA-A signalling
Use limited by risk of dependence, tolerance and withdrawal syndrome
Short half life for sleep treatment so reduced risk of tolerance and hangover effect
Has a sedative rather than anxiolytic effects and are less addictive than benzodiazepines due to it’s selectivity of alpha-1 subunit over alpha-2
Which GABA receptors are sensitive to benzodiazepines?
Must contain alpha 1,2,3,5 and gamma-2 subunits
What is the relevance of the combination of subunits of the GABA receptor?
Each subunit has distinct functions and thus leads to specific side effects
What is the function of α1 subunit?
anticonvulsant, sedative/hypnotic and addictive effects
What is the function of α2 subunit?
anxiolytic effects
What is the function of the α2, α3 and α5 subunits?
muscle relaxation
What is the relevance of the α5 subunit?
Mice lacking the α5 subunit have improved learning/memory and thus an α5 subunit selective inverse agonist could potentially be memory enhancing. For example, diazepam (Valium)
Lorazepam
used for its sleep-inducing effects and produces less tolerance than a longer acting drug.
Orexin
Stimulates wake promoting circuitry by activating VGCaC activity and decreases potassium channel activity.
Where are orexin containing neurons found?
At lateral hypothalamus
Suvorexant
Orexin (OX1 and OX2) receptor antagonist
OX1- Gq coupled
OX2- Gq/Gi coupled
Ramelteon
melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor agonist.
Both receptors are Gi coupled
Acts on neurons of the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Melatonin
Sleep inducing hormone that sets bodys circadian rhythm
Pitolisant
a H3 inverse agonist promotes wakefulness used in the treatment of narcolepsy.
H3 is an inhibitory autoreceptor
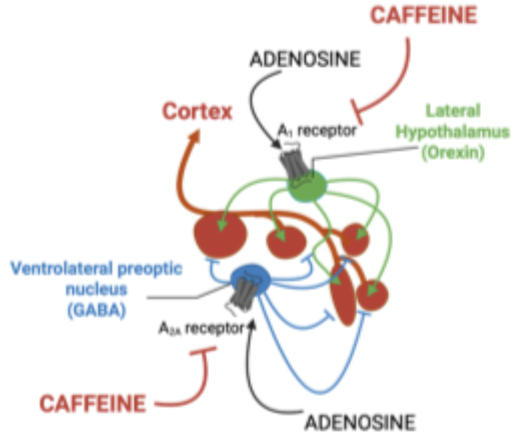
Caffeine
non-selective antagonist of adenosine receptors.
narcolepsy
The transitions from wakefulness to sleep are abnormally rapid and are associated with onset of sleep paralysis.
-Narcoleptic attacks are irresistible and can be triggered by positive emotional states.
-The cause of narcolepsy was unknown for many years, but in 2001, it was found to be due to destruction of hypothalamic neurons containing the peptide transmitter orexin (also called hypocretin).
Adenosine
endogenous somnogen whose levels rise in brain during neural activity
Triggers sleep by:
- inhibiting wake promoting signal: inhibits orexogenic neurons via A1 receptors
-enhances sleep promoting signals: stimulates GABAergic neurons in the VLPO via activation of A2a receptor
What is the role of NA in wakefulness?
Activation of noradrenaline neurons induces alertness and vigilance and is importance for maintaining arousal and attention. Directly involved in:
• Sleep-wake cycle.
• Sensory stimuli.
• Central control of blood pressure.
• Mood.
Amphetamine (dexamphetamine)
NET/DAT +VMAT substrate
enhances wake- promoting action of noradrenergic neurons. Also used to treat ADHD.
Lead to mania and psychosis (DA)
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
NET/DAT inhibitor
used to treat ADHD, may also be used to treat narcolepsy
Modafinil
Weak DAT inhibitor + enhances 5-HT, glutamate, histamine release and inhibits GABA release
used to treat narcolepsy
Amantadine
antiviral with weak DAT inhibitor and NMDA antagonist activity
used to treat fatigue in MS (also used in Parkinson’s disease)
Serotonin
Has dual function: both to promote wakefulness and suppress REM sleep, depending on the receptor subtype involved.
Buspirone
acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT-1A receptor to act as an anxiolytic and is structurally distinct from benzodiazepines and SSRIs.
Not a major sleep promoting drug but helps with easing other factors like stress and anxiety which affect sleep.